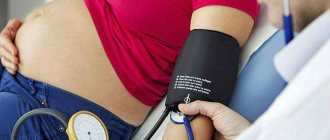
Blood pressure is one of the most important indicators of health, depending mainly on vascular tone and the volume of circulating blood. Everyone knows about the dangers of high blood pressure. What do doctors say about low?
The normal blood pressure level at any age is less than 140/90 mmHg. Art. Increased blood pressure above 140/90 mm Hg. Art. called arterial hypertension, or hypertension. This condition is dangerous due to the development of strokes, heart attacks and other cardiovascular complications; it requires treatment and medical supervision even if you do not feel it. What can we say about low blood pressure?
Natalya Polenova—candidate of medical sciences, family doctor, cardiologist, pediatric cardiologist, nutritionist at GMS Clinic.
Hypotension (a blood pressure drop of less than 90/60) is usually not dangerous to health. Constantly low blood pressure levels often occur in young girls of fragile constitution, but this, as a rule, does not affect the quality of life.
Persistent hypotension if you feel well does not require treatment. But, if the pressure drops sharply and this leads to fainting or causes a pre-fainting state, medical attention and additional examination may be required.
Reducing blood pressure in the following situations deserves special attention:
Orthostatic hypotension is loss of consciousness when there is a sudden change in body position from horizontal to vertical, for example when suddenly rising from bed. Because of this, the volume of circulating blood is redistributed and the blood supply to the brain is temporarily reduced. This condition often occurs in pregnant women due to changes in the circulatory system and a shift in the center of gravity. Therefore, during pregnancy, it is important to avoid sudden movements and carefully get out of the car or get up from a chair.
Taking medications to lower blood pressure. The goal of antihypertensive therapy is to achieve a sustained reduction in blood pressure below 140/90 mmHg. Art., but without episodes of sharp decline. An inappropriate dosage of the drug can cause hypotension - this leads to weakness, fatigue during physical activity and dizziness. In this case, it is necessary to conduct daily monitoring of blood pressure and adjust therapy.
Fainting is a short-term loss of consciousness due to impaired blood supply to the brain. For complete loss of consciousness, a sudden cessation of cerebral blood flow for 6–8 seconds is sufficient.
Types of fainting:
- reflexive, due to fear, pain, heat or stuffiness;
- orthostatic, with a sharp transition to a vertical position;
- cardiogenic, for diseases of the heart or blood vessels, as well as due to heart rhythm disturbances.
After a sudden loss of consciousness, especially if it is a repeated occurrence, you should seek medical help. You may need to consult a therapist, cardiologist, or neurologist. In addition, it is important to undergo examinations: Holter monitoring, record an ECG and conduct an MRI of the brain. And also examine the level of sugar, iron and thyroid hormones.
Headache and hypertension
Why, if the pressure is relieved, does my head continue to hurt? First, you need to understand the following thing: it matters how exactly the pressure was reduced. Let's take a closer look at what happens in various cases.
If you have lowered your blood pressure with medication, the mechanism may be as follows. With high blood pressure, intracranial pressure rises accordingly. The heart works hard, and first of all it is necessary to “calm it down.” Tablets that lower blood pressure affect the heart rate, making it more regular, therefore, the pressure drops, blood does not flow as much to the brain, and the headache should disappear.
You can get more information about this and many other aspects of health related to blood pressure, osteochondrosis, atherosclerosis, ask your questions to Dr. Shishonin and just chat by joining our community - the Club of
Former Hypertensive Patients
.
Treatment of headaches with low blood pressure
Headache with low blood pressure is typical for hypotensive people - people who experience a chronic decrease in blood pressure. This condition can be caused by overeating, alcohol, stress, and changes in weather conditions. A typical clinical picture of this condition is the appearance of dull, throbbing pains that are pressing and paroxysmal in nature.
Vascular headaches are often caused by:
- decreased venous tone, manifested by bursting pain in the back of the head;
- decreased tone of the cerebral arteries, which is characterized by aching pain in the temples, crown of the head and lasting for a long time.
