Heart pain can arise from completely different reasons. Some pains do not pose a danger and can simply be tolerated, while other pains are strictly contraindicated and must be relieved immediately. How to find out what kind of pain you have? You need to see a doctor and undergo an examination, without waiting for obvious signs, at the slightest suspicion.
Diagnosis of heart pain
An experienced doctor can determine its origin based on the description of the pain. But to confirm the diagnosis you need to undergo an examination. First of all, an electrocardiogram (ECG) is done, including with physical activity. If no abnormalities are detected, the ECG is recorded throughout the day (24-hour monitoring).
If pain in the heart appears after a sore throat, then an ECG, echocardiography (ultrasound examination of the heart), and blood tests are required, which can reveal inflammation in the heart muscle.
If you have pain in the heart area, be sure to consult a doctor - he will help you figure out how serious it is. What methods are used today to study cardiac activity? There are quite a few of them, and the specific diagnostic set in each case is determined by the attending physician.
- The well-known ECG - taking a cardiogram - is a mandatory technique for any suspicion of heart disease. Stress ECG is also widely used - recording data during physical activity (usually velometry or treadmill test), as well as Holter ECG (when an electrocardiogram is taken during the day).
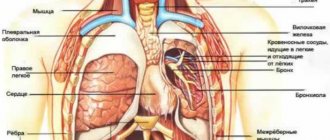
- Often, the doctor prescribes a graphical recording of heart sounds and noises (phonocardiography), a study of the valves and muscles of the heart, as well as the speed of blood flow in the heart cavities using ultrasound waves (echocardiography). Coronary arteries are studied using a radiopaque method (coronary angiography). How well the myocardium is supplied with blood can be determined by radionuclide diagnostics (scintigraphy).
- To exclude damage to other organs as the cause of heart pain, patients are prescribed a spinal examination (X-ray, computed tomography, MRI), consultation with an orthopedist, neurologist, gastroenterologist, and even a psychotherapist.
Experienced doctors know that some (and fairly accurate) conclusions can be drawn by listening carefully to the patient. When a person describes his feelings in detail, keeps and shows the doctor a kind of diary of the occurrence and nature of pain in the heart area, most likely the heart itself has nothing to do with it. Also, an “external” source of pain is indicated by patient reports of varying durations of attacks, a strong and very disturbing heartbeat - of course, if the person does not have heart failure. But if the patient perfectly remembers all his painful sensations, but describes them sparingly and reluctantly, there is a high chance of diagnosing serious heart disease.
In any case, remember: the main thing to do if your heart hurts is to consult a specialist and give him the right to draw conclusions about your health.
Heart pain can be a consequence of cardioneurosis, a disease of the nervous system. They intensify under stress and have a constant aching character. Such pain is relieved with sedatives (for example, valocardine or valerian). But you need to remember that only a doctor can make a diagnosis of cardioneurosis after an examination.
Pain in the heart due to inflammation of the heart muscle (myocarditis) is prolonged, aching, sometimes it is combined with stabbing pains, they are usually felt not behind the sternum, but to the left of it. The pain intensifies with physical activity, usually combined with shortness of breath, a feeling of “interruptions” in the heart’s work and its “fading”, weakness, malaise, and sometimes with a slight fever. Such pains often appear 2-3 weeks after a sore throat or other illness. You can’t joke with these pains - you need to see a doctor immediately, the treatment will be long-term.
Heart pain can occur when the arteries that supply nutrients and oxygen to the heart muscle spasm (compress). Such attacks of pain are called angina pectoris, they are very dangerous and cannot be tolerated.
How to distinguish heart pain?
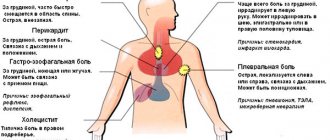
One of the signs of heart problems is pain. Diseases in which such symptoms are possible include: Angina pectoris. There is a feeling of discomfort or pain of a pressing, squeezing or burning nature. The pain radiates (transfers, spreads) to the left shoulder or the inside of the arm. A painful attack often begins against the background of physical activity or strong emotional impact. It can last up to 10 minutes and is relieved with nitroglycerin.
Aortic dissection . If at least one of the following symptoms appears, you should immediately (!) call an ambulance: sharp migrating pain, with possible irradiation to the area of the left arm or neck; burning, pressing or tearing pain; possible fainting; cyanosis (pallor) of the upper half of the body is observed; bradycardia (slow heart rate).
Myocardial infarction. Severe chest pain and fear of death are the most characteristic signs of a heart attack. In the peripheral form, the pain radiates to the neck, extends to the left limb and little finger. The following symptoms are typical for a heart attack: attack of suffocation, unproductive cough; the duration of pain is more than 15 minutes; pain does not go away after taking nitroglycerin; the pain intensifies with movement.
Myocarditis. With myocarditis, you may feel general malaise and persistent pain in the heart area. Myocarditis is an inflammatory process often accompanied by heart rhythm disturbances. Physical activity increases pain; Possible low-grade fever due to an infectious process.
Pulmonary embolism. Accompanied by symptoms such as: tachycardia (rapid heartbeat), shortness of breath, prolonged chest pain.
