Atherosclerosis: causes of the disease
There are 3 groups of factors influencing the development of the disease:
- irremovable;
- removable;
- potentially removable.
The first include the patient's gender, age and heredity. The risk of atherosclerosis increases in people after 40-50 years of age. In men, this process begins earlier, although by the age of 55 the number of cases among both sexes is the same, which is explained by a decrease in estrogen production in women. Atherosclerosis is more often diagnosed in patients whose relatives also suffered from this disease.
Removable factors include factors that a person himself can remove from life (smoking, sedentary lifestyle, poor diet). When smoking, nicotine tars negatively affect the condition of blood vessels. Atherosclerosis develops faster if a person eats a lot of fatty foods. With physical inactivity, metabolic and blood flow disorders also occur.
Potentially remediable diseases include changes in fat metabolism, hypertension, infectious diseases and intoxication. If you exclude these factors, you can slow down the development of pathology and prevent its consequences.
On double target
The above-mentioned new class of anti-sclerotic drugs acting at the gene level includes substances that activate the so-called PPARs - special cellular receptor proteins. PPARs are transcription factors
: they “turn on” the work of certain genes, stimulating the production of corresponding proteins involved in the regulation of the most important physiological processes, including lipoprotein metabolism.
There are three forms of these receptor proteins - α, β and γ, and each of them is activated by its own specific compound ( agonist
) – for example, fatty acids or prostaglandins involved in the anti-inflammatory response. Each form regulates different, although overlapping, cascades of biochemical processes. For example, PPARα “activators” affect lipoprotein metabolism and are used to treat lipid metabolic disorders; PPARγ activators involved in glucose metabolism – for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
It has long been known that patients with atherosclerosis often develop diabetes and have problems with lipid and carbohydrate metabolism in general. Therefore, recently there has been great interest in the creation of drugs based on double (α and γ) glycazars - tezaglitazar, ragaglitazar
) and even triple agonists of these receptors.
Research has shown that even small changes in the chemical structure of PPAR agonist compounds dramatically affect their ability to selectively bind to the target, which means that the pharmacological properties of such substances can vary greatly - because in this way we interfere with very subtle processes of metabolic regulation.
In general, this class of anti-atherosclerotic substances looks very promising, since they work in significantly lower doses than statins: after all, significantly fewer molecules are required to send a signal through relatively few receptors than to inhibit a large number of enzyme molecules. Hence the significantly lower toxic load on the body: tens to hundreds of times less than for statins, and thousands of times less than for conventional hypoglycemic drugs.
Symptoms of atherosclerosis
With atherosclerosis, the inside of the vessels becomes covered with fatty plaque. Gradually it becomes denser, and the vascular walls can no longer expand and contract. Sometimes lipids form plaques inside the vessel, as a result of which the lumen narrows and blood circulation is impaired.
The accumulation of lipids occurs for years unnoticed by the patient himself. There is an asymptomatic period in the course of the disease, when the patient is not even aware of its existence.
The first signs appear when the lumen of the vessel narrows by 50% or more. Further in the course of the disease there are 3 stages:
- Ischemic. Insufficiency of the organ's blood circulation is diagnosed. Atherosclerosis of the coronary vessels leads to the development of angina.
- Thrombonecrotic. At this stage, thrombosis of the altered arteries appears.
- Fibrous. In organs with poor blood supply, connective tissue grows.
Clinical manifestations depend on the location of the disease. Atherosclerosis of the abdominal aorta makes itself felt by flatulence, abdominal pain, constipation, and numbness of the extremities.
When the thoracic aorta is damaged, burning pain behind the sternum is bothersome, which radiates to the neck and arms. If blood circulation in the brain is disrupted, the patient's mental state changes. When the vessels of the extremities are damaged, numbness and chilliness occur.
Atherosclerosis of the lower extremities
With atherosclerosis of the lower extremities, the femoral, popliteal and tibial arteries are affected. At the first stage of development of the pathology, the patient does not feel any symptoms. Later, pallor or cyanosis of the skin of the legs, a decrease in temperature, and convulsions occur. The patient develops lameness, nails split, and ulcers appear on the heels and toes.
Other symptoms are possible:
- pain in the leg muscles, in the foot;
- rapid freezing of fingers;
- pain along the artery;
- purple skin tone;
- darkening of the skin (the first symptom of beginning gangrene).
At first, symptoms appear in only one limb. If the pathology becomes symmetrical, this is a sign that both arteries are affected.
Diagnostics
To make an accurate diagnosis, the vascular doctor prescribes a complex of diverse examinations to the patient.
