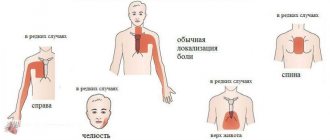
The appearance of pain indicates disturbances in the functioning of the body. We are talking about pathologies. The most common problem is discomfort in the heart area. They can be pulling, cutting, blunt or sharp. They have different intensity and duration. In some cases, the pain radiates to the arm or head. Then the problems are associated with neighboring organs of the human body.
What causes pain in the area of the heart and left shoulder blade? How to get rid of poor health, and which specialist should I contact? At the KDS Clinic, medical workers will conduct examinations, diagnose the disease even at an early stage and prescribe effective treatment.
In addition to pain in the heart area and under the shoulder blade, the patient experiences a number of other symptoms. These include dizziness, chronic fatigue, nausea and vomiting, migraines, and gastrointestinal disorders. It is extremely important to contact a medical facility on time. Ignoring pain leads to the development of the disease and deterioration of the condition. The treatment started will normalize the functionality of the body and prevent the development of the disease.
Why does my back hurt?
This may be associated with diseases of the internal organs, spinal trauma (including fracture), neurological pain usually indicates osteochondrosis, and sometimes it is a symptom of gastrointestinal pathology, kidney stones, etc.
In addition, the back is somewhat prone to injury and pain. The spine performs at least 4 functions: supporting, protective, shock-absorbing and motor. Therefore, if pain appears, it may be a consequence of poor posture, strong one-time load, sudden movement or turn.
What to do if you have back pain?
See a doctor and get examined. Based on the diagnosis, it will become clear how to cure back pain, depending on its root cause.
Reasons for appearance
Almost all degenerative-dystrophic changes in the musculoskeletal system, in general, and the spine in particular, are a consequence of overload. As a result of overload, in addition to gradual mechanical destruction, which with age begins to prevail over recovery processes, a disruption in the nutrition of anatomical structures (intervertebral discs, joint cartilage) occurs.
Excess weight, heavy physical labor, regular sports with predominant axial loads (weightlifting, running, jumping), prolonged static loads (“sedentary” work, especially at the computer), poor sleep conditions - all these are factors that overload the musculoskeletal system. .
Overload of the supporting structures of the spine and joints is aggravated by: impaired spring function of the feet (longitudinal, transverse flatfoot), smoothness or absence of shock-absorbing physiological curves of the spine, the presence of pathological ones (scoliosis, hyperkyphosis), weakness of the paravertebral muscles. A predisposing factor is also burdened heredity - the presence of relatives suffering from “osteochondrosis”, “radiculitis”, “arthrosis”, etc.
Causes of back pain
Finding out why your back hurts is not easy. The fact is that the spine is at the same time a support, protection, and shock absorption of the body. If chronic back pain appears, the problem is a violation of any of these functions.
If you feel back pain between the shoulder blades, it may be associated with bronchitis and cough. If your back muscles hurt, the discomfort may be due to overexertion due to heavy lifting the day before. Back pain on the right or left can be caused by a sudden rotation of the body.
There are more serious causes of periodic sharp pain. For example, inflammation of internal organs, kidney stones, spinal bruise. If diagnostics of the back do not show degenerative changes, it is worth examining the internal organs. Thus, discomfort in the lumbar region may be a symptom of nephrosis.
In one case or another, the treatment is different, so first of all you need to establish the cause.
Types of diseases based on the nature of back pain
Possible causes of aching pain :
- myositis;
- lumbago;
- intervertebral hernia.
It worsens when lifting weights, physical work, hypothermia, or staying in one position for a long time.
Causes of shooting pain in the limbs :
- intervertebral hernia;
- radiculitis;
- osteochondrosis.
Discomfort increases with walking, bending, coughing and sneezing. Feeling weak in the legs and arms.
Causes of throbbing pain :
- intervertebral hernia;
- osteochondrosis;
- lumbago;
- spondylosis.
The discomfort does not go away even after taking an analgesic.