In hypotensive patients, headaches often develop as a result of reasons such as:
- physical fatigue;
- daytime sleep;
- intellectual overstrain;
- first trimester of pregnancy;
- starvation;
- stay in transport;
- being indoors.
Sometimes cephalalgia becomes a precursor to a migraine attack in hypotensive patients. Shortly before the attack, the patient becomes nervous and irritable, after which an attack of pain begins in the forehead and temples, it is pulsating and very intense. Treatment of headaches and pressure should begin as early as possible, since the result depends on this. In this case the following is used:
- Baralgin;
- Vitamins (B12, C);
- Antispasmodics;
- Citramon;
- Paracetamol;
- Tincture of ginseng or eleutherococcus;
- Caffeine.
Please note: It is impossible to treat headaches during pregnancy and lactation without consulting a doctor, since many drugs are prohibited during this period.
Why does my head hurt?
If the venous outflow is disrupted, that is, the veins are pinched, you take pills, the heart stops pumping blood in large quantities, but it cannot descend back from the brain in full, which means the headache does not disappear. In this case, you should definitely consult a doctor and check the condition of the blood vessels, since excessive accumulation of blood in the brain is very dangerous.
Important:
If the venous outflow is impaired, the pressure in the body system drops, but the intracranial pressure remains high, which provokes a headache.
This is the main reason why, when taking medications, the headache may not go away, but remain the same, and it does not matter how sharply the pressure drops. In this case, do not panic and take other pills that have pain-relieving properties. After some time, the pain will go away, and neck exercises will help speed up this process. They normalize blood flow and help veins cope better with their function.
Prevention of a sharp decrease in blood pressure
Avoid situations that provoke a decrease in blood pressure (do not get out of bed abruptly, try to avoid stuffy and hot rooms, as well as stress).
Drinking cold water quickly can also prevent orthostatic hypotension (fainting when suddenly changing body position).
Simple exercises such as crossing your legs or clenching your hand into a fist can help quickly and effectively increase blood pressure and prevent fainting.
Tilt training - regular training that simulates getting up from a lying position in young people with recurrent fainting can significantly reduce the incidence of hypotensive conditions.
What to do?
At Dr. Shishonin’s clinic, specialists very often encounter cases where the patient complains of a headache that does not disappear after the pressure is reduced. Then an ultrasound examination is required to find out the condition of the vessels of the skull.
The doctor says:
Dr. Shishonin draws the attention of patients to the fact that almost every second case of headache with which they come to him is associated with a violation of the venous outflow.
If you relieve pressure through correction, that is, without medications, normalizing venous outflow and arterial inflow naturally, as happens in Dr. Shishonin’s clinic, then this problem does not arise. With a natural decrease in pressure, when blood circulates freely, the head will not hurt, which means the blood vessels will be in order.
Advice:
Gymnastics for the neck, which Alexander Yuryevich recommends to all his patients, will help reduce blood pressure naturally and normalize the outflow and inflow of blood without the use of drugs that poison the liver.
This problem can only happen if you reduce your blood pressure with medication. The pills affect the heart, causing it to work less forcefully, and intracranial pressure remains at the same level. As a result, the tonometer will show that your blood pressure is normal, but your head will hurt. What to do in this case? This situation means that the neck and its vessels are affected, and the neck needs to be treated. Check out other videos on the “Club of Former Hypertensive Patients” channel and find out how you can use gymnastics to get rid of vascular problems, improve the health of the cervical spine and get rid of pain forever. Be healthy!
