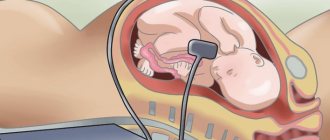
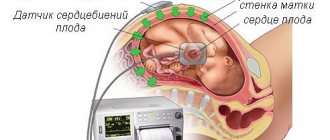
What is hyperechogenicity in the fetal heart?
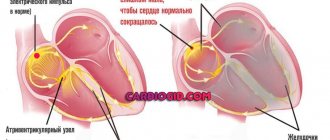
A hyperechoic focus of the fetal heart implies the presence of a compaction in the structure of the heart muscle.
As a result, ultrasonic waves are reflected to a greater extent from the myocardial area and produce a bright spot on the screen. The inclusion, as a rule, has a diameter of 2-3 millimeters. Most often it is found in women over 35 years of age at 18-22 weeks of pregnancy. The phenomenon is most typical for representatives of Asian countries. On the European continent, this phenomenon occurs much less frequently (in 7-10% of cases). Usually the lump disappears by the end of the third trimester, but often remains until childbirth.
Most often, a hyperechoic inclusion is found in the left ventricle of the fetal heart, however, it can also be visualized in other parts of the organ. The presence of increased echogenicity in the right parts is considered more dangerous.
This phenomenon can be considered pathological only in cases where it accompanies other signs of congenital diseases. It is also important to remember that this is just a diagnostic sign, which is not an independent pathology and does not carry any negative consequences in the future.
What are the consequences?
The prognosis for a hyperechoic focus of the left ventricle of the fetal heart is in most cases favorable, since the cause of this is most often a slight deposition of salts, which resolve by the end of pregnancy. After the birth of the child, an additional examination is carried out, the results of which are transferred to the local pediatrician.
It is also recommended to be periodically examined by a cardiologist to diagnose this pathology and monitor its development. In most cases, the heart murmur created by the additional membrane goes away without a trace before the age of three. Then the cardiologist gives a conclusion that the child is completely healthy.
When a child is diagnosed with such a deviation, the doctor must take the pregnant woman under constant supervision. This is done due to the fact that such a violation can lead to a malfunction of the myocardium, and the result of this change is often a circulatory disorder in the baby in the womb. It is known that the main function of blood is to deliver nutrients to all organs and systems of the body, so if this process fails, serious problems can arise, including miscarriage.
Experts believe that identifying hyperechogenicity in the left ventricle of the heart is not as dangerous as a disorder in the right side of the organ. If such a compaction appears on the right, then this indicates an inevitable pathological process that can even lead to the death of the fetus. Therefore, a child with such a deviation must be observed by a cardiologist.
If a baby was born with impaired blood circulation and myocardial function, then his health may deteriorate greatly.
Symptoms:
- difficulty breathing;
- weakness, lethargy;
- pain in the heart area;
- swelling of the arms and legs;
- pallor of the skin, even blueness;
- disturbance of heart rhythm, increase in the rate of contraction of the organ;
- loss of appetite.
The expectant mother should monitor her health, since the correct development of the child depends on her condition. You need to protect yourself from any infectious diseases, because such diseases most often cause severe complications in the fetus. If in the early stages of pregnancy the expectant mother has suffered from a disease of viral origin, then there is a high risk of pathology developing in the child.
Specialists should monitor fetal development regularly; a lot depends on such diagnostics. A woman is also obliged to pay close attention to the health of her child and attend all the required examination methods as planned. A hyperechoic focus in the fetal left ventricle is not uncommon. This condition has been well studied, so there is no need to be alarmed if a similar deviation is detected in your baby.
Causes
The source of hyperechoic inclusion of the fetal heart may be the deposition of calcium salts in the papillary muscles of the left ventricle. During this period, significant activation of mineral metabolism and intensive formation of the skeletal system occur. Over time, the salt is absorbed into the blood and the seal disappears.
In some cases, a similar symptom is caused by the presence of an additional chord. This is a connective tissue thread that runs from the heart valves to the papillary (papillary) muscles. Most often, each muscle corresponds to one thread, but in this case several of them are formed.
As blood passes through the chordae, turbulence will occur, which can produce a heart murmur heard on auscultation. This should be remembered, because in the future, due to the presence of this phenomenon, the pediatrician may make an incorrect diagnosis. Despite the fact that this phenomenon is considered an abnormality of the heart, this development option is accepted as normal.
Detection of an additional chord does not require further examination and treatment. As a rule, they grow together before birth or in the first years of life.
Previously, it was believed that LVEF was a clear sign of Down syndrome or other chromosomal diseases. But in recent years, many scientific works have appeared, thanks to which we now know that this is true only in the presence of additional symptoms. The detection of this sign alone is not a cause for concern and no further examination is required.
Why register with a doctor?
Most scientific experiments conducted to study in more detail the hyperechoic focus in the left ventricle of the fetal heart have shown that the appearance of an additional string is a consequence (in most cases) of chromosomal pathology. This pathology is mainly inherited through the female line.
