- Types and causes of placental insufficiency
- Diagnosis of placental insufficiency
- Treatment of placental insufficiency
Most women know that the placenta connects mother and baby during pregnancy and through it, nutrients and oxygen are supplied to the baby.
Are there situations when the placenta stops performing its function correctly and fully? Is it possible to somehow prevent this?
The essence of the Dopplerography method of uteroplacental blood flow
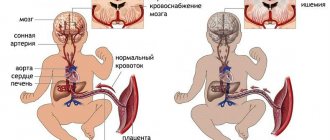
The newly formed fetal blood supply system supplies nutrition not only to the unborn baby, but also to the placenta - the protective membrane. Not only the physical protection of the fetus depends on the completeness and timeliness of blood supply. Good blood supply affects:
- the ability of the placenta to prevent the penetration of toxins;
- the baby's development in the following weeks;
- the ability of the mother's body to neutralize toxins.
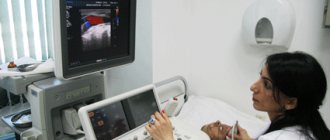
Doppler ultrasound (DPM) is a study using a conventional ultrasound machine. The essence of the technique is to use the Doppler effect: when reflected from moving objects (red blood cells), ultrasound waves change their frequency. The device records the received data and displays an image of the blood flow on the screen. An experienced doctor, based on research, determines whether there are deviations in the functioning of the blood supply system, and how dangerous they are.
Diagnostic methods
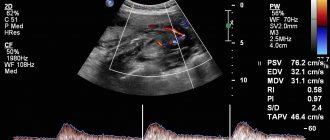
Dopplerography can provide the most reliable and complete information about this pathology. This diagnostic procedure is based on the use of ultrasonic waves and is completely safe for the expectant mother and baby. Using the procedure, signs of circulatory disorders are diagnosed, such as a decrease in diastolic velocity, an increase in the resistance index, and a dicrotic notch in the blood flow curve. The table provides information on how this pathology is diagnosed.
| Diagnostic method | Type of study | Purpose of the event |
| History taking | Analysis of the patient’s complaints, correlation of abdominal circumference with standard indicators corresponding to the gestational age | Making a preliminary diagnosis, developing a plan for further action |
| Physical examination | Auscultation | Determination of fetal heart rate |
| Laboratory research | Blood analysis | Determination of the amount of estrogens, progesterone, human chorionic gonadotropin |
| Instrumental studies | Ultrasound of the pelvic and abdominal organs | Determining the size of the fetus and the condition of the placenta |
| Cardiotocography | Study of the child’s heart function | |
| Dopplerography | Assessment of the intensity of blood flow, determination of the state of intraplacental circulation, flow speed and direction of blood in the vessels of the uterus and umbilical cord |
Indications and contraindications for diagnostics
The basis for Dopplerography of uteroplacental blood flow are several groups of factors:
- Diseases of a pregnant woman: diabetes mellitus, hypertension, collagen vascular diseases, preeclampsia (increased blood pressure after 20 weeks), kidney disease, Rh sensitization (Rh difference between spouses).
- Diseases and malformations of the fetus: growth retardation, causeless oligohydramnios or dropsy, premature ripening of the placenta, discrepancy between fetal weight and gestational age, heart defects, etc.
- Other reasons: abdominal injuries, age more than 35 or less than 20 years, pathological type of cardiotocogram, postmaturity, unsuccessful previous pregnancies, entanglement of the fetal neck with the umbilical cord.
The doctor has the right to prescribe DPM for any condition of the pregnant woman or fetus that causes fear for the life of the unborn child. The study is used to assess the effectiveness of treatment for uteroplacental insufficiency and the threat of late miscarriage.
Causes that can lead to pathology
Many factors contribute to the appearance of disturbances in uterine blood flow. Many of them are capable of influencing the placenta not only at the stage of its formation, but also at later stages. Possible causes of deterioration of uteroplacental circulation:
- Anemia. Due to a decrease in the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood, hemodynamic parameters increase in all blood vessels, including the uterine ones. This is due to the fact that the body seeks to restore the supply of oxygen to tissues by increasing the speed of blood flow, including uterine.
- Incorrect attachment of the placenta. Accompanied by a decrease in blood flow due to thin muscles in the lower segment of the uterus. This problem occurs when the placenta is attached to its scarred area. This zone cannot provide uteroplacental blood circulation, as a result of which the blood supplied to the embryo may not be enough for full intrauterine development.
- Late toxicosis. This condition, during which small blood vessels are affected, often provokes a violation of the uteroplacental-fetal blood flow (UPFB).
- Infectious diseases suffered by a woman during gestation. A number of pathogenic agents negatively affect the condition of the placenta, causing pathological changes in its tissue. Consequence – the IPC was violated.
