- What does upper and lower pressure show?
- What can lead to a decrease in lower pressure?
- Types of arterial hypotension
- Causes of low lower pressure
- Mechanisms of reduction in systolic and diastolic pressure
- Symptoms
- Diagnostic procedures
- Treatment methods
The state of low blood pressure is called arterial hypotension. It occurs if the readings fall below 100/60 mmHg. In some patients, upper and lower pressure (systolic and diastolic) decreases. Sometimes a situation arises when the upper indicator is normal, and the lower indicator falls below normal. This is regarded as isolated arterial hypotension and requires the attention of specialists.
What does upper and lower pressure show?
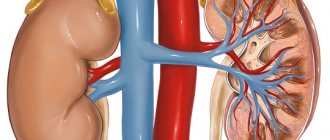
The upper pressure is called systolic. It refers to the force with which blood is pushed out of the heart and moves through the vessels, saturating organs and tissues with oxygen. Diastolic - lower pressure, indicates the pressure of blood on the walls of blood vessels at the moment between heartbeats.
As a rule, as people age, they experience an increase in upper blood pressure. Elevated lower levels are more common in patients under 50 years of age and then begin to decline. Problems with diastolic pressure begin due to deterioration in the elasticity of blood vessels. The capillaries narrow, become stiffer, and this leads to excess blood pressure on their walls. This phenomenon is observed even at rest.
Basic principles of nutrition
To maintain good health, hypertensive patients should pay special attention to their diet. Remember, the patient’s health depends 80% on compliance with the doctor’s instructions and diet therapy.
Nutrition rules for hypertension:
- Limit your daily salt intake. Considering that NaCl increases fluid retention in the body, consumption of large doses of salt is fraught with swelling of the tissues surrounding the capillaries. At the same time, due to increased pressure on the arteries, blood release from the heart cavities increases (the beginning of the development of hypertension). However, the product cannot be completely excluded from the daily menu of hypertensive patients (due to the possible accumulation of nitrogenous compounds in the blood plasma). The optimal portion of salt is 4–5 grams per day. To improve the taste of food, you can use spices (basil, dill, garlic, parsley, onion), cranberry and lemon juice.
- Sharply limit animal fats (saturated) in the menu. The most common cause of high blood pressure is blockage of blood vessels with “bad” cholesterol. To improve capillary permeability, it is extremely important to avoid foods that worsen lipid metabolism. Namely: offal, sausages, fried or smoked lard, processed cheese, fatty meats.
- Enrich your diet with foods containing potassium and magnesium. Arterial hypertension, in 70% of cases, is accompanied by massive edema, circulatory failure, and cholesterol metabolism disorders. To minimize these problems, potassium and magnesium are included in the patient’s daily diet. These microelements improve myocardial function (including increasing its endurance), accelerate the removal of excess fluid from tissues, have a relaxing effect on the arteries, reducing spasm of smooth muscles, and prevent the accumulation of atherosclerotic plaques on the walls of capillaries.
Natural sources of potassium are dried apricots, bananas, prunes, potatoes (baked), melon, watermelon, raisins, pumpkin, rose hips (fruits), avocado.
Magnesium is present in large quantities in bran, cereals (oatmeal, barley, buckwheat, wheat), leafy greens (parsley, lettuce), vegetables (carrots, beets), nuts (almonds, hazelnuts, walnuts).
- Eliminate alcohol, nicotine, and caffeine-containing drinks from your diet. When taking stimulants, most hypertensive patients experience increased heart rate and some parts of the brain are overexcited. Due to the increased load on the cardiovascular system, blood pressure readings “grow” upward.
- Replace simple carbohydrates with complex ones. Saccharides are the main suppliers of energy to the human body. When consuming simple carbohydrates (sugar, confectionery, jam), a sharp increase in blood glucose levels occurs, which leads to the release of large doses of insulin. As a result, its excess is transformed into adipose tissue (since the monosaccharides in the modern human diet are 4 times higher than normal). In addition, excessive intake of monostructures is fraught with the development of metabolic syndrome, which, in 90% of cases, is accompanied by arterial hypertension.
