Osteochondrosis is a very dangerous disease. It occurs unnoticed, and from mild uncomfortable sensations develops into serious disorders of the spine, which sometimes result in disability.
This disease is treated by therapists, neurologists, orthopedists, vertebrologists and other specialists at the Yusupov Hospital.
Features of chest pain in various pathologies
A description of the discomfort will help distinguish heart pain from neuralgia and osteochondrosis. But the perception of pain is individual, so such a diagram can only provide approximate information.
| Osteochondrosis | Neuralgia | Angina pectoris | |
| Nature of pain | Stitching, aching, cutting, lumbago | Aching, burning, cutting | Stitching or burning |
| Conditions of occurrence | If you are in an uncomfortable position for a long time, sleep in an uncomfortable position, or undergo prolonged or sudden physical activity | With a deep breath, frequent breathing, being in an uncomfortable position, physical activity | During physical or emotional stress, less often in a stuffy room |
| Localization | Behind the sternum on the right or left | Behind the sternum or on the skin on the affected side | Behind the sternum on the left or in the center - in the region of the heart |
| Duration of attack | From a few minutes to several hours | A one-time outbreak of pain when inhaling, until shortness of breath ceases during physical activity, aching - constantly | 5-10 minutes, maximum duration – 30 minutes |
| Terms of termination | Changing body position, stopping activity, therapeutic exercises, massage, deep breathing, anti-inflammatory ointments | Reducing the depth of breathing, changing body position, stopping physical work, ensuring access to oxygen (open a window, go outside) | Stopping physical activity, calming techniques, taking nitroglycerin |
| Seizure frequency | Depends on the patient's physical activity | 1-2 times a month | Extremely variable - from rare attacks once a year to several a day |
| Additional symptoms | Decreased back flexibility, neck crunch, tinnitus, sleep disturbances, decreased cognitive function, back pain | Breathing disorders, shortness of breath, feeling of shortness of breath, dizziness, headaches | Weakness, palpitations, dizziness, fear of death, feeling of lack of air, tinnitus, darkening of the eyes |
Many signs are the same; it is difficult to distinguish pain caused by different causes. Typically, the patient thinks about heart pathology when a heart attack has already occurred. In other cases, angina becomes an incidental finding during examination for other diseases.
Treatment and prevention of symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
Treatment of symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis of the spine should be carried out comprehensively. In each case it is necessary to find an individual approach. Medicines, physical therapy, massages and some folk remedies can help cope with the disease.
If osteochondrosis is in an acute stage, then its treatment will be aimed at improving blood circulation and eliminating spasms and pinching. The doctor can prescribe medications to the patient that will improve blood flow, as well as relieve inflammation and reduce pain.
Medicines for the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
Clinical studies have shown that during exacerbation of cervical osteochondrosis, analgesics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs work well. In addition to them, the doctor prescribes chondroprotectors, antispasmodics and drugs that stimulate blood circulation in the tissues.
For complex therapy in the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis, the following are used:
- Analgesics. Eliminate pain. Some of them can have an anti-inflammatory effect. Most often, analgesics are prescribed for lumbar osteochondrosis, which has a wide localization of pain;
- Antispasmodics. They have an analgesic and antispasmodic effect. Eliminate muscle spasms, block the sensitivity of nerve endings;
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. Relieve pain, reduce inflammation;
- Vasodilators. Necessary for improving blood circulation. Reduces the recovery time of the body after osteochondrosis;
- Chondroprotectors. Necessary for tissue restoration in damaged cartilage. One of the most effective drugs today is Artadol. It contains chondroitin sulfate, which actively fights the degradation of articular cartilage. The drug stimulates the production of proteoglycans. Improves metabolic processes in cartilage and bone tissue.
Regardless of the stage of the disease and the degree of pain, doctors strongly recommend refraining from self-medication. Only after examination by a specialist, analyzes and tests can the doctor prescribe adequate and effective treatment for cervical osteochondrosis.
Massage for cervical osteochondrosis
Massage is necessary to relieve pain and improve muscle tone. Different techniques are used, which depend on the stage of the disease. In the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis, the following are effective:
- stroking;
- squeezing;
- rubbing;
- kneading.
