Red blood cell distribution index (RDW) is a very important factor during a complete blood count. This indicator shows the size and shape of red blood cells.
Red blood cells perform the transport function, thereby assisting in the penetration of oxygen into all tissues and organs and at the same time taking away toxins and carbon dioxide accumulated in the cells. In their normal state, red blood cells are approximately the same size, which allows them to quickly stick together, forming blood clots.
The indicator of red blood cells in the blood may reflect the presence of pathological processes in the body, especially if the sizes of these cells vary significantly. Next, we will talk about in what situations the erythrocyte distribution index decreases, how this manifests itself and what it indicates.
Reduced RDW: norm and pathology
A person in good health has red blood cells of the same shape, density and color. In case of deviation, especially in the presence of autoimmune diseases or oncology, the failure occurs at the level of microcells, when young cells do not receive a certain number of components, which, in fact, inhibits their performance. Thus, anemia occurs - a pathology during which the body does not receive the required amount of oxygen, in other words, the metabolic function in red blood cells is disrupted.
What does RDW mean in a blood test?
During a general blood test, the erythrocyte distribution index is determined. If the presence of a specific disease is suspected, a blood test is prescribed to determine only this indicator.
Most often, the width of the distribution of red blood cells by volume is determined together with the MCV indicator. This is the average volume of red blood cells. This happens because these indices (in quantity and volume) are closely related to each other and help in determining the type of anemia.
It happens that the erythrocyte distribution index is reduced. What does it mean? The thing is that for a qualitative judgment about the state of red blood cells, not only their concentration in the blood is important, but also their shape. An increased distribution of red blood cells is observed in 1 out of 10,000 cases, but if the RDW index is reduced, which is much less common, we are talking about the presence of serious problems in the human body.
A blood test to determine the erythrocyte distribution index can be carried out both during medical examinations (routinely) and as prescribed, if there are suspicions of any abnormalities in the hematopoietic function. The analysis is required before surgery, during pregnancy and in childhood.
Pathological consequences
Normal RDW
Anemia with normal RDW may indicate thalassemia. A low Mentzer index, calculated from a complete blood count, may indicate this disease, but hemoglobin electrophoresis may be diagnostic. Anemias of chronic diseases show normal RDW.
High RDW
High RDW may result from the presence of fragments, agglutination groups, and/or abnormally shaped red blood cells.
- Iron deficiency anemia usually presents with a high RDW and low MCV.
- Anemia caused by folic acid and vitamin B 12 deficiency usually manifests as a high RDW and a high MCV.
- Anemia with mixed deficiency (iron + B 12 or folic acid) usually presents with a high RDW and variable MCV.
- Recent bleeding is usually accompanied by a high RDW and normal MCV.
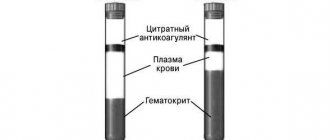
- If instead
citrated bloodused
blood with anticoagulant
EDTA, a falsely high RDW value may occur. Cm.
Pseudothrombocytopenia
Why is it necessary to do an RDW analysis?
It was already mentioned above that the index of distribution of red blood cells in the blood makes it possible to conduct a qualitative assessment of the composition of red blood cells, taking into account their size.
But why is this necessary? The thing is that these cells are very similar to each other, which gives them the opportunity to replace each other or form blastulas. An increase in cell size entails an increased need for nutrition and, in addition, this means that their life expectancy is reduced. All this directly affects the overall indicator of red blood cells in the blood and the human condition.
When a large number of red blood cells die, iron is released and more bilirubin becomes available, which puts increased stress on the liver, and as a result, it cannot process these substances.
The RDW index is directly related to the pathological process, during which the dimensions of erythrocytes change (anisocytosis). This condition is a complex chemical process that causes all blood cells to suffer.
Determination of the distribution width of red blood cells
The RDW value shows the heterogeneity (diversity) of red blood cells (Er) in size. Normally, the average erythrocyte volume (MCV) in an adult is from 80 fL to 95-100 fL (μm3). The appearance of small erythrocytes (microcytes) and/or large Er (macrocytes) is noted in blood pathologies.
Various types of anemia and myeloproliferative diseases are accompanied by changes in the size of red blood cells. Transformed Er appears in the blood, the sizes of which are smaller or larger than normal.
The range of Er size values from the smallest microcytes to the largest macrocytes is called the width of the erythrocyte volume distribution.