Complex saccharides (as opposed to simple ones) are absorbed more slowly, without causing metabolic disorders and sudden increases in blood glucose. The best sources of high molecular weight carbohydrates are whole grain bread, cereals, berries, herbs, vegetables, and fruits.
- Use gentle cooking methods. The best options for heat treatment of food are baking, stewing, steaming, and boiling. Avoid frying food, as heating fat releases large amounts of carcinogens and “bad” fats.
- Follow a fractional diet. The optimal frequency of meals is 5 – 6 times a day.
- Maintain the ratio of the main components of food. The daily diet of a hypertensive patient should include: 15% proteins (90–100 grams), 30% fats (80–85 grams), 55–60% complex carbohydrates (350–400 grams).
- Maintain drinking regime. Among hypertensive people, there is an opinion that you need to consume less water, since it increases blood pressure. This is a dangerous misconception. In fact, with a lack of fluid in the body, blood viscosity increases, vascular turgor decreases, and the concentration of low-density lipoproteins increases.
The daily portion of water (in addition to drinks) is calculated based on the ratio of 35 - 50 milliliters per kilogram of body weight.
Interestingly, each cup of coffee drunk (volume 150 milliliters) removes 4 equal portions of liquid (600 milliliters) from the body. The body, trying to retain such a valuable resource, creates edema, as a result of which blood pressure rises.
In case of hypertension accompanied by obesity, the energy value of the daily menu is reduced to 1000–1500 kilocalories (by reducing the daily dose of carbohydrates and increasing the daily portion of proteins and healthy fats).
Strict low-calorie diets and fasting with high blood pressure are contraindicated. Overweight hypertensive patients are allowed to have vegetarian fasting days 2 times a week.
What can lead to a decrease in lower pressure?
Arterial hypotension can act as an independent disease (primary form) or one of many symptoms (secondary form). According to statistics, low upper and/or lower blood pressure is more common in women than in men. This phenomenon can also occur in adolescents.
In older people, lower blood pressure decreases due to decreased vascular tone. The main culprit of the problem is atherosclerosis. Secondary hypotension can occur against the background of neurological and cardiac diseases, and hormonal disorders.
Products that lower blood pressure
The basis of a hypertensive person’s diet should be products that improve lipid metabolism, reduce cholesterol levels in the blood, increase the strength of blood vessels, accelerate the removal of excess fluid from tissues, eliminate capillary spasms, and improve the functioning of the heart muscle. When drawing up a daily nutrition plan, it is better to give preference to foods that include vitamins B4, , , , , , macroelements (potassium, magnesium, iodine, selenium), and polyunsaturated fats (omega-3).
List of products that lower blood pressure:
- Unsalted seafood (fish, oysters, scallops, seaweed). They contain a large amount of polyunsaturated fats (omega-3, omega-6), amino acids (arginine, tryptophan, lysine, threonine, tyrosine), micro- and macroelements (selenium, iodine, zinc, phosphorus, magnesium, potassium). Thanks to its rich ingredient composition, seafood reduces the level of harmful cholesterol, regulates the tone of blood vessels, improves the functioning of the heart muscle, and normalizes blood viscosity.
- Low-fat fermented milk products (whey, cottage cheese, cheese, kefir, yogurt, fermented baked milk). Supplies easily digestible calcium to the body. This nutrient is extremely important for the cardiovascular system, as it reduces the permeability of the capillary wall, participates in blood clotting mechanisms, and stimulates the regenerative potential of the myocardium.
- Vegetables (jerusalem artichoke, beets, potatoes, zucchini, pumpkin, cabbage, avocado, eggplant). These are natural sources of dietary fiber that have an anti-sclerotic and detoxifying effect on the human body.