Possible causes of bursting and pressing pain :
- in the chest area - pulmonary embolism and myocardial infarction;
- on any part of the spine - spondyloarthrosis;
- in the lumbar region - intestinal obstruction;
- in the neck area - atherosclerosis.
| Nature of pain | Diseases that cause it |
| Aching back pain (acute and chronic) | Lumbago (shooting in the lower back). The reason is hard physical labor. It usually goes away on its own within a few days. |
| Myositis, muscle strain, sudden heavy lifting, hypothermia, maintaining an uncomfortable position for a long time, for example during work. | |
| Displacement of intervertebral discs. The most common cause is osteochondrosis, but displacement can also occur with sudden heavy lifting and constant high physical activity. | |
| Sharp, radiating to the extremities | Osteochondrosis. Causes nagging pain in the back that radiates to the leg and becomes stronger when sneezing, coughing, or straining. |
| Radiculitis. Constant sharp (stabbing) or dull pain. It is usually localized on one side, can radiate to the thigh, buttock, leg, lower leg, and sometimes causes numbness and itching. The pain can also be burning and intensifies with movement. | |
| Intervertebral hernia. With this pathology, pain occurs when bending over, lifting heavy objects, intensifies when sneezing, coughing, moving, and is accompanied by weakness in the leg. | |
| Throbbing pain, severe, may not go away after taking an analgesic | Osteochondrosis, cracks in the vertebrae, lumbago, intervertebral hernia, spondylosis. |
| Bursting | In the upper back and in the middle of the sternum - may indicate angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, pulmonary embolism. In the lower back - intestinal obstruction, spondyloarthrosis. |
| Pressing | Angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, problems with the gallbladder (pain occurs after eating), atherosclerosis, hypertensive crisis. |
Why does my back hurt after sleep?
After waking up in the morning, you feel stiffness, discomfort and pain below the shoulder blades, in the right or left side, in the lumbar region. These sensations can be associated not only with an incorrect sleeping position or resting on an incorrectly selected mattress. After sleep, your back hurts for the following reasons:
- during the day physical work was performed with sudden lifting of weights;
- back muscles are weakened;
- intervertebral hernia or osteochondrosis is diagnosed;
- hypothermia occurred;
- the spine is curved, causing the muscles to contract unevenly;
- obesity, due to which the load on the spine is distributed unevenly;
- pregnancy;
- stress.
Diseases associated with joints and the spinal column
Back pain in the spinal area can occur due to the development of pathologies of the musculoskeletal system such as:
- Ankylosing spondylitis. The paravertebral muscles spasm, so to relieve discomfort the patient tilts the body forward. Over time, the vertebrae become woody, inflamed and fused, so the flexibility and mobility of the spine is impaired.
- Spondylolisthesis and spondylolysis. Due to these diseases, pain is mainly localized in the lumbar region. The vertebrae move forward or backward and compress the nerve endings;
- Osteochondrosis. The depreciation of the spine worsens. The discs between the vertebrae crack, the fibrous ring ruptures, and through the resulting cracks the core of the disc comes out and is pinched.
- Rheumatoid arthritis. Develops in the knees, shoulders, hip joint and moves to the cervical spine. In the morning, you feel stiffness and lumbago due to excess pressure on the nerves from the affected vertebrae.
- Osteomyelitis. Infection of the bone tissue of the spine causes inflammation and severe muscle pain.
- Reiter's disease results from inflammation of the small supporting muscles of the back.
- Intervertebral hernia due to the fact that during movement the protrusion between the vertebrae is compressed and pinched.
Muscle-related diseases
When determining the causes of back pain, tightness and spasms of the muscular corset that supports the spine are often discovered. Mobility is impaired as a result of:
- Fibromyalgia. My back hurts from my neck to my lower back. Neurological symptoms can be observed - sensitivity increases when pressing certain points on the back.
- Polymyositis. The back muscles become inflamed due to hypothermia and overexertion. It hurts to turn the body, muscle weakness is felt.
- Dermatomyositis. The skin near the striated and smooth muscles of the back becomes inflamed.
- Charcot's disease. The peripheral nerves that run along the spine become inflamed. Sensitivity worsens, muscle weakness increases, and gait changes.
- Polymyalgia rheumatica. It is difficult to raise your arms and stand on your feet without the help of someone else. The asymmetry of the back is noticeable.
Spinal cord pathologies
Back pain often occurs due to spinal cord compression. The spinal cord is the connecting link between the brain and the body. It runs from the head to the tailbone in the spinal canal between the vertebrae. There are 31 branches leaving the spinal cord. Each nerve is responsible for the innervation of one or another part of the body. The back may hurt due to pinching or inflammation of any part of the spinal cord as a result of:
- compression of the spinal membranes due to a spinal fracture, abscess or hematoma;
- cerebrovascular accidents;
- inflammation of nearby muscles;
- lack of vitamins and minerals;
- hemorrhages;
- complications of syphilis or HIV;
- multiple sclerosis;
- back tumors of various etiologies.