The need for a child with golf ball syndrome to be under constant medical supervision is primarily due to the fact that such structural compaction in the heart cavity often leads to disruption of the rhythm of the myocardium (heart muscle). Due to the fact that the string is short, the volume of the ventricular cavity decreases, and this leads to its incomplete relaxation and, accordingly, poor filling with blood. The result of this anatomical pathology is a violation of the blood circulation of the fetus itself.
The main function of blood in the body is to deliver oxygen and various nutrients to cells, tissues and organs. Weakening of blood flow can then cause oxygen starvation of the fetus or damage to the inner lining of the heart muscle, with a high probability of subsequent miscarriage.
But still, according to most experts, the presence of a compacted string in the left ventricle of the fetus is not such a serious pathology compared to the compaction that can occur in the right ventricle of the heart.
Diagnosing a focus of increased echogenicity of the right ventricle of the fetal heart inevitably leads to complications and often incompatible with life. In such circumstances, the best option is surgical correction of the defect.
All of the above is clear evidence that in order to timely identify problems with blood circulation, the child will definitely need to be registered with a cardiologist.
At the initial stage, dysfunction of the left ventricle does not have clearly defined symptoms.
The presence of a seal (a string stretched between the right atrium and the right ventricle) leads to increased pressure in the cavity of the left atrium. This condition occurs due to insufficient blood flow from the left atrium to the right ventricle.
The atrium is not completely emptied, and the ventricle does not receive blood in the required amount. A natural consequence of such dysfunction is that the fetal organs receive insufficient oxygen and nutrients. This state of affairs will negatively affect the state of all life systems of the unborn child, and in advanced cases (if diagnosis is delayed) can lead to the death of the fetus.
The occurrence of golf ball syndrome in utero often has negative consequences for both the newborn and the child during the first years of his life.
In this case, the most striking symptoms characteristic of this pathology are:
- increased fatigue;
- apathy;
- attacks of pain in the heart area;
- dyspnea;
- cardiopalmus;
- swelling of the limbs;
- characteristic pallor of the skin with a tendency to subsequent blue discoloration.
From the editor: Symptoms and complications of thoracic aortic aneurysm
Attacks of tachycardia (due to rapid contraction of the heart muscle) are often observed; as a result, the pulse can exceed 200 beats per minute. Timely symptomatic therapy in most cases helps to cope with the consequences of intrauterine additional education.
A set of measures aimed at ensuring that pregnancy and subsequent births occur without complications (if the above syndrome is detected in the fetus) should include the need for treatment and monitoring of the expectant mother.
It is extremely important to protect the expectant mother from contact with a possible source of pathogenic viruses or microorganisms. It is women who have had various diseases of an infectious nature who form the main risk group in the early stages of pregnancy.
The development and formation of the fetus occurs quite quickly. The main systems of the body are improved literally in a matter of weeks
Taking into account the peculiarities of intrauterine development, it is necessary to constantly monitor the condition of the fetus, which will certainly contribute to the timely detection of a hyperechoic focus in the left ventricle of the heart
Timely identification of golf ball syndrome will prevent possible complications.
In cases where markers are detected in the blood of the expectant mother indicating the presence of genetic malfunctions or abnormalities in the development of the fetus, parents may be advised to terminate the pregnancy.
Action tactics
In most cases, if a hyperechoic inclusion is detected, additional research is indicated. In this case, they can assign:
- repeat ultrasound to clarify the diagnosis;
- echocardioscopy (performed only until the 25th week);
- blood chemistry;
- karyotyping.
Invasive diagnostic procedures are used quite rarely:
- amniocentesis (taking a sample of amniotic fluid through the abdominal wall);
- placentocentesis (biopsy of placental cells);
- fetoscopy (examination of the fetus using a video probe).
First of all, of course, genetic causes of hyperechoic inclusion should be excluded. To do this, the diagnostician searches for other small markers of chromosomal pathologies. These include congenital heart defects, thickening of the cervical fold, developmental disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and skeletal system. They are usually detected during ultrasound examination. If they are detected, consultation with a geneticist is necessary.
If no additional signs are found, the fetus can be considered completely healthy. However, a follow-up echocardiogram is recommended in the first months after birth. This procedure will make sure that there are no pathological changes.
Diagnostics
If this pathology is detected on a routine ultrasound, the following diagnostic methods are prescribed:
- Ultrasound with volumetric reconstruction, that is, 3D ultrasound, which allows you to examine the structure of the heart muscle in more detail;
- echocardioscopy of the fetal heart - study of the work and structure of the heart using ultrasound;
- Dopplerography is a type of ultrasound of the heart;
cardiac cardiotocography – recording the fetal heart rate.
In some cases, additional studies are indicated:
- cordocentesis - puncture of the umbilical cord with further blood sampling for research;
- amniocentesis - puncture of the amniotic sac with collection of amniotic fluid.
If all previous diagnostic methods have not given an accurate positive diagnosis, then the pregnant woman is referred to a geneticist for examination. In this case, it is necessary to donate blood for a more detailed diagnosis of the changes.
conclusions
Thus, a hyperechoic inclusion detected by ultrasound is not an independent diagnosis. According to the system for assessing markers of chromosomal abnormalities, he is awarded only one point, which cannot be a cause for concern.
