Tinnitus is an auditory sensation observed in the absence of an external sound signal. In most cases, we are talking about subjective tinnitus (only the person himself can hear it), and only sometimes about objective noise (if, for example, the auditory sensation is caused by involuntary muscle vibration, then the doctor can also hear it - using a phonendoscope).
Data on the prevalence of tinnitus vary widely. This is explained precisely by the fact that tinnitus is not recorded objectively. The following experiment was conducted: people who had never complained of tinnitus before were placed in conditions of absolute silence. And 93% of those who took part in the experiment said they heard some kind of noise. On the one hand, we can simply not pay attention to the fact that we have tinnitus, since we live in a constant external sound background (for a city resident, this is a standard situation). On the other hand, in the absence of an external signal, hearing becomes sharper and begins to “read” the noises of the body itself, or the nervous system “makes up” for the missing sounds by generating a signal on its own (at the level of the nervous system this is no longer an acoustic vibration, but an electrochemical process).
How does tinnitus manifest?
Tinnitus may also be described as ringing, rustling, creaking, or buzzing in the ears.
In most cases, tinnitus does not interfere with normal life. At the same time, the symptom may intensify. Doctors distinguish four degrees of tinnitus (depending on the patient’s condition):
- first degree – tinnitus does not affect a person’s well-being;
- second degree – noise causes discomfort in quiet conditions and interferes with sleep;
- third degree - discomfort from tinnitus is constantly felt, the person does not get enough sleep, the quality of life deteriorates significantly;
- fourth degree - tinnitus creates unbearable discomfort.
An important point: noise is felt in one or both ears. Noise in one ear is caused by a local cause; if there is noise in both ears at once, then the problem is most likely systemic in nature.
It is also important what other symptoms are observed along with tinnitus. For example, is tinnitus accompanied by hearing loss (hearing loss). Sometimes tinnitus is accompanied by symptoms such as headache, dizziness, and nausea.
Symptoms
If clicks in the ears are associated with swelling of the inner ear, then the ENT doctor will be able to objectively record them during the initial examination. Patients with inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs are also concerned about fever, congestion and pain in the ears (usually “shooting”), and possible ear discharge. With lesions of the jaw joints, patients complain of pain when chewing and a feeling of dislocation, often accompanied by an increase in temperature.
With tinnitus, against the background of high blood pressure, patients complain of weakness, headache, nausea, spots before the eyes. The skin of these patients is hyperemic, and convulsions may occur. With heatstroke, your body temperature rises, your pulse becomes rapid and weak, and your breathing becomes faster. These conditions require emergency medical attention.
Causes of tinnitus
Tinnitus can be caused by a wide range of causes, including some serious medical conditions. First of all, tinnitus is caused by pathologies of the hearing aid. They can be classified by area of localization.
Pathologies of the inner ear:
- presbycusis – atrophic and dystrophic changes in the inner ear of an age-related nature. In this case, tinnitus usually accompanies the development of hearing loss;
- noise damage to the inner ear. The reason may be, for example, listening to loud music on headphones for a long time;
- long-term use of certain medications that are characterized by ototoxicity (adverse effects on the hearing organs);
- otosclerosis (pathological growth of bone tissue of the inner ear). With otosclerosis, noise and hearing loss are observed first in one ear, and a few months later the pathology may develop in the second ear;
- Meniere's disease (fluid accumulation in the inner ear cavity). The main symptom of the disease is dizziness;
- labyrinthitis (inflammation of the inner ear). It also manifests itself primarily as dizziness. Tinnitus is a minor symptom.
Middle ear pathologies:
- Otitis media (inflammation of the middle ear). The main symptoms are ear pain, fever, and possible purulent discharge from the ear. Ear congestion and noise are caused by the presence of fluid (such as pus) in the tympanic cavity;
- exudative otitis (accumulation of fluid in the middle ear cavity). This type of otitis media is worth highlighting separately, since, as a rule, there are no other symptoms with it, except for hearing loss and tinnitus;
- damage to the eardrum (for example, as a result of sound trauma).
Pathologies of the external ear:
- sulfur plug;
- an insect or foreign body entering the ear canal.
Other possible causes of tinnitus
Tinnitus can also be caused by:
- pathologies of the cardiovascular system
. In particular, with atherosclerosis, plaques on the walls of the arteries lead to disruption of blood flow, and turbulence (turbulence) occurs. This uneven movement of blood causes vibration, which is perceived by the hearing aid and is felt as tinnitus. The sensation of tinnitus intensifies with an increase in blood pressure, which can be persistent (hypertension), or can be caused by situational factors such as stress, alcohol or caffeine consumption;
- pathologies of the nervous system
. Noise in one ear, accompanied by hearing loss, dizziness and a sensation of “goosebumps” crawling across the face, is observed with a neuroma (tumor of the auditory nerve). Tinnitus can also be a symptom of multiple sclerosis or migraine.
What to do when there is a knocking in the ear - how to treat it?
It is not possible to treat pounding in the ear separately, since it is not an independent disease, but only a clinical symptom. If you experience a knocking sound in your ear, you should seek medical help as soon as possible.
The first thing to do if there is a knock in the knot is to make an appointment with a vertebrologist. This doctor is well versed in pathologies of the spinal column. He will conduct an examination, make an accurate diagnosis, and give all the necessary recommendations for rehabilitation treatment.
