Blood pressure (BP) is considered one of the most important indicators of the functioning of the heart and blood vessels. Most changes in the body affect blood pressure levels, which can increase or decrease. There are generally accepted standards for the indicator, which can vary depending on a person’s age, his emotional state, the consumption of a number of products and the use of certain medications.
The average norm is 120 to 80 (units of measurement are millimeters of mercury). If we talk about pressure 110 over 80, such numbers in some people may be a variant of the norm or a temporary physiological condition that does not require correction and does not entail serious consequences. Sometimes such pressure can be a manifestation of the beginning of the development of a pathological condition, especially if it causes a headache, dizziness, increased heart rate, or other unpleasant symptoms. The following questions are discussed about what pressure 110 over 80 means and in what cases help is needed.
Characteristics of indicators and their norm
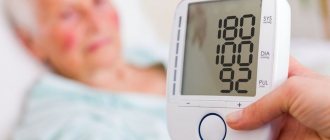
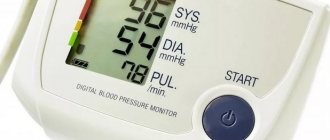
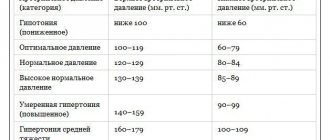
Blood pressure level is 120 at 80 mm Hg. Art. considered normal for an adult. If we look specifically at these numbers, then 120 means systolic pressure (upper). The indicator indicates the pressure with which the blood acts on the vessels when the heart muscle contracts. 80 - lower pressure (diastolic), recorded at the moment of diastole (relaxation of the heart). The difference between the numbers should be from 30 to 40 mm Hg. Art. This indicator is called pulse pressure.
The level of blood pressure in a particular person may depend on the age group he belongs to, his body constitution, gender, weight, climate, emotional and physical state, his level of physical activity, as well as the presence of concomitant pathologies and the state of hormonal balance.
If systolic pressure rises to 140 mm Hg. Art. and higher, experts talk about hypertension, and in the case of a persistent increase - about arterial hypertension. With a stable decrease in upper pressure below 100 mm Hg. Art. We are talking about hypotension. If we talk about the diastolic indicator, then hypertension is diagnosed at numbers above 90 mmHg. Art., and hypotension – below 60 mm Hg. Art. Quite often there is an increase or decrease in only one indicator: either only the upper one, or only the lower one. In addition, the level of blood pressure depends on the force with which myocardial contraction occurs, on the state of the blood coagulation system, the elasticity and tone of blood vessels, as well as the volume of circulating blood.
Diagnostic methods
The reason why low blood pressure decreases can be determined through comprehensive diagnostics. The list of survey activities includes:
- General blood analysis. Biochemical research allows us to identify anemia, which often causes low blood pressure, especially in young women.
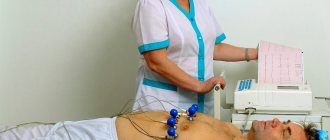
- ECG. An echocardiogram gives a complete picture of the structure of the heart and whether its functioning is normal. In this way, it is possible to determine heart valve disorders and other severe pathologies in a person of any gender and age.
- X-ray. Through X-ray examination, it is possible to identify a number of diseases that can lead to fluctuations in blood pressure, accompanied by an increase or decrease in heart rate.
As a sign of hypotension
Not only the blood pressure level is important, but also the presence of concomitant manifestations that would indicate the development of hypotension, namely:
- headache;
- attacks of nausea;
- dizziness;
- drowsiness;
- emotional breakdown and depression;
- decreased performance;
- rapid pulse (up to 112-115 beats per minute).
Classification
There are several types of arterial hypotension. In the case of long-term decreased levels, we are talking about hypotension. The first type is physiological, that is, one that occurs for a short time and is associated with climate or weather changes. It is not characterized by complications and does not require drug intervention. The second type is pathological. It, in turn, is divided into primary hypotension, which is manifested by a persistent and pronounced decrease in blood pressure, as well as significant accompanying symptoms, and secondary hypotension.
The latter develops against the background of taking a number of medications, with oncological processes, infections, anemia, chronic heart failure, pathologies of the thyroid gland and adrenal glands, as well as diseases of the nervous system. Depending on the duration of the decrease in blood pressure, stable and transient hypotension are distinguished.
There is also a separate classification based on the provoking factors in the development of pathology. This includes orthostatic hypotension, which occurs when getting out of bed. There are also postprandial decreases in blood pressure that occur after food enters the body, tension hypotension (during significant physical exertion), and hypotension during psychoemotional stress. Separately, a drop in blood pressure during night rest and neurogenic fainting are distinguished.
In the elderly
In people of this group, due to aging changes, including those of the heart and blood vessels, the normal level of blood pressure shifts slightly upward, so the pressure is 110 to 80 mHg. Art. for most older people it is a sign of hypotension. This can occur due to long-term use of medications that have a hypotensive effect, due to constant bed rest, for example, which must be observed in case of serious illnesses.
