There is a certain category of diseases in which the patient faces problems eating. This is due to impaired body functions. With a normal diet, you need to chew solid food thoroughly and swallow. But not all patients can do this. In such cases, doctors prescribe tube feeding - feeding the patient through a medical tube system. The patient receives a balanced diet, the menu is calculated based on the general condition of the body and the diagnosis. While taking food, the patient does not make chewing or swallowing movements. With this feeding, food enters the gastrointestinal tract in a state suitable for digestion.
Why and in what cases is tube feeding organized?
As a rule, a tube is installed for food intake:
- if it is impossible to get adequate nutrition through the mouth during radiation treatment (pain, swelling);
- if necessary, isolate the oral cavity from food intake (grade III mucositis);
- with swallowing problems and the risk of developing aspiration pneumonia;
- after operations on the larynx, esophagus (in this situation, a probe is also necessary for decompression).
Positive aspects of tube feeding:
- You will be able to take enough food regardless of your appetite and taste; as you know, during treatment, appetite is often reduced and taste sensations are distorted.
- Food will not irritate the oral mucosa and cause pain.
- Your condition will not be complicated by aspiration pneumonia.
- You will not lose weight or your strength.
- You will be able to continue treatment without interruption.
Remember that proper and sufficient nutrition reduces the number of treatment complications and allows you to complete radiation therapy as planned and feel well.
Feeding process
The procedure is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- The patient's body is given a semi-sitting position;
- The outer part of the probe is lowered below the patient’s neck and compressed with a special clamp;
- The funnel is connected to the syringe, it rises to a level of up to half a meter above the stomach, after which the clamp is removed.
- Food is served slowly, with virtually no pressure; no more than 150 ml should be administered in 5-6 minutes.
- After finishing feeding, it is necessary to rinse the area by applying 30-50 ml of water through it.
- Next, the tube is clamped again, lowered, and the inlet is closed with a plug.
Tube is a modern and effective way of feeding seriously ill patients. It has a lot of advantages. Unlike intravenous nutrition, in this case atrophy of the gastric mucosa is not allowed, the gastrointestinal tract system remains in working order. The enteral system can be used for a long time. The probe is installed for three weeks. The administration procedure must be carried out by a doctor, and he must also give his recommendations regarding the feeding procedure and diet.
What is a nasogastric tube?
This is a tube made of a special non-toxic material. The end of the probe is smooth, sealed and rounded so as not to injure the mucous membrane, and there are round holes on the sides to facilitate the introduction of nutrition into the probe.
Probes come in different sizes, and the doctor selects the appropriate one for each patient. There are marks on the probe indicating its length; you can use them to control its location. The probe is installed for various periods - up to three weeks. If longer tube feeding is required, then percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy is performed.
Benefits of rehabilitation
Feeding through a tube is a complex procedure, during which you must strictly follow the rules, monitor sterility and hygiene. It is very difficult for an ordinary person to do everything correctly. Our rehabilitation center employs experienced professionals who are well acquainted with the features of tube feeding. Health workers will monitor the feeding schedule and follow all doctor’s recommendations regarding the menu and amount of food.
Caring for a bedridden patient is a task with which relatives of patients often turn to us. Our employees pay special attention to compliance with all medical recommendations. In addition to nutrition, our responsibilities include:
- 24-hour care;
- prevention, treatment of bedsores;
- physiotherapy;
- massage.
The center has its own psychologists and speech therapists. These doctors help patients of all ages undergoing rehabilitation.
How is a nasogastric tube placed?
This manipulation is performed by the attending physician or a doctor in the endoscopy department when there is a need for endoscopic control. The probe, under local anesthesia, is inserted through the nasal passage into the pharynx and slowly moves into the stomach, while the patient helps the doctor by making swallowing movements. When setting, there is no need to resist, as this brings even more discomfort.
What can be given after NMC and what cannot be given
The diet of bedridden patients after a stroke can be of two types in the first days after a stroke:
- menu for patients who swallow normally;
- diet (nutrition) of patients after a stroke with swallowing disorders (nutrition for dysphagia)
If a person is conscious and SWALLOWS FOOD NORMALLY, there are no special dietary restrictions.
In the first days after returning home and in the next month, I would recommend giving everything in pureed form - puree, minced meat, broth, jelly.
The main thing we care about:
- Treatment after a stroke with folk remedies
- prevention of food aspiration and aspiration pneumonia;
- prevention of constipation
Nutrition to prevent aspiration:
- First, it is advisable to feed the patient SITTING, or with the head of the bed raised by 45% (two pillows under the head), slightly turned to the side. If the patient can talk, then you need to ask which side is easier for him to swallow food on.
