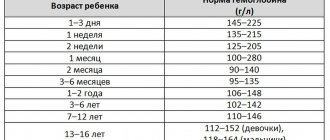
Why is human blood red?
Science knows that different living organisms on the planet have different blood colors.
However, in humans it is red. Why is blood red? This question is asked by both children and adults.
The answer is quite simple: the red color is due to hemoglobin, which contains iron atoms in its structure.
What makes blood red is hemoglobin, which consists of:
- From a protein called globin,
- The non-protein element heme, which contains the ferrous ion.
There are four hemes in hemoglobin molecules.
Their number is 4 percent of the total mass of the molecule, and globin accounts for 96 percent. The main effect in the activity of hemoglobin belongs to the iron ion.
Ferrous oxide makes blood red.
The metal that promotes the reproduction of red blood cells is continuously produced by the human body.
Nitric oxide, in turn, plays an important role in regulating blood pressure.
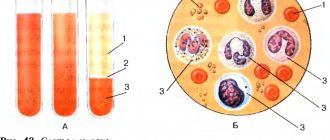
Types of blood
| Arterial | Venous |
| Rich in oxygen, comes from the heart. A bright scarlet hue distinguishes arterial blood from venous blood. | Gives oxygen to organs and returns to the heart. The dark red tint is a distinctive feature. What makes this blood dark is the carbon dioxide that fills it. |
Biology at the Lyceum
Formed elements of blood. Red blood cells
Erythrocytes (Greek erythros - red, cytos (kytos) - cell), or red blood cells, are nuclear-free blood cells containing hemoglobin. They have the shape of a biconcave disk.
They are flexible and elastic, easily deformed and pass through blood capillaries with a diameter smaller than the diameter of a red blood cell. They are formed in the red bone marrow and destroyed in the liver and spleen. Life expectancy is 100 - 120 days.
Normally, 1 μl (mm3) of blood in men contains 4 - 5 million red blood cells, in women - 3.7 - 4.7 million, in newborns up to 6 million.
Functions of red blood cells
1. Respiratory - thanks to hemoglobin, they transport O2 and CO2.
2. Nutrient - they carry amino acids on their surface and deliver them to the cells of the body.
3. Buffer - maintaining blood pH using hemoglobin.
4. Regulatory - they transport vitamins, hormones and various enzymes on their surface.
the hemoglobin they contain
. Hemoglobin is able to easily combine with oxygen and easily release it. Red blood cells carry oxygen from the lungs to all organs.
Unlike other classes of vertebrates, mammals (including humans) have red blood cells that do not have a nucleus.
It is pushed out as the cell matures, and the erythrocyte acquires a biconcave shape, which increases the surface of contact of the erythrocyte with the air of the pulmonary vesicles and increases its useful volume (the erythrocyte nucleus of other vertebrates does not contain hemoglobin!). Carbon dioxide from tissues to the lungs is partially transferred by blood plasma, and partially by hemoglobin of erythrocytes.
Hemoglobin is a complex chemical compound found in red blood cells and consists of two parts: the globin protein and four heme molecules. Thus, hemoglobin is a complex protein - a chromoprotein. Heme contains an iron atom that can attach and release an oxygen molecule. In this case, the valence of iron does not change (it remains divalent).
In the capillaries of the lungs, hemoglobin attaches to oxygen and becomes oxyhemoglobin , which gives arterial (oxygen-rich) blood its bright scarlet color.
In tissue capillaries, hemoglobin gives up oxygen and turns into reduced hemoglobin , which gives venous blood a dark cherry color.
When hemoglobin combines with carbon dioxide (CO2), carbohemoglobin .
When hemoglobin is exposed to strong oxidizing agents, iron is oxidized and goes from divalent to trivalent, and hemoglobin turns into methemoglobin , which gives the blood a brown color.
Hemoglobin combines very easily with carbon monoxide (CO) to form carboxyhemoglobin . This connection is very strong, and hemoglobin ceases to be an oxygen carrier.
Therefore, even 0.1% carbon monoxide in the air causes 80% of hemoglobin to bind to it, and this is life-threatening. At a carbon monoxide concentration of 1%, death occurs within minutes.
When red blood cells are destroyed, hemoglobin is released into the blood plasma, which turns red and becomes transparent - “lacquer blood”. The process of destruction of red blood cells and release of hemoglobin is called hemolysis .
It can occur when osmotic pressure decreases, which first leads to swelling and then destruction of red blood cells, when exposed to chemicals that destroy the membrane of red blood cells (ether, chloroform, alcohol, bile acids, etc.
), with strong mechanical effects on the blood, for example during its transportation, during freezing and thawing of blood, when it is heated to 65 - 68 ° C, during transfusion of incompatible or poor quality blood, during bites of poisonous snakes, scorpions, during immune reactions.
Skeletal muscles and myocardium (heart muscle) contain muscle hemoglobin - myoglobin . It differs from blood hemoglobin in the smaller molecular weight of globin (protein part). The purpose of myoglobin is to supply the working muscle with oxygen at the moment of contraction, when the blood flow in it is reduced or stops altogether.
Source: https://biolicey2vrn.ru/index/ehritrocity/0-329
Compound
Blood is a rapidly renewing connective tissue that continuously circulates throughout the human body.
It was possible to find out what gives the red color, but its elements turn out to be no less interesting. What elements give it this color is an equally interesting aspect.
Blood contains:
- Plasma. The liquid is light yellow in color, with its help the cells in its composition can move. It is composed of 90 percent water, with the remaining 10 percent made up of organic and inorganic components. Plasma also contains vitamins and microelements. The light yellow liquid contains many beneficial substances.