- Ultrasound with Doppler of the arteries of the lower and upper extremities to compare indicators in the arms and legs.
- Duplex ultrasound of the arteries of the lower extremities, which allows you to assess how much atherosclerosis has affected the vessels directly, whether there are aneurysms or other pathologies in the walls.
- Load tests (bike treadmill, treadmill running).
- Multislice CT.
- Angiography of the arteries of the pelvis and legs.
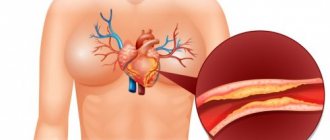
Atherosclerosis of heart vessels
With atherosclerotic heart disease, the lumen of the aorta and coronary vessels narrows, and blood flow to the organ is limited. If the disease is not diagnosed in a timely manner, serious complications are possible, including coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction, and aneurysm. In the most severe cases, death occurs.
The main factor in the development of pathology is elevated cholesterol levels. Often the disease develops in people with excess body weight, metabolic disorders, and with an abundance of animal fats in the diet. The risk group also includes people with low physical activity, nicotine addiction, hypertension, and over the age of 45 years.
If the blood supply and functioning of the heart are impaired, the patient feels pain in the chest on the left side. Unpleasant sensations intensify with exertion
Atherosclerotic heart disease also manifests itself as shortness of breath, dizziness, anxiety, and sometimes loss of consciousness.
Make an appointment with a cardiologist
The prognosis of patients with critical ischemia makes them think about their health and lifestyle in general, immediately get diagnosed by a doctor and begin treatment at the slightest sign of obliterating atherosclerosis with critical ischemia. The situation ends with limb amputation in 25% of cases, death in 20% of cases during the first year, and 50% over five years.
You can avoid this by entrusting your health to the specialists of a private Multidisciplinary Medical Center. Sign up for a paid consultation with a cardiologist if you have symptoms of atherosclerosis, or if you are over 40 years old for a preventive conversation with a doctor and prevention of the disease.
The best cardiologists in our center will help you get rid of heart and vascular diseases or transform them into a decompensated form. Information about prices for appointments and the work schedule of the cardiology department of the center can be obtained on the website or by phone.
Moscow, st. Krasnodarskaya, house. 52, bldg. 2
+7
We work on weekdays and weekends from 8.00 to 21.00
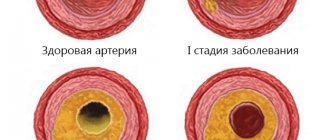
Stages of disease development
There are 3 stages in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Systemic arterial damage occurs against the background of changes in protein and lipid metabolism.
First
At the initial stage, a fat spot is formed. In areas of vessel branching, microcracks appear on the walls, and a local slowdown in blood circulation occurs. The walls of blood vessels swell and become loose, but thanks to protective mechanisms the body still manages to dissolve lipids.
When these resources are depleted, complex compounds of lipids and proteins are formed. They are deposited on the inner surface of the vascular walls.
Second
In areas of lipid deposits, connective tissue begins to grow: an atherosclerotic plaque is formed. At an early stage of formation, it has a semi-liquid form and undergoes dissolution.
But there is also danger at this stage. Due to their loose structure, plaques can spread and clog arteries. The vascular walls lose their elasticity and become ulcerated, which leads to the formation of blood clots.
Third
The plaque thickens and calcium salts accumulate in it. Gradually it grows, narrowing the arterial lumen. The blood supply to the organ that the artery supplies is disrupted. When the lumen of a vessel is blocked by a blood clot or plaque decay products, a heart attack or gangrene develops.
Treatment of atherosclerosis
If atherosclerosis is suspected, consultation with a cardiologist is indicated. Aortography reveals signs of calcification, elongation and thickening of the aorta. Coronary angiography allows you to assess the condition of the coronary arteries. If blood circulation in other arteries is impaired, angiography (contrast study of blood vessels) is used. Atherosclerosis of the lower extremities is diagnosed using rheovasography.
Medication
The use of drugs for vascular atherosclerosis can be indicated at an early stage. The most commonly prescribed drugs include the following groups of drugs:
- Nicotinic acid and drugs based on it reduce cholesterol levels in the blood. Treatment with tablets for atherosclerosis with nicotinic acid is contraindicated in patients with liver pathologies.
- Fibrates. The drugs reduce the production of the body's own fats. Treatment with fibrates for atherosclerosis helps reduce lipids.
- Bile acid sequestrants. Medicines for the treatment of atherosclerosis that bind and remove bile, lowering lipid and cholesterol levels.
- Beds. Reduces cholesterol production. They are taken at night, since at this time the synthesis of the substance is activated.