- The second absolute requirement: DO NOT give anything that crumbles. INCLUDING PROHIBITED BREAD, SOOOKED CRUSKS, crumbly porridges, pasta!
- DO NOT tempt fate - do not give fish (bones), berries with seeds, seeds, nuts!
Diet to prevent constipation comes down to:
- Limiting all flour products should be limited to semolina porridge, rice porridge, pancakes, cakes, etc.
- meat is necessary, but no more than one small portion per day, it is better to give liver
Proper nutrition to prevent constipation is
- vegetable purees, zucchini, peas, pumpkin, potatoes (not the best choice), etc. Mashed potatoes less often. Grated or very finely chopped salads from fresh cucumber, tomato, bell pepper, etc. are very healthy.
- Fruit jelly, juices, puree: puree - dried fruit jelly, fresh fruit - prunes, plums, kiwi, apples, bananas, watermelon should be given daily. Berries with small seeds - grapes, figs, raspberries NOT allowed!
- the liquid is given in small sips, from a spoon or from a syringe: compote with caution. Water is absolutely essential! If a person swallows on his own, he should be given up to 1.5 liters of water per day to drink. It is more convenient to drink through a syringe. I use a 5-10 ml syringe.
- Fermented milk products - fermented baked milk, cottage cheese, kefir, soft cheese - daily, but without fanaticism. Prolonged feeding of only dairy products leads to anemia and acidosis.
Important!
If medications are prescribed that reduce blood clotting and prevent the formation of blood clots (anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents), then nutrition after an ischemic stroke requires a special approach!
Products that affect blood viscosity should be avoided . A list of foods that increase or decrease blood viscosity can be found in the article on nutrition while taking warfarin.
If you feed correctly, the patient will have good tests.
Once a month, it is advisable to do laboratory tests (at a minimum: complete blood count, analysis of electrolytes, urea, uric acid, creatinine).
If the tests are good, then you are doing everything right! And if the tests are “not very good,” then you need to consult a doctor.
How will you feel?
Slight pain in the nasal cavity, pharynx and vomiting are possible, but not all patients experience this. It is important to listen to your doctor's commands and breathe properly through your mouth. Almost all patients tolerate both this manipulation and treatment with an installed probe satisfactorily. Don't worry, nasal breathing will continue. Sometimes it takes 2-3 days to get used to the probe. In extreme cases, the doctor may prescribe painkillers, antiemetics and antispasmodics. At first, you need to listen to yourself and understand what position you should be in in order to reduce discomfort in this area. The main thing is to remain calm and remember that this is a necessary and temporary measure. According to many patients, their fears about inserting a probe were greatly exaggerated.
Supplemental oral nutrition
Supplemental oral nutrition (supplementary feeding) is used to provide additional nutrients and energy to the body. The patient independently consumes the mixture in small sips. This method increases absorption and improves tolerance of therapeutic nutrition.
Benefits of a supplemental oral nutrition drink
This is a specialized high-calorie liquid mixture that is completely balanced in all nutrients.
- The composition is optimal in terms of content and ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates
- Contains daily requirement of vitamins and microelements
- Contains omega-3 fatty acids from fish oil, essential fatty acids
- Blends containing and not containing dietary fiber
- Small volume - after a stroke, eating small portions is recommended
- Sterility - in patients with reduced immunity will help prevent the development of nutrition-related infectious complications
- Pleasant taste and good tolerance
Features of nutrition through a gastrostomy tube
What is a gastrostomy?
Percutaneous gastrostomy is a special system for feeding through the anterior abdominal wall and an artificial entrance to the stomach cavity.
How is percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy performed?
- The entire procedure is performed under anesthesia. At the first stage, esophagogastroduodenoscopy is performed to exclude pathologies of the upper gastrointestinal tract that prevent the installation of a gastrostomy tube.
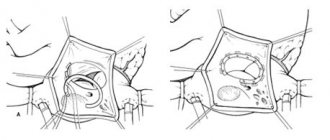
- An endoscopist performing an examination of the stomach determines the most convenient place for installing a gastrostomy (the anterior wall of the lower third of the body of the stomach) and uses the endoscope to “illuminate” the place where the gastrostomy is installed on the skin.
- The assistant doctor, guided by endoscopic “illumination,” makes a small (about 7-9 mm) incision at the site of the planned installation of the gastrostomy tube and inserts a thin plastic pointed rod into the stomach.
- The rod inside has a channel through which a conductor is inserted into the lumen of the stomach. The endoscopist grabs the guidewire with forceps and, removing the endoscope, removes the thread from the stomach and esophagus into the patient’s oral cavity. The other end of the thread is held by a medical assistant.
