Pain in the heart area when inhaling
Pain in the heart when inhaling usually occurs unexpectedly. In addition, it may intensify immediately after a person changes body position, or it may weaken. This is due to several factors, among which diseases and excessive physical activity are not the least important.
Many people who have experienced these sensations note increasing pain, which is accompanied by fatigue of the whole body. In order to understand the causes of the disease, an outpatient analysis should be carried out, which will give a clear explanation of what caused the pain.
How does a pinched nerve manifest?
Intense, stabbing or shooting (like an electric shock) pain in the neck, lower back or chest. The pain can spread to the arm, to the back of the head, along the rib into the chest, often to the heart area, or to the leg. In the compression zone, the muscles are tense, spasmed, and there may be swelling of the soft tissues. Muscle tension leads to curvature of the spine; on the side of pain, the shoulder, shoulder blade, and thigh rise. This “distortion” of the back muscles is called a painful (algic) pose. If proper treatment is not given, a pinched nerve can persist for several weeks and significantly impair the patient's quality of life.
Causes of pinched nerve:
- The most common cause is osteochondrosis. In this case, the roots of the spinal nerves are pinched in the intervertebral foramina at the site of protrusion (bulging) of the intervertebral disc. An additional cause of pinched nerves is bone growths of the vertebrae (osteophytes).
- A herniated disc is a complication of osteochondrosis and, as a rule, leads to persistent pinching of the nerve root. In this case, the pain spreads along the arm or leg and is accompanied by decreased reflexes, impaired skin sensitivity, a feeling of “tingling needles” or weakness in the fingers or toes.
- Constant intense physical activity leads to compression of the nerve between the muscles and tendons. These are the so-called “tunnel” syndromes. They occur in people of certain professions: athletes, tennis players (pinched nerve in the elbow), typists and other “typing” people (compression in the wrist).
Heart disease or pinched nerve?
Therefore, intercostal neuralgia causes pain not only in the heart, but also in the lower back, back, and also under the shoulder blade.
With intercostal neuralgia, irritation or compression of the roots of the intercostal nerves occurs at the point where they exit the spine. Also, pain in the heart area can be caused by excessive tone of one or more muscles of the shoulder, back or shoulder blade.
The causes of neuralgia are varied: exposure to heavy metals, certain medications, bacterial toxins, diseases of the nervous system (polyradiculoneuritis, multiple sclerosis, etc.), trauma, various infections (tuberculosis, influenza, etc.), spinal pathology or congenital anomalies (hernias). discs, osteochondrosis, etc.), allergies.
Another cause of intercostal neuralgia can be changes in the spine, which are caused by hormonal disorders in women. The development of the disease can be affected by alcohol abuse, metabolic disorders of B vitamins, and diabetes mellitus. Older people are susceptible to this disease when all of the above reasons affect the background of age-related changes in the blood vessels.
It should be remembered that nerve endings are everywhere, so intercostal neuralgia can imitate, for example, lung diseases, renal colic, pain that occurs with herpes zoster and, most often, cardiac pathologies. Conversely, other diseases are often mistaken for neuralgia with similar symptoms.
How to eliminate pain
Treatment prescribed for intercostal neuralgia must be comprehensive. First, the causes of the disease should be corrected or eliminated. During an exacerbation, bed rest is required for three days. The bed should be firm and level; it is better to place a shield under the mattress.
During attacks, it is necessary to place mustard plasters on the paravertebral area or wrap the chest with a warm scarf. If the pain intensifies, then you should take analgesics (sedalgin, analgin, etc.). It is also recommended to take B vitamins.
To prevent intercostal neuralgia from becoming chronic, it is necessary to reduce physical activity, try to avoid stressful situations and not abuse alcohol.
How to distinguish intercostal neuralgia from heart disease
Pain during angina occurs quickly and also passes quickly (within 2-5 minutes), it can be relieved with nitroglycerin. Heart pain does not change when moving or changing position, when exhaling or taking a deep breath, it is accompanied by an irregular pulse and an increase or decrease in blood pressure.
To clarify the cause of chest pain, magnetic resonance imaging and radiography should be done.