Back pain due to psychosomatics
Increasingly, back discomfort is not associated with physical illness. After the examination, no pathology is detected, which means that pain in the back and joints is caused by psychological factors. Unpleasant sensations can be triggered by depression, chronic stress, nervous tension, and sexual dissatisfaction. Due to nervousness, the gait changes, lumbago worsens, and sensory disturbances appear.
What examinations to do
The effectiveness of treatment depends on making the correct diagnosis, therefore a clinical examination by a doctor and additional instrumental and laboratory research methods are used:
- electrocardiography (ECG) is a type of recording of the electrical activity of the heart, which is used to diagnose angina and myocardial infarction. The most informative is a recording during an acute attack of pain;
- echocardiography (ECHO-CG) is an ultrasound method for visualizing the chambers of the heart and great vessels. Used to diagnose dissecting aortic aneurysm, valve defects and hemodynamic disorders after a heart attack;
- X-ray of the chest organs - for the diagnosis of rib fractures, acute bronchitis. Examination of the abdominal cavity using contrast helps establish the diagnosis of hiatal hernia. Not administered to women during pregnancy due to the harmful effects of ionizing radiation on fetal development;
- radiography of the spine in the cervical, thoracic and lumbar regions - for the diagnosis of traumatic injuries or osteochondrosis;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy is an endoscopic method for visualizing the hollow organs of the gastrointestinal tract, which is used to evaluate changes in the mucous membrane of the esophagus and stomach.
Laboratory diagnostics involves determining an increased number of leukocytes (nonspecific markers of inflammation) and troponins (sharply increased - a marker of myocardial infarction).
Causes of back pain by location
At different points of the back and spine, discomfort can be caused by different factors. Let's take a closer look at them.
Pain on the right side
Most often, the right side from the back hurts due to lordosis, kyphosis or scoliosis, as well as displacement of the intervertebral disc. The development of the following pathologies can be assumed:
- appendicitis;
- kidney stone disease;
- cholecystitis;
- salpingitis;
- oophoritis;
- nephritis;
- obesity;
- myositis.
Pain on the left side
If the unpleasant sensations are localized under the rib or near the lower back on the left side of the back, the following may develop:
- splenitis;
- urolithiasis;
- pinched spine;
- duodenitis.
Pain on the left in the hypochondrium indicates bronchitis, pleurisy, intercostal neuralgia, and heart pathologies. If the left side of the back hurts from below, doctors suspect a disease of the pelvic organs.
Pain in the lumbar region
The lumbar spine is the most mobile area and is subject to heavy loads. Because of this, the five lumbar vertebrae most often become inflamed from radiculitis, intervertebral hernia and osteochondrosis. Slightly less frequently diagnosed:
- infections – spinal tuberculosis or brucellosis;
- Reiter's disease;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- osteoporosis;
- sciatica;
- sciatica.
In the lumbar area on the right
Burning and cutting pain just above the lower back appears with curvature of the spine, spinal tuberculosis, neuralgia, osteomyelitis. The pain extends not only to bone tissue, but also to the muscle corset.
Nagging pain signals the development of scoliosis, myositis, and degenerative changes in the vertebrae. If therapy does not bring results within several months, the patient is examined for a malignant tumor.
Acute and sharp pain indicates the need to diagnose stones in the urinary or gall bladder, inflammation of the kidneys or neoplasms in them.
Left lumbar region
Most often, the left side hurts from below after running or sports training. This usually goes away within a few hours. But if the aching pain only increases, you need to exclude the possibility of circulatory disorders, scoliosis and osteochondrosis. Most often, these diagnoses occur in people who work while sitting.
Constant pain on the left side while walking is typical for patients with diabetes mellitus and radiculitis. A distinctive feature is that it passes at rest.
The most dangerous pain is on the left side between the left shoulder blade and lower back during myocardial infarction. Unpleasant sensations radiate along the left half of the body, so you need to quickly provide medical assistance.
Shoots in the left side of the lower back with a stomach ulcer, but the difference is in the nature of the pain. The pain in this case is acute, “dagger-like”.
Pinched nerve
Sciatica is compression of the sciatic nerve without destruction of the myelin sheath. Most often, sciatica is a consequence of osteochondrosis. The pain in this case is characterized by sharp and sharp jabs that radiate to the lower limb, sacrum, and lower back.