- Leafy greens (parsley, celery, basil, cilantro,
- Fruits, berries, dried fruits (lemon, cranberries, rose hips, viburnum, black currants, grapes, apples, oranges, grapefruit, dried apricots, prunes). These products contain natural “strengtheners” of cell membranes (rutin, vitamin C, quercetin), which prevent capillary permeability when pressure increases. In addition, fruits and berries are rich in powerful antioxidants (polyphenols), which prevent the deposition of cholesterol on the arterial wall, and also enhance the production of nitric oxide, which “creates” a vasodilating effect.
- Unrefined vegetable oils (olive, cedar, flaxseed, camelina). These are natural sources of omega-3 fats that reduce the concentration of exogenous deposits in blood vessels, reduce the fragility of the capillary wall, and prevent the development of inflammation in the heart muscle.
- Whole grain products (rye bread, bran, green buckwheat, brown rice, unpolished millet, flattened oats, coarse wheat pasta). An essential food for overweight hypertensive patients, as it contains “slow” carbohydrates that prevent the rapid transformation of glucose into fat.
Along with this, cereals are a source of dietary fiber and protein structures that accelerate the elimination of cholesterol metabolism products and stimulate intestinal motility. With regular consumption of whole grain foods, the rheological parameters of the blood improve, the load on the kidneys and liver decreases, and the permeability of the capillary bed increases.
- Legumes (lentils, soybeans, beans). Champions among plants in terms of easily digestible protein content. With regular consumption of legume products, the distensibility of the arterial wall increases, the risk of developing myocardial hypertrophy decreases, and the concentration of low-density lipoproteins decreases.
- Herbal teas. A rise in blood pressure, in 70% of cases, is accompanied by neurological disorders (insomnia, palpitations, headaches, anxiety). To reduce psycho-emotional excitability in the diet of a hypertensive patient, it is important to include decoctions of sedative herbs: valerian, lemon balm, mint, chamomile, motherwort, hops, hawthorn, calendula, peony, oregano.
Remember, for moderate to severe hypertension, along with healthy food, it is important to follow your doctor's instructions and take medications regularly.
Types of arterial hypotension
There are three types of arterial hypotension:
- physiological;
- pathological;
- symptomatic.
Low blood pressure as a physiological norm may be a congenital feature characteristic of a particular person due to his constitutional type. A similar situation is observed among professional athletes, residents of high mountain areas and tropical latitudes. Thanks to the decrease in pressure, the body adapts to physical activity and climate conditions. In this case we are talking about a compensatory function.
The pathological form of the disease is of two types: orthostatic and neurocirculatory. Orthostatic hypotension occurs when there is a change in body position when a person gets up after resting or sleeping. The neurocirculatory form is associated with disruption of the autonomic nervous system. The patient may periodically experience low blood pressure or have hypotension, in which diastolic pressure is chronically low.
Symptomatic hypotension is secondary. Its causes are disruption of the functioning of various organs and systems, intoxication.
Preventive measures
Signs of primary hypotension are easily eliminated, so there is no need to panic if your blood pressure drops. It is important to know how to increase blood pressure when it drops sharply and follow the rules of prevention, which boil down to the following:
- do exercises in the morning;
- spend more time in the fresh air;
- take vitamins;
- ensure yourself healthy sleep;
- eat rationally;
- drink enough liquid, especially in the hot season;
- try not to be nervous;
- control your weight;
- do acupressure.
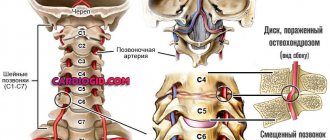
Causes of low lower pressure
According to statistics, the main cause of primary hypotension is neurocirculatory dystonia (NCD). It is otherwise called heart neurosis. With neurocirculatory dystonia, various disorders of autonomic regulation are observed, and this condition is not associated with damage to the endocrine or nervous systems.
