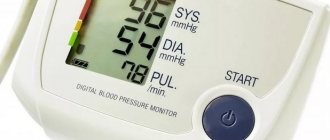
Blood pressure (BP) is an integral indicator of systemic blood flow. It includes two main values: experts call them systolic and diastolic pressure, and common people talk about upper and lower, respectively. The presence of a tonometer in almost every home allows you to monitor blood pressure levels at any time: morning and evening, at night, after meals, physical activity, etc.
Most patients roughly understand what numbers indicate increased or decreased indicators, especially if they change in direct proportion to each other. What to do if non-standard values appear on the tonometer and how to decipher them? This article will focus on just such a case – a pressure of 140 over 70. What this blood pressure level means, whether it is normal and whether correction of values is necessary is discussed below.
About pressure and its norm
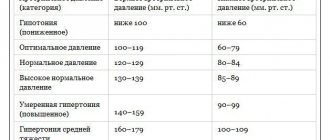
The first number of blood pressure is called the systolic indicator. This is the maximum value of blood pressure in the chambers of the heart and arteries at the height of contraction of the heart muscle. The figure has a direct relationship with the systolic volume of the heart, the contractile function of the myocardium, the pulse rate, the elasticity of the vascular walls and the volume of circulating blood, as well as the viscosity of the latter. The norm is not lower than 100 mm Hg. Art., not higher than 139 mm Hg. Art. The average optimal value is 120 mmHg. Art.
Diastolic indicator is the minimum value of blood pressure in the arteries and chambers of the heart at the end of the period of myocardial relaxation. Depends on heart rate and the degree of resistance to blood flow in the periphery. The norm is not lower than 60 mm Hg. Art., not higher than 90 mm Hg. Art. Optimal – 70–80 mmHg. Art.
There is another important indicator that not all patients know about: pulse pressure. Its significance also deserves detailed consideration. Pulse blood pressure is the result of the direct interaction of factors of the arterial system and stroke volume of the heart. The indicator is the functional equivalent of the pulse volume of blood, which enters the vessel during myocardial contraction and leaves it during the period of relaxation of the heart muscle.
The level of pulse pressure depends on the contractility of the heart, the magnitude of the reflection wave, the degree of distensibility and elasticity of the arteries. Calculation of the indicator = systolic blood pressure – diastolic blood pressure. Normal values are considered to be between 35 and 50 mmHg. Art. Pulse pressure control should occur dynamically. Why is that?
When measuring pressure, the upper and lower numbers on the tonometer correspond to different cardiac cycles, which means that one systolic (or diastolic) indicator may correspond to different values of pulse blood pressure. To characterize the patient’s hemodynamic state, it is necessary to obtain the relationship between all three indicators over a certain period of time. Only qualified specialists do this.
Pressure analysis 140 to 70:
- 140 is the upper limit, which can be a symptom of mild hypertension or be a normal “working” indicator for an elderly person;
- 70 is the absolute norm, but in the case of high “working” blood pressure in combination with poor health, it may be a manifestation of hypotension;
- 140-70=70 – high pulse pressure, which indicates the presence of pulse hypertension.
No ads 1
Reasons for the large difference between upper and lower pressure
An increase in the pulse rate can be physiological and pathological. Physiological pulse hypertension is observed during and after heavy physical exertion. In professional athletes, a similar condition occurs against the background of an increase in stroke volume of the heart. If a person is healthy, the readings on the tonometer stabilize within 10–15 minutes after the end of physical activity: systolic blood pressure decreases slightly, and diastolic blood pressure remains at the same level, that is, both values become normal.
Pathological causes of pulse hypertension can be:
- atherosclerotic vascular lesions;
- hyperfunction of the thyroid gland;
- chills and fever;
- anemia;
- period of bearing a child;
- stressful situations;
- inflammatory heart pathologies, blockades;
- increased intracranial pressure.
Important! Pulse hypertension in combination with a slow heartbeat (bradycardia) is especially dangerous.
Experts say that keeping pulse pressure at high levels for a long time increases the likelihood of developing pre-infarction and pre-stroke conditions, atrial fibrillation, and cerebral hypoxia.
Possible complications
If pulse pressure rises frequently, this may be an indication of the presence of serious pathologies. They can provoke quite serious consequences over time. Here is a list of the most dangerous of them:
- stroke;
- brain abnormalities;
- wear and tear of the heart;
- Alzheimer's disease;
- kidney diseases;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- oxygen starvation;
- myocardial infarction;
- hypertonic disease.
