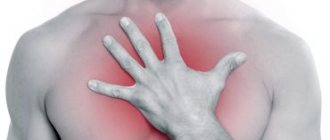
Causes of heart pain
Acute aching pain in the heart area occurs in a person regardless of age, conditions and circumstances. However, not every one of them may indicate heart problems. Depending on the mechanism of formation, all chest pains can be divided into cardiac and non-cardiac etiologies.
Stitching pain in the heart area can occur for various reasons, with diseases of other organs with irradiation of the pain syndrome into the chest.
- Diseases of the neuromuscular system:
- Thoracic osteochondrosis;
- Pain in the cervical spine;
- Myalgia;
- Intercostal neuralgia.
- Pathologies of large vessels:
- Aortic aneurysm;
- Pulmonary embolism.
- For pathology of the digestive system:
- For stomach diseases and heartburn;
- Pancreas;
- Esophagus;
- Gallbladder.
- Diseases of the respiratory system:
- Bronchial asthma;
- Pneumothorax;
- Pneumonia;
- Pleurisy;
- Tuberculosis.
- Nervous system diseases:
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- Panic attacks.
- Diseases of viral etiology:
- Shingles.
If, with pain in the heart area, there is pressure and radiates to the left hand and little finger, this may result in angina pectoris. Acute pain syndrome develops with myocardial infarction, dull pain characterizes chronic ischemic heart disease.
Treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis and its prevention
Conservative treatment of osteochondrosis in the thoracic spine is intended to stop or at least slow down degenerative changes, restore normal back mobility and eliminate symptoms that cause discomfort to the patient.
Therapeutic treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis involves the simultaneous use of:
- medications
(chondroprotectors, neuroprotectors, muscle relaxants, anti-inflammatory drugs, analgesics); - methods of physiotherapeutic complex
; - therapeutic exercises
; - orthopedic regime
.
Patients are also advised to change their diet and lifestyle.
In case of severe irreversible changes in the intervertebral joints , in which pain and nerve conduction disorders are not relieved by medications,
surgery is recommended for patients
. It helps stop the death of nerve tissue and prevent life-threatening or disabling consequences of thoracic osteochondrosis. Depending on the situation, complete or partial resection of the intervertebral disc or its replacement with an artificial one, narrowing of the spinal canal or other surgery may be indicated.
Treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis
Physiotherapy
The objectives of physiotherapy for osteochondrosis of the thoracic region are to reduce pain and inflammation, relieve spasms, strengthen the muscle corset, restore the function of the nerve roots and normal blood circulation.
To relieve the symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis, the following are successfully used:
- Magnetic therapy
is one of the most effective anti-inflammatory techniques. Improves metabolic processes in tissues and relieves swelling. - Laser therapy
. Promotes biological activation of regenerative processes. Helps eliminate the consequences of trophic disorders and relieve inflammation. - Drug electrophoresis
. Allows you to restore tissue nutrition and relieve inflammation - the effect of the procedure depends on the medications used. - Medicinal phonophoresis
. Ensures deep penetration of the active ingredients of medications into soft tissues. - Massotherapy
. Helps relax muscles, eliminate tension and improve the supply of nutrients to the tissues of the spine. In the early stages, it eliminates the main symptom of thoracic osteochondrosis - a feeling of pain in the sternum - in a few sessions. - Acupuncture
. Stimulation of muscles and nerve endings helps relieve pain, restore sensitivity and eliminate swelling. - Ultrahigh frequency therapy
. Increases the permeability of capillary walls, improves blood flow and ensures the flow of protective cells into the site of inflammation. - Shock wave therapy
. It starts the processes of restoration of bone and cartilage tissue, prevents the deposition of calcium salts on the vertebral surfaces. - Balneotherapy
. As a rule, mud and ozokerite applications are used, less often paraffin. Radon and hydromassage baths are also recommended for patients. They help improve metabolism and restore sensitivity in affected tissues. - Amplipulse therapy
. It has a neurostimulating, analgesic and trophic effect, activates metabolic processes, and facilitates breathing. - Kinesiotherapy
(physical therapy, massage, traction therapy, kinesiotaping). Allows you to strengthen ligaments and skeletal muscles, restore mobility in the back and eliminate even persistent spasticity. Prevents the formation of osteophytes and narrowing of the canals in which the spinal roots are located.
