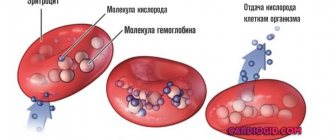
The norm of red blood cells in the blood of women
By the number of red blood cells in a woman’s blood, urine and smear, one can judge the state of her health and the effectiveness of the treatment.
The main factor influencing the indicator of red blood cells contained in the blood of women is age.
The norm of red blood cells in the blood of women by age:
| Age | Norm in million/μl |
| 4 – 6 months | 3,9 – 5,5 |
| 6 – 9 months | 4,0 – 5,3 |
| 9 – 12 months | 4,1 – 5,3 |
| 1 – 3 years | 3,8 – 4,8 |
| 3 – 12 years | 3,7 – 5,1 |
| 12 – 18 years and older | 3,9 – 5,2 |
One of the factors that has a significant impact on the number of red blood cells is the menstrual cycle. In the initial phase of menstruation, increased levels are recorded. However, as more and more blood is lost, the number of red blood cells decreases. At the onset of ovulation, the lowest values of this indicator are observed.
Pregnancy also affects a woman's blood condition. During this period, the level of red blood cells increases significantly. Moreover, changes in indicators have a wave-like character. In the first three months, the number of blood cells begins to slightly exceed normal values. Over the next three months, there is a slight decrease in the level of red blood cells. The third trimester will again be marked by increased values of this indicator.
During the birth of a child, the mother sometimes loses a significant amount of blood, which leads to a decrease in the level of red blood cells, sometimes to 3*1012/l. In this condition, women may experience weakness, nausea and dizziness. But this is no reason to be afraid. This process is absolutely normal and natural.
Description of the causes of erythrocytosis
An excess of red blood cells in the blood plasma is called erythrocytosis. As a result, the blood begins to thicken and moves through the capillaries with difficulty. Red blood cell production spontaneously increases in the body when oxygen levels in cells decrease. Lack of oxygen can be caused by congenital pathology of the heart muscle, heart failure, hemoglobinopathy, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and excessive smoking.
It is possible to regulate the formation of red blood cells with the help of certain drugs. These include anabolic steroids, erythropoietin protein and some groups of antibiotics intended for the treatment of infectious and inflammatory processes in hematopoiesis.
The consequence of an increase in red blood cells in blood cells can be dehydration, which occurs as a result of an increase in temperature in the body, the occurrence of gag reflexes and loose stools. During such deviations, the concentration of red blood cells increases, but their number does not change.
Cases of complications
Sometimes not only red blood cells are found in the urine, but also other blood cells - leukocytes, as well as protein compounds. This is clearly a pathological condition, which indicates the development of pathogenic processes. As a rule, they are associated with the following reasons:
- hemorrhagic cystitis;
- urolithiasis;
- inflammation in the kidneys;
- tuberculosis;
- tumors of various nature in the urinary tract.
It is important to take action immediately and get tested. Otherwise, kidney pathology can become chronic, resulting in renal failure.
Symptoms of increased red cells
An increased number of red blood cells can be determined by a blood test. External manifestations are not so noticeable. Only a few symptoms can indicate their increase. Signs of oversaturation with red blood cells in the human body can be:
- constant fatigue
- presence of shortness of breath,
- pain syndromes in the joints,
- dampness on the feet and palms,
- skin itching,
- bad dream.
Polycythemia, which occurs when the level of red blood cells increases, leads to blurred vision, headaches, muscle and chest pain, dizziness, high blood pressure and tinnitus. With mild polycythaemic syndrome, there are often no symptoms.
Increase in red blood cells: prevention
Leukocytes
Leukocytes are a large group of diverse cells whose task is to provide protection to the body. In international medicine, they are often referred to as WBC - white blood cells. This abbreviation denotes the total content of leukocytes in the analyzer form. The reason for the increase in WBC is various damaging factors: infections, injuries, ischemia and tissue necrosis, and others. Simply put, an increase in the number of white blood cells means that the immune system is actively involved in the fight against damage. At the same time, low values of the indicator may indicate a lack of immunity under the influence of radiation, medications, certain viral infections, as well as diseases that are accompanied by impaired formation or increased destruction of leukocytes.