Blood pressure also decreases during bleeding and after surgery. The pathological factors of hypotension in such patients are considered to be a decrease in circulating blood volume, which is accompanied by the development of anemia, neurocirculatory dystonia of the hypotonic type (typical for 40%). Hypotension can occur against the background of damage to the endocrine and other organ systems (every tenth patient).
Important! With persistent hypertension, a decrease in pressure to 110 to 80 mmHg. Art., which is not a consequence of taking medications, is considered a critical condition.
In pregnant women
For pregnant women of the atonic type, such numbers on the tonometer are considered absolutely normal. But, if the woman who is carrying the child is obese, this can also be a symptom of a pathological condition. Hypotension in pregnant women develops against the background of early toxicosis, since frequent vomiting provokes dehydration of the body.
Hypotension during pregnancy naturally manifests itself as vascular disorders, so in the third trimester it can provoke the occurrence of late gestosis, characterized by the appearance of edema, proteinuria, and increased blood pressure (oddly enough). Moreover, in such patients, blood pressure may not exceed normal values, that is, not go beyond 140 to 90 mm Hg. Art., but at the same time it will be one third higher than the initial one, which is considered to be a pathology.
If the pressure readings do not stop at 110 to 80 mm Hg. Art. and will continue to decrease, the risk of threatened miscarriage and fetal growth retardation during intrauterine life increases, since uteroplacental blood flow is reduced. Complications may occur during labor, which are manifested by disruption of the contractile activity of the uterus.
Any decrease in blood pressure (minor or critical) is not an indication for termination of pregnancy
Reasons for a one-time drop in blood pressure in patients
A single decrease in blood pressure rarely indicates complex pathologies of any profile. More often there are natural, physiological factors.
Among them:
- Overwork. As a result of increased stress on the body, cerebral circulation is impaired with inhibition of the regulatory centers of cerebral structures responsible for normal vascular tone. Usually the violations are not critical and are completely reversible.
- A sharp change in body position in space, unreasonably rapid movements. They cause so-called orthostatic hypertension. It is not only temporary, but also lasts no more than a few seconds or minutes. After the attack ends, everything returns to normal. But there may be adverse consequences such as fainting or dizziness and falling.
- Menstrual cycle. Lasts for different periods of time. Throughout the entire cycle, changes in the nature of cerebral circulation are observed. The decrease and increase in pressure is not one-time, but temporary, short in duration, therefore it cannot be classified as a pathology.
- Abuse of antihypertensive pharmaceutical drugs. The problem of patients with hypertension. If the dosage is incorrect, the pressure will begin to jump and become unstable.
- Post-stroke or post-infarction condition. During the rehabilitation period, a decrease in the tonometer reading is acceptable, but it is necessary to constantly monitor blood pressure levels and the general condition of the patient.
This is not a complete list, but the reasons presented are the most common in clinical practice. They are not dangerous and are reversible.
As a sign of hypertension
We are talking about infants and preschool children. What blood pressure is considered normal for them? Here the numbers are in the range of 90-100/60-65 mmHg. Art. That is, 110 by 80 mm Hg. Art. for such patients the indicator is increased. First of all, the specialist should think about “white coat” hypertension, that is, an increase in blood pressure as a reaction to the doctor or the environment in medical institutions. If this factor is excluded, the pediatrician analyzes why the baby’s blood pressure may still rise. Possible causes of hypertension in children:
- hereditary predisposition in combination with other provoking factors;
- obesity;
- violation of metabolic processes;
- a large amount of salt in consumed dishes;
- mental or physical stress;
- sedentary lifestyle.
If hypertension is suspected, parents voice the following complaints of the baby or the results of their own observations of him:
What does pressure 100 over 65 mean?
- sleep disturbance;
- dizziness;
- noise in ears;
- nausea;
- headache;
- nosebleeds;
- pain in the heart area.
Low values in older people
If a pathological condition is diagnosed in an elderly person, the risk of developing disorders of the cardiac and vascular systems increases. As a rule, a decrease in tonometer values in people aged 50 is associated with insufficient elasticity of the arterial walls and the formation of an atherosclerotic process. The development of hypotension is dangerous for an elderly person, since there is a risk of acute vascular and cardiac pathologies. A common complication of hypotension is coronary heart disease.
Low diastolic pressure in old age is manifested by a disorder of urination, due to reverse vascular resistance, which prevents the filtration of urine. Metabolites accumulate in the bloodstream, which leads to the formation of mild renal failure.
Important! A characteristic sign of low blood pressure in an elderly person is orthostatic hypotension, which occurs with a sudden change in body position. It manifests itself as dizziness, lightheadedness, weakness, and visual disturbances.
Recommendations
Next, we consider the recommendations of specialists in the case of hypotension in elderly patients and pregnant women, as well as in cases of hypertension in children under 5 years of age.
