How to determine the Rh factor
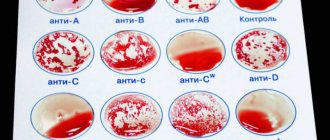
Blood is a biological fluid that contains a huge amount of antibodies and carries genetic information. The Rh factor is a special agglutinogen protein that is part of the blood. There is a distinction between Rh positive and Rh negative. The latter is detected in 15% of people in the world and means the absence of protein in the blood. In medicine, there is the ABO system, which is used to detect antibodies in human blood. The Rh factor is determined by one of the most significant antigens, D. If it is absent in the blood, then the Rh factor is negative. Today in medicine, this research in the laboratory is carried out very quickly and accurately. If, for example, blood containing this protein is transfused to a person who does not have it, then the formation of specific antibodies begins in the blood, which leads to the appearance of disorders called Rh conflict. Repeated injection of blood with incompatible Rhesus promotes agglutination of red blood cells and contributes to the occurrence of severe complications. That is why during transfusion, only blood with the same Rh factor is used.
Why is the Rh factor important in blood transfusions?
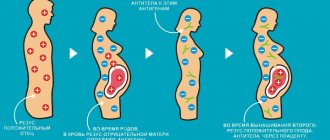
When blood is transfused from a person with Rh+ to a person with Rh-, a conflict occurs regarding the Rh factor
. But if, in the case of a conflict regarding the blood group, the destruction of red blood cells (hemolysis) begins immediately, then in the case of a conflict regarding the Rh factor, there is no hemolysis during the first transfusion. The first contact with antigen D only leads to sensitization of the recipient, that is, his body produces specific antibodies, and sensitivity to the antigen increases. But if the antigen enters the blood of a person with a negative Rh factor again, the body begins to react to the penetration of a foreign agent: red blood cells begin to stick together inside the vessels and destroy. A person feels tightness in the chest, difficulty breathing, pain in the lumbar region. Blood pressure decreases and acute renal failure develops. This complex of symptoms is called hemolytic shock.
Currently, hemolytic shock from blood transfusion is practically excluded. In today's medical practice, blood that matches the recipient's blood group and Rh factor is used for transfusion. In order to eliminate errors, before any operation, the analysis to determine the blood group and Rh factor is done again.
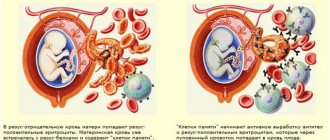
Rh factor is negative and the occurrence of Rh conflict
When a pregnant woman first contacts a gynecologist, he will require a blood test to determine the group and Rh factor. This study is important for the successful course of pregnancy and the life of the fetus. Rh negative in the mother and positive in the father in 60% of cases indicates that the child’s Rh factor will be positive. During the gestation process, an exchange occurs through the blood from mother to fetus. If the child’s blood proteins begin to enter the mother’s blood, then her immune system receives a signal about foreign proteins. The active growth of antibodies begins, which are aimed at destroying the child’s red blood cells. A blood test will show an increased amount of bilirubin, which increases the likelihood of damage to the fetal brain.
How modern medicine helps save the lives of newborns
“The only way to avoid Rh conflict is the timely administration of anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin. The Rh factor in an adult is determined using a medical laboratory test. The fetal Rh factor can be determined using NIPT, a non-invasive prenatal test. This is an accurate and completely safe study for mother and fetus.”
freepik.com/
The baby's Rh factor can be found out at the tenth week of pregnancy. Modern medicine provides for the administration of such injections intramuscularly to all pregnant women with Rh(-) at 28 weeks - as a preventive measure.
This is interesting: Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation appreciated the benefits of sports during pregnancy
Why does Rh conflict occur?
The conditions for the occurrence of Rh conflict are:
- Rhesus is negative in the woman and positive in the father.
- Second pregnancy of a woman with negative Rh.
- The baby's red blood cells in the mother's blood, remaining after the first pregnancy.
- Manipulations with blood transfusion with incompatible Rhesus before pregnancy.
- Various pregnancy disorders (placental abruption or uterine bleeding).
- The presence of diabetes mellitus in the mother.
- Abortion in a woman with negative Rh.
A woman who is about to give birth to a child for the first time and has a negative Rh factor is able to give birth to a healthy child, and the pregnancy will generally proceed normally. If she has not encountered Rh-positive blood before, then she does not have antibodies. In this case, the chances of Rh incompatibility with the baby are small. But in future pregnancies, the likelihood of incompatibility occurring is very high, since the mother’s body will already contain antibodies to fight the incompatible protein. If both parents are Rh negative, then there is no reason to worry. And in case of Rh conflict, modern medicine gives couples a chance to carry and give birth to a healthy baby.