In addition to physical therapy sessions, for the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis, patients may be recommended an orthopedic corset, which allows them to relieve the load on the spine.
Exercise therapy and massage
Therapeutic exercises and massage help strengthen the back muscles and relieve stress on the spine. With daily sessions, they help achieve stable drug-free remission, increase range of motion, and eliminate neurological manifestations of the disease. These treatment methods also prevent complications of osteochondrosis.
. For example, congestion in the lungs (with thoracic osteochondrosis it is difficult to breathe deeply), due to which patients are susceptible to pneumonia, as well as coronary heart disease.
Dosed physical activity helps relieve compression of the nerve roots, improve blood circulation and nutrition of the intervertebral discs. The optimal frequency and duration of gymnastic classes is determined by the exercise therapy instructor. As a rule, 3-4 exercises of 10-15 minutes a day are enough.
.
The exercises recommended for the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis include the following:
- Stand straight, feet together, hands at your sides. As you exhale, raise your arms up and bend back, then inhale deeply. Lower your arms and lean forward, slightly arching your back in a dome-shaped manner (to do this, lower your head and shoulders as you exhale).
- Sit on a chair and, while inhaling, place your hands behind your head. Bend back and rest your shoulder blades on the back of the chair, exhaling.
- Get on all fours and arch your back. After maintaining the position for 3 seconds, bend your back with a crampon.
- Lying on the floor on your stomach, place your palms on the floor and, raising yourself on your arms, try to move your head as far back as possible, lifting your chest off the floor.
- Lie on your stomach and extend your arms at your sides. Perform the “yoke” exercise, trying to simultaneously raise your head and legs.
- Sit on the floor and stretch your legs in front of you. Reach the fingers of your right hand to the toe of your left foot and vice versa.
- Do a plank exercise (about 30 seconds).
- Perform hangs on the horizontal bar (or, in the absence of a horizontal bar, secure your fingers on the door frame and try to stretch your back as much as possible).
Bends to the side while raising your arm will also be helpful. All exercises should be performed 8 to 10 times
.
To treat thoracic osteochondrosis, various massage techniques are used, incl. acupressure and vacuum massage. For self-massage at home, patients are recommended the following movements:
- stroking the cervical-collar, scapular and axillary areas
; - squeezing with the thumb and index finger
(grabbing the skin and soft tissues); - trituration
; - kneading
(it should be done extremely carefully, it is advisable to entrust this technique to a specialist).
Massage should not be performed during exacerbations of the disease or during severe inflammation.
Drug treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis
To treat the symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis, the following groups of drugs are used:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- help relieve pain, calm inflammation and disperse swelling. They can be used both systemically (in the form of tablets, capsules and injections) and locally (in the form of ointments, gels, creams, compresses and solutions for medicinal electrophoresis). - Hormonal drugs
- to eliminate acute and chronic neurological pain. Used in cases where NSAIDs demonstrate insufficient effectiveness. - Muscle relaxants
are prescribed to reduce muscle tone and eliminate spasms of skeletal muscles. This helps alleviate pain and has a positive effect on tissue trophism. - Blood circulation correctors
- strengthen the walls of blood vessels and improve blood circulation in small capillaries that nourish the periosteum and other structural elements of the vertebral joints. Reduce discomfort and reduce the risk of complications. - Neuroprotectors
- to preserve and restore sensitivity during compression of nerve roots and relieve neurological symptoms. This group also includes cholinesterase inhibitors, which improve nerve impulse transmission and help restore normal muscle tone.
For structural restoration of tissues affected by the degenerative process, the following are used in the treatment of thoracic osteochondrosis:
- chondroprotectors (Artracam)
are essential bioactive substances that trigger the processes of regeneration of cartilage and bone tissue. Serves to prevent the growth of osteophytes and narrowing of the spinal canal. They help a weakened body grow stable and resilient cartilage cells. Taking Artracam significantly improves the shock-absorbing properties of intervertebral discs, making them more elastic and resistant to damage; - vitamin complexes
- help normalize metabolic processes and prevent excess oxidation in tissues.