- Conflict between the Rh factors of the woman and the fetus. This leads to the development of anemia in the baby, which is fraught with a deterioration in the blood supply to his body.
- Pressure surges. They negatively affect blood circulation in the vessels, provoking the development of NMPK.
- Abnormal structure of the uterus. The bicornuate organ has a septum. Pregnancy develops in one of the two cavities formed. The danger in this case lies in the disruption of the child’s full blood supply. Normally, this is provided by two uterine arteries. During gestation, their diameter increases, which leads to the formation of a large number of vessels connecting them, which help normalize blood flow. In a uterus with such an abnormal structure, these processes are absent, so the required volume of blood does not reach the placenta.
- Defects of the umbilical cord vessels. When their number changes, NMPC develops.
- Endometrial pathologies. Their development is caused by inflammation, surgical interventions, and bad habits of the expectant mother.
- Myoma. With the development of neoplasms, their blood supply increases, and the flow of blood to the fetus, on the contrary, decreases.
- Multiple pregnancy. When two or more fertilized eggs are implanted, the placental area increases significantly. In addition, it is possible for a larger volume of blood flow to transfer to one of the embryos. Not only the donor child suffers, but also the recipient fetus, because his heart muscle is not ready for such an amount of incoming blood.
- Diabetes. By affecting the internal walls of the arteries, this pathology triggers the development of placental insufficiency.
Features of Doppler testing
The examination procedure is absolutely safe and is almost no different from a regular ultrasound:
- The patient lies on the couch on her back and exposes the abdominal area.
- The doctor applies a special gel to the pregnant woman’s skin to improve image quality.
- The specialist first examines the general condition of the uterus and fetus for possible abnormalities.
- After this, the doctor turns on the Doppler function and examines the condition of the area of \u200b\u200bthe circulatory system of interest: the aorta, cerebral arteries, etc.
- The results are automatically entered into a special section of the program and analyzed.
If there are deviations, this is immediately visible on the screen. The duration of the procedure is from several minutes to half an hour. The time depends on the volume of the area requiring inspection and the level of qualification of the specialist.
There are no contraindications to the procedure - this is a safe ultrasound examination method, which has been confirmed by many years of clinical trials.
Features of treatment during pregnancy
Therapeutic tactics depend on the degree of the pathological process and the pathogenesis of the disorders. This disease can be treated with medications only in the first degree of circulatory impairment. The second degree is considered borderline. If the pathology has reached the third degree, surgical intervention is indicated. The doctor decides which treatment method to choose on an individual basis.
Conservative methods of therapy
Therapeutic tactics are based on a complex effect on all elements of the hemodynamic process:
- For minor deviations from the norm, Hofitol is used. If symptoms are severe, the patient is prescribed drugs with more active ingredients (Pentoxipharm, Actovegin) (see also: Actovegin: instructions for use during pregnancy).
- When a pregnant woman is diagnosed with a tendency to form blood clots, medications are used that can improve the flow of blood through the blood vessels (Curantil).
- To dilate blood vessels, Drotaverine or No-Shpa is used orally, Eufillin is used as injections.
- For uterine hypertonicity, drip administration of magnesia and enteral use of Magne B6 are indicated.
- The negative consequences of circulatory disorders must be eliminated with the help of ascorbic acid and tocopherol, which have an antioxidant effect.
Medicines are prescribed by the attending physician. Self-medication is strictly prohibited. If the chosen treatment tactics do not improve well-being, the patient is indicated for inpatient treatment. This measure will allow for constant medical monitoring of the condition of the expectant mother and fetus.
Surgical intervention
If signs of pathology are pronounced (grades 2 and 3 MPC), emergency delivery is resorted to. In situations where conservative therapy did not give the expected result, including that which was carried out with diagnosed 1st degree of blood flow impairment, a decision on further actions is made in the next 48 hours. In this case, as a rule, doctors perform a caesarean section. If childbirth in this way is planned to take place before 32 weeks of gestation, the baby’s condition and vital signs must be assessed.
Consequences of violations identified during the inspection
Timely diagnosis detects the emergence and development of pathological conditions at the earliest stages. The accuracy of examinations largely depends on the doctor’s experience and the availability of modern equipment.
When referring for Dopplerography of uteroplacental blood flow, the procedure must be completed without fail. Otherwise, negative consequences are possible:
- abnormalities in child development;
- fetal death;
- increased likelihood of miscarriage;
- low birth weight of the child;
- hormonal imbalance;
- pathologies of the heart and blood vessels.
The good health of the unborn child is the most important incentive for a happy life for most people. Correct implementation of DPM can detect the presence of developmental disorders in the early stages - and respond in a timely manner.
The Harmony clinic has everything you need to carry out Doppler measurements: qualified doctors, modern equipment, affordable prices and first-class service. If you want the procedure to be guaranteed to be not only accurate, but also safe for the baby, then come to us!