To prevent their occurrence, do not delay diagnosis and treatment. And if episodes of pulse hypertension have already occurred, then you should regularly measure blood pressure for monitoring and prevention purposes.
Increase in systolic rate
Pressure 140 at 70–75 mmHg. Art. may mean that the patient has mild isolated systolic hypertension. This condition is also called borderline arterial hypertension (AH). The reasons for the development of pathology are:
- sedentary lifestyle;
- violation of healthy eating rules (abuse of salty, smoked and fried foods);
- exposure to stress and high mental stress;
- excess weight;
- alcohol abuse and smoking;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland or adrenal glands;
- hereditary predisposition;
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- “aging” of the cardiovascular system.
Experts distinguish several forms of borderline hypertension. The development of pathology during menopause in women is called the menopausal form, in athletes during high loads - sports, in adolescence - youthful. If we are talking about an increase in pressure indicators that are associated with physical factors (for example, vibration or noise), we talk about the professional form of hypertension. And there is also a psychoneurological form that occurs against the background of stressful situations and nervous overstrain.
The listed forms of the pathological condition are not dangerous to human health and can be corrected quite simply. For example, for the psychoneurological type of borderline hypertension, it is recommended to take sedatives; for menopause, hormone therapy is prescribed; athletes are advised to reduce the level of physical activity.
No ads 2
Diagnostics
In order to establish the cause of the pathology, the doctor prescribes daily blood pressure monitoring and other clarifying studies for such patients. The most common:
- general blood and urine analysis;
- lipid profile;
- blood chemistry;
- blood sugar test;
- coagulogram;
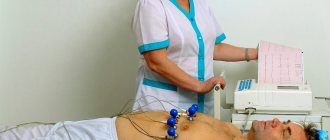
- electrocardiogram;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and renal vessels.
If necessary, the patient is prescribed to undergo consultation with other specialists:
- vascular surgeon;
- endocrinologist;
- neurologist.
Associated symptoms
For a fairly long period of time, maintaining the systolic indicator at a high level can occur without pronounced clinical signs. Many patients do not even know there is a problem. Others, on the contrary, are aware of their condition, but since there are no accompanying symptoms, they believe that they do not need to seek help from specialists.
It is important to conduct a comprehensive examination so that the doctor can determine whether what is happening to the patient is normal, or whether measures need to be taken to lower blood pressure and prevent the development of complications. Against the background of a pressure of 140/70, the following symptoms may occur that require correction:
- severe pain in the back of the head, temples, forehead;
- dizziness;
- attacks of nausea and vomiting;
- discomfort in the heart area;
- dyspnea;
- problems with memory and visual acuity.
Important! The manifestations may intensify due to changing weather conditions.
If a person feels good
Enter your pressure
130
on
90
Search in progress Not found
It should be borne in mind that medical concepts of normality are very relative. So, for example, a person can feel great all his life with a blood pressure of 90 over 60 and this is the norm for him, but as soon as the pressure jumps slightly to a seemingly good reading of 120/80, headaches, nausea and poor health begin.
In other words, if you are hypotensive in life, then you don’t need to be like everyone else. You should lower the pressure or increase it only if this is not the norm in your specific case. That is, if you begin to feel unwell. Thus, a person's blood pressure of 140/60 may well be normal for him.
Relationship with heart rate
What does pressure 140 over 50 mean?
In parallel with blood pressure readings, specialists also evaluate heart rate (pulse). This is also an important sign of the presence or absence of problems with the cardiovascular system. The normal heart rate is between 60 and 90 beats per minute. The numbers below indicate the appearance of bradycardia, the figures above indicate tachycardia.
If we talk about pressure 140/70, it is necessary to analyze pulse indicators in combination, since both tachycardia and bradycardia can be dangerous against the background of increased systolic pressure. The physiological reactions of the body are configured in such a way that an increase in blood pressure is almost always combined with tachycardia. But this happens in relatively healthy people. The appearance of bradycardia against a background of pressure 140/70 in some cases is dangerous for the patient’s health.
Combination with bradycardia
Low heart rate due to high blood pressure has physiological and pathological causes. If the pulse is rhythmic, without interruptions and is at around 55–60 beats, the patient feels well; this may be a physiological reaction of the body. And also the physiological mechanism of development may have a slight bradycardia in chronic hypertensive patients, athletes, people living in low temperatures, as well as those who take medications that slow down the pulse rate.