If pain is observed only on one side of the neck, then the massage begins with a healthy part of the body, gradually moving to the sick one. It can be performed at home or in a specialized institution. But you should be extremely careful, since incorrect movements and influences can only aggravate the situation.
Therapeutic exercises for symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis
Therapeutic gymnastics is used in complex therapy in the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis and gives excellent results. Unlike medications, it has no contraindications or side effects. Exercise therapy aims to improve blood flow to damaged parts of the body. It is important that the patient does not feel pain when performing certain exercises.
Therapeutic gymnastics is designed to strengthen the muscles in the neck area, and also serves as an excellent prevention of osteochondrosis.
How to distinguish heart pain from osteochondrosis and neuralgia
It is possible to distinguish heart pain from osteochondrosis of the thoracic region by a number of signs presented in the table:
| Diagnosis | Symptoms | How long does an attack last? | Associated symptoms | Where is it localized? |
| Angina pectoris | The appearance of severe pressing pain | About 4 minutes | Fear of dying, desire to empty the bladder | Left side of the chest, back, left upper limb |
| Heart attack | Begins with general weakness, then develops into angina pain | About 3 days | Pale skin, shortness of breath, feeling nauseous | Left hypochondrium, occipital region and abdomen |
| Pericarditis | pain in the heart area | Long-term | Frequent breathing, sudden increase in temperature, swelling of the facial skin and thickening of the blood vessels in the neck | Heart pain extending to the neck and lower jaw |
| Thoracic aortic aneurysms | Feeling of dull, piercing pain radiating to the left upper limb | Long-term | Convulsive cough, shortness of breath and difficulty swallowing | Pain in the heart area, radiating to the left shoulder blade |
| Intercostal neuralgia | Point pain | Over the course of several days | Hypersensitive skin | Along the costal arch |
| Psychosomatic chest pain | Penetrating pain that increases with movement | From several hours to several days | Increased heart rate, body tremors, shortness of breath | Under the chest and in the upper left limb |
| Extrasystole | Pressing sensation under the chest | Individually | Difficulty swallowing, belching | Under left breast |
| Thoracic osteochondrosis | Symptoms of angina pectoris that do not go away when taking Nitroglycerin | Long-term | Painful movements, sharp increase in symptoms when inhaling | Area of the heart and shoulder blades |
| Vegetovascular dystonia | The appearance of a dull aching pain | Less than an hour | The appearance of causeless tachycardia, tremor, poor sleep, increased fatigue | Chest, upper left limb |
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic methods are widely used for the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis after the completion of the acute stage of the inflammatory process. They can further reduce the severity of back discomfort, and also have a number of other positive effects on the body.
Most often, for thoracic osteochondrosis, the following are prescribed:
- electrophoresis with the introduction of drugs - this method allows for deeper penetration of the drug components into the tissues and enhances their therapeutic effect through the use of a weak electric current;
- magnetotherapy is a method of physiotherapeutic treatment, which is based on the beneficial effects of a magnetic field on the body, which helps stimulate blood circulation in the area of influence, which leads to the activation of metabolic processes, a decrease in pain and swelling;
- laser therapy is a method that allows you to achieve a pronounced anti-inflammatory and vasodilator effect, which will also lead to an improvement in the condition of the intervertebral discs and a reduction in pain;
- Ultrasound therapy is a physiotherapeutic procedure that provides an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect;
- diadynamic currents are an effective method of physical influence, thanks to the use of which there is a decrease in the severity of pain, an increase in metabolic rate and an improvement in the condition of muscle tissue.
As a rule, physiotherapeutic procedures are prescribed in courses of 10-15 sessions. But each of them has its own contraindications, which must be taken into account when choosing a specific type of exposure.
Electrophoresis
The main characteristics of pain arising from cardiac pathologies
Heart disease is divided into several types of pathology: angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, pericarditis, myocarditis.
Each pathology is accompanied by specific signs, having an idea of which, a person can sound the alarm in time and seek help from a medical institution.