NCD and the resulting decrease in diastolic pressure are most often observed in women during puberty and at the onset of menopause, with impaired ovarian function. In young people and middle-aged patients, hypotension occurs against the background of chronic fatigue, stress, psycho-emotional and physical overload. The high-risk group includes people with alcohol and tobacco addiction, patients who have recently experienced psychological trauma, and who are depressed.
Secondary arterial hypotension can be acute or chronic. Low diastolic pressure is encountered by patients with stomach ulcers, diabetes, low thyroid function, osteochondrosis, arrhythmia, heart failure, and chronic infectious processes. In people with such diseases, blood pressure may be constantly low, but due to the body's ability to adapt, the disease does not manifest itself with pronounced symptoms.
A sharp drop in upper and lower blood pressure occurs with significant blood loss, dehydration, anaphylactic shock, or poisoning. These conditions are extremely dangerous for health and life, as they lead to serious circulatory disorders.
One of the possible reasons for a decrease in diastolic blood pressure is a lack of vitamins B, C and E in the diet. The body can also respond to a strict diet or an overdose of drugs (adrenergic blockers, anti-hypertension drugs) with arterial hypotension.
Recommendations of Dr. Shishonin
Alexander Yuryevich recommends that every home always have ammonia on hand. After all, this substance reflexively improves blood circulation in the nasal cavity. Ammonia is a fairly strong toxic substance. As a result of its use, a hypertensive reflex appears, that is, the pressure rises so that the kidneys can remove this substance from the body.
In cases where the pressure drops significantly, for example 80/40 mm. rt. Art., A.Yu. Shishonin recommends using Cardiamine. This medicine is good for lowering blood pressure. People of normal build should take no more than 30 drops of this drug. For obese patients, the dose can be increased to 40 drops.
If Cardiamine is used according to the instructions, it will never provoke the development of a hypertensive crisis, that is, it is not a dangerous drug. Doctors often prescribe it to normalize blood pressure.
Note.
Only an experienced specialist can answer why the blood pressure of a hypertensive patient has dropped; his competence includes prescribing treatment.
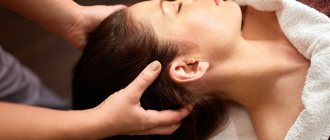
If you have neither Cardiamine nor ammonia at hand, then you can use the knowledge of Eastern healers to increase blood pressure. Thanks to the effect on reflex points, blood pressure is normalized. To carry out this procedure you will not need any medications.
FIRST POINT
It is located on the little finger immediately behind the periungual fold at the root of the nail on the side of the ring finger. With strong compression of the little finger, cardiac activity is activated, which leads to normalization of blood pressure.
SECOND POINT
This is the point of general stimulation. In Eastern medicine it is also called the He-Gu point. It is located in the center of the triangle, which is placed between the thumb and forefinger. This point needs to be stimulated on both sides using your fingers.
THIRD POINT
It is located between the upper lip and nose. You need to stimulate the indicated point for 10 to 15 seconds. With a slight decrease in pressure, 5 seconds is enough.
All of the above methods provide 100% therapeutic results. It should also be noted that there are never any failures when working on these points.
Mechanisms of reduction in systolic and diastolic pressure
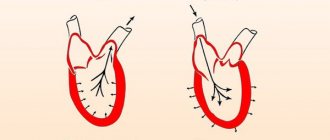
A decrease in blood pressure is caused by one of four possible reasons:
- the stroke and cardiac output decreases;
- the flow of blood to the heart through the veins decreases;
- vascular resistance decreases;
- the volume of circulating blood decreases.
A decrease in cardiac output and stroke is observed in cases of disturbances in myocardial function caused by infarction or myocarditis. The same situation occurs with an overdose of adrenergic blockers.
Vascular tone can decrease with infectious diseases, intoxication, and anaphylactic shock.
A decrease in the volume of circulating blood occurs against the background of bleeding due to trauma to tissues and blood vessels, rupture of the spleen, and ulcerative lesions of the stomach.