At our chiropractic clinic, we treat musculoskeletal conditions, many of which can cause pounding in the ear. For example, to treat cervical osteochondrosis complicated by posterior vertebral artery syndrome, we use the following techniques:
- manual traction of the spinal column - allows you to increase the intervertebral spaces, which creates favorable conditions for the complete straightening of the discs and eliminating pressure on the surrounding soft tissues;
- osteopathy to restore microcirculation processes of blood and lymphatic fluid, which has a beneficial effect on the condition of all tissues;
- massage to relax overly tense muscles of the neck and collar area;
- kinesiotherapy and therapeutic exercises to restore normal muscle fiber tone and start the disrupted process of diffuse nutrition of cartilage discs;
- physiotherapy, laser, reflexology and much more.
You can right now make an initial free appointment with a vertebrologist or neurologist at our manual therapy clinic in Moscow. To do this, fill out the registration form located further on the page.
When should you see a doctor if you have tinnitus?
If you begin to hear tinnitus, that is, if it appears and does not go away, you need to see a doctor and find out its cause in order to exclude the development of the most dangerous diseases.
You should definitely consult a doctor if you experience the following along with tinnitus:
- hearing loss;
- neurological symptoms (dizziness, loss of coordination, nausea, vomiting);
- severe headache or pain in the heart area.
You should also see a doctor if the intensity of the noise increases (if the tinnitus is causing a deterioration in your quality of life).
Diagnosis of headaches and noise
In the fight against noise in the head, diagnosis plays an important role. One of the most important stages in the treatment of pathology is establishing the cause.
At the initial appointment, it is important for the neurologist to hear all the patient’s complaints. He studies medical history, asks about recent head injuries, hearing problems, and stress. Afterwards, the neurologist examines the cervical spine to identify areas of vascular compression, checks reflexes, and conducts motor tests to identify possible neurological disorders.
If, after studying the anamnesis, it becomes obvious that the ringing in the head is due to diseases of the ENT organs or mental disorders, the patient is referred to an otolaryngologist or psychotherapist, respectively.
Diagnosis of noise in the head is painless and safe
To make a correct diagnosis, instrumental and laboratory tests are required. Let's consider what examinations a doctor can prescribe for noise in the head:
- otoscopy – microscopic examination of the ear and eardrum;
- audiometry – involves measuring hearing acuity, determining auditory sensitivity to sounds of different frequencies;
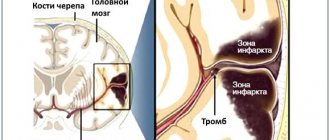
- MRI of the brain - shows tumors, stroke, ischemic areas, increased intracranial pressure and other problems;
- CT or MRI of the cervical spine is informative for diagnosing osteochondrosis, hernia and protrusions that lead to compression of arteries and nerve endings;
- Ultrasound of cerebral vessels - helps to identify the cause of hypoxia (lack of oxygen), aneurysm, thrombosis and other vascular diseases;
- MRI of the inner ear - shows neuritis, tumors, consequences of the inflammatory process, age-related changes;
- laboratory research - a clinical and biochemical blood test is prescribed.
Magnetic tomography is of great importance in the diagnosis of ringing in the ears and head. With its help, it is possible to identify any diseases of the brain, hearing organs, blood vessels, damage to the soft tissues of the head and neck, and assess the severity of the consequences of injuries suffered. MRI can be done at the SmartMed clinic, where a modern MRI scanner is installed, which has high resolution.
Treatment for tinnitus
Treatment for tinnitus involves identifying and treating the underlying condition. Unfortunately, some pathological changes that cause tinnitus are irreversible (such as age-related changes). In some cases, eliminating the cause of tinnitus is quite simple (for example, the doctor will remove the wax plug immediately). In other cases, serious examination and medication may be required.
The sooner you see a doctor, the greater the likelihood of restoring your hearing acuity and getting rid of tinnitus.
Drugs for treatment
To eliminate tinnitus, the otolaryngologist selects drug treatment based on the diagnosis.
The therapy includes different groups of drugs:
| Category | Name | Therapeutic effect |
| Drops, ointments (for ear inflammation) | Otinum | Drops that have an antiseptic and analgesic effect. The drug relieves inflammation. |
| Sofradex | The ointment eliminates inflammation and fights infection. Has a mild antiallergic and analgesic effect. | |
| Combinil | The drops have an antibacterial effect. The drug is active against most gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. | |
| ACE inhibitors (for heart and vascular diseases) | Enap | It goes on sale in tablet form. Has an antihypotensive effect. |
| Diroton | The tablets normalize blood pressure. The drug prevents the development of heart failure. | |
| Kapoten | Antihypotensive drug in tablet form. A prophylactic against myocardial infarction. | |
| Nootropics (for cerebral vascular damage) | Glycine | The drug is in tablet form. It has an adrenergic blocking and antioxidant effect. |
| Piracetam | It has several forms of release: capsules, solution, tablets. It has a psychostimulating and nootropic effect. | |
| Pantogam | Release form: syrup and tablets. Has anticonvulsant and nootropic effects. | |
| Chondroprotectors (for osteochondrosis) | Teraflex | Available in capsule form. Promotes the restoration of cartilage tissue. |
| Alflutop | Release form: solution for injection. The drug restores metabolic processes inside cartilage. | |
| Structrum | Available in capsule form. It has anti-inflammatory, chondroprotective and regenerating effects. |
When overworked, experts recommend taking vitamins. The drugs listed above have contraindications.