Less known clinical manifestations of iron deficiency include:
- neurotic reactions and neurasthenia;
- decreased muscle performance and general exercise tolerance;
- disturbances of metabolic processes in the myocardium;
- disorders of peripheral circulation and microcirculation.
The diagnosis of IDA is based on the characteristic clinical picture, changes in the blood and absolute iron deficiency.
Diagnosis of anemia
The diagnosis is established after a laboratory blood test, namely the number of red blood cells and hemoglobin.
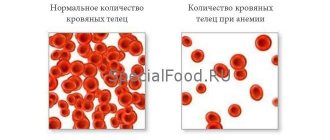
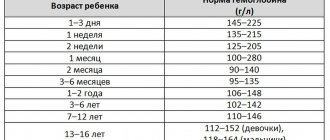
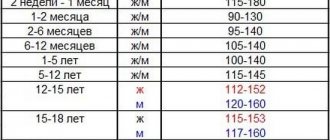
They speak of anemia if the amount of hemoglobin is less than 110 g/l, red blood cells are less than 3.5 x 10¹²/l. These indicators correspond to a mild degree of anemia. Moderate anemia is established with the following indicators: hemoglobin less than 90 g/l, red blood cells up to 2.5x10¹²/l, severe anemia with hemoglobin less than 70 g/l, red blood cells less than 2.5x10¹²/l. When anemia is detected, the child is consulted by specialized specialists: gastroenterologist, nephrologist, allergist and others as appropriate.
Recommended for diagnosing IDA
- general blood test: assessment of hematocrit (Hct), study of the level of erythrocytes in the blood and study of the level of reticulocytes in the blood with determination of the average content and average concentration of Hb in erythrocytes;
- All patients with suspected IDA are recommended to study serum indicators of iron metabolism: ferritin, serum transferrin, serum iron binding capacity (IBC), serum iron level and transferrin iron saturation coefficient (TIS).
When identifying IDA, it is necessary to conduct a set of studies to determine the cause of the development of IDA and diagnose concomitant pathologies.
Symptoms of anemia
Signs of anemia affect many organs and systems. The first visible signs appear on the skin, which becomes pale and flaky. Nails and hair become brittle, flake, and lose their shine. If you examine the earlobes in the light, you will see their transparency (Filatov’s symptom). The tongue may become inflamed, and aphthae (superficial ulcers) appear in the mouth. The nervous system suffers: babies become lethargic, whiny, they often feel dizzy, and there is noise in their ears. Sleep becomes shallow, bedwetting (enuresis), and fatigue may occur. Children who experience severe anemia before the age of 1 year may fall far behind their peers in development. Cardiovascular system disorders manifest themselves in low blood pressure, fainting, and rapid heartbeat. Systolic (at the moment of contraction) heart murmurs may appear.
The basic principles of treatment of iron deficiency anemia in children include
- eliminating the causes of iron deficiency;
- correction of regime and diet;
- prescription of iron supplements.
Treatment with iron supplements is usually long-term and ranges from 3 to 6 months, depending on the severity of anemia. Poor tolerance to iron supplements (abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea) is a reason to consult your doctor for advice. It is possible to change the drug or short-term decrease in its dose.
Children aged 2–5 years who do not have risk factors are screened for IDA annually.
Among school-age children and adolescent boys, children with a history of IDA or special needs due to health conditions or low dietary iron intake should be screened for anemia.
Beginning in adolescence, all non-pregnant women are screened for anemia every 5 to 10 years throughout their childbearing years.
Children and adolescents with IDA are observed by a doctor for one year from the date of diagnosis.
The well-being and general condition of the patient are monitored. Before removing a child from clinical observation, a general blood test is performed, all indicators of which must be within normal limits.
With timely diagnosis, identification of the causes and proper treatment, IDA can be cured in 100% of cases. So-called “relapses” of IDA most often indicate an undetected (not eliminated) cause of the disease or incorrect diagnosis and treatment.
Causes of anemia.
In order for the process of blood formation in a child to proceed normally, during the period of intrauterine development, his body needs to receive and accumulate a sufficient amount of iron from the mother. At 28-32 weeks of intrauterine development, the most intense transfer of iron from the mother and its accumulation in the child’s body occurs.
Disruption of the normal course of pregnancy during this important period leads to a disruption in the exchange of iron between mother and child and, as a consequence, to its insufficient accumulation in the body.
Maternal anemia and premature birth are the reasons why anemia is detected in all children from birth or from about the 3rd month of life. Multiple pregnancies also lead to the development of anemia.
After birth, anemia can be caused by damage to red blood cells due to hemolytic disease of the newborn and impaired hemoglobin formation.
Most often, anemia is caused by nutritional reasons. In children of the first year of life, anemia develops most often due to monotonous milk feeding, with a poor iron content in breast milk; early transfer of the child to artificial or mixed feeding; using unadapted formulas, cow's or goat's milk for feeding; not timely introduction of complementary foods into the child’s diet.
Premature babies and children born with increased body weight especially need an increased intake of iron into the body.
Therefore, a discrepancy between the intake of iron into the body and its consumption in children of the first year of life can also cause anemia.