A decrease in venous return of blood to the heart occurs with massive ascites or pleurisy due to blood retention in the smallest vessels.
Bee products against hypertension
To increase the effectiveness of antihypertensive therapy, in conjunction with traditional methods of treatment, bee waste products (apiproducts) are used.
Beneficial features
Propolis (“black wax”)
It has antiseptic, regenerating, antioxidant, hypocholesterolemic, diuretic (light) and anticoagulant (blood thinning) effects on the body. With regular use of propolis, lipid metabolism improves, myocardial endurance increases, vascular wall rigidity decreases, platelet aggregation decreases, and pain in the heart region decreases.
For people suffering from the first stage of hypertension, it is advisable to use pure propolis (under the tongue) or a phytocomposition with lingonberry juice (20 drops of 30% “black wax” tincture per 50 milliliters of nectar). For moderate and severe hypertension, the product is taken in the form of an aqueous solution as an addition to the main treatment (35 drops of 30% alcohol extract per 200 milliliters of liquid).
In addition, propolis-based ointment has an excellent hypotensive effect. To create a healing mixture you will need: 5 grams of “black wax” (crushed), 15 milliliters of honey, 15 grams of butter. These ingredients are mixed and then heated to 40 degrees in a “water bath”. The cooled mixture is applied to the feet, after which cotton socks are put on.
Royal jelly
A powerful metabolic agent containing high concentrations of potassium and magnesium. Royal jelly improves myocardial nutrition, stabilizes heart rate, reduces psycho-emotional excitability, eliminates vascular spasm, strengthens capillary walls, stimulates hemoglobin synthesis, and removes excess fluid from the body.
At the first stage of the disease, bee milk is used mainly fresh (20 - 30 milligrams under the tongue). Before using the product, the oral cavity is thoroughly cleansed with vegetable oil.
At higher blood pressure levels (grade 2 and 3), royal jelly is used in combination with antihypertensive herbs (valerian, mint, horsetail, cucumber, motherwort, hop cones, sweet clover). To prepare the composition, the dry ingredients are mixed in equal volumes. After this, 30 grams of the mixture is poured with 500 milliliters of hot water. Herbal tea is consumed three times a day, 100 milliliters (40 minutes before meals). After taking the decoction, dissolve 3 milliliters of a mixture of honey and royal jelly (proportion 1:100).
Wax moth extract
Bee parasite larvae (moths) contain a unique digestive enzyme (cerase) that dissolves low-density lipoproteins. As a result, the concentration of endogenous deposits on the walls of the arteries decreases, the vascular lumen increases, and blood lipid parameters are normalized.
Bee venom
An effective remedy for “hypertension”, used in the form of “bee stings”. Under their influence, arterial spasms are eliminated, the frequency of nerve impulses is normalized, the work of the heart muscle is stabilized, and the peripheral vessels of the kidneys are relaxed.
Bee venom is an excellent remedy for relieving hypertensive crises (in the first stages of the disease).
Remember, this method of reducing pressure can only be used under the supervision of a doctor (to avoid an allergic reaction). To increase the effectiveness of therapy, the “healing” poison is combined with other apiproducts: propolis, honey, beebread, royal jelly.
Perga (pollen)
Includes a huge amount of nutrients (vitamins, salts, organic acids, proteins, fats, enzymes) necessary for hypertensive patients to replenish wasted resources (especially after diuretic therapy). In addition, beebread normalizes the tone of the vascular bed, strengthens the capillary wall, promotes blood thinning, inhibits the oxidation of “good” lipoproteins, and reduces the permeability of veins and arteries (due to the high content of rutin).
To prevent hypertensive crises, take 5–15 grams of bee pollen per day (start with 1 gram).
