Why do they measure?
Hematocrit in a blood test is designated as Ht. It shows how well red blood cells perform their function, that is, delivering oxygen to tissue cells and removing carbon dioxide.
Hematocrit is determined during a general blood test, which is prescribed during a routine examination, preparation for surgery, and for various diseases. It is indicated in the following cases:
- with bleeding;
- when dehydrated;
- when assessing the effectiveness of anemia therapy and dynamic observation.
The analysis result is interpreted taking into account other indicators, such as hemoglobin level, color marker, etc. If the hematocrit deviates from the norm, this indicates the presence of cardiovascular or oncological diseases, anemia, gastrointestinal diseases and other pathologies.
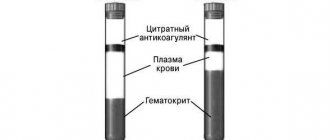
Hematocrit depends on the number of cells in the blood
Functions in the body
Hematocrit number is a specific laboratory sign that characterizes the ratio of blood cells to the total volume of biological fluid.
The source of a decrease or increase in the content of erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets are various factors of an age-related, physiological, pathological nature:
- dysfunction of internal organs;
- inflammatory processes;
- malignant or benign neoplasms;
- pregnancy;
- hormonal changes;
- various diseases of the endocrine system;
- injuries;
- bacterial and viral infections, much more.
Each indicator separately does not have significant diagnostic significance. To assess the entire clinical picture in its entirety, a hematocrit value has been developed.
This laboratory sign makes it possible to identify pathological abnormalities at the initial stage of their development and formation. It provides grounds for more detailed diagnostics.
This is the main function of hematocrit in the body. This number is a kind of marker of diseases and pathological disorders. Based on the percentage of the liquid fraction of blood and formed components, the level of plasma state and active agents is determined.
Norm Ht
Normally, plasma should make up about 60% of the total blood volume, the remaining 40% are formed elements, 99% of which are red blood cells. In analyses, Ht is expressed in liters per liter or as a percentage. For example: 0.43 l/l or 43%.
The normal hematocrit is:
- for adult men – from 0.41 to 0.53 l/l,
- for adult women – from 0.39 to 0.46 l/l,
- for newborns – from 0.44-0.62;
- for children under one year old – 0.36;
- from one to 10 years – 0.37.
Table 1
| Index | Designation | In men | Among women |
| Red blood cells (x 1012/l) | R.B.C. | 4-5,1 | 3,7-4,7 |
| Average erythrocyte volume (fl or µm3) | MCV | 80-94 | 81-99 |
| Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (mm/h) | ESR | 2-15 | 2-10 |
| Anisocytosis of erythrocytes (%) | RDW | 11,5-14,5 | 11,5-14,5 |
| Hemoglobin (g/l) | HGB | 130-160 | 120-140 |
| Average hemoglobin level in erythrocyte (pg) | MCH | 27-31 | 27-31 |
| Average erythrocyte hemoglobin concentration (%) | MCHC | 33-37 | 33-37 |
| Color index | CPU | 0,9-1,1 | 0,9-1,1 |
| Hematocrit (%) | HCT | 40-48 | 36-42 |
| Platelets (x 109/l) | PLT | 180-320 | 180-320 |
| Average platelet volume (fl or µm3) | MPV | 7-11 | 7-11 |
| Reticulocytes (%) | RET | 0,5-1,2 | 0,5-1,2 |
| Leukocytes (x 109/l) | WBC | 4-9 | 4-9 |
How to measure
To measure hematocrit, a special graduated glass tube is used. To do this, it is filled with blood and centrifuged for an hour to separate plasma and cells. At the same time, red blood cells begin to settle to the bottom to a certain level, which is the result. Today, hardware methods are used for calculations - a hemolytic analyzer. When calculating Ht, RBC (absolute number of red blood cells) and MCV (average red cell volume) are taken as a basis. Even with minor blood loss, for example, during menstruation, it is not recommended to take the test, since Ht will be underestimated due to a compensatory increase in the amount of plasma.
Indications for the study
A blood test to determine the hematocrit number is prescribed if the patient has a history of genetic mutations, hereditary diseases, or renal failure.
Common provocateurs of disturbances in the proportions of blood cells:
- oncology of any localization;
- abnormally low levels of protein compounds in plasma and serum;
- thalassemia - inhibition of the secretion of polypeptide chains that are part of the structure of hemoglobin;
- multiple myeloma;
- peritonitis;
- dynamic injuries of internal organs;
- fractures;
- hemoblastosis – a tumor of hematopoietic and lymphatic tissue;
- renal vessel stenosis;
- dysbacteriosis;
- cirrhosis;
- malaria;
A laboratory analysis to determine the Ht indicator is prescribed by a hematologist or family doctor for varicose veins of the esophagus, damage to the spinal cord of any origin, poisoning with hemolytic poisons and salts of heavy metals.
In 20-25% of cases, hematocrit disorder is provoked by anemic pathologies.
The risk group includes people with certain physiological conditions:
- consuming a large daily volume of liquid;
- 4th month and later pregnancy;
- active stage of the menstrual cycle;
- excessive absorption of table salt;
- postpartum period.
