Donating blood is a noble cause and, of course, very useful for those who urgently need it. Donors are always in demand. Many people need their help: people with blood diseases, people involved in accidents, victims of disasters, women giving birth, patients undergoing surgical operations.
But what about those who give it away regularly? Surely every person who decided to become a donor was looking for an answer to the question of whether donating blood is harmful. Transfusiologists assure that this is completely safe for the health of the donor if all the rules are followed. Thus, to the question of whether it is useful to donate blood and plasma, doctors give a positive answer.
Why isn't it harmful?
As you know, no more than 450-500 ml can be taken from a donor at a time, which does not have any negative effect on the body. Moreover, the law establishes the frequency of testing: for women no more than 4 times a year, for men no more than 5 times. The interval between procedures when donating whole blood should not be less than two months. If you donate plasma, then for at least one month.
The human body is capable of self-healing. The volume that is donated in one procedure is replenished without consequences in two weeks or a month, which is why you cannot donate more often. If a person comes to the transfusion point for the first time, they may take half the norm.
Blood Center
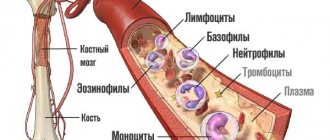
Each donated unit of blood is examined as follows:
- determine the blood group according to the systems (AB0, Rh- and Kell);
- tested for the presence of antibodies to red blood cells and
- for the presence of pathogens of four blood-borne diseases: hepatitis B, hepatitis C, syphilis and HIV.
The blood type of the primary donor is determined according to the ABO system already at the first visit, since the determination is carried out using the express method during a medical examination and later checked in the laboratory. The Rh factor is determined only in the laboratory, and the donor finds it out during the second visit to the Blood Center.
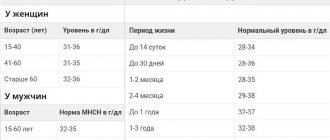
Before donating blood, the hemoglobin level in a drop of blood taken from the donor's finger is also determined. Hemoglobin content standards:
- in women 125-165 g/l
- in men 135-180 g/l
If necessary, donors' blood pressure and pulse are measured. Their standards:
- blood pressure 100/60-180/100 mmHg. Art.
- pulse 50-100 beats per minute
Laboratory specialist Liina Teder determines the donor's blood type
To ensure blood safety, the following tests are performed for each unit of blood donated:
- hepatitis B virus surface antigen (Hbs Ag)
- Hepatitis B virus DNA (HCV DNA)
- hepatitis C virus antibodies (Anti-HCV)
- Hepatitis C virus RNA (HCV RNA)
- antibodies to HIV (Anti-HIV-1,2) and HIV antigen (HIV p24)
- HIV-1 virus RNA (HIV-1 RNA)
- causative agent of syphilis
Tests of donated blood are carried out in accordance with the directives of the European Union and the laws of the Republic of Estonia. In 2007, testing of donated blood for viruses took another big step forward and the determination of the HIV antigen was replaced by the molecular biological test of HIV-RNA PCR, which is today the most sensitive and high-tech method of viral diagnosis. With this method, the window period is only 8-12 days. By identifying HIV-RNA, the highest possible level of safety of donated blood is ensured.
All viral tests of donated blood are automated and performed using testing systems from internationally recognized companies. Test results are transmitted from the analyzers directly to the Estonian Blood Service Information System (EVI). The blood center cannot issue blood components that have not been analyzed or have shown inappropriate results, since EVI does not allow this.
If the test results require additional verification, the donor is called for repeat tests. The dose of blood in which the infectious agent is detected is destroyed.
Why is it useful?
Doctors say that donating blood is useful for the following reasons:
- Donation reduces the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. This is especially true for men, who are susceptible to them even at a young age.
- The body is being renewed.
- The work of the hematopoietic system is stimulated.
- The body's immune defense improves.
- The body adapts to periodic blood loss, which will alleviate the condition in the event of an accident or injury.