Leukocyte indices
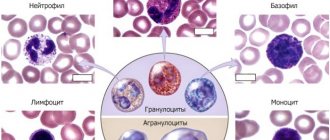
In addition, in assessing the content of leukocytes, leukocyte indices , or in old forms - leukocyte formula . The general clinical analysis with the latter is called detailed. There are several types of leukocytes, which differ from each other in morphology and functional characteristics. The leukocyte formula reflects their percentage of the total number, and modern analyzers also display the absolute content of each type of these cells. They can be identified on the form by the following abbreviations:
- LYM - lymphocytes;
- MXD - agranulocytes (monocytes, basophils and eosinophils);
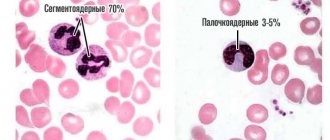
- NEUT—neutrophils;
- MON - monocytes;
- EO - eosinophils;
- BA - basophils.
If there is a “%” sign after the abbreviation, then we are talking about percentage, and the “#” sign means their absolute content. Changes in the leukocyte formula can serve as an indicator of a wide variety of problems in the body. Let's take a closer look at them.
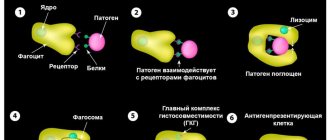
The main task of neutrophils is phagocytosis - the absorption of foreign objects and their destruction. They always rush to areas of inflammation and tissue breakdown, where they perform this work, so their increased content indicates active inflammation.
In addition to neutrophils, the function of phagocytosis is performed by macrophages, into which, in the process of their development, monocytes . A high level of the latter also serves as a marker of inflammation, usually of an infectious nature.
Eosinophils take part in reactions associated with the allergic component. An increase in their number is observed in allergies, parasitic infestations, some infections and cancer.
Basophils take part in inflammation and allergies by releasing heparin, histamine and serotonin. They rarely increase in isolation, although such a phenomenon in some forms of leukemia has a serious prognostic significance.
Lymphocytes are actively involved in a wide variety of conditions, including immunodeficiencies, allergies, inflammation, and autoimmune disorders. Their high content may be a sign of childhood infections, viral hepatitis, mononucleosis, tuberculosis and a number of other diseases.
Assessment of leukocyte indices and leukocyte formula requires an understanding of the pathological and physiological processes in the body, and should not be carried out solely on the basis of tabular data. You absolutely cannot diagnose yourself based solely on the results of the analysis.
Prevention of increased red blood cells
The cause of the increased production of red blood cells is determined by the doctor. To maintain normal red blood cell levels, it is enough to adhere to preventive measures.
To avoid increased blood concentrations, it is recommended to drink more fluid. The water must be purified, so it is better to buy it in bottles or collect it from wells.
Eating fresh vegetables and fruits has a good effect on blood composition. They contain many vitamins and microelements that regulate the content of red blood cells.
You can reduce the concentration of red cells in the blood by eliminating foods containing iron from your diet. You will have to give up red meat, liver, beans, lentils, spinach, cabbage, prunes and raisins. Avoid drinking caffeinated drinks, smoking or taking aspirin. Regular physical activity will help regulate red blood cell levels.
How is an increased content of red blood cells in urine determined?
The analysis consists of 2 stages:
- Studying the color - if the urine has a brown, reddish tint, this indicates a repeated violation of the norm.
- Microscopic examination - if there are more than 3 red blood cells in the urine, doctors diagnose microhematuria.
When establishing an accurate diagnosis, doctors determine the type of red blood cells:
- Unchanged - they contain hemoglobin, and are found in the urine in exactly the same form as in the bloodstream.
- Modified - alkaline. They do not contain hemoglobin, and the cells lose their red color and become colorless. They look like rings (normally they should look like disks with a biconcave surface).
If blood elements are found in the urine, this clearly indicates a pathological process, and it can be very dangerous. Therefore, you must immediately consult a doctor for further examination and consultation.
Treatment of anemia
The course of medical therapy is carried out on the basis of the diagnosis and includes the prescription of a special diet and medications, as well as, if necessary, surgical intervention to eliminate the causes of blood loss.
A balanced diet is of great importance for anemia. It compensates for the lack of iron and microelements involved in hematopoiesis. Nutritionists recommend eating foods rich in vitamin B12, folic acid and iron. The diet must contain meat, offal (liver, heart, tongue), fish, egg yolks, mushrooms, buckwheat, legumes, black currants, pomegranate, strawberries, nuts, apples, rose hip decoction, dried fruits. Vitamin C accelerates the absorption of iron by the body, while strong tea, coffee, and calcium hinder it. Strong alcoholic drinks are harmful to a patient with anemia.