The following erythrocyte indices have clinical significance and are necessary for diagnosing anemia and bone marrow pathologies:
- RDW-CV is the coefficient of variation (CV) of Er dimensions;
- RDW-SD - means the relative width of the distribution of red blood cells by volume.
What the RDW-CV shows
The RDW-CV index is measured as a percentage and is calculated based on the Er distribution width graph. The coefficient of variation is calculated in the following way:
RDW-CV = SD*100%/MCV.
The calculated distribution of the width of CV erythrocytes depends on the average size of erythrocytes; if RDW- CV is increased, this may mean an increase in the number of macrocytes and an increase in microcytes.
The SD value is the deviation of the Er value from the average value to the greater and lesser sides from the midline on the graph.
Changes in this index can be monitored using the erythrocyte histogram.
- As the coefficient of variation increases, the shift of the histogram to the right increases when a significant number of macrocytes appear.
- The predominant content of microcytes leads to a shift of the histogram to the left, towards smaller values of erythrocyte cells.
RDW-SD index
The hematology analyzer calculates the RDW-SD indicator automatically and produces a ready-made result based on the red blood cell histogram. This blood index is measured in fl (µm3), and means the difference between the largest and smallest Er.
And if RDW- CV using a formula, then to calculate RDW- SD a red blood cell ( RBC) histogram is needed. On it, along the OX axis the Er values, measured in fl, are indicated, on the OY axis - the total number of erythrocytes in percent.
The RDW-SD value is numerically equal to the length of the straight line segment on the OX axis drawn on the erythrocyte histogram at the 20% level along the OY axis.
How is it calculated?
The RDW indicator is calculated as a percentage, the norm of which is considered to be the limit from 11.5 to 14.8. The red blood cell distribution index is determined using a mathematical equation that represents the ratio of modified red blood cells to their total mass.
Nowadays, laboratories use computer technologies that make it possible to calculate the percentage of deviation from the established norm. The calculation results are presented in the form of a histogram depicting a curve that indicates probable changes in the dimensions of red blood cells.
Degrees of anisocytosis
Erythrocyte anisocytosis is divided into four stages:
- I degree. Diagnosed when 27% or 50% of red blood cells have a different volume.
- II degree. Occurs when 55% or 70% of red blood cells have a change in size.
- III degree. More than 75% of blood cells are modified and have different dimensions.
- IV degree. Almost 100% of blood cells are different from normal.
Clinical analysis reveals blood levels of rdw, ranging from a slight degree to a pronounced degree, when the highest percentage of deviation from the blood flow composition standards is detected. In ideal condition, the size of red blood cells should vary between 7-9 micrometers. According to the degree of change in the size of red blood cells in one direction or another, anisocytosis is classified into:
- Macroanacitosis - a larger number of red blood cells of increased volume.
- Microanacitosis is the predominant number of red blood cells of small diameter.
- Mixed type, combining macrocytes and microcytes.
There are also megalocytes, which have the maximum possible blood cell size of more than 12 microns. Macrocytes are red blood cells whose size is more than 8 microns. Their normal amount should be in the range of 12−15%. Microcytes include blood cells smaller than 6.9 microns. Mixed anisocytosis is characterized by the presence of both reduced and enlarged blood cells in the bloodstream. Combined studies are carried out using the calculation method using the Price-Jones curve.
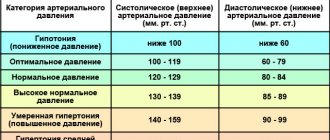
Normal indicators
The norms of the erythrocyte distribution index depend on gender, age and the presence of certain conditions that occur in the human body. For children under one year of age, the normal rate is 11.5-18.7%. At one year of age and older, the values tend to the generally accepted norm of 11.5-14.5%.
For the female half of humanity, the upper limit shifts to 15.5%, since their hormonal levels change too often: during pregnancy, lactation, taking oral contraceptives, menopause.
For analysis, blood is taken on an empty stomach in the morning (before 9 am). It is very important that before this procedure the person does not take any medications and is in a balanced internal state.
Preparing for the study
To obtain a reliable and accurate result, it is important to follow the recommended rules for preparing for analysis. Therefore, experts advise adhering to the following recommendations:
You should donate blood on an empty stomach. The interval between food intake and collection of biomaterial should be at least eight hours
Therefore, doctors advise taking it in the morning. Before the analysis, avoid drinking alcoholic beverages the day before. It is recommended not to smoke a few hours before the diagnosis. An hour before the manipulation, it is important to eliminate physical and emotional stress. Immediately before the procedure, you need to sit quietly for at least 15 minutes. If a person took medications the day before, it is important to inform the laboratory assistant about this. After some diagnostic procedures, for example, after a rectal examination, it is advisable to donate blood after a certain time.