- Serves as a prevention of liver and spleen diseases.
- The donor's life expectancy increases by 5-7 years.
- It is useful to donate blood to women after 40 years of age. During this period, changes occur in the body associated with the approach of menopause; donors tolerate its symptoms much easier.
- Moral satisfaction from the benefit brought.
- The donor gets two days off.
How does donation affect the health of the donor?
“Maximum benefit to the patient - no harm to the donor” - this principle is strictly observed by the Blood Service employees.
Donation does not harm the body if the person is healthy. Procuring blood from a donor is permissible only on the condition that his health will not be harmed. In this case, the volume of one donation should not exceed 12% of the circulating blood volume, which normally amounts to 6.5-7% of body weight. The standard volume of blood collection (donation) of 450 ± 50 ml, excluding the amount of blood taken for tests (up to 40 ml), for persons weighing at least 55 kg, ensures the safety of the health of the blood donor.
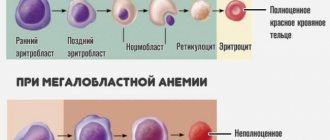
Each blood loss in a standard volume causes a number of changes in the donor’s body: the hemoglobin level decreases (within 5 days after donation by 2-10% compared to the initial value), the number of red blood cells decreases (from the first hours after blood collection and over the next 5 days ).
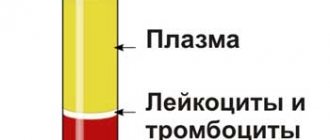
Complete restoration of blood composition occurs within 40-50 days. The rate of recovery of different blood components (plasma and blood cells) is different. Red blood cells are restored in the donor's body within 4-6 weeks, and leukocytes and platelets - by the end of the first week, plasma composition - within 1-2 days, hemoglobin level - within a month. It has been proven that in people who have given blood multiple times, the restoration of peripheral blood parameters occurs faster than in primary (donating for the first time) donors. This is explained by the “training” of the hematopoietic organs through repeated bloodletting.
To restore your blood composition faster, it is recommended to drink more fluids - juices, tea. The donor's diet should always contain protein, which determines the level of hemoglobin in the blood (foods containing protein: meat, beets, buckwheat, lentils, beans and all legumes, fish, etc.).
The reaction to blood collection varies from person to person. It depends on many factors: psycho-emotional state, physical activity, nutrition, living conditions of donors, weather conditions.
The loss of a standard blood volume is accompanied by changes that have a dual origin. Immediately after giving blood or in the next few hours, a so-called stress reaction develops to the situation and the blood collection procedure, depending on the type of nervous system and hormonal characteristics of the donor, and a reaction to the loss of cells and substances contained in the blood. Immediately after taking blood from donors, changes in some hemodynamic parameters are observed: a decrease in venous and blood pressure, acceleration of blood flow, and a slight increase in heart rate. The reaction to blood loss is short-lived; normalization of cardiovascular activity occurs within 30-60 minutes. During this period, donors are advised to rest.
After donation, some donors may experience a slight decrease in muscle strength, as well as an increase in the percentage of errors when solving test mathematical and logical problems. This indicates changes in the regulatory mechanisms of the nervous system, which affects work activity. In this regard, donors whose work is associated with great emotional stress and requires quick and accurate reactions (for example: transport drivers, crane operators, high-altitude workers, etc.) are not recommended to start it immediately after donating blood.
For any healthy adult, the process of donating blood is safe and does not harm the body. Repeated blood draws have a beneficial effect on the central nervous system, and through it on the metabolic processes of the entire body. According to a study by Finnish scientists, men who donate blood are ten times less susceptible to myocardial infarction and coronary heart disease; data from American researchers confirm that male donors suffer 30% less from cardiovascular diseases; Regular blood donation maintains cholesterol levels at the proper level, which, in turn, ensures prevention (prevention of the development) of atherosclerosis.