Hypotension and its causes Low blood pressure (doctors also call it arterial hypotension) is considered a condition in which blood pressure drops below 100/60 mm Hg. in men and below 95/60 mm Hg. among women. For older people, blood pressure is below 105/65 mmHg. is already considered reduced. Low blood pressure is not necessarily a sign of poor health. There is also so-called physiological hypotension. At the same time, against the background of low blood pressure, the person feels great, has normal performance, and has no complaints. Pathologically low blood pressure brings many problems to people. Often, a predisposition to low blood pressure is inherited from parents who suffered from this disease. In most cases, this problem worries women. A tendency to low blood pressure is usually observed from childhood. Such children are lethargic, inactive, and quickly get tired of playing with their peers. Hypotonic adults are characterized by a so-called asthenic constitution - tall height and low weight. Most of them are thin people with pale skin. Who suffers from hypotension? The overwhelming majority of these are people who have been subjected to strong and prolonged psycho-emotional stress. Another possible cause may be prolonged mental stress, as a result of which the body falls into a state of decompensation. A traumatic brain injury can also leave behind a trace in the form of low blood pressure. Occupational hazards, such as high noise levels, vibration, overheating, can in turn lead to disruption of the functioning of the vasomotor centers. Many hypotensive patients suffered severe infections in childhood or their nutrition was disrupted. Pathologically low blood pressure is often recorded in people exposed to ionizing radiation. The most common cause of hypotension is autonomic vascular dysfunction. The next most common cause is pathology of the endocrine glands. Main symptoms. Most of the unpleasant symptoms of low blood pressure are associated with impaired blood circulation in the vessels of the brain. In this case, a throbbing pain is felt in the temples, less often in the back of the head. But pain in another location (in the forehead, heaviness in the temples) may also bother you. Often there are migraine-like pains localized in one half of the head. They may be accompanied by nausea and vomiting. The pain is dull and constant. Many people note the appearance of complaints when the weather changes, during magnetic storms. Dizziness and darkening of the eyes are often a concern, especially when suddenly getting out of bed. Some hypotensive patients experience fainting, but they are rare. Another symptom that is often found in hypotensive patients is weakness and fatigue. By the end of the working day, these people feel a decrease in performance. Concerned about absent-mindedness, memory loss. As a result of a slowdown in blood flow, the vital activity of the body decreases. Often, hypotensive people are irritable, emotionally unstable, subject to sudden mood swings, and prone to depression. Reduced vascular tone creates certain disturbances in the functioning of the heart, which can manifest itself as pain behind the sternum and in the cardiac region. These unpleasant sensations are permanent and may be accompanied by palpitations and sensations of interruptions in the functioning of the heart, not associated with physical or nervous stress. Hypotonic people seem to lack air; they yawn constantly. More often, sensations of lack of air occur during physical activity. People with low blood pressure often experience coldness and numbness in their hands and feet, and increased sensitivity to heat and cold. Emergency care for acute drop in blood pressure. What should you do if the person next to you feels worse, feels dizzy, gets dark in his eyes, turns pale? Unfortunately, this sometimes happens to hypotensive people, especially in a stuffy room in the hot sun. In this case, you need not to get confused and take the following measures: 1. The person needs to be put down as quickly as possible, since in this position the blood supply to the brain is facilitated. 2. The head should be positioned as low as possible; you should not place a pillow, as in this position the blood flow to the brain is hampered. 3. If it is not possible to lay the person down, you should sit him down, lowering his head as low as possible between his knees. Be sure to give water or tea to drink. 4. A couple of essential oils have a beneficial effect in such a situation. A bottle with a mixture of rosemary and camphor oils or peppermint oil just needs to be brought to the person’s nose. A few breaths are usually enough to restore well-being. You can put a few drops on a handkerchief and periodically bring it to your nose. Normalizing blood pressure includes various wellness procedures: regular physical exercise, massage, water and air procedures. They have a positive, tonic effect on the body, normalize the functioning of the nervous system, and therefore the functioning of internal organs. Herbs and herbal infusions have proven themselves to be effective against low blood pressure. However, before starting treatment, you must consult your doctor. Phytotherapy. 