- A gastrostomy tube is attached to the withdrawn part of the guidewire. The assistant doctor, by pulling the thread from the opposite end, ensures the movement of the gastrostomy tube through the esophagus into the stomach. In this case, the gastrostomy tube is brought to the surface of the skin and fixed to it with a plate, and the flat rubber part (cannula of the gastrostomy tube) is pressed tightly against the wall of the stomach from the inside. Thus, the anterior wall of the stomach is connected to the skin of the anterior abdominal wall, and water and nutritional mixtures can be injected directly into the lumen of the stomach through a plastic tube.
- This minimally invasive procedure lasts about one hour and is performed under constant endoscopic control in order to avoid complications.
- During the first 24 hours after the gastrostomy tube is installed, you should not administer nutritional mixtures or any other liquids through it.
How will you feel?
Minor pain is possible, which can be easily relieved with painkillers prescribed by your doctor.
Important: feeding through a gastrostomy tube can only be started after the permission of the attending physician. The amount of food and frequency of administration in the first days are discussed additionally!
How to care for a gastrostomy tube?
- Regularly change the sterile dressing placed around the incision site between the skin and the restraint. During the first week, dressings are performed daily, and then every other day. The area of skin around the stoma and the fixation device should be well dried. Every day, rotate the plastic probe 180 degrees around its axis and move it up and down 1.0-1.5 cm so that it does not stick to the walls of the stoma.
- Make sure that the external fixation disc is at least 5 mm from the surface of the skin. If you have gained or lost weight, it becomes necessary to loosen or tighten the fixation device.
- After each meal, rinse the gastrostomy tube with 20-40 ml of water. The tube must be washed every 8 hours, even if you did not administer nutritional formula through it. Clean with a damp cloth and then dry the skin around the stoma and the retainer to avoid infection. Ask your healthcare provider which skin disinfectant you should use.
- If your gastrostomy tube falls out, contact your doctor immediately.
What food can you eat?
Food can only be taken in liquid form (the consistency of cream) and without lumps, so that the tube does not become clogged. Remember that food should contain a sufficient amount of quality protein and healthy fats (butter and vegetable oil). Daily calorie content should be approximately 2000 kcal. The daily volume is divided into equal portions of 150-200-300 ml, administered every 2-3-4 hours and is approximately 2000 ml. The temperature of the food introduced should be approximately 40-45 degrees (with the exception of specialized mixtures that are consumed at room temperature).
Main courses: blended (carefully chopped) low-fat boiled vegetables, diluted with broth, meat, poultry; liquid mashed porridge with added butter.
You can use baby meat, vegetable and fruit food, diluting them to the appropriate consistency with cream or broth. Also use milk, fermented milk products, sour cream. Boiled eggs can also be crushed and added to food. You can use compotes, fruit drinks, and juices as drinks.
In our medical institution, a probe table will be prepared for you in the kitchen. If necessary, the attending physician will prescribe nutritional support in the form of ready-made specialized mixtures, and part of the daily diet can be replaced with them. You can also use your own blender and prepare the necessary mixtures yourself from the dishes offered for the common table. When taking diluted food, you do not need additional fluid intake if you are not thirsty, especially since after each meal you need to rinse the tube with 50-60 ml of warm water.
If you have a favorite food or drink (tea, coffee), then do not deny yourself the pleasure and add it to your diet.
What to eat?
You will be given two Janet syringes (150 ml), and now they will serve as utensils.
What do you need to prepare for meals?
You will need:
- the finished mixture, its temperature should be approximately 40 degrees;
- drinking water at room temperature or slightly warmer;
- 2 syringes Janet;
- 2 containers with a volume of 200 and 500 ml (glass, mug, glass);
- spoon;
- napkin;
- blender (optional, for advanced users).
Why is nutritional therapy important for stroke patients?
Stroke is a disease that affects the body as a whole. A person who has suffered a stroke is forced to start living again: it is necessary to learn to move, walk, talk and even eat again.
One of the consequences of a stroke is the loss of the ability to eat independently due to partial or complete paralysis. In addition, disturbances in nervous regulation cause weakness in a variety of muscles, so some patients are unable to eat on their own: they must be spoon-fed.
Malnutrition is one of the most common disorders observed in stroke patients. The causes of nutritional deficiency are usually insufficient food intake due to disturbances in consciousness and swallowing or loss of appetite.
This is also facilitated by the characteristics of such patients:
- elderly age;
- disturbances of consciousness;
- slowing down the pace of movements, lack of coordination;
- visual inattention and/or loss of visual fields;
- communication problems and speech disorders (not being asked to eat or drink);
- decreased appetite and thirst;
- depression and dependence on others.