To relieve excruciating pain that interferes with the patient’s daily activities, the doctor may recommend a medical blockade with anesthetics. Diuretics are used to eliminate swelling and relieve compressed nerves and blood vessels.
Prevention of thoracic osteochondrosis
To prevent symptoms of thoracic osteochondrosis, you should:
- Take care to maintain healthy posture. This is facilitated by walking, swimming and therapeutic exercises to strengthen the muscles of the back, chest, abs, and shoulder complex.
- When working sedentarily, properly arrange your workplace and perform physical warm-up whenever your back and neck begin to become stiff (ideally, bend to the sides, stretch, and rotate your shoulders every 2 hours).
- Avoid back injuries and promptly seek help from an orthopedic traumatologist, even in the case of a seemingly insignificant bruise. Other diseases of the musculoskeletal system should not be triggered, especially in the joints of the lower extremities.
- If possible, unload the spine during the day (to do this, just lie on the floor for 40 minutes).
- Protect yourself from hypothermia and stress.
- Take chondroprotectors to protect joints for at least 3 months a year. Regardless of the strength of the muscular corset, the human spine is anatomically not adapted to vertical loads, and therefore requires additional support.
- Adjust weight if it is overweight. In addition to maintaining a low-carb diet, you should eat a diet high in vitamins and minerals. In the spring-autumn period they can be taken in tablet form.
- Sports activities that involve jumping from heights or lifting heavy weights should be limited.
- It is advisable to sleep on a semi-rigid bed, and for prolonged sitting, choose hard furniture. This helps maintain muscle tone and relieve stress on the spine. If possible, you should purchase an orthopedic mattress and shoe insoles.
- Do not lift loads weighing more than 10 kg. The load should be distributed evenly, with muscle tension and without transferring to one side. If necessary, use a special sports corset. It is undesirable to hold loads in outstretched arms for a long time.
- Women should avoid wearing high-heeled shoes. The optimal heel height is 2-4 cm.
These recommendations will also be useful for those who are already sick - they will have a beneficial effect on the condition of the spine and will help to significantly slow down pathological changes.
And remember: the main thing in the prevention of thoracic osteochondrosis is consistent adherence to healthy habits.
Let chest pain never bother you!
What are the symptoms of pain in different diseases?
Often, pain in the heart area when inhaling is attributed to purely heart diseases, without even suspecting that the real reason lies in something completely different.
How the pain syndrome manifests itself depends on the causes and level of progression of the disease. For example, with heartburn, a burning sensation also occurs in the sternum area. They occur when gastric juice enters the esophagus. Heartburn is also characterized by the appearance of belching and an unpleasant sour taste. These symptoms appear after eating, when bending the body, or in a lying position. In this case, antacid medications are prescribed for relief. When heartburn occurs and pain radiates to the heart area, the cause does not always lie in the esophagus.
- These may be symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), which is also characterized by heartburn;
- Spasm of the esophagus with disruption of muscle function, which leads to problems with swallowing and moving food in the stomach;
- With achalasia, this pathology manifests itself in disruption of the valve between the stomach and esophagus, with food retention and the appearance of pain in the chest.
Depending on the nature of the pain in the heart area, inflammatory diseases can be diagnosed:
- Gall bladder with the development of cholecystitis;
- Pancreas and acute manifestations of pancreatitis;
- Gallstone disease (GSD).
Painful symptoms in these diseases can radiate into the chest cavity and resemble heart pain.
Pulmonary diseases can also be accompanied by sharp and dull pain in the chest. These signs can occur with pneumonia, pleurisy , with characteristic inflammation of the lungs and tissues that line the chest cavity, respectively. These diseases are characterized by increased pain when inhaling, the appearance of a cough, and an increase in temperature to critical values. Also, diseases can accompany each other and after pneumonia complications arise, which manifest themselves in the form of pleurisy.