If pain is felt under the left shoulder blade, you will need a cardiogram. Author: K.M.N., Academician of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences M.A. Bobyr
What examinations are necessary for a pinched nerve?
An important diagnostic method is electromyography (EMG). It is this study that objectively assesses the degree of compression (damage) of the nerve. An EMG records the conduction of electrical impulses along the nerves of an arm or leg and gives the doctor an assessment of the state of the peripheral nervous system.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) can assess the condition of the vertebrae and intervertebral discs, the presence of hernias and protrusions, and spinal cord damage.
X-ray of the spine
informative in case of poor posture - scoliosis, kyphosis, as well as injuries: fractures and subluxations of the vertebrae.
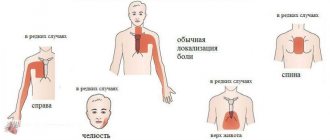
Pain in the heart area. note
Heart pain is one of the most common reasons people seek emergency care. So, every year, several million people seek emergency medical help with this symptom.
Pain in the heart area is not always pain in the heart. Often it is not associated with heart problems. However, if you are experiencing chest pain and are not aware of the state of your cardiovascular system, the problem may be serious and it is worth taking the time to find out the cause of the pain.
Causes
Pain in the heart area can be very different. It is not always possible to describe it. The pain can be felt as a mild burning sensation or as a severe blow. Since you cannot always determine the cause of pain on your own, there is no need to waste time on self-medication, especially if you belong to the so-called “risk group” for heart disease.
Pain in the heart area has many causes, including those that require close attention. The causes of pain can be divided into 2 large categories - “cardiac” and “non-cardiac”.
"Heart" reasons
(Tegiocardial infarction - a blood clot that blocks the movement of blood in the arteries of the heart can cause pressing, squeezing pain in the chest that lasts more than a few minutes. The pain can radiate to the back, neck, lower jaw, shoulders and arms (especially the left). Other symptoms may include shortness of breath, cold sweats, and nausea.
(Angina pectoris Over the years, fatty plaques can form in the arteries of your heart, restricting the flow of blood to the heart muscle, especially during exercise. It is the restriction of blood flow through the arteries of the heart that causes attacks of chest pain - angina. Angina pectoris is often described by people as a feeling of pressure or squeezing in the chest. It usually occurs during exercise or stress. The pain usually lasts about a minute and stops with rest.
Other cardiac causes. Other causes of chest pain include inflammation of the lining of the heart (pericarditis), most often due to a viral infection. Pain with pericarditis is most often acute, stabbing in nature. Fever and malaise may also occur. Less commonly, the pain may be caused by a dissection of the aorta, the main artery in your body. The inner layer of this artery can separate under blood pressure and the result is sharp, sudden and severe pain in the chest. Aortic dissection can be the result of chest trauma or a complication of uncontrolled hypertension.
"Non-heart" reasons
Heartburn. Acidic stomach acid that flows from the stomach into the esophagus (the tube that connects the mouth to the stomach) can cause heartburn, a painful burning sensation in the chest. It is often combined with a sour taste and belching. Heartburn chest pain is usually associated with food intake and can last for hours. This symptom most often occurs when bending or lying down. Taking antacids relieves heartburn.
Panic attacks. If you experience attacks of unreasonable fear, combined with chest pain, rapid heartbeat, hyperventilation (rapid breathing) and profuse sweating, you may be suffering from “panic attacks” - a unique form of dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system. Pleurisy. Sharp, localized chest pain that gets worse when you inhale or cough may be a sign of pleurisy. The pain occurs due to inflammation of the membrane lining the inside of the chest cavity and covering the lungs. Pleurisy can occur with various diseases, but most often with pneumonia.
Tietze syndrome. Under certain conditions, the cartilaginous parts of the ribs, especially the cartilage that attaches to the sternum, can become inflamed. Pain in this disease can occur suddenly and be quite intense, simulating an attack of angina. However, the location of pain may vary. With Tietze syndrome, pain may increase when pressure is placed on the sternum or ribs near the sternum. Pain during angina pectoris and myocardial infarction does not depend on this.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical and thoracic spine leads to so-called vertebrogenic cardialgia, which resembles angina pectoris. In this condition, there is intense and prolonged pain behind the sternum, in the left half of the chest. Irradiation to the arms and interscapular area may be observed. The pain increases or decreases with changes in body position, head turns, and arm movements. The diagnosis can be confirmed by performing an MRI of the spine.