The nerve can become pinched in late pregnancy due to a change in the center of gravity. Less commonly, the pathology is caused by spasm of the piriformis muscle, spinal canal stenosis, or infection of bone tissue.
Intervertebral hernia
A herniation is a protrusion of the disc core after the destruction of the fibrous ring and a decrease in the elasticity of the disc. The deformity is associated with increased load on the spine, lack of nutrients and impaired metabolism. With the slightest load and heavy lifting, the distance between the vertebrae decreases, so the hernia protrudes more. The pain is sharp and sharp. It radiates to the buttock, arm or leg, and is also accompanied by a decrease in sensitivity of the limbs.
In the area of the shoulder blades
The paired bones in the clavicle and humerus area connect the back muscles and the shoulder corset. The pain is localized under the shoulder blades, between them, on the left or right side, between the ribs. Depending on the cause, back pain in the area of the shoulder blades can occur spontaneously, after an equal period of time, in paroxysms.
The characteristics of the pain indicate a possible diagnosis:
- If the pain is dull or aching, increases gradually, is relieved with medication, a stomach ulcer may develop. In this case, the pain is accompanied by dyspepsia, heartburn, bitterness in the mouth, and nausea.
- If the pain is aching and radiates to the shoulder, intensifies when moving the arm, scapular-costal syndrome develops. Accompanied by a crunching joint.
- If the pain is unbearable and intensifies during inhalation, body movement, coughing or sneezing, then this is intercostal neuralgia.
- If there is pain between the shoulder blades, but at the same time you feel dizzy, your blood pressure changes, and your arms go numb, then this is osteochondrosis.
- If there is pain under the shoulder blade on the left, while discomfort is felt in the chest and under the collarbone, then angina pectoris has worsened.
Pain along the spine and in the back
Pain throughout the spine or at a specific point indicates that the nerve endings are pinched. Exacerbation occurs with curvature.
If the pain is not severe, we can assume protrusion. As discomfort increases, protrusion can develop into osteochondrosis.
Vertebral pain occurs with myalgia, osteoarthritis, vertebral fracture, spondylosis. With ankylosing spondylitis, the pain is constant and sharp.
Causes of pain below the lower back
Basically, the lumbosacral region is susceptible to osteochondrosis and spondyloarthrosis, but less often the lower back and tailbone hurt due to displacement of intervertebral discs, scoliosis, pregnancy, endometritis, vulvitis, cervicitis, Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis.
Causes
The peculiarities of the sensitive innervation of the chest are due to the large number of internal organs and the close location of the main nerve bundles.
In addition, in medicine they use the concept of crossing zones of external and visceral (from internal organs) sensitivity with the formation of Zakharyin-Ged areas . Therefore, the appearance of sharp pain in the heart from the back is caused by the following conditions:
- injuries to the neck, chest or spine with pinched nerve fibers;
- diseases of the esophagus - tumors, diverticula (pathological protrusions of the muscle wall), strictures (narrowings caused by inflammation), varicose veins or rupture (perforation) of the wall;
- hiatal hernia;
- Osteochondrosis is a degenerative disease affecting intervertebral discs and vertebrae. It is characterized by pathological growth of bone tissue, increased load on the spine with the development of radicular pain syndrome, most often in the thoracic region and lower back;
- intercostal neuralgia - pain that occurs along the nerve (most often in the intercostal spaces), associated with mechanical action (spasmodic muscle or bone growth puts pressure on the nerve fiber, irritating it);
- Myocardial infarction is an acute condition characterized by necrosis (death) of part of the muscle mass of the heart due to impaired blood flow through the coronary vessels. More often it occurs after the rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque, the development of a thrombus (blood clot) or arterial spasm;
- dissecting aortic aneurysm - a violation of the integrity of the vascular wall associated with the leakage of blood between the layers and further destruction of the artery. The pathology is characterized by an acute attack in which the heart hurts and radiates to the back;
- angina pectoris is a variant of coronary heart disease, when compressive pain behind the sternum is observed with irradiation to the back, shoulder blade and left arm after physical activity. The disorder occurs due to a transient decrease in blood flow in the coronary vessels;
- acute bronchitis, tracheitis - inflammatory diseases of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract.
In elderly patients, with spinal curvatures, and diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular pathologies occur atypically: the heart hurts from the back.