Most often, GEF occurs as a result of physiological processes or benign anomalies of cardiac development (the appearance of a false chord). However, if no other anatomical or functional abnormalities are found, no further examination or treatment is required. Monitoring during a routine ultrasound in the third trimester of pregnancy will be sufficient.
RESPONSIBILITY
RESULTS ¾ ROOM ROOM ½Ñи RESULTS REPORT:
- RESULTS ROOM диагноз, жРµÐ½Ñине до беÑеменноÑÑи необÑодимо Ð ¿ÑойÑи полное обÑледование и ÑолÑко Ð¿Ð¾Ñ Ð»Ðµ ASSURANCE в ÑемÑе. RESULTS RESULTS µÐ´Ð¸ÑÑ ÑÐµÐ±ÐµÐ½ÐºÑ Ð² Ð¼Ð¾Ð¼ÐµÐ½Ñ ÑоÑмиÑÐ¾Ð²Ð°Ð½Ð¸Ñ ÑеÑдÑа и дÑÑÐ³Ð¸Ñ Ð¶Ð¸Ð·Ð½ÐµÐ½Ð½Ð¾ важнÑÑ Ð¾Ñганов.
- ROOM ROOM ROOM RESULTS ROOM, ROOM и, даже Ñ Ð´Ð¾Ð¼Ð°Ñними.
- У Ñебенка ÑеÑдÑе бÑеÑÑÑ Ð½Ð°ÑÐ¸Ð½Ð°Ñ Ñ 5 недели вР½ÑÑÑиÑÑÑобного ÑазвиÑиÑ. RESULTS RESULTS ´Ð¾Ð²Ð°Ð½Ð¸ RESULTS RESULTS а.
- RESULTS ASSURANCE RESEARCH его ÑождениÑ. RESULTS.
RESEARCH RESULTS RESULTS й ÑазвиÑиÑ. RESULTS и пÑинÑÑÑ ÑооÑвеÑÑÑвÑÑÑие меÑÑ.
RESEARCH
RESULTS ROOM в бÐ" Ð ° ð³ page, ñ ° ° ðº ð ° ° ð ð¿¿ññð^ ññices ñµ ñ ð ² ð ð ñ ² ð ðuzz " . RESULTS ROOM RESULTS .
RESULTS RESULTS · а ее ÑазвиÑием. ROOM ¾Ð·Ð´Ð°ÐµÑ дополниÑелÑÐ½Ð°Ñ Ð¼ÐµÐ¼Ð±Ñана, пÑоÑоР´ÑÑ Ð±ÐµÑÑледно в возÑаÑÑе до ÑÑÐµÑ Ð»ÐµÑ. registry ROLLUP
Consequences and complications
At the initial stage, dysfunction of the left ventricle does not have clearly defined symptoms.
The presence of a seal (a string stretched between the right atrium and the right ventricle) leads to increased pressure in the cavity of the left atrium. This condition occurs due to insufficient blood flow from the left atrium to the right ventricle.
The atrium is not completely emptied, and the ventricle does not receive blood in the required amount. A natural consequence of such dysfunction is that the fetal organs receive insufficient oxygen and nutrients. This state of affairs will negatively affect the state of all life systems of the unborn child, and in advanced cases (if diagnosis is delayed) can lead to the death of the fetus.
In this case, the most striking symptoms characteristic of this pathology are:
- increased fatigue;
- apathy;
- attacks of pain in the heart area;
- dyspnea;
- cardiopalmus;
- swelling of the limbs;
- characteristic pallor of the skin with a tendency to subsequent blue discoloration.
Attacks of tachycardia (due to rapid contraction of the heart muscle) are often observed; as a result, the pulse can exceed 200 beats per minute. Timely symptomatic therapy in most cases helps to cope with the consequences of intrauterine additional education.
The prognosis for a hyperechoic focus of the left ventricle of the fetal heart is in most cases favorable, since the cause of this is most often a slight deposition of salts, which resolve by the end of pregnancy. After the birth of the child, an additional examination is carried out, the results of which are transferred to the local pediatrician.
It is also recommended to be periodically examined by a cardiologist to diagnose this pathology and monitor its development. In most cases, the heart murmur created by the additional membrane goes away without a trace before the age of three. Then the cardiologist gives a conclusion that the child is completely healthy.
At the initial stage, dysfunction of the left ventricle does not have clearly defined symptoms.
The presence of a seal (a string stretched between the right atrium and the right ventricle) leads to increased pressure in the cavity of the left atrium. This condition occurs due to insufficient blood flow from the left atrium to the right ventricle.
The atrium is not completely emptied, and the ventricle does not receive blood in the required amount. A natural consequence of such dysfunction is that the fetal organs receive insufficient oxygen and nutrients. This state of affairs will negatively affect the state of all life systems of the unborn child, and in advanced cases (if diagnosis is delayed) can lead to the death of the fetus.