Anemia can occur due to blood loss, for example, with frequent nosebleeds. In children with neurodermatitis, food allergies, and exudative diathesis, there is an increased loss of iron from the skin epithelium, so children suffering from such diseases are at risk for developing iron deficiency anemia.
In addition to the direct loss of iron, disturbances in its absorption and metabolism lead to the development of anemia. This can occur, for example: with rickets or lactase deficiency.
The deficiency of B vitamins and microelements is of great importance, which is why a complete and balanced diet is so important.
Any infectious or chronic somatic disease can cause anemia.
Nutritional Features
In order for a sufficient amount of iron to enter the body, it is necessary to include foods rich in this element in the diet. Iron is found in both animal and plant foods. But there is a difference between plant and animal products in the form of iron they contain. This is why pediatricians primarily recommend consuming more meat and liver. The iron they contain is absorbed much better.
Foods rich in iron include: veal, beef, liver, heart, buckwheat, oatmeal, beans, lentils, tomatoes, beets, currants, apples, persimmons, pomegranate, spinach.
Nutrition for iron deficiency anemia in infants first of all needs to be adjusted by the mother. She must carefully compose her menu, including the above products. If the baby is bottle-fed, you need to choose a formula that contains a sufficient amount of iron, and also refuse to use cow's and goat's milk as a replacement for mother's milk.
Prevention of anemia
Prevention begins with good nutrition for the pregnant woman, allocating sufficient time for walking and sleeping. Children of the first year of life need to add complementary foods to breast milk after 6 months of age; for older children, a varied, balanced diet should be organized. It is important that during the warm season the baby spends as much time outdoors as possible and takes sunbathing. The team of doctors at the SM-Doctor clinic will help your baby cope with anemia and develop individual preventive measures. Contact professionals to create ideal conditions for the growth and development of your child!
What is iron deficiency anemia?
IDA is a disease characterized by a decrease in iron levels in the human body, which affects the function of the hematopoietic system. The condition that develops in this case is associated with an insufficient amount of hemoglobin and, accordingly, red blood cells. These blood cells provide vital oxygen to the body's cells. Accordingly, the syndromes that occur during the development of IDA are closely related to a lack of oxygen. Despite the fact that there are many types of anemia, iron deficiency anemia is the most common form (90%).
Risk factors
If a woman had an iron deficiency during pregnancy, the child will also have it. The fetus receives iron through the placenta, and an iron depot is created in its body. The child uses up this reserve until the 5th-6th month of life, after which he needs to be introduced to complementary foods. If the mother had little iron, the reserves will be scarce and will quickly be used up.
Premature babies also have lower iron reserves. A baby who has been in the stomach for 9 months accumulates 300–400 mg of iron. The one born 7 months later has only 100–200 mg.
Related news
Stress during pregnancy can cause iron deficiency in the baby. In the first months of life, the baby not only uses up the iron reserves made during pregnancy, but also receives it from breast milk. The iron contained here is highly bioavailable, that is, it is well absorbed. If for some reason the baby is transferred to artificial feeding from birth, the risk of anemia increases. Especially if the “artificial” eats unadapted mixtures.
The likelihood of anemia increases during periods of active child growth: in the first years of life and adolescence. Iron is consumed faster at this time, and the previous diet does not always cover its losses.
An additional risk factor for girls is menstruation, especially heavy menstruation. After all, along with the blood, the body inevitably loses iron.
Diseases that impair iron absorption contribute to the development of anemia: intestinal problems, stomach ulcers, erosive gastritis, parasite infection.
Features in infants
Symptoms in infants are not always immediately apparent. Sometimes anemia does not manifest itself externally, and only a blood test can show a decrease in hemoglobin levels, which indirectly indicates this pathology. The mother may notice that the baby begins to show restlessness during the day, sleep and eat poorly. With iron deficiency anemia, children experience lethargy, pale skin, and dryness. Such babies often spit up, gain weight poorly and develop poorly. If the disease is not detected in a timely manner, you can already see changes in the hair, nails and mucous membranes (“stubs” in the corners of the mouth), decreased immunity and a lag in neuropsychic development.
Signs of iron deficiency anemia
Symptoms of iron deficiency anemia that you may notice in your child (and, accordingly, suspect the development of this pathology) are: increased fatigue, irritability, decreased performance at school, pale skin, the appearance of “jams” in the corners of the mouth, dizziness. One of the clearest signs is a perversion of taste and smell. What does this say? If a child eats raw pasta and cereals, paper, chalk or clay, this indicates that he has a change in taste. A change in the sense of smell is indicated by the desire to smell some sharp odors (gasoline, paint, glue, etc.).
Treatment of anemia
Methods for correcting anemia depend on age.
When breastfeeding, it is necessary to introduce vegetable, fruit and meat complementary foods on time, and spend a lot of time in the fresh air, including in the sun. The room must be well ventilated, kept clean, and sanitary rules for child care must be observed. For older children, it is enough to streamline their diet and daily routine to improve their blood tests. The diet includes beef liver, legumes, seafood, fresh vegetables and fruits, and herbs. If necessary, the timing of vaccination is postponed, massage and ultraviolet irradiation are used.
Medicines are prescribed by a doctor. Iron supplements and vitamins are indicated. The minimum duration of drug treatment is 1 month.