The pathological causes of this combination are the following conditions:
- heart pathologies (inflammation, heart attack, coronary disease);
- arrhythmia;
- weakness of the sinus node;
- vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- pathologies of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pituitary gland.
The condition is dangerous due to disruption of the blood supply to vital organs. Hypertension is manifested by vasoconstriction, and low contractility of the heart is accompanied by a slowdown in blood flow. The result is that the brain, kidneys, and heart do not receive enough oxygen and other nutrients.
The combination of hypertension with bradycardia is manifested by the following set of complaints: headache, feeling of pressure in the back of the head, temples, nausea and vomiting, pain in the chest. There is a feeling of weakness, dizziness, a feeling of lack of air, a feeling of slow heartbeat. Even loss of consciousness is possible.
No ads 3
Combination with arrhythmia
Arrhythmia is a violation of the rhythm of heart contractions (that is, the pulse can be 70 beats per minute, which is normal, but interruptions in myocardial contractions occur). There is the concept of hypertensive arrhythmia - a pathological condition in which a combination of pulse rhythm disturbances and increased blood pressure occurs.
Arrhythmia of the hypertensive type occurs against the background of bad habits, when metabolic processes are disrupted, due to abdominal obesity. Provoking factors are considered to be excessive consumption of salty foods, low levels of calcium and magnesium in the blood.
Important! An abnormal heart rate due to increased blood pressure can be observed during pregnancy. If you follow the recommendations of specialists after the baby is born, the problem disappears.
What to do if your blood pressure is 140/70
You should not self-medicate. This is the first and most important rule for normalizing indicators, since in the case of pressure 140/70 it is the top number that needs to be adjusted. Taking a number of drugs for hypertension can “lower” both values at the same time, which is fraught with the development of diastolic hypotension. And you also need to learn how to measure blood pressure correctly so that you can control it at home.
Recommendations for patients:
- before recording indicators, you should not smoke, drink alcohol or drink caffeine-containing drinks;
- before measuring, you need to take a comfortable position: your back is leaning against the back of the chair, your hand is at the level of your heart;
- It is prohibited to talk, spin, fidget in the chair, or change the position of the hand during the diagnosis;
- after 5 minutes, measure the indicators on the other hand, following all the above recommendations;
- Each time the obtained values must be recorded on paper so that the attending physician can assess the blood pressure level over time.
The upper pressure figure is not so high that it immediately becomes necessary to prescribe medications. Doctors recommend starting with non-drug methods. First of all, you need to normalize your diet and lifestyle in general. You should avoid smoked and pickled foods, pickles, fried, fatty meats and fish, store-bought sauces, sausages, etc. Preference is given to vegetables and fruits, first courses in vegetable broths, cereals, and legumes.
You need to completely stop smoking, limit your alcohol consumption as much as possible, and try to normalize your body weight. Adequate physical activity will also help reduce weight and normalize blood pressure: walking, light exercise, swimming, water aerobics, cycling. And the following will also benefit:
- taking medicinal baths;
- UHF therapy;
- massages;
- electrosleep;
- electrophoresis, etc.
The progression of hypertension requires the use of medications. In this case, it is recommended to take ACE inhibitors, diuretics, calcium antagonists, and beta blockers. Folk remedies will also be useful: herbal teas that have diuretic and antihypertensive effects.
When combined with bradycardia
The occurrence of an attack requires assistance to the patient. It must be placed on a bed or couch with support (pillow, bolster or blanket) under its back. Apply mustard plasters or a warm heating pad to your feet. It is prohibited to walk and perform active actions of any nature. And you should also not drink alcohol or any drinks containing caffeine. Next, you need to take one of the medications previously prescribed by your doctor. Self-medication is prohibited!
Important! The combination of hypertension with a critical form of bradycardia may be an indication for surgical intervention or installation of a pacemaker.
How to normalize blood pressure at home
People suffering from hypotension and hypertension know very well how to quickly stabilize their condition when their blood pressure rises. Hypertensive patients always keep Corvalol on hand, use lemon balm decoctions, tincture of valerian or hawthorn. For hypotension, take tincture of ginseng, Rhodiola rosea, and other means that stimulate blood circulation and excite the nerve centers. Healthy, adult men and women, to prevent pressure surges, should lead an active lifestyle, follow a diet, diet, and worry less.