Iron supplements are considered the most effective for combating anemia. They are better absorbed, increase hemoglobin levels faster, restore its reserves in the body, and eliminate weakness and fatigue. Based on blood test data for each patient, depending on a number of indicators (type of anemia, severity of the disease and the cause of its development, age of the patient), an individual daily dose, course duration, and preventive measures are calculated. In severe cases, intramuscular and intravenous administration of ampoule iron preparations in a hospital setting is possible to avoid adverse reactions and allergies.
It is advisable to take iron supplements one hour before meals or two hours after meals. Medicines should not be taken with tea or coffee. These drinks reduce iron absorption. You must use water or juice.
The prognosis for iron deficiency anemia is favorable in most cases. The patients' condition improves significantly, the body's resistance increases, sleep and appetite normalize. The basis for preventing anemia is a balanced diet. Do not get carried away with protein foods and sweets. There should be vegetables, herbs and fruits on the table all year round. Another rule is to maintain a healthy lifestyle, exercise, walks in the fresh air, proper rest and good sleep.
Sign up for an anemia screening
Make an appointment
Anemia in men and women
Anemia is one of the most common diseases among the adult population of the Earth today. Risk groups for developing anemia include:
- lovers of vegetarian cuisine.
- patients suffering from large blood losses due to the physiological characteristics of the body or a number of chronic diseases.
- pregnant women.
- professional athletes.
Anemia in men is diagnosed in the presence of malignant neoplasms or hidden bleeding of the gastrointestinal tract, peptic ulcer, hemorrhoids and other pathologies. A decrease in the level of hemoglobin in a woman’s blood can be associated with heavy menstruation, pregnancy and lactation, and a period of hormonal changes during menopause. Varying degrees of anemia also appear in children due to lack of adequate nutrition, impaired absorption of iron in the gastrointestinal tract, gastritis or parasitic diseases, limited exposure to fresh air and physical inactivity.
Table of normal blood test values
In conclusion, we provide a table of the main normal indicators of a general blood test in adults and children. We remind you that its results can only be assessed in conjunction with examination data, other laboratory data, including biochemical blood tests and instrumental diagnostic methods. In addition, reference, that is, acceptable, values depend on the type and model of diagnostic equipment. In this case, in the form of the automatic analyzer, next to the result obtained, normal values for a specific model are reflected.
| Index | Adults | Children | ||||||
| Men | Women | up to a year | 1-2 years | 2-4 years | 4-6 years | 6-10 years | 10-16 years | |
| RBC, *10^12/l | 4,3-5,7 | 3,8-5,1 | 4,1-5,3 | 3,8-4,8 | 3,7-4,9 | 3,8-4,9 | 3,8-5,2 | |
| HGB, g/l | 132-173 | 117-155 | 113-141 | 110-140 | 115-145 | 115-160 | ||
| HCT, % | 39-49 | 35-45 | 33-41 | 32-40 | 32-42 | 33-41 | 35-45 | |
| MCV, fl | 80-99 | 81-100 | 71-112 | 73-85 | 75-87 | 75-90 | ||
| MCH, pg | 27-31 | 31-37 | 24-33 | 26-32 | ||||
| ESR, mm/h | 2-15 | 2-20 | ||||||
| WBC, *10^9/l | 4-10 | 6-17 | 5,5-15,5 | 5,5 -15,5 | 4,5-13,5 | 4,5-13 | ||
| LYM#, 10^9/k | 1-4,8 | 2-11 | 3-9,5 | 3-9,5 | 1,5-7 | 1,5-6,5 | 1,2-5,2 | |
| NEUT#, *10^9/l | 1,8-7,7 | 1,5-8 | 1,8-8 | |||||
| MON#, *10^9/l | 0,05-0,8 | 0,05-1,1 | 0,05-0,6 | 0,05-0,5 | 0,05-0,4 | |||
| BA#, *10^9/l | 0-0,08 | |||||||
| EO#, *10^9/l | 0,02-0,5 | 0,05-0,4 | 0,02-0,3 | 0,02-0,5 | ||||
| PLT, *10^9/l | 180-320 | 160-390 | 150-400 | 180-450 | 150-450 | |||
| MPV, fL | 9,4 -12,4 | |||||||
| PCT,% | 0,108-0,282 | |||||||