Pain or heaviness in the right hypochondrium
Hepatitis
Jaundice
Vomit
41038 05 April
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Pain or heaviness in the right hypochondrium: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
The right hypochondrium is one of nine areas into which the anterior abdominal wall is conventionally divided. This area belongs to the so-called “upper floor” of the abdominal cavity.
In the right hypochondrium there are the liver, gallbladder, hepatic angle of the colon, and swollen loops of the small intestine can also be projected into this area. The organs listed above belong to the digestive system.
The liver is a parenchymal (spongy) organ with a very good blood supply. The outside of the liver is covered with a capsule in which nerve endings are located. The liver is involved in the metabolism of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, and plays a vital role in detoxification of the body.
Harmful substances that enter the liver are subjected to “chemical” processing, which makes them less toxic to the body and promotes faster elimination through the gastrointestinal tract and urine.
In addition, liver cells produce bile necessary for digesting food, primarily fats. Bile enters the gallbladder, located on the lower surface of the liver, where bile accumulates, which is released from it into the duodenum during the next meal.
From above, the liver is adjacent to the diaphragm - a kind of muscular partition between the abdominal and thoracic cavities. From below, from the side of the abdominal cavity, the diaphragm is lined with peritoneum (which covers the entire abdominal cavity and organs located in it from the inside), and from above, from the side of the lungs, by the pleura, which lines the pleural cavity from the inside and covers the lungs from the outside. Both the pleura and peritoneum have good innervation, which is important to know to understand the causes of pain and heaviness in the right hypochondrium. The peritoneum also covers the gallbladder and intestinal loops.
Types of pain or heaviness in the right hypochondrium
The pain in the right hypochondrium can be acute, sometimes “dagger-like”, which makes you think about a serious illness. This pain is characteristic of hepatic colic and is often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, increased sweating, increased heart rate and a drop in blood pressure.
In chronic diseases and the gradual development of acute diseases, the pain is often dull, bursting in nature, or is described by the patient as “heaviness, discomfort” in the area of the right hypochondrium.
Pain syndrome can be spontaneous, or it can be provoked by food intake, alcohol, physical activity, change in body position, etc.
Possible causes of pain or heaviness in the right hypochondrium
There is only one mechanism for the development of pain: stimulation of pain receptors. As mentioned above, the peritoneum has good innervation. Also, a large number of nerve endings are localized in the wall of hollow organs (intestines, gall bladder). Therefore, inflammatory processes in these organs naturally manifest themselves as pain.
Pain also occurs when the liver capsule is stretched. This can occur due to an increase in the volume of the organ (which in most cases is associated with tissue swelling), due to the accumulation of any fluid (most often blood) under the capsule (with a traumatic rupture of the liver), or damage to the capsule.
Unpleasant sensations in the area of the right hypochondrium are caused by excessive distension of the intestinal loops by intestinal contents or gases. In addition, since the organs of the chest are located close to the right hypochondrium, in case of development of pleurisy (inflammation of the pleura), the pain syndrome can also be localized in the right hypochondrium and imitate diseases of the abdominal organs.
Diseases that cause pain or heaviness in the right hypochondrium
Among acute diseases accompanied by pain in the right hypochondrium, it is worth mentioning first of all those that require emergency surgical intervention.
These include
acute calculous cholecystitis
and
renal colic
.
Both conditions are a consequence of cholelithiasis
. Inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis) develops against the background of an already advanced process of stone formation or, conversely, is the cause of the formation of stones. With renal colic, a calculus (stone) becomes wedged into narrow segments of the biliary tract, which is accompanied by severe pain, impaired bile outflow, and in more severe cases – jaundice (yellowing of the sclera and skin).
Other diseases of the biliary tract, such as
biliary dyskinesia
,
chronic cholecystitis
, cause recurrent pain in the right hypochondrium, usually associated with an error in diet.
Another disease classified as an “acute abdomen” that can cause pain in the right hypochondrium is appendicitis.
(inflammation of the appendix).
Despite the fact that the classic position of the appendix corresponds to the right iliac region, an abnormal position of the appendix in the right hypochondrium is quite common, especially in children.
Overdistension of intestinal loops can develop as part of
intestinal obstruction
.