Symptoms that accompany back pain
The clinical picture of spinal pain depends on the location:
| Cervical spine | Thoracic spine | Lumbar spine |
| Headaches and dizziness | Burning in the chest | Change in the number of urinations |
| Numbness and weakness of the hands down to the fingertips | Difficulty in inhaling/exhaling | Numbness and weakness of the lower extremities, including the buttocks and toes |
| Blood pressure surges | Feeling of tightness in the chest | Low sensitivity during bowel movements |
| Floaters and flashes in the eyes | Pain between and under the shoulder blades | Erectile dysfunction and decreased libido |
Situations in which you need to see a doctor as soon as possible
Usually the pain subsides within a few days. If the discomfort only increases, the pain is intense, then medical attention is needed.
You should call a medical team or go to the clinic yourself in the following cases:
- there has been a recent spinal injury or back injury;
- it is not possible to find a comfortable body position in which it becomes better;
- at night the condition worsens;
- the patient is under 20 years old or over 55 years old;
- the patient has a fever;
- neurological symptoms increase - limbs go numb, tingle, weaken;
- gait has changed;
- lumbago is felt in the shin;
- corticosteroids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs do not relieve pain;
- limbs become numb, tingle, and weak.
Diagnostic measures
Our specialists will make a more precise diagnosis after carrying out the necessary laboratory and instrumental diagnostics using the most modern equipment. When indicated, the following will be carried out:
- blood tests;
- urine test to evaluate kidney function;
- performing liver function tests;
- gastric endoscopy;
- Ultrasound for diagnosing somatic disorders, cardiac and vascular conditions;
- CT scan of the liver, pancreas;
- ECG of the heart;
- X-ray of the sternum.
Based on the fact that pain under the left shoulder blade from the back may not be a symptom of a single disease, a comprehensive examination by several specialists is not excluded. Our clinic offers patients one of the modern comprehensive types of examination - check-up, which includes many types of tests with the smallest set of diagnostic procedures. Timely contact with our specialists and a guaranteed correct diagnosis will help the patient undergo high-quality and successful treatment.
Diagnostics
To make a diagnosis of back pain, you need to make an appointment with a neurologist, take tests if necessary, and also undergo hardware testing as prescribed by a specialist.
- Blood tests.
They allow you to determine the presence of infection, ESR (increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate, which indicates inflammation, infection). If an increased level of leukocytes is detected, then this is also a sign of inflammation and infection. Also, blood tests can determine iron deficiency anemia, the cause of which may be oncology. - Hardware diagnostics.
- Duplex and triplex ultrasound scanning of the vessels of the neck and brain. Allows you to anticipate the structure and patency of blood vessels, the presence of narrowing or dilatation, plaques, blood clots, as well as compliance of blood flow with standards. It is used in diagnosing the causes of headaches, dizziness, high blood pressure, as well as in cases of suspected cerebrovascular accident, and in the early diagnosis of pre-stroke conditions.
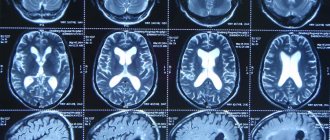
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging). The most accurate and effective examination method. Allows you to visualize tumors on the vertebrae, herniated intervertebral discs, compression (and its degree) of the spinal nerves and spinal cord, narrowing of the spinal canal, inflammatory changes, including post-traumatic ones. MRI is required before surgery and in the postoperative period.
- CT (computed tomography). Detects vertebral fractures and their nature, allows you to find even very small fragments if they were formed due to injury. Based on the data obtained, you can create a 3D image of the desired area. CT “sees” what went unnoticed during radiography.
- Radiography. Allows you to assess the condition of bone structures. It is carried out to diagnose fractures, arthritis, spondylolisthesis, and the degree of postural impairment. It can be performed with functional tests, that is, when the patient flexes and extends the spine during the examination. Visualizes inflammation of the joints in the spine, helps to identify the localization of compression of the nerve processes by indirect signs. The degree of color intensity of the vertebrae in the image allows you to evaluate their strength (with osteoporosis they are more “transparent”, and when healthy they are bright white).
- Electromyography (EMG). A study aimed at determining the condition of nervous tissue. It evaluates the electrical impulses produced by the nerves, as well as the reaction of the muscles to them. Electromyography helps identify nerve compression caused by stenosis (narrowing) of the spinal canal or intervertebral hernia.
- Bone scan. This test is necessary if the doctor suspects a bone tumor or compression fracture due to osteoporosis.