Those who donate blood regularly have a better chance of surviving extreme situations such as road accidents, burns, and major surgeries. The body of a donor who regularly donates blood and its components quickly activates the hematopoietic system during blood loss, which contributes to a speedy recovery. In addition, donors’ blood is renewed more often, “old” blood cells are eliminated, and donors, according to the World Health Organization (WHO), live on average 5 years longer than those who do not donate blood.
Donation of blood and its components is useful for the prevention of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (stomach, intestines, pancreas, liver), metabolism and diseases of the immune system, which is associated with the renewal of the body and activation of the immune defense.
Deputy Chief Physician A.I. Verigo
06/09/2016
Why is it safe?
Many believe that even if the body does not suffer in any way when donating blood, there is always a danger of contracting infectious diseases through instruments. Nowadays, such a probability is practically zero. During the procedure, only disposable instruments are used, which are opened directly in front of the donor. In addition, they are manufactured in such a way that they cannot be reused. It is best to donate blood or plasma in a modern facility that uses the latest equipment.
During the procedure, donors are in comfortable conditions; all instruments and materials used are disposable only.
In order to feel normal after the procedure, you need to follow the doctors’ recommendations, that is, eat right before donating blood, lead a healthy lifestyle and get a good night’s sleep. After donation, in order not to faint, you should drink sweet tea or juice and sit quietly in a relaxed state. It is best to stay at the blood transfusion station for an hour in case medical attention is needed. Over the next two days, you need to eat nutritiously in order to recover faster. If you feel unwell, it is not recommended to donate blood, and there is no need to hide your condition from the doctor. If you follow these simple rules, the procedure does not pose any danger. You can learn about the rules and preparation for donating blood from this article.
April 20 is National Donor Day. Being a donor means benefiting not only others, but also yourself. Regular blood donation prevents many diseases; donation also helps to prolong youth, avoid strokes and make new acquaintances.
We talked with the chief physician of the Blood Transfusion Station of the Moscow Department of Health, Olga Andreevna Mayorova, about the benefits of donation, who should not donate blood, and how to become a donor .
Maya Milich, AiF.ru: - April 20 is National Donor Day. What set of events are planned to be held in Moscow in connection with this date?
Olga Mayorova: — In connection with this date, we are holding a round table dedicated to National Donor Day, attracting students from secondary specialized educational institutions. We need to educate donors from a very early age, so our guests will be young people. In addition, the transition of our service to work seven days a week was timed to coincide with National Donor Day. The blood transfusion station is now open 7 days a week, excluding only public holidays. We consider this our achievement, because we are the first blood transfusion station in Russia that completely adapts to the interests of donors and operates seven days a week.
In preparation for National Donor Day, we also host large outreach events with the participation of various institutes and universities. After the holiday, we plan to hold outreach events with student youth.
— How is donation popularized today?
“I would like to believe that the active propaganda measures that we are carrying out with targeted categories will lead to results and the influx of donors will increase. As practice has shown, simply hanging large posters on the street has little power. Now we work with targeted categories, with executive authorities, with school teachers, with educational institutions, and not only medical ones, with bikers who actively come and donate blood. We are trying to carry out our work more targeted and targeted in order to attract entire communities of people.
Contraindications
— What diseases prevent people from becoming blood donors?
— People from 18 years of age to any age can donate blood if there are no contraindications in the form of serious illnesses, somatic diseases, hepatitis, infectious diseases, or vegetative-vascular dystonia. Temporary contraindications are allergic diseases in the acute stage, pregnancy, menstruation, and taking antibiotics.
Sometimes the peculiarity of the structure of the veins can become an obstacle, because donation means donating blood in a fairly large volume and the veins must be pronounced. If there are no these contraindications, then a person can be a donor even at 70 years old. We even have several donors who have crossed the 70-year mark, mostly career plasma donors who have been donating for a very long time. Partly due to their active donor position, they maintain health and vitality.
Avoid stroke
— Tell us about the benefits of donation for humans.