Pulmonary embolism. This type of embolism occurs when a blood clot enters the pulmonary artery, blocking the flow of blood to the heart. Symptoms of this life-threatening condition may include sudden, sharp chest pain that occurs or gets worse with deep breathing or coughing. Other symptoms are shortness of breath, palpitations, anxiety, loss of consciousness.
Other lung diseases. Pneumothorax (collapsed lung), high pressure in the blood vessels supplying the lungs (pulmonary hypertension), and severe asthma may also cause chest pain. Muscle diseases. Pain caused by muscle diseases usually begins to bother you when you turn your body or raise your arms. Chronic pain syndrome such as fibromyalgia. May cause persistent chest pain.
Damage to ribs and pinched nerves. Bruises and fractures of the ribs, as well as pinched nerve roots, can cause pain, sometimes very severe. With intercostal neuralgia, pain is localized along the intercostal spaces and intensifies with palpation.
Diseases of the esophagus. Some diseases of the esophagus can cause difficulty swallowing and therefore chest discomfort. Esophageal spasm can cause chest pain. In patients with this disease, the muscles that normally move food down the esophagus work uncoordinated. Since esophageal spasm can resolve after taking nitroglycerin - just like angina - diagnostic errors often occur. Another swallowing disorder known as achalasia can also cause chest pain. In this case, the valve in the lower third of the esophagus does not open as it should and does not allow food to pass into the stomach. It remains in the esophagus, causing discomfort, pain and heartburn.
Shingles. This infection, caused by the herpes virus and affecting the nerve endings, can cause severe chest pain. The pain can be localized in the left half of the chest or be of a girdling nature. This disease can leave behind a complication - postherpetic neuralgia, which causes prolonged pain and increased skin sensitivity.
Diseases of the gallbladder and pancreas. Gallstones or inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis) and pancreas (pancreatitis) can cause pain in the upper abdomen that radiates to the heart. Because chest pain can have many different causes, do not self-diagnose, self-medicate, or ignore severe or prolonged pain. The cause of your pain may not be so serious - but in order to establish it, you need to contact a specialist.
When should you see a doctor?
If you experience sharp, unexplained, long-lasting chest pain, perhaps in combination with other symptoms (such as shortness of breath) or pain that radiates to one or both arms. Under the shoulder blade - you need to urgently consult a doctor. Perhaps this will save your life or calm you down if no serious problems with your health are found.
Diagnostics
Pain in the heart area does not always indicate heart disease. Tests that can help determine the cause of pain include: (Electrocardiography (ECG)) This test helps your doctor diagnose heart disease. It records the electrical activity of the heart through electrodes placed on the skin. Heart impulses are recorded as "waves". Because damaged heart muscle cannot conduct electrical impulses normally, an ECG may show that the patient has heart disease.
Blood tests. Your doctor may order tests to look for elevated levels of certain enzymes. Damage to heart cells during myocardial infarction leads to the release of these enzymes and their entry into the bloodstream. Myocardial scintigraphy. This method helps doctors determine the “heart cause” of pain, for example. Narrowing of the coronary arteries. A small amount of a radioactive substance (such as thallium) is injected into the bloodstream. Special cameras capture the radioactive substance and track its passage through the heart and lungs.
(Angiography) This test helps to see the arteries of the heart and any obstructions in them. A liquid contrast agent is injected into the arteries of the heart through a special catheter - a long, hollow tube that is passed to the heart through an artery (usually the femoral one). X-rays make the arteries visible. (Echocardiography (ECHO CG)) This method uses ultrasound waves to obtain an image of the beating heart.
Electron beam tomography (CRT). This unique method allows, by identifying microcalcifications in the wall of the coronary arteries, to detect the early stages of the development of coronary heart disease even before symptoms appear.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the spine will help determine the cause of pain in the chest if it is caused by pinched nerve roots or the presence of herniated intervertebral discs.