Treatment for back pain
Most often, patients do not know which doctor to see. A neurologist provides comprehensive treatment for back pain. It is he who should be contacted for problems with the spine. However, before a specialist arrives or visits him, you need to provide first aid for back pain.
How to relieve or relieve pain at home?
The most important thing is to relax. To do this, you need to lie on your stomach on a hard and flat surface. Best of all - on the floor. After a few minutes, you need to carefully roll over onto your back and raise your legs, fixing them so that your hips are at an angle of 90 degrees. This will take the load off your spine.
You can use anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of ointments and creams. After relieving the pain, you need to carefully get up and fix the painful area, for example, by bandaging it with a scarf or towel.
How to relieve pain if there are no painkillers?
Severe pain can be relieved with something as simple as a cold compress. It will not give complete relief, but it will alleviate the condition. This could be a product from the freezer, an ice pack, etc. You can also help with pain by applying a heating compress or heating pad. It’s just important not to overheat the sore spot.
What else helps?
Light physical activity aimed at warming up the muscles and increasing blood circulation will help relieve discomfort. This could be a leisurely walk, muscle stretching exercises.
Medicine against pain: methods of medical intervention
First of all, the disease that caused the pain is determined and its treatment begins. Along the way, medications are used to relieve discomfort and treat chronic pain:
- analgesics, NSAIDs, in rare cases – narcotic painkillers;
- B vitamins;
- muscle relaxants.
The person is prescribed bed rest and wearing a fixing corset (for example, for neuralgia).
An important stage of treatment is physiotherapy . Its main methods:
- electrophoresis with drugs;
- phonophoresis;
- laser therapy;
- magnetic therapy.
Reflexology is also provided :
- electrical neurostimulation;
- acupuncture techniques.
Massage, osteopathy, manual therapy, exercise therapy are effective for back pain. These techniques are used when pain is caused by diseases of the muscles and spine, during rehabilitation after injuries.
conclusions
The appearance of pain localized in the sternum is caused by pathologies of the heart and structures located behind the pericardium. Determining the underlying cause by detailing the pain syndrome (character, intensity, irradiation and connection with breathing, physical activity and food intake) helps to choose further diagnostic tactics.
More often, pain of such localization is characteristic of myocardial ischemia or damage to nerve fibers. Patients who have aching heart or back are prescribed instrumental and laboratory procedures that confirm a certain diagnosis, after which adequate therapy is selected, aimed at eliminating both the symptom and the cause of the pain.
Prevention
Clinical recommendations for the prevention of intervertebral hernias and osteochondrosis :
- move more, do gymnastics in the morning, do yoga;
- take a contrast shower followed by rubbing with a towel to enhance metabolic processes;
- undergo a massage course every six months (up to 10 sessions);
- maintain liver health, because collagen production depends on it;
- increase immunity;
- avoid stress, establish a smooth psychological background;
- control your weight, because every extra 10 kg is approximately 0.5 kg of additional load on one vertebra, which leads to rapid wear.
In addition, it is important:
- Stand and walk correctly. Correct posture is when you stand against the wall and touch it with the back of your head, shoulder blades, buttocks and heels. When walking and standing, you should try to maintain exactly this position.
- Sit in the correct position: do not lean too far back, do not lean forward. You should press your back tightly against the back of the chair, have support for your lower back and neck. Every 15 minutes – change the position of your legs, stretch.
- Sleep on an anatomically correct or orthopedic mattress.
- After waking up, while still in bed, do simple exercises with your legs and arms, stretch before getting up (this should be done without sudden movements).
- Do not carry heavy bags in one hand. It is better to distribute purchases evenly into two packages.
- Do not carry a bag over your shoulder. Better for your back is a backpack with two straps.
- A small child should be carried with a straight back, without bending backwards. It is best to carry a very small baby on the chest in a special sling, and a slightly older one - on the back.
- When carrying heavy objects, do not bend or turn your body.
- Do not bend over when cleaning - use an extension cord for the vacuum cleaner handle and a mop (do not wash the floors with just a rag while kneeling).
- Eat grapes, apples, strawberries, pears, lentils, hazelnuts, pumpkin, green salad, and raspberries more often.
- Monitor the balance of magnesium and potassium in your diet. Eat nuts, fish, seafood, spinach, cabbage, beans, peas.
- Eliminate bad habits - alcohol and smoking.
- Swimming, running (but only with shock-absorbing insoles and special sports shoes), skiing.
Be sure to visit doctors for preventive examinations to prevent the situation from worsening if you have an illness and to begin treatment on time.