Angina pectoris
An attack of angina is an acute heart failure caused by vasospasm, resulting in insufficient oxygen reaching the heart. The heart begins to contract harder, causing unpleasant sensations such as:
- sudden pain like a prick;
- pain radiates to the upper limbs;
- appear: panic, anxiety, fear of death;
- lack of air, suffocation;
- increased sweating;
- pallor of the skin.
With angina pectoris, pain appears, similar to an injection.
The pain disappears in a short time, as unexpectedly as it appeared. Heart rhythm returns to normal.
The nature of the pain helps differentiate angina from thoracic osteochondrosis. Pain when nerve endings are pinched always occurs or disappears with body movement and does not go away after using heart medications (nitroglycerin). The pain that occurs with this cardiac pathology is provoked by stress, intense physical activity, sudden temperature changes, overeating and goes away after taking nitroglycerin.
The intensity of pain during angina pectoris does not increase with coughing or movement, but may reappear during exercise.
Myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction occurs as a result of a blood clot formed in an artery, which clogs the lumen of the vessel. Blood circulation in this place stops, the integrity of the vessel is disrupted, which leads to bleeding and death of nearby tissues. All this is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- sharp, sudden pain that occurs in most cases at night;
- inability to move due to pressing pain behind the sternum;
- panic attacks, resulting in an increase in the level of adrenaline in the blood. Due to the release of adrenaline, the coronary vessels dilate, the pressure drops, and the person loses consciousness;
- severe weakness, feeling of cold, vomiting, thready pulse.
During myocardial infarction, sharp, sudden pain appears.
Life-threatening pain is the main symptom that distinguishes a heart attack from osteochondrosis.
Heart attack pain generally does not arise out of nowhere, but is the result of atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease.
Pericarditis
Pericarditis occurs when the serous membrane of the heart becomes inflamed. Inflammation disrupts the contractile function of the heart, causing unpleasant symptoms:
- pain of increasing nature;
- hyperthermia;
- respiratory dysfunction;
- nausea and vomiting;
- When listening to the heart, a murmur is heard.
Inflammation of the lining of the heart during pericarditis
The main difference between cardiac pain during pericarditis and chondrosis is increasing pain, the intensity of which increases for several days.
- What you can’t do and what you can do at home if your heart hurts
Myocarditis
Myocarditis is an inflammation of the heart muscle, accompanied by the following symptoms:
- slow heartbeat;
- low blood pressure;
- sensations of pain behind the sternum, pressing in nature;
- breathing problems, shortness of breath;
- pale skin with a bluish tint;
- swelling.
Inflammation of the heart muscle with cardiac myocarditis
Symptoms of pain of a pressing nature are a distinctive feature from pain with osteochondrosis.
Causes of osteochondrosis
The causes of osteochondrosis are quite varied.
Firstly, with age, the elasticity of the intervertebral discs is gradually lost.
This means that our back requires special attention. Prolonged stay in a position that causes spinal misalignment can cause irreversible changes. You should avoid sitting in an asymmetrical position, fight the habit of lying on only one side, and carrying a load (for example, a bag) in only one hand.
A sedentary lifestyle has a detrimental effect on the health of the spine. It is necessary to move, but physical activity should be moderate. The spine should be given the opportunity to recover after stress, and it is also advisable to avoid injuries that also lead to the development of spinal pathologies.
The second group of reasons is associated with metabolic disorders
and
poor nutrition
. Food rich in carbohydrates and fats saturates the body with calories, which we, in our sedentary city life, often simply have nowhere to spend; As a result, energy is stored as fat tissue, creating excess weight. Obesity is an increased load on the spine, which leads to the development of osteochondrosis. In addition, such a diet usually contains insufficient amounts of microelements (calcium, potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, manganese and others), which are so necessary to strengthen bone tissue. Endocrine diseases are often the cause of excess weight. At the same time, a violation of energy, water or mineral metabolism can also negatively affect the tissues involved in the structure of the spine.
Factors contributing to the development of osteochondrosis may be:
- flat feet;
- hormonal changes;
- infectious diseases;
- local circulation disorders,
as well as some other factors.