*Materials from the website www.corallcenter.ru
Effective treatment for pinched nerves
Traditional treatments for pain symptoms include anti-inflammatory painkillers (NSAIDs), muscle relaxants (drugs that relax muscles), drugs that improve blood circulation, B vitamins, and physical therapy. These methods reduce symptoms, but do not affect the causes and mechanisms of the disease.
Blockades of pressure points and paravertebral blockades are a classic effective method of treating muscle-articular pain. The doctor specifically introduces a complex of pain medications (into the pain “trigger” zone or along the pinched nerve). Pain relief occurs a few minutes after the injection.
An alternative modern method for treating osteochondrosis, scoliosis and herniated intervertebral discs is shock wave therapy. The principle of UVT is the effect of low-frequency sound waves on tense muscles and ligaments, joints, and bones. The acoustic wave reduces inflammation of the pinched nerve, restores blood circulation and starts the process of cell regeneration. There are known cases of restoration of bone structure after the onset of bone necrosis.
The First Neurology clinic actively uses more than 20 types of treatment for pain syndromes in the back and limbs, as well as headaches. Modern high-tech methods relieve pain after 2-3 sessions and reduce the drug load (the amount and duration of taking pain medications).
These methods include, first of all, carboxytherapy. The introduction of small amounts of carbon dioxide into the projections of the spine and joints causes blood flow and stimulates blood circulation in the area of the pinched nerve. Carboxytherapy has a rapid analgesic effect, improves trophism (nutrition) of intervertebral discs and nerves. The undoubted advantage of the method is the absence of side effects.
Mesoinjection therapy has been used at the First Neurology clinic for more than 10 years. This is a method of introducing drugs into the deep layer of skin - mesoderm. Locally - in the projection of the pinched nerve, the neurologist administers muscle relaxants (muscle relaxers) or vascular, anti-inflammatory drugs. The absorption and effect of the drug last more than 2 weeks, so mesotherapy is performed once every 14 days.
Hi Top high-tone therapy is the method of choice in the treatment of a pinched nerve in an arm or leg. By applying pulsed current to the sensory endings of the peripheral nerve, Hi Top stimulates the nerves, muscles and spinal cord.
Dosed traction of the spine is carried out at the First Neurology clinic using the specialized orthorpedic complex ORMED-Professional. Traction eliminates pinched spinal nerves, reduces back muscle tone, and quickly relieves pain in the spine.
Heart hurts, left hand goes numb, reasons
Pain in the left arm and heart appears when the functioning of one of the systems in the body is disrupted. Numbness of the limbs on the left is a clear sign of the development of the disease. Experts identify a lot of reasons that influence the deterioration of well-being. They are divided into cardiac and non-cardiac causes. Among them:
Cardiac causes of heart pain and numbness in limbs
- Cardiac ischemia. With coronary heart disease, the patient feels a sharp dagger pain in the heart area, which radiates to the left arm. In such situations, you cannot do without painkillers and without the help of doctors. We are talking about damage to the heart muscle. Stress, emotional stress, and chronic lack of sleep lead to the development of cardiovascular disease. Also, coronary heart disease occurs in people who work physically. The patient's heart and arm hurt. In advanced cases, deterioration in health is accompanied by dizziness and a pulling sensation in the left shoulder area. The person is in a state of panic and breaks into a cold sweat. The nervous system is overloaded and therefore cannot function normally. If ignored, these symptoms lead to myocardial infarction and angina. An attack of angina lasts about ten minutes. It is recommended to use nitroglycerin and vasodilators. Do not self-medicate. The KDS Clinic will prescribe the necessary treatment and stop the progression of the disease.
- Myocardial infarction. The heart hurts and radiates to the arm when myocardial infarction develops. The disease is extremely dangerous to human life and will lead to death. There is a strong sharp pain in the heart, the hand goes numb. In some cases, the face also becomes numb. The patient feels a panicky fear of death and is shaking. If symptoms worsen within an hour and do not stop after taking medication, then the patient is guaranteed to have a heart attack. It's worth calling an ambulance. Sometimes a myocardial infarction goes away without any symptoms.