Some clinics recommend bringing disposable sterile gloves and a scarifier with you. They can be purchased at any pharmacy.
Raising RDW
The RDW level can be elevated in some situations. The most common cause of this pathology is iron deficiency anemia. The indicator can change at different stages of pathology development, which is clearly reflected in the histogram of red blood cells:
- The initial stage of anemia development is characterized by normal indices, but hemoglobin will be greatly reduced. This is the result of healthy functioning of the spinal cord.
- The next stage of development in the histogram will show an increase in RDW. When there are problems with hemoglobin, indicators such as the average concentration and content of hemoglobin in a blood cell and the average volume of red cells decrease.
When treating IDA, it is necessary to normalize the level of concentration of iron-containing protein and its characteristics in the human blood.
What do the reduced numbers mean?
Patients often ask what this means: “red blood cell distribution index is reduced.” Since the erythrocyte distribution index cannot be assessed without a volume indicator, it is necessary to familiarize yourself with all the options for underestimated indicators and their relationship:
- RDW is low and MCV is below average - indicating problems with the spleen and liver.
- RDW is lowered, and MCV is higher than the normal level - indicates the presence of oncological pathologies, mainly the development of metastases in the bone marrow.
The fact that the erythrocyte distribution index RDW sd is reduced, from a biological point of view, cannot, in principle, be observed. For this reason, most often the patient is offered to donate blood again, observing the following conditions:
- stop smoking and drinking alcohol for 24 hours before blood sampling;
- do not take any medications before the analysis;
- Avoid eating smoked and salty foods the day before.
In the case when the erythrocyte distribution index RDW sd is indeed reduced, which is necessarily confirmed by deviations from the norm in the MCV indicator, then this indicates the occurrence of certain pathologies. These include:
- Hypochromic microcytic anemia - sometimes also called anemia. A condition in which irregularly shaped red blood cells die because they have no biological value in the body.
- Malignant tumors - usually in this case we are talking about mastopathy, bone marrow and lung cancer.
- Hemolysis of red blood cells is a process during which red blood cells die without reaching their target. As a result, active hemoglobin is released.
Causes
So, the erythrocyte distribution index is reduced - what does this mean? There are several reasons that can reduce the RDW indicator:
- Acute blood loss due to injuries and pathological bleeding.
- Frequent operations.
- A metabolic disorder during which the food consumed is not completely digested.
- Hormonal imbalance, which most often occurs in women.
- Deficiency of B vitamins and iron in the body.
- Blood diseases characterized by rapid destructive processes.
What measures to take?
What to do when the red blood cell distribution index is low?
A highly qualified doctor during a consultation will most likely ask the patient to take the test again, because the RDW indicator is almost never underestimated. Because this suggests that all cells are ideal in their parameters, but this cannot happen in principle. If the indicator is confirmed by repeated analysis, then a full examination of the body’s condition is carried out, paying special attention to oncological examinations.
Preventive measures
You can prevent a reduced RDW by following these simple rules:
- The diet should be balanced, which includes plenty of fresh fruits, lean meats and vegetables.
- It is recommended to breathe fresh air as often as possible.
- An active lifestyle will help prevent a decrease in the RDW index.
- It is very important not to skip routine medical examinations, during which most often serious deviations from the norm are detected that do not have external symptoms.
As a result, we learned that the red blood cell distribution index reflects their dimensions relative to each other and makes it possible to learn about their biological value. A decrease in RDW is very rare, but if the erythrocyte distribution index is decreased, this means that various pathologies may be present.
The index is calculated based on the results of a general blood test, but can only be fully valid in conjunction with the MCV indicator, since they are closely interrelated.
Treatment
If the erythrocyte distribution index is low or above normal, the first step should be to treat the underlying disease. In some situations, therapy is limited only to:
- changing your usual diet;
- refusal to consume alcohol;
- introducing foods fortified with iron and other micronutrients into the menu;
- taking vitamin and mineral complexes.
In other circumstances, therapy will be purely individual:
- when cancerous tumors are detected, they turn to medical intervention, radiation treatment and chemotherapy;
- for gastrointestinal pathologies, drug tactics and diet therapy are used;
- myelodysplastic syndrome is eliminated through the use of physiotherapeutic procedures and other conservative methods.
Recovery is spoken of in such cases: improvement in well-being and complete absence of clinical signs, positive dynamics regarding changes in general blood test parameters.