Swelling of the liver tissue is characteristic of hepatitis (inflammation of the liver parenchyma). Hepatitis can have a variety of origins: viral hepatitis A, B, C, etc., autoimmune, toxic, incl. alcoholic. These diseases are usually accompanied by pain, as well as weakness, nausea and vomiting, yellowing of the skin and sclera, change in the color of urine and feces.
Subcapsular hematomas of the liver (accumulation of blood between the liver tissue and its capsule), as well as ruptures of the liver capsule, are usually traumatic in nature.
Among the diseases of the chest that can cause pain in the right hypochondrium, it is worth mentioning pleuropneumonia (inflammation of the lung tissue and pleura), heart failure, intercostal neuralgia and herpes zoster. The latter is characterized by the appearance of blistering-type skin rashes, which are preceded by severe pain.
Which doctors should you contact if you experience pain or heaviness in the right hypochondrium?
If sudden, progressively increasing pain appears in the area of the right hypochondrium, you should contact a doctor to exclude acute surgical pathology. If the pain is not acute, the examination can begin at or. If necessary, the patient can get advice from a hepatologist (a specialist in liver diseases) and other specialized specialists.
Diagnostics and examinations for pain or heaviness in the right hypochondrium
After a detailed survey and comprehensive clinical examination, the doctor, as a rule, needs laboratory and instrumental confirmation of the diagnosis. For this purpose, the following studies are used:
- A clinical blood test with determination of the leukocyte formula, based on the results of which one can suspect the presence of an inflammatory process in the body and determine its severity.
How to help with acute pain in the heart?
It is no coincidence that when pain appears in the heart area, they do not know what to do until the doctor arrives. Call the hotline number +7 (863) 226-18-17 , which is best entered into the phone’s memory in advance. Experienced private medical doctors help in emergency situations and transport the patient to the hospital. Emergency medical care is provided in clinics, hospitals and at home.
Before the doctor arrives, you should stop moving and take a lying position, and be sure to call a specialized ambulance. If your heart hurts, self-medication can end sadly and lead to death.
In case of high or low blood pressure, take the tablet as indicated. The patient is prescribed sedative drops , Corvalol, motherwort, valerian, and nitroglycerin. If the pain has passed, there is no need for nitroglycerin; it is also contraindicated for low blood pressure. You can put validol under your tongue. Treatment of cardiac pathologies is prescribed by a doctor according to indications.
Treatment methods
If you experience sharp pain in your heart, you must take a sitting position and unfasten your collar and cuffs. If your blood pressure is elevated and you suspect an angina attack, you should take a nitroglycerin tablet. It is also important to provide access to fresh air into the room. If symptoms do not go away after 15–30 minutes, you need to call an ambulance.
The treatment regimen is selected individually, depending on the exact diagnosis, the patient’s age and other factors. During an exacerbation of diseases, hospital treatment may be necessary, but then it is necessary to follow doctors’ orders at home. Thus, the treatment regimen may include the following steps:
- taking medications - prescribed individually, necessary for long-term use for certain diseases;
- proper nutrition - to reduce the load on the heart, you need to avoid fatty and salty foods;
- surgery - is prescribed only if there is a threat to life due to a blood clot or heart defects.
At the Clinical Brain Institute, treatment is carried out both in an inpatient and outpatient setting. At the center you can receive 24-hour medical supervision, as well as recommendations for doing it at home. The effectiveness of treatment depends on the timely use of medications, as well as proper nutrition and other factors.
What diseases cause pain in the heart?
Acute pain syndrome can also appear with pulmonary diseases such as bronchial asthma and pneumothorax. Asthma attacks cause pain throughout the chest cavity. An equally severe form and painful condition is characterized by pneumothorax , in which air penetrates from the outside into the chest cavity and the lungs can collapse with the appearance of pain.
Among the main causes of painful attacks in the sternum area is also pathology of the peripulmonary vessels. They intensify when inhaling with the formation of a cough with pulmonary embolism , pulmonary hypertension with increased pressure in the vascular system supplying blood to the lungs.