- Myocarditis. Heart and arm pain due to myocarditis. This pathology indicates serious disorders of the cardiovascular system. The disease is not easy to diagnose. Symptoms include shortness of breath, tinnitus, constant fatigue, insomnia, a feeling of anxiety and fear for your life, dizziness, and cold sweats. The patient is concerned about tachycardia and blood pressure disorders. Severe pain appears in the chest and heart. Hands and feet become numb. The development of myocarditis is not associated with physical activity.
- Congenital heart defect.
- Cardiomyopathy.
- Vegetovascular dystonia.
- Pericarditis.
- Consequences of nervous breakdowns and stress.
Our specialists
Tarasova Svetlana Vitalievna
Expert No. 1 in the treatment of headaches and migraines. Head of the Center for the Treatment of Pain and Multiple Sclerosis.
Somnologist.
Epileptologist. Botulinum therapist. The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Physiotherapist. Doctor of Medical Sciences.
Experience: 23 years.Derevianko Leonid Sergeevich
Head of the Center for Diagnostics and Treatment of Sleep Disorders.
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Vertebrologist. Somnologist. Epileptologist. Botulinum therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 23 years.
Palagin Maxim Anatolievich
The doctor is a neurologist. Somnologist. Epileptologist. Botulinum therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 6 years.
Romanova Tatyana Alexandrovna
Pediatric neurologist. Experience: 24 years.
Temina Lyudmila Borisovna
Pediatric neurologist of the highest category. Candidate of Medical Sciences.
Experience: 46 years.
Zhuravleva Nadezhda Vladimirovna
Head of the center for diagnosis and treatment of myasthenia gravis.
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Physiotherapist. Experience: 16 years.
Mizonov Sergey Vladimirovich
The doctor is a neurologist. Chiropractor. Osteopath. Physiotherapist. Experience: 8 years.
Bezgina Elena Vladimirovna
The doctor is a neurologist of the highest category. Botulinum therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 24 years.
Drozdova Lyubov Vladimirovna
The doctor is a neurologist. Vertebroneurologist. Ozone therapist. Physiotherapist. Experience: 17 years.
How dangerous are tingling sensations in the heart?
Natalia Denisova
August 19, 2016
Lately my heart has been pounding very often, so much so that I really thought that a heart attack was inevitable. Of course, when this started to bother me more than once every six months, I turned to my therapist. The doctor immediately asked what kind of pain in the heart area was bothering me. Then I thought: why in the region? I feel that this heart is probably pinching something in this muscle, or maybe, in general, something with the valves.
As a result of an incredibly educational conversation for me, it became clear that stabbing pain on the left often does not touch the heart at all, because this type of ailment is not typical for this organ. Now, if the pain is pressing, burning or pulling, you need to run to the doctor as soon as possible, because such signals from the body sometimes indicate a great danger to your life. For example, the first signs of a heart attack and angina are pressure and burning chest pain, nausea and even vomiting. In this case, it is better to take nitroglycerin and call an ambulance. Heart failure is also characterized not by tingling of the heart, but by shortness of breath, increased fatigue, lips, as well as fingers and toes become very pale or even with a blue tint. Well, stabbing pain can occur for a huge list of reasons; of course, you shouldn’t ignore them either, but go to a therapist, who, after listening to you, will send you to the right doctor. The most important thing is not to think that it will go away soon, but to try to find out the cause of the pain. As you know, the body does not give us pain signals just like that; it warns us about the development of some kind of disease. Tingling in the heart area is dangerous in any case, as it leads to certain diseases. There is no need to postpone a visit to the doctor, even if it is not your heart that hurts. For example, stabbing pain in the heart area can occur with lung disease. You can understand this by following the dynamics of pain when inhaling and exhaling or coughing. The list of diseases characterized by this type of ailment includes pneumonia, tuberculosis, inflammation and cancer of the left lung. In addition to pain, a person with a similar disease may experience shortness of breath, fever, and even intoxication of the body. Pain under the left rib may be one of the signs of a diaphragmatic hernia. This disease, predominantly in older people, occurs as a result of weakening of the diaphragm muscles. The left side of the diaphragm is located in the upper part of the abdominal