Associated pain
Patients often make an appointment with a urologist and gynecologist due to pain in the lower abdomen. This is how osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral spine manifests itself. Formed osteophytes infringe on the spinal roots, causing disruption of innervation. Therefore, when patients ask whether osteochondrosis can cause pain in the lower abdomen, vertebrologists answer in the affirmative. The progression of the pathology is indicated by the absence in the clinical picture of characteristic signs of urogenital diseases - bleeding, the appearance of cheesy discharge, cutting and burning during urination. But difficulties with emptying the bladder and intestines due to disrupted innervation cannot be ruled out. With exacerbation of osteochondrosis, other specific symptoms may occur:
- pain in the mammary glands, requiring differential diagnosis to exclude benign or malignant tumors;
- pain in the hypochondrium, epigastric region, reminiscent of an attack of gastritis, cholecystitis, pancreatitis, hepatic colic, hepatitis.
There have even been cases of toothache occurring during relapses of cervical osteochondrosis. Also, a person’s condition can be complicated by increased blood pressure, headaches, and dizziness. The psycho-emotional state is often destabilized - sleep is disrupted, anxiety and fatigue arise.
Why does pathology of the thoracic spine occur?
This part of the spine experiences moderate load and limited mobility. However, the pathology is common. The disease can be caused by one of the reasons or their combination:
- injuries and damages;
- excessive load on the department, including in childhood;
- age-related changes associated with decreased nutrition of disc tissue between the vertebrae;
- endocrinological diseases, especially during menopause;
- age-related impairment of calcium absorption;
- excess body weight;
- problems with blood vessels, atherosclerotic deposits in the vessels of the thoracic region;
- weak muscle corset.
Symptoms for various pathologies
The development of diseases of the central organ of the circulatory system is characterized by certain symptoms and varying degrees of pain.
Angina pectoris
Signs of discomfort that occur with angina pectoris due to acute lack of blood supply to the myocardium:
- pain is paroxysmal, occurs when walking, climbing, emotional stress, during physical activity after eating and disappears after 3-5 minutes in the absence of physical effort;
- 1-3 minutes after taking nitroglycerin, the discomfort in the heart area completely disappears.
Heart attack
With myocardial infarction, the pain is intense, burning and stabbing in nature, manifests itself most often in the morning and lasts several tens of minutes. The syndrome cannot be relieved with medications .
Inflammation of the outer membrane
Inflammation of the outer lining of the heart or pericarditis is characterized by a strong pain symptom, which turns into fever after 2-3 hours from the onset of the acute stage.
Discomfort increases with changes in body position:
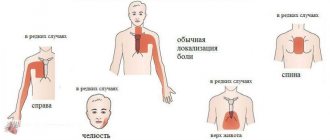
- Pain in the heart area: causes, types and first aid
- if a person stands , the pain radiates to the left shoulder;
- when lying down , it intensifies and radiates to the left hand.
Degenerative changes
Degenerative changes in the myocardium or myocarditis often do not have a clear clinical picture and are asymptomatic. In some cases, patients complain of:
- mild or severe pain in the heart, accompanied by shortness of breath;
- general fatigue;
- swelling;
- sweating
Thromboembolism and aortic aneurysm
Acute, stabbing pain in the heart area, aggravated by breathing, and the appearance of shortness of breath at rest may indicate blockage of a blood vessel by a thrombus (in this case, pulmonary embolism). Symptoms may be localized in the right hypochondrium, accompanied by bloating and prolonged hiccups.
In some diseases, local expansion of the aortic wall occurs .
The clinical picture of an aortic aneurysm depends on the location of the vessel and is often characterized by the absence of symptoms in the early stages. A person may complain of pain in the chest, back, lower jaw, and difficulty breathing.
Pain due to lumbar osteochondrosis
This species, according to statistics, accounts for half of the total diversity of the disease. And if with its thoracic variety the organs suffer less, since they are surrounded and held by the ribs, then the picture is completely different with the lower back. There are many nerve endings here, so the pain will be severe and sharp. Possible acute, subacute and chronic course. Acute pain syndrome in lumbar osteochondrosis is called lumbago or lumbago. At the same time, the person, as they say, cannot breathe or gasp, his lower back burns or goes numb. The duration can be up to a week, and from time to time, if a person is hypothermic, turns sharply, or physically works for a long time, it can come again and last a whole month. Irradiation is observed in the leg, buttock, and sacrum.