Painful vascular diseases include dissecting aortic aneurysm with characteristic damage to large vessels. This emergency condition can be life-threatening. In this case, the pain is initially felt in the heart area and gradually moves down the abdomen. The patient's blood pressure drops sharply, tachycardia occurs and he loses consciousness.
A classic example of the appearance of pain in the chest area is osteochondrosis , which occurs in the thoracic and cervical spine. The pain is reminiscent of angina attacks with radiation to the left shoulder blade and arm. The difference lies in the intensification when moving, raising arms, turning the head, bending the body.
Sharp stabbing pain is characteristic of intercostal neuralgia, Tietze syndrome . It occurs at the joints and spaces between the ribs and becomes more intense when inhaling. The patient cannot take a deep breath, shallow breathing is observed. In case of pathology, strong anti-inflammatory and painkillers are prescribed.
An extremely painful condition in the heart area is characterized by inflammation of the muscle fibers of the chest and back . It resembles similar acute pain in intercostal neuralgia and osteochondrosis.
Shingles , which occurs as a result of infection of the body with the herpes virus, is no less painful In this case, the nerve endings are affected, characteristic rashes appear on the skin, which becomes sensitive, and this whole clinical picture is accompanied by acute pain in the chest.
Painful attacks can occur during panic attacks, nervous disorders of various etiologies.
This category of patients is often young, with an unstable nervous system, and in a depressed state after stress. In this case, pain can appear spontaneously or be systematic.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
For moderate chest pain on the right side caused by a bruise, it is enough to rest for several days, apply dry compresses and ointments with anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve discomfort. If the pain does not subside and is accompanied by swelling and bluishness of the skin, you should visit a specialist to promptly identify a rib fracture as the probable cause of the symptom. Pain syndrome that occurs against the background of coughing and shortness of breath is an indication to consult a doctor - independent treatment of diseases of the respiratory system is fraught with serious complications.
Conservative therapy
In most cases, it is enough to treat the underlying cause of pain, but for severe and unbearable pain in the right chest, analgesics (both NSAIDs and narcotic drugs) are indicated. To eliminate pain, physiotherapy methods are used: electrophoresis, compresses on the affected area with dimexide, corticosteroids, and anti-inflammatory drugs. The following medications are prescribed as etiotropic therapy:
- Antibiotics
. Medicines are used to destroy bacterial microorganisms that cause pneumonia or purulent bronchitis. Beta-lactam antibiotics and macrolides are often taken or administered. Fluoroquinolones and interferon are effective for the treatment of atypical pneumonia. - Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
. NSAIDs reduce the production of cytokines and active mediators, reduce local manifestations of the inflammatory process, and reduce febrile fever. For chest injuries, they relieve pain well. The products are used both orally and externally in the form of ointments. - Expectorants
. Medicines thin the mucus, which clears the airways and speeds up recovery time. Mucolytics and reflex herbal remedies are used. To sanitize the upper respiratory tract, gargling with antiseptics is recommended. - Derivatives of ursodeoxycholic acid
. The drugs reduce the concentration of toxic acids and reduce the rate of stone formation in the gallbladder by normalizing the chemical composition of bile. UDCA also has hypolipidemic and hypocholesterolemic effects and protects hepatocyte membranes. - Vitamins.
Thiamine, pyridoxine and other B vitamins improve the nutrition of nerve fibers and accelerate the regeneration of the myelin sheath. For better absorption, they can be combined with ascorbic acid. Tocopherol is prescribed as an antioxidant.
How to understand that your heart hurts?
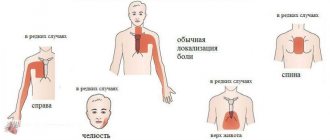
Pressing sharp pain in the heart occurs with angina pectoris or “angina pectoris,” which is the main precursor to the development of coronary heart disease (CHD). It radiates to the shoulder, left hand and little finger, and can radiate to the jaw. The intensity increases with nervous tension and physical activity. It occurs as a result of coronary vascular spasm and insufficient oxygen supply to the heart muscle due to atherosclerosis. The pain may go away on its own with rest and rest.