— The benefits of donation are undeniable. In human donors, the incidence of cardiovascular diseases, in particular strokes, is significantly reduced, because the blood is actively renewed. Our regular donors of both blood and plasma, especially men, are better protected from vascular accidents.
In addition, any donation is, although mild, stress for the body. And it has been proven that the presence of just such mild stress increases a person’s resistance to the effects of adverse environmental factors.
Thanks to donation, blood cells are regularly renewed, because they too tend to age. Usually their natural restoration occurs, and in donors this process occurs with greater frequency. There is a theory that the female body is more resistant to negative external factors precisely because monthly blood loss occurs.
Donation is very useful in the presence of a genetic disease - hemochromatosis, associated with the accumulation of iron, the excretion of which is impaired. In the United States, half of blood donors are people with this hereditary disease. For them, one of the physiological ways of treatment is bloodletting, which makes them physically feel better.
Another category is people with high levels of cholesterol and fats in plasma. Everyone knows that in this case plasmapheresis is used for treatment and prevention. In commercial clinics, this procedure is quite expensive. But not everyone knows that donor plasmapheresis is almost the same procedure.
People who have crossed 50 and 60 years of age are very active in donating plasma simply because they feel good afterwards. Donation allows you to prolong youth and lead an active lifestyle.
Don't forget about the psychological factor. Donation is a confirmation of one’s own importance; people experience great moral satisfaction. These are lives saved.
In addition, donors are a certain club, especially plasma donors, who come on the same days, at the same time. Acquaintances are made, which is important given the shortage of direct communication today due to the rise of social networks.
By the way, if your loved one or just a new acquaintance of the opposite sex you like is a personnel donor, then anything is possible with him, because he is obviously healthy. After all, being a donor with a frequency of 2 weeks, a person receives testing for the most complex and severe diseases.
How to become a blood donor?
— How to properly prepare for donation and recover after donation?
— First, you need to understand for yourself that being a donor is very important, and that there is never too much donor blood. In my opinion, every healthy person should be a donor. After all, it is not necessary to donate blood monthly, at least 2 times a year.
First you need to choose a time that is convenient for you. Because you need to come to donate blood or its components in a good mood, thanks to this there are significantly fewer complications. And when the donor constantly looks at his watch and realizes that in 30 minutes he needs to be on the other side of Moscow, then, of course, the whole procedure will take place in a nervous state.
For 2-3 days, you need to exclude fatty foods, coloring foods from your diet, stop smoking and drinking any type of alcohol. All these factors during testing can change the normal parameters of the biochemical analysis and such blood will simply be rejected.
The night before, get a good night's sleep. On the day of blood donation in the morning - a light breakfast, sweet tea and a sandwich with low-fat cheese. It is better to avoid coffee; it leads to increased vascular tone.
You can visit the nearest blood donation point, it could be a blood transfusion station, it could be a department. In Moscow today there are more than 30 points where you can donate blood.
It is also very important to take your passport with you, without which donor registration is impossible. If a person is not a resident of Moscow, then it is advisable to have confirmation of registration, although today this is not mandatory. Then simply follow all the instructions that you receive.
After donation, you will receive either a food package or compensation for food. Already from the second time, that is, when the person is no longer the primary donor, you can take advantage of social support measures.
At least six months after the first blood donation, you must come back for a second examination. The plasma is quarantined for 6 months and before it is released into the medical network, it is necessary to re-examine the donor to exclude the possibility of infection if the donor had an incubation period, for example, hepatitis.
https://www.aif.ru/health/life/1152959
Possible harm
Most doctors claim that donation is good for the health of the person donating blood, and there is no question of any harm, as long as there are no contraindications and all the rules for donation are followed. The only disadvantages could be considered a minor wound from an injection on the arm and the time spent. This is where the so-called harm ends, the rest is benefit.
There is an opinion that regular donation changes metabolism, and a person cannot do without it, otherwise his health may worsen.