cavity, there is an opening through which the esophagus passes and if the muscles of the diaphragm weaken, the opening becomes larger. Because of this, the upper part of the stomach and the abdominal part of the esophagus exit into the chest cavity. Weakening of the diaphragm can also be caused by other reasons that increase intra-abdominal pressure. For example, such reasons may be: • obesity; • hard physical labor; • age-related changes in the body; • pregnancy, but this is quite rare. Intercostal neuralgia is also a cause of pain. This type of pain is considered common and relatively safe. Usually it is concentrated in the lower parts of the sternum and intensifies with sudden movements and deep breathing. One of the characteristic signs of pain in neuralgia is discomfort upon palpation of the intercostal spaces. This could be due to excessive pressure on the nerve or damage/pinching. In addition, such pain can occur if a person is in an uncomfortable position for a long time. One of the rare causes of neuralgic pain in the left part of the hypochondrium may be abdominal migraine. It often occurs in children or adolescents. This pain is paroxysmal in nature, quite often accompanied by nausea or vomiting, pale skin, and cramps of the abdominal wall muscles. Stress and anxiety, obesity, frequent drinking of alcohol and, of course, smoking are the worst enemies of a healthy heart. Coffee, despite what most people think, is absolutely not dangerous. Strong feelings and worries are not as harmless as they might seem at first glance. The feeling of the heart pounding or jumping out of the chest often provokes a sudden increase in blood pressure and sometimes a stroke. Neuralgic aching pain in the chest can be confused with heart pain. Doctors advise taking a comfortable position and applying heat or a pepper patch. Such measures will relieve neuralgic pain, but will not help with a heart attack.
Natalia Denisova
Tags:
- Heart and blood vessels
- colitis
Read also
Chiari malformation
What is Chiari Malformation?
Chiari malformation (formerly Arnold-Chiari malformation) is a congenital defect of brain development that involves the dislocation of the cerebellar tonsils into the spinal canal through a large... Read more
Myelitis
Myelitis is a neurological pathology characterized by inflammation of the gray and white matter of the spinal cord, which leads to damage to myelin (the substance that forms the sheath of nerve fibers) and the axon (the process...
More details
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
– “One of the most terrible human diseases... 3 letters...” – “Cancer” – “Not suitable...” Yes, dear ones, there is something worse than cancer. And this disease is called amyotrophic lateral sclerosis or...
More details
Consequences of traumatic injuries to the skull, spine, brain and spinal cord
Traumatic brain injuries, or traumatic brain injuries, are damage to the brain that impair brain function. Brain injuries are divided into two large groups - closed...
More details
Syringomyelia
Syringomyelia is a disease caused by the formation of spaces in the substance of the spinal cord filled with cerebrospinal fluid. They expand the spinal cord at the level of the lower cervical and thoracic regions...
More details
Non-cardiac causes of heart pain and numbness in limbs
Most often, the patient’s left arm and heart hurt, in the case of a disease not of the heart, but of neighboring organs. We are talking about pathologies of the lungs, kidneys, and musculoskeletal system. Among them:
- Osteochondrosis. With the development of osteochondrosis, the load also goes on the cardiac system. In addition to unpleasant sensations in the spine, there is severe pain in the heart and numbness in the limbs. Requires special attention from medical professionals to prevent the development of the disease.
- Consequences of injuries. After injuries, disturbances occur throughout the body.
- Duodenal ulcer. With a duodenal ulcer, the limbs often become numb. You should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
- Pancreatitis. Associated symptoms include nausea, vomiting, dizziness, pale face, and fever.
- Gastrointestinal tract disorders. With gastrointestinal disorders, the patient feels unbearable pain not only in the stomach, but also in the heart. A lot of stress is placed on the heart.
- Neuralgia.
- Hormonal disorders. Most often the heart hurts and radiates to the arm in women. In some cases, symptoms are associated with hormonal imbalances.
- Pregnancy. During pregnancy, the functionality of a woman’s body completely changes. The load occurs on all organs, especially the heart. As a result, the pregnant woman feels unwell and has numbness in her limbs.
- Pathologies of the mammary glands.
- Benign and malignant tumors.
- Tuberculosis.
- Bronchial asthma.
- Dry pleurisy.