If treatment of atherosclerosis with drugs does not produce effective results, surgical intervention is resorted to.
Surgical
Endarterectomy is an operation in which the plaque is excised along with part of the internal vascular wall. The intervention is indicated for arterial occlusions measuring 7-9 cm. For the doctor and the patient, this is an opportunity to restore blood flow in the distal limbs.
In case of atherosclerosis of the heart vessels and the threat of a heart attack, coronary bypass surgery is performed. The essence of the surgical intervention is to create a bypass for blood flow using shunts that are fixed to the aorta and the affected vessel.
Stenting
The operation involves widening the lumen of the vessel using balloon angioplasty and subsequent installation of a stent. Surgical intervention is effective for local occlusion.
A catheter is inserted through a puncture in the femoral or axillary artery and inflated with air. It expands the lumen of the vessel. Then a stent, which is a mesh tube, is implanted into the affected area. In the future, it maintains the patency of the artery. The entire operation is performed under X-ray control.
Victory is for nature
Researchers continue to search for more effective and safe natural substances with a statin-like structure, and are also trying to synthesize new compounds with the desired properties.
However, on this path they encounter considerable difficulties. First, it turned out that the synthesis of the lactone fragment, which determines the therapeutic effect of the compound, is a technically challenging task. Secondly, although quite a lot of purely synthetic drugs have been obtained for the treatment of hyperlipidemia ( fluvastatin, atorvastatin, cerivastatin
), they are not superior in therapeutic properties to the well-known compactin and mevinolin, which are today obtained biotechnologically.
That's why mevinolin is still called lovastatin
continues to be used in medical practice, and the leader of the pharmacological market is the drug
ineji
- a combination of the closest analogue of mevinolin,
simvastatin,
with ezetimibe. The record for effectiveness was broken by the natural compound FR901512, recently isolated from the same molds (Inoue and Nakada, 2007).
Nevertheless, the process of searching and creating new synthetic statin drugs does not stop. Currently, drugs are being developed that are fundamentally different from natural ones: the lipophilic part of the molecules of these compounds contains polar fragments, which, when interacting with the enzyme, change its conformation (shape). This new type of interaction ultimately allows for greater cholesterol synthesis inhibition.
It is possible to influence the conformation of the enzyme and ensure better fixation of the statin in its active center using other methods. A similar effect is achieved, for example, when using a complex of simvastatin and atorvastatin with glycyrrhizic acid, which is obtained from the roots of licorice (Tolstikov et al., 2006; 2008).
Diet for atherosclerosis
If lipid metabolism is disturbed, it is necessary to saturate the menu with vegetables, fruits, and bran, which help cleanse blood vessels. The diet must include foods that have an anti-sclerotic effect:
- oranges or tangerines;
- apples;
- tomatoes;
- beet;
- salad;
- cucumbers;
- rhubarb;
- garlic;
- fenugreek.
According to the chemical composition, food should be distributed as follows: 100 g of proteins, 80 g of fats (30% of which are vegetable), 400 g of carbohydrates (of which only 40 g are fast).
The maximum calorie content of the daily diet should not exceed 2500 kcal. If the patient is overweight, this volume is limited to 1800 kcal. The amount of salt is reduced to 3 g per day. Among the cooking methods, preference is given to boiling, stewing, and baking.
Prices for consultation and appointment with a cardiologist
| Name | Price |
| Blood pressure measurement | 60,00 |
| Consultation after MRI/MSCT | 540,00 |
| Initial consultation with a pulmonologist | 1800,00 |
| Initial appointment with a cardiologist (consultation) | 1800,00 |
| Initial appointment with a rheumatologist | 1800,00 |
| Repeated consultation with a pulmonologist | 960,00 |
| Repeated appointment with a cardiologist | 960,00 |
| Repeated appointment with a rheumatologist | 960,00 |
| Preoperative examination by a cardiologist (doctor’s appointment, ECG, interpretation) | 2460,00 |
| ECG interpretation | 600,00 |
| Taking an ECG | 360,00 |
| 24-hour blood pressure monitoring | 2400,00 |
| 24-hour Holter ECG monitoring | 3000,00 |
| ECG with stress | 1950,00 |
Prevention of atherosclerosis
To prevent the disease, it is necessary to eliminate the factors contributing to its development:
- maintain physical activity to increase blood flow;
- eat right, limiting fried, salty, fatty foods as much as possible in your diet;
- monitor body weight;
- avoid stress that increases blood pressure.
Atherosclerosis is a disease that can lead to serious complications and death. Proper nutrition and compliance with preventive measures will help prevent this dangerous pathology.