Honey
A natural source of easily digestible carbohydrates (glucose, fructose, oligoses), enzymes (amylases, lipases, proteases, invertases), amino acids (lysine, isoleucine, phenylalanine, arginine, tyrosine), micro- and macroelements (potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, sulfur, calcium ), vitamins (, , B6).
Honey, thanks to its rich ingredient composition, strengthens the heart muscle, “calms” the nervous system, increases the elasticity of the vascular wall, improves cholesterol metabolism, eliminates anxiety, stabilizes heart rate, and relieves headaches. This product is used to treat the “mild” stage of hypertension.
For preventive purposes, to strengthen the heart muscle, it is advisable to use a honey-rosehip mixture. To do this, 15 grams of crushed berries are poured with 400 milliliters of hot water (80 degrees) and left in a thermos for 7 - 8 hours. Then the resulting extract is filtered and combined with 15 milliliters of flower honey. The composition is taken 100 milliliters three times a day. Interestingly, chestnut and buckwheat honey have the most pronounced hypotensive effect.
In addition, apiproducts are used for the prevention and treatment of coronary heart disease, myocardial dystrophy, vascular atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, non-rheumatic myocarditis,
Symptoms
With a physiological decrease in lower pressure, patients do not experience a deterioration in their well-being. If the problem is caused by pathology, then oxygen starvation gradually develops. It is characterized by the following symptoms:
- weakness and dizziness;
- colored spots before the eyes;
- pallor;
- fainting state.
Patients with chronic arterial hypotension constantly feel fatigue, drowsiness, and a desire to rest. A person with low blood pressure experiences increased sweating and may experience headaches. Low blood pressure makes it difficult to concentrate on work or study and makes a person emotionally unstable. Women with chronic hypotension may experience menstrual irregularities, and men have reduced potency.
In severe forms of arterial hypotension, patients experience vegetative crises. They are accompanied by a decrease in temperature, sweating, difficulty breathing, chest pain, nausea and vomiting, slow pulse, and loss of consciousness.
First aid
Sometimes a decrease in diastolic pressure can take a person by surprise not only at home, but also at work or in transport. This often happens in hypotensive people in the summer, during the heat. Therefore, you should know what to do in this case:
- Lie in a horizontal position. There is no need to put a pillow under your head, you need to put it under your feet - they should be slightly above the level of your heart. This will provide additional blood flow to the brain and supply it with oxygen.
- If it is not possible to lie down, for example, a sharp decrease in pressure caught you in transport, you need to sit down and bend over, lowering your head below your knees.
- Open a window or vent to let in fresh air.
- Remove tight clothing or at least unbutton it.
- Drink a cup of strong sweet tea, to which you can add something tonic (tincture of ginseng, eleutherococcus). Remember that coffee and caffeinated drinks increase tachycardia, which can adversely affect your well-being in this case.
- Measure your blood pressure every fifteen minutes. If it remains low for half an hour, despite all the measures taken, you should call an ambulance. In addition, you should immediately seek medical help in cases where the acute occurrence of hypotension is accompanied by the appearance of other serious symptoms: for example, pain in the heart, impaired consciousness, weakness in half the body.
Diagnostic procedures
To normalize blood pressure, it is important to identify the reasons for its decrease. The approach to diagnosing arterial hypotension is complex. First of all, the doctor needs to assess the blood pressure level. Daily monitoring is best suited for these purposes. The procedure helps to identify how pressure readings change during the day. A technique for measuring blood pressure three times with an interval of 3-5 minutes is also used.
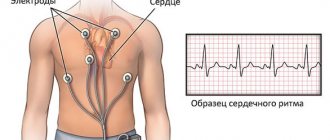
To choose treatment, you need to determine whether a decrease in lower pressure is an independent disease or a symptom of another disease. The patient is prescribed laboratory tests for hormones, electrolytes, glucose and other indicators. Among the hardware methods for diagnosis, electroencephalography, ECG, and orthostatic test are used.
A person with chronic arterial hypotension needs to consult a neurologist, cardiologist, or endocrinologist.