1. Cinnamon rose hips – 40 g; Lungwort herb – 30 g; stinging nettle leaves – 30 g; black currant fruits – 20 g; common barberry fruits – 20 g. 2. Common chicory root – 30 g; lanceolate plantain leaves – 30 g; black currant leaves – 30 g; stinging nettle leaves – 30 g; dandelion root – 20 g. 3. Red rowan fruits – 40 g; creeping wheatgrass rhizomes – 30 g; wild strawberry leaves – 25 g; small centaury herb – 10 g. The herbal infusions described in recipes 1-3 are prepared according to the same scheme: mix the prepared ingredients. Take 2 tbsp. spoons of herbal mixture and pour 400 ml of boiling water over them. Leave to infuse for 4 hours. Strain. Take 100 ml 3 times a day before meals. 4. Black currant leaves – 30 g; crushed cinnamon rose hips – 30 g; stinging nettle leaves – 30 g; silver birch leaves – 30 g; wild strawberry leaves – 20 g. 1 tbsp. Pour 250 ml of boiling water over a spoonful of herbal mixture. Bring to a simmer over low heat for 2 minutes. Then leave to infuse for 1 hour. Strain. Take ½ glass 3-4 times a day before meals. Simple rules for hypotension 1. For hypotension, the best medicine is movement, not lying on the couch. Physical activity improves the supply of oxygen to the brain and other organs. By loading your body, you will sleep better, and, therefore, you will feel more alert in the morning. 2. Eat lightly. Overeating leads to strain on the digestive processes and energy consumption. Eat as much as you need, but not to the point of feeling drowsy. 3. Don't skip meals, especially breakfast. Low sugar content is bad for brain function. If you are not hungry, you can eat some fruit. This will maintain the desired sugar level and saturate the body with vitamins and microelements. 4. Be careful with coffee. You should not overuse this invigorating drink, otherwise you risk becoming a coffee addict. A cup of coffee in the morning may be necessary for you. But she should follow a light breakfast, under no circumstances on an empty stomach. Try to drink no more than 2 cups of coffee a day, and after lunch it is better not to drink it at all. 5. For many hypotensive patients, daytime sleep is a good medicine. Don't neglect this in your free time. If you do not suffer from insomnia, 15-20 minutes of sleep during the day will do you good, replenish your energy and give you vigor. 6. Allow yourself to relax. Sometimes it's very difficult. But the body needs rest in order to regain strength and energy. Massage and aromatic baths not only relieve muscle fatigue, but also give energy. 7. Think positively. Our thinking largely determines our condition. Tune in for luck, imagine how you will feel when you achieve your goal. Instead of thinking about the hassles of the task at hand, think about the satisfaction you will have when you complete it.
How to help someone with migraine
Since this type of cephalgia is not a symptom of the disease, it is necessary to eliminate the provoking triggers. To do this you need:
- normalize nutrition;
- avoid skipping meals;
- get enough sleep;
- reduce mental stress;
- engage in moderate physical activity;
- relieve stress.
If you don't know exactly what causes a headache, it can be helpful to keep a diary and write down what preceded the next attack. But it is not recommended to carry out drug therapy on your own. Headache attacks may conceal more serious pathologies that require special treatment. It can be:
- malignant neoplasms of the nervous system;
- transient ischemic attack;
- ischemic cerebral stroke;
- subarachnoid hemorrhage;
- dissection of the carotid or vertebral artery;
- cerebral vasculitis.
For the treatment of migraine, medications are selected depending on the intensity of the attack. For mild forms, non-steroidal painkillers can be used. Evidence of effectiveness is available for the following medicines:
- Aspirin tablets;
- Paracetamol in tablets or suppositories;
- Ibuprofen tablets;
- Diclofenac tablets or injections.
Sometimes, for greater effectiveness, a combination of different types of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is prescribed: Brustan, Trigan, Panoxen. It is effective to add caffeine to the therapy regimen, as in the tablets Solpadeine Fast, Askofen, Citramon.
If painkillers are ineffective, triptans are included in the treatment regimen. This is a class of substances that are effective in 75% of patients with headaches. They are marketed under the names Sumatriptan and Sumamigren. These drugs have few side effects, but can cause myocardial ischemia in patients with diseases of the cardiovascular system. For those for whom triptans are not contraindicated, the effect can be enhanced with naproxen.
For those for whom triptans are contraindicated, metoclopramide is prescribed. It helps relieve headache attacks and is often used as an emergency remedy. Also in development are new generation drugs that are agonists of serotonin receptors or belong to the group of monoclonal antibodies that block an excess of a certain neurotransmitter.
In children, the only approved drugs are ibuprofen or paracetamol. In adolescence, it is allowed to use their combination Ibuklin Junior.