Among the most dangerous heart diseases associated with the cardiovascular system of the body is myocardial infarction . It occurs as a result of blockage (thrombosis) of a coronary artery by an atherosclerotic plaque and cessation of blood supply to an area of the heart muscle. In this case, necrosis occurs and part of the muscle dies.
Pain during myocardial infarction causes severe weakness, lack of air, radiates to the left arm, encircles the shoulder and spreads under the left shoulder blade, sometimes to the neck, jaw, and can form far from the heart area. Sometimes the temperature rises. The person breaks into a cold sweat, shortness of breath, and in some cases nausea.
Chest pain occurs in the case of cardiac pathologies of inflammatory etiology, these include endocarditis , myocarditis , pericarditis. They appear after illnesses caused by viral and bacterial infections.
Symptoms for which you need to call an ambulance
The manifestations of different types of acute coronary syndrome are similar, and it is often impossible to distinguish between angina and heart attack based on symptoms alone.
The symptoms of angina are quite typical. People usually experience an attack of pressing, squeezing pain under the shoulder blade or behind the sternum. People often interpret this sensation as discomfort or heaviness rather than pain. Discomfort may also occur in the shoulder or on the inside of either arm, spreading through the back into the throat, jaw or teeth. However, in people with unstable angina the picture changes. Attacks of pain occur more frequently or more severely, or attacks occur at rest or after light physical activity. About two out of three people who have a heart attack experience unstable angina, shortness of breath or fatigue in the days or weeks before. This change in chest pain patterns can lead to a heart attack.
With a heart attack, the most recognizable symptom is usually pain in the middle of the chest, which may spread to the back, jaw, or left arm. Less commonly, the pain spreads to the right arm. The pain of a heart attack is similar to that of angina, but is usually more severe, lasts longer, and is not relieved by rest or nitroglycerin. Less commonly, the pain is felt in the abdomen, where it may be mistaken for indigestion, especially because burping may provide partial or temporary relief.
For unknown reasons, women often experience atypical symptoms that are less likely to be accurately diagnosed as a heart problem. About a third of people who have had a heart attack do not experience chest pain. Typically these include women, people over 75, those with heart failure or diabetes, and those who have had a stroke.
Other symptoms of an attack include feeling lightheaded or faint, sudden heavy sweating, nausea, shortness of breath, and fast heartbeat (tachycardia).
During a heart attack, a person may become restless, anxious, sweat profusely, and may experience a feeling of impending doom. Lips, hands or feet may turn slightly blue. During the first hours of a heart attack, a heart murmur and abnormal heart sounds can be heard with a stethoscope.
How is differential diagnosis carried out?
If chest pain occurs, you should immediately call an emergency doctor. Before the specialist arrives, if possible, relieve emotional and physical stress, calm down, lie down and understand the nature of the pain in order to properly notify the doctors.
The doctor's examination includes consultations with specialized specialists, instrumental studies, and an electrocardiogram. It shows how the heart works, detecting signs of a heart attack depending on the stage and location.
Medical care and consultations can be prescribed by various specialists, a neurologist, cardiac surgeon, infectious disease specialist, pulmonologist, surgeon, gastroenterologist, psychiatrist. In case of nervous experiences, you may need the help of a psychologist.
Diagnostic methods
After the examination, the doctor will prescribe an examination regimen to assess the patient’s general condition and to understand the cause of pain in the heart area. It will include only those techniques that allow you to determine the cause of deterioration in health:
- blood tests - include general and biochemical studies, as well as determination of the level of cholesterol, lipids and other specific elements;
- ECG (electrocardiography) is a method of assessing the work of the heart, which consists of recording electric fields, can be carried out within a few minutes or 24 hours;
- Cardiac ultrasound is an informative diagnostic method that allows you to identify heart defects, anomalies in the structure of valves and large vessels;
- Ultrasound of vessels with the addition of a contrast agent - prescribed to assess the speed and intensity of blood circulation, the presence of blood clots;
- other methods - may include examination of the cervical spine, diagnostic tests, ultrasound of internal organs, fluorography.