One of the most unpleasant types of pain is burning. The causes of burning pain are varied: it can be associated both with heart disease, the symptoms of which are described above, and with problems of the stomach and esophagus. The main cause of burning pain behind the sternum, not associated with the heart, may be: gastritis, pleurisy, esophagitis, intercostal neuralgia, gastric or duodenal ulcer. The main difference between such pains will be clear localization. Pain associated with the gastric tract is not relieved by nitroglycerin. But the main feature of cardiac burning pain behind the sternum will be its diffuse nature - it is difficult for the patient to show a specific location of its localization. In addition, this type of pain can radiate to the left arm and neck. Nitroglycerin will help determine heart disease: after taking it, the pain should go away or weaken. In the case of angina pectoris, nitroglycerin will help relieve pain completely, but in case of a heart attack - only slightly.
Discomfort and pain associated with breathing is a fairly common symptom. Pain when breathing is not always associated with the lungs. Similar pain can occur with: pulmonary embolism, intercostal neuralgia, pneumonia, pleurisy, ARVI, pneumothorax, advanced scoliosis, tuberculosis, lung abscess. For any of the above diagnoses, you should seek help from a doctor.
An ordinary one-time pain, or a stabbing pain associated with any action, is considered not so dangerous. It is worth understanding that stabbing pain is not typical for heart disease. Much more dangerous is pressing, squeezing or burning pain. But stabbing pain can mean serious problems with the lungs; it also occurs with thrombosis or embolism.
The first step is to understand what exactly led to the pain. Does it recur with physical activity? Does it occur when you assume a certain position? After this, try to find the place where the stabbing pain occurs. But you shouldn’t diagnose yourself and prescribe treatment on your own. If the pain recurs, consult a doctor.
Chest pain in an elderly person: what to do ? With age, the likelihood of developing various diseases increases. In an elderly person, pain may be associated with uncontrolled arterial hypertension, heart failure, arrhythmias, and chronic bronchitis. In addition to the reasons described above, chest pain can be caused by ischemia of the heart muscle. Coronary heart disease can manifest itself in an elderly person in the form of angina pectoris. In this case, the pain is associated with physical activity, even minor. It should be understood that the defense mechanisms of older people are reduced, so you should not hesitate or doubt when calling an ambulance.
What to do if you have chest pain? First of all, you should unfasten the top buttons of your clothing. If you have a heart disease previously diagnosed by a doctor, you must take the prescribed medications. If this happens for the first time, give the victim a nitroglycerin tablet (it is better to put it under the tongue). If there is no positive effect, repeat the dose after 5-10 minutes. If repeated use does not produce results, you must call an ambulance. Delay may cost the patient his life. If you don't have nitroglycerin on hand, you can put validol or mint gum under your tongue. Mint irritates the receptors located under the tongue, which reflexively relieves vascular spasm. Cases when it is necessary to quickly call an ambulance: pain of a squeezing, pressing nature; irradiation of pain to the left arm, neck, attack of pain is not relieved by nitroglycerin; long-term disturbances in pulse and blood pressure are observed; disturbance of consciousness.
Many people ignore these signals or interpret them incorrectly. Heart pain in different diseases has a different nature, and it is worth understanding that only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis.
Remember! Excessive self-confidence and procrastination can lead to serious consequences for the patient.
Prepared by a doctor on medical prevention
Healthcare Institution "Slonim Central District Hospital" Vataev O.L.
Angina pectoris
Attacks of angina pectoris occur first during exercise or stress (this is called angina pectoris), and then at rest (rest angina pectoris). In typical cases, the pain is squeezing or pressing in nature and manifests itself either in the upper part of the sternum or to the left of it. Pain can radiate to the left arm, the left half of the face and neck, to the lower jaw, left ear, to the left shoulder blade, sometimes to the right shoulder or both shoulders and both arms, and the back. Sometimes the pain spreads to the left side of the abdomen and lower back, and to the legs. The onset of pain is rarely sudden; usually the pain is of an increasing nature, lasts for several minutes, then disappears. This pain is different in that it can be relieved with nitroglycerin, a drug that relieves spasm of the coronary arteries (which supply blood to the heart muscle).
If such pain occurs at least once, the patient should consult a doctor, get examined and clearly know what to do during an attack. During an attack of angina, you need to:
- take a nitroglycerin tablet (under the tongue);
- lie down, open a window or window;
- if after 2 minutes the pain has not decreased, then take another nitroglycerin tablet and call an ambulance. Nitroglycerin begins to act within 1-2 minutes, its vasodilating effect lasts 20-30 minutes. Remember: neither Corvalol nor validol will help with angina - only nitroglycerin!
Myocardial infarction
If an attack of angina pectoris lasts a long time, then the heart muscle, not receiving nutrients and oxygen, begins to quickly deteriorate, its necrosis (death) occurs, this is myocardial infarction. That is why you should never tolerate pain due to angina pectoris.
Myocardial infarction is manifested by attacks of severe pain in the chest, which are not relieved by nitroglycerin. The duration of this pain is from 20-30 minutes to several hours. In such cases, the sooner the patient receives medical assistance, the greater the chance of recovery.
What is important to the patient?
- pain behind the sternum and in the heart area can be a consequence of angina pectoris or myocardial infarction - conditions that directly threaten a person’s life;
- if chest pain occurs, it is necessary to seek medical help from qualified specialists as soon as possible, since delay in this situation can cost a person’s life;
- Only a cardiologist can decide on a cardiac or non-cardiac cause of chest pain after conducting the necessary examination;
- Treatment of patients with coronary heart disease should be carried out only in the cardiology department of the hospital, equipped with an intensive care ward.