Migraine prevention
To reduce the likelihood of headache recurrence, lifestyle changes are necessary. If a connection is made with certain trigger factors, it is recommended to avoid them in everyday life. Patients who experience attacks more than 2 times a week are prescribed drug prophylaxis. Topiromat tablets can be used for this; Metoprolol. Magnesium supplements improve the condition of the nervous system.
Physical therapy can help prevent migraines. To do this, work with a psychotherapist is prescribed, and methods of cognitive and behavioral therapy are used. Additionally, massage, acupuncture, physiotherapy and other methods of prevention are used.
Budik Alexander Mikhailovich, neurologist, CMN, chief physician of medical offices 36.6
THERE ARE CONTRAINDICATIONS, BEFORE USE YOU MUST CONSULT WITH A SPECIALIST
Headache in the back of the head with problems with the cervical spine. Treatment
A common cause of cephalgia is osteochondrosis in the cervical spine. The chronic disease is associated with deformation and thinning of the intervertebral cartilage. Provoking factors: neck injuries, vertebral displacements, physiological loss of elasticity with age, excessive physical activity, excess weight, inactivity.
At first the pain is localized in the neck, but then spreads to the back of the head. This is due to compression of the nerves and vessels carrying blood to the brain. At the first signs of the disease, you should visit a neurologist for diagnosis and recommendations. In the early stages, therapeutic massage, physical therapy, and manual therapy help.
Migraine symptoms
Migraines can go through several stages. The prodromal phase occurs in every fourth case. A few hours before this, a disturbance in well-being appears. The person becomes lethargic, irritable, sensitive to sounds and smells. Less commonly, unexplained euphoria develops and hyperactivity appears.
The aura phase (noted in 20% of cases) is expressed in the occurrence of additional symptoms:
- visual impairment;
- the appearance of blind or flickering areas in the field of view;
- tingling in fingertips;
- numbness of part of the face;
- confusion of speech.
Neurological disorders may be more pronounced and resemble an ischemic attack. In this case, sensitivity is impaired, a shaky gait appears, and coordination of movements suffers. Less commonly, confusion, stupor, or disruption of the coordination of movement of body parts appears, which indicates involvement of the brain stem in the process.
The headache itself is pulsating and concentrated on one side. The frontotemporal region is most often affected. But the second half of the head may also be involved. The pain increases gradually, intensifies with physical activity, and weakens at rest. It can last from several hours to three days.
Phono- and photophobia is often associated; loud sounds and bright lights intensify headaches. Therefore, they prefer to be in a dark room in complete silence during an attack. Painful sensations can spread to other parts of the body. Migraines may be accompanied by pain in the neck or scalp.
Cephalgia is often accompanied by nausea, frequent urination, and sweating. Children experience digestive disorders. In older people, the number of accompanying symptoms decreases sharply or disappears completely.
After the attack ends, additional time is required to improve well-being. Many people continue to feel tired, fatigued, and have trouble thinking for several days. Some patients who have suffered a severe attack describe their subsequent state as feeling like a hangover. Disturbances in the functioning of the digestive tract and emotional disorders may persist. Sometimes low mood resembles depression.
Less commonly, after a migraine there is a surge of strength and a feeling of euphoria. How you feel may change with each attack.
Severe headaches in the back of the head due to drug addiction. Treatment
Often, patients with the development of cephalgia are limited to taking painkillers purchased independently, without consulting a doctor. Analgesics are taken unsystematically, often several times a day for weeks and months. Often a person exceeds the daily dosage of the medicine recommended by the manufacturer. The result is a paradoxical reaction. The headache disappears under the influence of the pill, but returns with renewed vigor immediately after its effect ends. A vicious circle is formed, which can only be broken by an experienced neurologist; sometimes the help of a psychotherapist is required.
Tension headaches in the back of the head. Causes and treatment
This is the most common type of cephalalgia. The reason is being in an uncomfortable position for a long time, in which the neck muscles are overstrained. The problem is for office employees who work at computers and are forced to sit with their heads bent or stretched forward. In this position, the neck muscles get tired, the blood supply to the brain is disrupted, primarily to the back of the head. The pain is low-intensity and can be easily relieved by taking painkillers. However, it gradually bothers me longer and more often. To get rid of it, you need to change your position more often, do exercises with turns and tilts of your head.