At the Clinical Brain Institute, you can undergo a complete diagnosis if pain occurs in the head and heart. Modern equipment is located here, thanks to which it is possible to obtain accurate results in a short time. In addition, patients are offered comfortable conditions for placement in a hospital for the period of examination and manipulation.
Instrumental studies
In addition to an electrocardiogram (ECG), in case of cardiac pathology, various instrumental diagnostic studies .
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- FEGDS examination of the digestive organs;
- Ultrasound of the heart, pulmonary vessels and aorta;
- FVD, examination of external respiration functions;
- Chest X-ray;
- CT, computed tomography;
- MRI, magnetic resonance imaging;
- EchoCG, echocardiography and others.
Prevention methods
Most diseases that cause pain in the head and heart can be prevented. To do this, it is enough to follow a set of simple rules recommended by cardiologists around the world:
- give up bad habits - smoking and drinking alcohol are dangerous for the heart and have a detrimental effect on the condition of blood vessels;
- eat right, avoid excess fat, salt and sugar in the diet;
- lead an active lifestyle - moderate physical activity improves the condition of the myocardium and strengthens the vascular walls.
The Clinical Brain Institute specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases that cause pain and discomfort in the head and heart. Our center has all the conditions for conducting examinations of various levels of complexity, as well as for treatment and rehabilitation. Specialist and generalist doctors are specialists with many years of experience. However, it is important to seek medical help promptly, since the effectiveness of treatment decreases as the disease worsens.
What signs confirm heart pain?
Critical conditions are caused by cardiac pathologies, which can be determined using simple manipulations. It is necessary to understand whether the pain intensifies when inhaling, when raising your arms, bending your torso, or whether you can take a deep breath. An increase in pain may indicate the presence of intercostal neuralgia or osteochondrosis.
The pain may intensify with physical exertion and decrease at rest when angina pectoris , with insufficient blood supply to the heart muscle in an active state.
Cardiac pathologies are often accompanied by sharp pressing pain, difficulty breathing, stress, discomfort in the chest, cold sweat, irradiation to the left shoulder, arm and under the left shoulder blade.
An emergency call to a private medical ambulance allows you to help in emergency situations, do an ECG, a rapid blood test for the protein troponin to determine myocardial infarction, and transport the patient to the hospital.
Rate this article
Article rating 4.31 out of 5. Votes: 59.
Latest articles
Sexual transmission of infections
Sexually transmitted infections or STIs are dangerous diseases that can undermine health and lead to dire consequences. Most of the diseases in this group are…
Hormonal disorders
A woman’s well-being largely depends on the endocrine system. Any hormonal imbalance can cause a sharp deterioration in health, weakening the immune system...
Cervical dysplasia
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia or cervical dysplasia is a precancerous condition expressed by pathological changes in cells. In most...
When should you see a doctor?
Seeking medical help is an important issue on which a person’s life may depend. It is better not to wait until the pain reaches its peak, but to immediately call an ambulance.
Even if pain does not initially seem like a serious symptom, it is better to be safe than sorry. However, some features of pain may indicate that acute myocardial infarction and other severe pathologies are unlikely.
Signs of a “relatively safe” variant of heart pain:
- the pain is stabbing in nature and lasts several seconds - most likely the cause of the symptom is overexertion or short-term dysfunction of the heart;
- it becomes easier during movements - in case of heart disease, pain intensifies with exertion;
- pain is associated with breathing - in acute heart diseases, shortness of breath may occur, but pain when inhaling, rather, indicates pathologies of the pulmonary system.
You should definitely not delay seeking medical help if:
- acute unbearable pain with a characteristic spread to the left shoulder blade lasting longer than 5 minutes;
- pressing pain in the heart for 30 minutes or longer;
- a sharp increase or decrease in pressure;
- shortness of breath or difficulty breathing;
- loss of consciousness;
- repeated episode of chest pain.
In any of these conditions, you must immediately call an ambulance - the wait can cost not only your health, but even your life.
Acute pain in the heart is an indication to immediately consult a doctor and get a cardiogram, even at a young age. And after 40 years, both women and men should be especially wary of myocardial infarction. In such situations, it is better to be safe than to waste time and not have time to save the heart.