Incredible? Obvious!
My child has negative Rh blood factor, while my husband and I have positive blood. My husband still teases me about this: they say, from whom did she cheat? I know that nothing happened. But the question haunts me: how could this happen? After all, a child will definitely inherit the blood of his parents. Is not it?
Olga, Kostroma
- No not like this. There is nothing supernatural in your situation. It is explained by the fact that a person with a positive Rh factor may be a carrier of a negative Rh gene, which is suppressed by a stronger positive gene.
But when this negative gene is present in the blood of both parents, then, doubling its strength, it can be passed on to the child and form a Rhesus with a minus sign. According to statistics, for Rh-positive parents this situation is possible in 25% of cases.
What are the peculiarities of pregnancy with negative Rh?
Rh negative is not an anomaly, since with constant medical supervision, pregnancy proceeds normally. There is a risk of developing anemia in the fetus, but this problem is easily eliminated by blood transfusion. In modern gynecology, they use a method of artificially lowering antibodies, which allows the fetus to develop normally and the woman to bear a child. The peak period for the formation of antibodies in the mother's body occurs during childbirth, so doctors strongly recommend administering an immunoglobulin drug, which will inhibit the development of antibodies in the future. This method allows to reduce pathologies in subsequent pregnancies.
Fetal pathologies that may appear during Rh conflict:
- Anemia
- Fetal brain damage
- Hemolytic disease
- Jaundice
Rapidly developing medicine makes it possible to cope with all this if you follow all the recommendations and undergo examinations on time, and, if necessary, agree to hospitalization.
Don't need stock?
I will soon have major heart surgery. But I have Rh negative blood. They say that in such cases you need to go to a blood transfusion station and donate it “in reserve” - in case of bleeding. Is it worth doing?
Vsevolod, Moscow
Article on the topic
Where to donate blood faster and cheaper?
– Rh negative blood is always in short supply. But, if we are talking about a planned operation, like yours, the medical institution, as a rule, orders blood for it in advance. Especially if the risk of bleeding is expected.
A difficult situation with Rh-negative donor blood can arise in the event of an emergency operation, when a person is admitted to the hospital after a traffic accident or other accident. You can't think about it anymore. We need to act. How? Contact blood transfusion stations located in large (preferably federal) medical centers. Or look for the blood you need in the city’s medical network. If it was not possible to resolve this issue in this way, you need to call out friends and acquaintances or go to the nearest military or fire station and look for voluntary donors with the blood Rh blood you need.
By the way, when getting ready for surgery, remember if you have ever had a massive blood transfusion (blood transfusion). In this case, you need to select donor blood especially carefully. Otherwise, with your next blood transfusion, you may experience serious or even life-threatening problems, regardless of your Rh factor.
Rh negative and its impact on the child’s health
If you follow the recommendations of doctors, then the chances that the baby will be born healthy are very high. Such children in the first years of life need more attention, since health threats still exist.
- Premature birth is possible. This is due to the increased nervous tension of the mother during pregnancy.
- High level of bilirubin in the child's blood In the first years of life, such a child will be prohibited from physical activity. Also, such a child has an increased risk of developing hepatitis.
- Low level of hemoglobin A child needs to increase the level of hemoglobin in the blood, since in adolescence its deficiency can lead to low blood pressure, depression and apathy.
- Sports activities are recommended. Sports without overload will keep the body in good shape, and the level of bilirubin will gradually return to normal.
What are the features of managing an Rh-negative pregnancy? A pregnant woman who is Rh-negative will be indicated for hospitalization for conservation. This is important for the mother and child, because if there is a sharp increase and multiplication of antibodies in the blood, specialists will be able to give a blood infusion to a fetus with negative Rh. Mothers should avoid infectious and colds, as well as stress. A blood test to detect antibodies is performed once a week in a hospital setting. If the pregnancy is proceeding normally, then such an analysis is carried out once a month until the 32nd week, and after the 35th it is prescribed weekly until the birth itself.
What are the preventive measures and treatment for Rh-conflict? Preventive measures for Rh-conflict consist in timely identifying an increase in bilirubin levels and the appearance of antibodies in the mother’s blood and taking such a woman under the supervision of specialists. After childbirth, as well as abortion or ectopic pregnancy, no later than 72 hours, the woman is given an injection of immunoglobulin, which will prevent the occurrence of Rh conflict in the next pregnancy.