How dangerous is a 1st degree violation for a child?
The most common and dangerous consequence of these hemodynamic disorders (HDD) is oxygen starvation. Other complications of poor blood supply to the fetus include:
- decrease in body weight and physical parameters (intrauterine growth retardation);
- acid-base imbalance;
- disorder of the heart in the form of acceleration or deceleration of the pulse, arrhythmia;
- reduction of adipose tissue in the body;
- threat of pathological abortion;
- hormone imbalance;
- antenatal fetal death.
How is the manipulation done?
Diagnostics does not oblige the lady to specially prepare for the appointed date. The examination is carried out in the usual ultrasound room of the clinic. There are no special dietary requirements for the subject before the actual analysis. It can also be carried out at any time of the day without the risk of getting a result with a high percentage of error.
The examination is carried out in a supine position, for which there is a medical couch in the office. First, the diagnostician applies a gel to the sensitive sensor so that the contact with the skin is as dense as possible.
Next, the doctor slowly moves the sensor along the front of the abdominal wall, which makes it possible to assess the blood flow in all the vessels present there. Usually the procedure starts with checking the uterine arteries, and it doesn’t matter which one to start with - right or left. This allows you to identify symmetry problems.
Having completed the uterine part, the specialist switches to examining the structure of the placenta, which is necessary to exclude angiomas - vascular tumors. After this, the umbilical cord and certain problematic vessels such as the middle cerebral artery of the fetus are examined.
You also need to remember that it is not advisable to use the presented method before the 16th week of pregnancy. The reason for this is the unfinished formation of the placenta, which will not allow hemodynamic disturbances to be noticed.
An additional advantage of scanning is the ability, along with studying the clinical picture of the blood flow of the uteroplacental type, to also establish possible anomalies in the baby’s cardiovascular system. In total, the test lasts no more than twenty minutes.
Indications for use
Since there are many reasons that become the primary source of abnormalities in blood flow in the placenta and uterus, experts sorted all of them according to three thematic groups. They cover the following categories:
- on the mother's side;
- from the placenta;
- from the side of the fetus.
In the first case, the most common cause is late toxicosis, which in medical terminology is called gestosis. The condition is caused by the natural reaction of the female body to the presence of foreign tissues in the body.
No less common are:
- arterial hypertension;
- obesity;
- anemia.
The first point falls into the chronic disease camp and is persistent high blood pressure. Over time, unnatural blood pressure levels begin to affect the so-called target organs, which include not only the heart muscle, but also the brain, as well as the eyes.
An equally serious problem is obesity, which causes unnecessary pressure on the uterus. Because of this, the inflow and outflow of blood does not occur as intended by nature.
If, when deciphering the results of a duplex analysis, it turns out that the baby suffers from hypoxia, then the reason for this may be the mother’s anemia. It is caused by a decrease in the level of hemoglobin, which is responsible for transporting oxygen throughout the body. If you ignore the disease detected by scanning, the risks of miscarriage, premature birth or impaired development of the child increase.
Women who have previously been diagnosed with uterine fibroids can also be sent for testing. A benign formation of muscle tissue is considered not particularly dangerous, but not during pregnancy. In an interesting position, the neoplasm can compress the placenta and inhibit vascular patency.
Also, diseases on the mother’s side, after detection of which she will be sent for a specific ultrasound, are:
- Chronical bronchitis;
- pneumonia;
- bronchial asthma;
- respiratory failure.
As soon as the supply of oxygen to a new family member is reduced, there is a risk of deviations in child development. By an identical principle, cardiovascular failure poses a danger. The disease may be a consequence of:
- ischemia;
- cardiomyopathy;
- valve defects.
Once the heart's "pump" stops working at full capacity, it causes a drop in blood pressure, which blocks normal blood transport.
In addition to problems on the part of the mother herself, there are also a number of prescriptions that are explained by pathologies of the placenta. Among them are the following:
- changes in tissue homogeneity, which may be a cyst, tumor or previous heart attack;
- premature aging;
- mismatch with gestational age;
- presentation.
The latter option affects situations where the placenta is located in the lower part of the uterus, where blood does not flow particularly actively. This scenario increases the risk of hypoxia several times.
A little less often, the reasons for sending pregnant women for scanning are problems with the fetus itself. Most often, they begin to be suspected after undergoing an initial classical ultrasound, which involves determining developmental delay. This indicates a discrepancy between the growth dynamics of the baby and the established gestational age. A large fruit weighing over 4 kilograms can also become a problem.
Separately, young ladies with diabetes and those who were found to have intrauterine infections during laboratory testing were at risk.
Despite the stereotypes that any examination negatively affects the well-being of the unborn newborn, duplex scanning is not included in this list of risky procedures. The truth is confirmed by the fact that the only significant contraindication for its implementation is the serious condition of the woman. Then the victim requires immediate emergency care first.