Women and children are more likely to experience a decrease in Ht, while men are more likely to experience an increase.
Ht increased
An increased hematocrit may occur in the following cases:
- primary and secondary erythrocytosis: chronic pulmonary diseases, erythremia, high altitude, polycystic kidney disease, kidney tumors.
- with dehydration (dehydration of the body), this happens with increased sweating, vomiting, diarrhea;
- pathologies in which the volume of plasma circulation in the blood decreases; these include shock conditions, peritonitis, burns and more;
- smoking.
Possible complications
Imbalance of the blood formula leads to acid-base imbalance in the body, dysfunction of internal organs, and creates favorable conditions for the invasion of pathogenic pathogens. This is fraught with numerous complications and the formation of severe pathologies.
With increased blood viscosity, it is difficult to remove waste and toxins from the body, and the protective abilities of the immune system are suppressed.
Life-threatening pathologies resulting from hematocrit disorders:
- myocardial infarction;
- ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke;
- airway spasm;
- gangrene of the limbs requiring surgical amputation.
A change in the rheological properties of blood in a pregnant woman’s body leads to highly complicated labor and fetal hypoxia. A child may be born with severe disorders of the central nervous system, destruction of bones and muscle fibers.
In such a responsible physiological state, a woman needs to carefully ensure that the hematocrit is normal. By age, such a deviation is more typical for pregnant women after 35 years of age than for young girls. If the Ht value is very high, the risk of developing thrombosis and vein blockage increases sharply.
Ht reduced
A reduced hematocrit in the blood is detected in the following conditions:
- increase in plasma circulation volume during hyperproteinemia, during pregnancy (second half);
- overhydration - occurs when large volumes of liquid are introduced into the bloodstream, when swelling subsides;
- for anemia (B12-, iron-, folate deficiency);
- with cirrhosis of the liver;
- for oncological diseases of the bone marrow and blood.
On average, the volume of the erythrocyte fraction is about 45% of the total blood volume
Blood test for hematocrit
The manipulation is performed in the morning, blood is taken from a vein or from a finger. At the Medart clinic, the most modern equipment is used for analysis, so the sampling is most often done from a vein.
To obtain the material, special vacuum containers (vacutainers) are used. This is a modern syringe replacement that provides a number of benefits for the patient:
- Virtually painless procedure.
- Minimum time to obtain the required amount of blood.
- Accurate calculation of the amount of reagent and blood.
- Minimum time for conducting the study and issuing results to the patient.
Modern technologies allow the procedure to be carried out as quickly as possible, without consequences for health.
Ht during pregnancy
During gestation, the hematocrit is usually low. The normal blood level in women is from 40 to 46%, while during pregnancy it decreases quite significantly - to 34%. There is no need to worry about this as it is considered normal in this condition. But if during pregnancy the hematocrit is even more reduced (up to 20-25%), anemia may develop, which means your health will worsen, weakness and malaise will appear. You cannot self-medicate; you must consult your doctor who will monitor the condition.
Decoding the results
The analysis is interpreted by a doctor. However, the results of the study are not difficult to understand on your own. A balanced blood formula has a 6:4 ratio between plasma and the total content of formed elements.
Depending on the fluctuation in one direction or the other, the Ht indicator is considered increased or decreased. The average (reference) value is strictly correlated with age and gender. Additional physiological factors are usually at play.
Hematocrit (the norm for women by age should not go beyond 30-45%). For men, this figure varies in the range of 35-49%. A 5% deviation is acceptable. If it is greater, the hematocrit number is considered underestimated or overestimated.
This result may be caused by temporary natural causes and may not have diagnostic significance. But in any case, medical consultation and additional examination are strongly recommended.
Disturbances in the balance of blood cells are often associated with dangerous pathologies - oncological, endocrine, cardiovascular.
How to increase and decrease Ht?
A decreased hematocrit is less common than an increased one. Treatment will depend on the causes of the decrease. That is, drugs are needed to eliminate the primary disease. If this is due to iron deficiency anemia, you should change your diet and include more foods containing iron in your menu. In addition, iron supplements are prescribed. All this will help increase the level of this indicator.
If both red blood cells and hematocrit are elevated, the question arises of lowering it. To do this, you can use the following tips:
- eat fewer foods that contain iron;
- drink more fluids, as dehydration increases this indicator;
- you should avoid alcohol and coffee, which have a diuretic effect and therefore lead to dehydration;
- eat grapefruit every day, which contains a flavonoid that leads to the natural disposal of red blood cells;
- There are foods rich in antioxidants, these include beans, prunes, and various berries.
What examinations are needed
To identify the cause of the pathological process, a group of techniques is prescribed. Among the events:
- Consultation with a specialist. Specialized doctor. An oral survey for complaints and anamnesis collection are indicated.
- Electrocardiography.
- Ultrasound of the heart. To identify the nature of the pathological process, possible defects and anatomical disorders.
- Ultrasound examination of the digestive tract. First of all, specialists are interested in the condition of the liver.
- General, biochemical blood test. It is used as one of the main techniques.
A decrease in hematocrit occurs against the background of pathological processes and natural phenomena. It makes sense to carefully study the situation. After which, think about how to proceed. This is the task of doctors.