- Formed elements of blood cells. There are three types of cells: white blood cells, platelets and red blood cells. Each type of cell has certain functions and characteristics.
Leukocytes
These are white cells that protect the human body. They protect it from internal diseases and foreign microorganisms penetrating from the outside.
Leukocytes
This is a white element in color. Its white tint cannot be ignored during laboratory tests, so such cells are identified quite simply.
White blood cells recognize foreign cells that can cause harm and destroy them.
Platelets
These are very small colored plates whose main function is coagulation.
Platelets
These cells are responsible for ensuring that the blood:
- It coagulated and did not flow out of the body,
- Coagulates quite quickly on the surface of the wound.
Red blood cells
More than 90 percent of these cells are in the blood. It is also red because red blood cells have this hue.
Red blood cells
They carry oxygen from the lungs to peripheral tissues and are continuously produced in the bone marrow. They live for about four months, then are destroyed in the liver and spleen.
It is very important for red blood cells to carry oxygen to various tissues of the human body.
Few people know that immature red blood cells are blue, then acquire a gray tint and only then turn red.
There are quite a lot of human red blood cells, which is why oxygen reaches peripheral tissues so quickly.
It is difficult to say which element is more significant. Each of them has an important function that affects human health.
Infections such as gonorrhea and chlamydia can cause bleeding between periods
If you see blood before the approximate start date of your period, it makes sense to see a doctor.
During pregnancy, bleeding may or may not be a cause for concern. Sometimes this can be a sign of a miscarriage, sometimes not: every case is unique , so you should see your doctor whenever you experience any bleeding during pregnancy.
Another cause of heavy bleeding during menstruation or other phases of the menstrual cycle can be polyps or fibrosis. These benign growths can cause these symptoms, as well as pressure and pain.
Important! If you notice any unusual discharge from the vagina, be it blood or not, during menstruation or not, then it is better not to worry yourself by looking for possible causes on the Internet, but to consult a professional doctor for advice.
Any unusual discharge (unusual structure, smell, or occurring at an unusual time) may be signs of infections and sexually transmitted diseases. Take care of your health, you only have one and remember: it is easier and easier to treat any disease if treatment is started as early as possible after it is discovered!
Explanation for the child
Children often ask questions regarding the components of the human body. Blood is one of the most popular topics of discussion.
Explanations for children should be extremely simple, but at the same time informative. Blood contains many substances that differ in function.
Consists of plasma and special cells:
- Plasma is a liquid that contains useful substances. It has a light yellow tint.
- The formed elements are erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets.
The presence of red erythrocyte cells explains its color. Red blood cells are red by nature, and their accumulation leads to the fact that a person’s blood is exactly this color.
There are about thirty-five billion red cells that move throughout the human body in the blood vessels.
Red blood cells
These cells, called red blood cells, make up most of the formed elements - more than 90%. Their main function is to transfer oxygen from the lungs to peripheral tissues and carbon dioxide from tissues to the lungs for further removal from the body. Red blood cells are continuously produced in the bone marrow. Their lifespan is about four months, after which they are destroyed in the spleen and liver.
The color of blood varies depending on whether it flows from the heart or to the heart. The blood that comes from the lungs and then travels through the arteries to the organs is saturated with oxygen and has a bright scarlet color. The fact is that hemoglobin in the lungs binds oxygen molecules and turns into oxyhemoglobin, which has a light red color. Upon entering the organs, oxyhemoglobin releases O₂ and turns back into hemoglobin. In peripheral tissues, it binds carbon dioxide, takes the form of carbohemoglobin and darkens. Therefore, the blood flowing through the veins from the tissues to the heart and lungs is dark, with a bluish tint.
An immature red blood cell contains little hemoglobin, so at first it is blue, then becomes gray, and only when ripe it becomes red.
Why are veins blue
The veins carry burgundy blood. They are red, like the color of the blood that flows through them, but not blue. The veins only appear blue.
This can be explained by the law of physics about the reflection of light and perception:
When a ray of light hits the body, the skin reflects some of the waves and looks light. However, it transmits the blue spectrum much worse.
The blood itself absorbs light of all wavelengths. The skin gives a blue color for visibility, and the vein is red.
The human brain compares the color of the blood vessel against the warm tone of the skin, resulting in blue.
Blood of a different color in various living creatures
Not all living organisms have red blood.
The protein that gives this color in humans is hemoglobin, contained in hemoglobin. Other living beings have other fat-containing proteins instead of hemoglobin.
The most common shades besides red are:
- Blue. Crustaceans, spiders, mollusks, octopuses and squids boast this color. And blue blood is of great importance for these creatures, as it is filled with important elements. Instead of hemoglobin, it contains hemocyanin, which contains copper.
- Violet. This color is found in marine invertebrates and some mollusks. Typically, such blood is not only purple, but also slightly pink. The blood of young invertebrate organisms is pink. In this case, the protein is hemerythrin.
- Green. Found in annelids and leeches. The protein chlorocruorin is close to hemoglobin. However, iron in this case is not oxide, but ferrous.
The color of blood varies depending on the protein it contains. Whatever the color of blood, it contains a huge amount of useful substances necessary for a living organism. Pigment is important for every organism, despite its diversity.
Hemoglobin
This is a complex protein that includes a pigment group. One third of the red blood cell consists of hemoglobin, which makes the cell red.
Hemoglobin consists of a protein - globin, and a non-protein pigment - heme, containing ferrous ion. Each hemoglobin molecule includes four hemes, which account for 4% of the total mass of the molecule, while globin accounts for 96% of the mass. The main role in the activity of hemoglobin belongs to the iron ion. To transport oxygen, heme reversibly binds to the O₂ molecule. Ferrous oxide is what gives blood its red color.