According to statistics, about half of people who have had a stroke have difficulty eating.
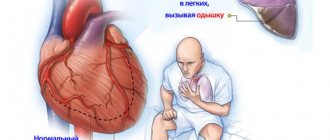
Problems with swallowing (dysphagia) can lead to malnutrition and weakening of the patient.
What are the consequences of undernutrition?
Inadequate nutrition is not only accompanied by loss of body weight, decreased physical performance, and deterioration of well-being, but also causes serious metabolic disorders, weakened immune defense and endocrine dysfunction, which affects the development of infectious complications and the acquisition of new diseases. Because of this, the recovery period is lengthened and the person returns to normal life much more slowly.
In order to avoid difficulties associated with eating and comply with nutritional requirements, special mixtures for therapeutic nutrition have been created. Such mixtures have a balanced composition, are easily digestible and do not put additional stress on the process of digestion and absorption of nutrients.
Malnutrition can be compensated by the use of special nutritional mixtures, and such treatment is more effective the earlier it begins.
General nutritional recommendations for stroke patients
Meals should be:
- complete and sufficient - it must contain all nutrients in the quantities required by the body, including dietary fiber to maintain normal intestinal function;
- contain vitamins and microelements - their deficiency leads to the development of various complications;
- balanced - maintain certain relationships between nutrients;
- easily digestible - does not cause additional stress on the processes of digestion, absorption and assimilation of nutrients by the cells of the body;
- depending on the state of the patient’s swallowing function: liquid, homogeneous, puree, mashed.
Meals should be taken in small portions, but often (5–6 times a day)
Diet features
- You should include vegetables, fruits, lean meat and fish in your diet.
- The best drinks are jelly, compotes, weakly brewed tea or herbal infusion, and freshly squeezed juices.
- It is important to adhere to a completely salt-free diet.
- Avoid eating fried, spicy and smoked foods, canned food, sausage, and large quantities of pasta.
- It is not recommended to drink strong tea, coffee, cocoa, carbonated drinks and packaged juices.
Massage against bedsores: how to do it
Bedsores are terrible in their consequences and unpleasant in their presence. I wouldn’t want to lose a loved one due to improper care: follow the recommendations and enjoy the positive results!
- Start by lightly stroking your dry palms over your dry back area to warm the skin. Switch to tapping your shoulder blades and the area between them to prevent lung problems.
- Turn the patient over on his side and lightly stroke his back and ribs.
- We stroke the buttocks and legs, then with light kneading movements we pull our hands from the foot to the sacrum along the flow of lymph. This is how we help clogged veins perform their function.
- At the end of the massage, we proceed to the problem areas on which the patient rests while lying down: gradually we translate the stroking into remembering and light rubbing. Do not overdo it so as not to damage delicate skin.
- Legs can be massaged with preventive ointments for varicose veins. They strengthen the vascular wall.
- To prevent thrombosis of the extremities, use compression stockings and tights, as well as bandaging.
- When massaging a specific area, the rest of the body should be covered with a blanket or sheet to prevent the person from getting cold.
- Massage can be combined with exercise: invite the patient to try to squeeze your hand. Raise and lower, bend and extend your limbs to improve blood flow.
Restoring limb mobility
You will have to go through the period of formation of the patient’s personality again: he will learn to speak, walk and work with his hands before your eyes.
Be patient and don't give up: physical therapy works wonders.
Damaged muscles need to be warmed up: with massage and attempts at action. You can squeeze a ball with your hands or try to hold a pen or pencil. Ask the patient to take the object from your hands, and one day he will do it.
The speech therapist works with the muscles of the tongue, conducts classes to warm up the speech apparatus with simple movements and exercises.
What is important to consider when feeding
A bed with a raised headrest will facilitate the process of eating and minimize the ingestion of chewed food and accidental ingestion of crumbs into the respiratory system. In the absence of special equipment, place a cushion from a blanket or a tightly stuffed pillow.
Create a diet taking into account the patient’s preferences; it should contain the optimal amount of vitamins, minerals, proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. It is advisable to serve warm, chopped. During tube feeding, monitor the tube and the patient's well-being.
The intestines and their emptying require special attention:
- Soft food - soft stool
- If you have constipation, seek medical advice and they will give you an enema.
- An accessible method is microenemas from a pharmacy: a special substance is injected into the anus and irritates its walls, followed by defecation without gastric lavage.
Do not feed the patient against his wishes - pieces of food can enter the lungs and cause aspiration pneumonia.
If the patient can handle cutlery himself, make this process easier for him: buy forks and spoons with rubberized handles.