Treatment consists of continuous monitoring of pregnancy. If there are high levels of antibodies in the blood, hospitalization and infusion of negative blood into the child through the umbilical cord will be indicated.
A negative Rh factor is not a death sentence, but simply a feature of the blood, so it is not only possible, but also necessary for women with such Rh factor to give birth. With proper monitoring and following the recommendations of doctors, the chances of carrying and giving birth to a healthy child are as high as with a normal pregnancy.
What is Rh negative?
Human blood consists of cells: red blood cells, leukocytes, platelets. There is a protein on the surface of red blood cells, which is also an antigen - this is Rhesus. But it may not exist. Cells that have protein on their surface are positive, and those that do not are negative.
80-85% of the world's population lives with positive Rhesus, which greatly simplifies their lives. Because if blood transfusion is needed, it will always be available in treatment centers. People with negative blood should be more prudent about their health, because there are only 15% of them in the world. Moreover, there is a frightening feature of patients with negative indicators. When transfusion of positive blood occurs, the body may attack an unknown protein. This will lead to death or serious complications. Also, pregnant women should be especially careful. Girls who carry a fetus with the opposite rhesus sign expose themselves and the child to mortal danger. Due to the body’s incorrect reaction to a fetus with different indicators. It is very important to register and undergo regular consultations with doctors.
By reporting accurate information about their blood in emergency situations, people with negative Rhesus have a chance to survive or carry a child to term. Not knowing can lead to death for the patient if the laboratory does not have time to conduct analysis in critical situations. We urge you to plan your pregnancy, be vigilant in extreme life situations and notify relatives about negative Rh.
Prevention and treatment
Until recently, a negative Rh factor in a mother was the reason for the birth of the only child in the family. Doctors advised such women to abandon their second and subsequent children, and in the case of the first pregnancy, they categorically did not recommend terminating it.
Today everything has changed, medicine has advanced so much that, thanks to prevention and treatment, an Rh-negative woman can have healthy children.
Thanks to effective methods of prevention and treatment, women with Rh- have the opportunity to bear and give birth to healthy children
When you first contact the antenatal clinic, blood is taken from each woman to find out the group, Rh, and antibody titer. If a pregnant woman has a negative Rh factor, but antibodies are not produced, she may be prescribed a course of immunoglobulins. If antibodies are detected in her blood, their levels are monitored throughout the entire period of gestation. The rules for managing pregnancy in such cases are as follows:
- preventing the mother's immune system from producing antibodies;
- if possible, avoiding procedures such as taking umbilical cord blood, chorionic villus sampling and amniotic fluid so that fetal red blood cells cannot reach the mother;
- suppression of antibody production with anti-Rhesus immunoglobulins to reduce the level of sensitization.
Thus, the following preventive measures are taken for pregnant women who have a negative Rh factor:
- donating blood for antibodies between the first visit and the 18th week of pregnancy;
- if the titer is less than 1:4, the analysis is done again at the 28th week, but in case of abnormalities in fetal development - earlier;
- if the titer is no more than 1:4, vaccination is prescribed at week 28;
- if the titer is more than 1:4, it is determined every week until the 20th week;
- if the mother has antibodies, the fetus is constantly monitored (using ultrasound); if the condition worsens, an intrauterine blood transfusion may be required;
- if a transfusion cannot be done, the issue of childbirth is resolved, since waiting in this case may result in the death of the child;
- within three days after delivery, the baby’s Rh is determined: if it is negative, then nothing is administered to the mother, if positive, antibodies are administered, but only if they are not in the blood;
- if antibodies were detected during pregnancy, then there is no point in administering immunoglobulins;
- Vaccination is needed after an abortion, spontaneous miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, after puncture of amniotic fluid, etc.
How do fetal red blood cells enter the mother's blood?
This is possible in the following cases:
- during blood transfusion;
- during termination of pregnancy;
- in case of miscarriage;
- during such medical procedures as puncture of amniotic fluid, taking blood from the umbilical cord, chorionic villus sampling and others;
- with placental abruption;
- during ectopic pregnancy.
When the blood of mother and fetus comes into contact, antibodies may begin to be produced. This process in medicine is called sensitization. Antibodies can freely cross the placenta, then enter the bloodstream of the unborn baby, after which the destruction of his red blood cells will begin. As a result, the fetus begins to become anemic, dropsy of the head occurs, and heart failure develops. This condition is called hemolytic disease of the fetus, which can lead to fetal death. This disease also occurs in newborns. At the same time, their bilirubin levels increase, and their skin turns yellow.