For pregnant
If hypotension is physiological in nature and does not manifest itself as a violation of the woman’s condition, then the patient does not need treatment. It is imperative to monitor your blood pressure levels every time you visit an obstetrician-gynecologist or therapist. To normalize blood pressure, pregnant women will benefit from morning exercises, physical therapy exercises, water procedures (showers, douses, contrast foot baths), and massage. It is important to normalize sleep, the duration of which should be at least 9-10 hours a day.
For insomnia, the doctor may prescribe mild sedatives, but not barbiturate-based sleeping pills, as they are dangerous for the child. You should also diversify your diet. It should be rich in protein foods, fruits and vegetables. You can drink tea or coffee with milk only in the morning or afternoon; it is not recommended in the evening so as not to disturb your sleep. Women are also advised to take a closer look at herbal medicine recipes.
Important! The use of any remedies (both traditional medicinal and folk) during pregnancy should be discussed with an obstetrician-gynecologist.
For the elderly
The recommendations are as follows:
- Every day it is necessary to measure readings on both hands and record the data in a personal diary.
- You should get out of bed slowly so as not to provoke the development of orthostatic hypotension.
- It is important to have a hearty breakfast and drink a cup of weak coffee. Your daily diet must include foods rich in vitamins and minerals. If there are no contraindications, you need to drink enough liquid; you should not completely give up salt unless your doctor says otherwise.
- It is necessary to avoid prolonged stay in stuffy rooms, protect yourself from stress and significant physical exertion.
- Make time for walking and light exercise every day.
- If significant symptoms of hypotension appear, seek help from specialists.
Before using folk remedies to normalize blood pressure, it is necessary to exclude the presence of contraindications
For children
It is important to conduct a comprehensive examination to identify the cause of the pathology and select the necessary treatment, trying to return the numbers on the tonometer to normal without medications. What do we have to do? First of all, non-drug methods are used: changing the daily routine, adjusting the child’s menu, normalizing the ratio of rest and physical activity, etc.
Possible complications
Constant identification of 90/50 parameters further increases the risk of stroke and cardiogenic shock as a result of prolonged starvation of brain neurons and heart muscle cells.
Primary hypotension with age can lead to the formation of hypertension due to sharp fluctuations in blood pressure, which leads to a decrease in vascular tone.
During pregnancy, hypotension is a risk factor for premature birth and miscarriage.
No ads 3
What treatment will be required?
You can improve your well-being only by undergoing a course of treatment of the primary pathology that causes hypotension. Therapeutic measures are prescribed by a doctor: a cardiologist, endocrinologist or neurologist.
Typically, pharmaceutical drugs are used:
- Tonic blood vessels (aspirin, Citramon).
- Substitutes for natural hormonal substances (preparations based on thyroid hormones, etc.).
- Sedatives of natural origin (Corvalol, Valerian, Motherwort).
But this is not enough. It is necessary to adjust your lifestyle: stop smoking, alcohol, adhere to a strict regime of physical activity and rest.
It is important to normalize the diet: eat as many fortified foods as possible, as little fatty, fried, smoked foods as possible. It is necessary to optimize the consumption of table salt. It has hypertensive properties (increases blood pressure).
What to do?
When the tonometer shows a critical value of 100/90, you should first make sure it is working properly and measure the pressure again. If the indicators remain the same, you should immediately call an ambulance. While waiting for specialists, you can take the following measures on your own:
- calm down and take a lying position;
- open windows for fresh air;
- normalize breathing;
- do not make sudden movements.
And also read on our website: What does blood pressure 180 to 80 mean - causes, symptoms, treatment
After examining and identifying the causes of hypotension, the doctor will prescribe the necessary treatment. In addition to basic therapy, the patient should adhere to the following recommendations:
- Follow a special diet. Eliminate fried and smoked foods, spicy and salty foods from your diet. Eat more fruits and vegetables.
- Quit alcohol and smoking.
- Drink at least one and a half liters of water per day.
- Limit physical activity.
Traditional medicine offers a number of safe means to strengthen the body and maintain normal blood pressure:
- for the cardiovascular system, beet juice diluted with water is used;
- Kidney diseases with a blood pressure of 100/90 are treated with a decoction of St. John's wort, oregano, sage and motherwort.
- Lingonberry juice with honey will help normalize low blood pressure;
- For pathologies of the thyroid gland, an infusion of valerian root is useful.
However, traditional methods of treatment are permissible only after consultation with a doctor.
Provoking factors
Even a slight decrease in pressure 120 to 55 can be caused by many provoking factors, including:
- Hormonal imbalance. Changes in hormonal levels can cause the lower value to decrease, especially in adolescents during puberty and in women during pregnancy.
- Chronic fatigue syndrome. Diagnosed in individuals prone to hypotension.
- Long-term diets, fasting. A monotonous diet with a minimum amount of vitamins and microelements affects the functioning of internal organs.
- Sleep disorder. Sleeping less than 8 hours provokes a decrease in diastolic readings.
- Oncological diseases. Malignant tumors are the main provocateurs of hypotension.