Release forms
There are two main forms of release of Nifedipine - tablets and gel-emulsion. Most often, patients are prescribed tablets. They contain a high content of active substance. Gel emulsion is an auxiliary preparation.
Tablets weighing 10 g can be packaged in blisters of 10 pieces each. These blisters are packed in cardboard boxes. Also, tablets of 20 or 50 pieces can be placed in plastic jars.
The gel emulsion is stored in a tube weighing 40 g. This medicine in this form of release is used only for the treatment of hemorrhoids.
There is also Nifedipine in the form of a solution for intravenous injection, as well as in the form of boluses that are injected into the coronary vessels.
How it affects the body
The medicine is a calcium antagonist and belongs to the group of slow calcium channel blockers (SCBC). The substance slows down the process of calcium penetration into the muscle cells of the heart, as well as into the cells of vascular muscles. Under the influence of the drug, the myocardium consumes less oxygen. Nifedipine lowers blood pressure and total peripheral vascular resistance, and the ability of the myocardium to contract is also slightly reduced.
Thanks to the medicine, the tone of the smooth muscles located in the vessels slightly decreases, therefore the peripheral and coronary arteries dilate. Due to this, blood flow in the coronary vessels is normalized. Myocardial conductivity is not inhibited. But you need to remember that Nifedipine does not act against arrhythmia and does not normalize heart rhythm.
Pharmacological properties of the drug Nifedipine
Nifedipine is an antagonist of calcium ions, inhibiting their entry into cardiomyocytes and smooth muscle cells of the coronary and peripheral arteries through slow membrane channels. Dilates coronary and peripheral arterial vessels, reduces myocardial oxygen demand, lowers peripheral vascular resistance and blood pressure. It is quickly absorbed in the digestive tract (when used in the form of a solution or tablets with normal release of the active substance). The maximum concentration in blood plasma when taking conventional dosage forms is achieved after 30–60 minutes. When using various retard forms, the maximum concentration of nifedipine in the blood plasma is observed several hours after oral administration, the duration of action is on average 10–12 hours, for some dosage forms - up to 24 hours.
Indications for use
The doctor prescribes Nifedipine for the treatment of many diseases and pathological conditions:
- angina pectoris, including vasospastic;
- hypertension;
- Raynaud's disease;
- hypertension;
- hypertensive crisis.
Nifedipine is necessary for the prevention and relief of angina attacks, as well as for lowering blood pressure.
The doctor may recommend that the patient take the medicine only once a day. This is due to the fact that Nifedipine is active throughout the day.
For hemorrhoids at any stage up to the 4th stage, the doctor can prescribe Nifedipine gel. This gel dilates blood vessels and normalizes blood flow, which means it will help with rectal bleeding.
Examples from medical practice
Example 1
The patient has just begun to develop a hangover syndrome. This is a normal reaction of the body to intoxication! The body is poisoned, it is excited, the body requires pressure to remove brain hypoxia as the end result.
Example 2
The patient completed a course of IV drips to cleanse the body, but for 3 days he still experiences pressure surges. Within 3 days, even after selecting a high-quality treatment for a hangover, we consider this to be the norm, unless of course the numbers rise to the critical 180, 200 mm. rt. Art. This will continue until the nervous system is completely restored, it is this that provokes the release of tonic substances! If the therapy is chosen incorrectly, the person walks around irritable, has insomnia and the prescriptions need to be reconsidered.
Example 3
The man recovered from a hangover, but he still had high blood pressure for a week. In this case, hypertension was already present, this can be confirmed by recording a cardiogram, where we see changes in the heart muscle in the form of hypertrophy of one of the walls, and the person believes that this is due to alcohol. No - hypertension was here initially but had an asymptomatic course. Our doctor immediately warns about this when recording an ECG and advises you to contact a cardiologist.
Instructions for use
The attending physician prescribes an individual dosage to the patient and selects the drug in a suitable release form.
How to take Nifedipine tablets - instructions:
- At the beginning of the course of treatment, the doctor may prescribe 1 tablet (10 mg) 3-4 times a day.
- Then it may be necessary to take 2 tablets (20 mg) 3-4 times a day.
- In severe cases, the dose is increased to 3 tablets (30 mg) 3-4 times a day. This occurs with severe hypertension, as well as with variant angina.
- In case of an acute attack of angina, it is recommended to take 1-2 tablets (10-20 mg) under the tongue.
An acute attack can be stopped with Nifedipine injections. Within 4–8 hours, injections of 5 mg of the drug are given.
For severe spasms of the coronary arteries, Nifedipine boluses of 100–200 mcg are used. They are injected directly into the vessels (intracoronary). To treat coronary stenosis, boluses of 50–100 mcg are taken.
You must take the medicine strictly in accordance with the recommendations and prescriptions of your doctor. You should not self-medicate, otherwise you can harm your health.
Features of treatment in different trimesters
During pregnancy, Nifedipine should only be prescribed by a qualified specialist. Self-medication with the drug can provoke the most severe complications, especially in the early stages of pregnancy. Before using the drug, a woman is prescribed all the necessary tests that will help identify contraindications and prevent the negative effect of the drug on the body of the mother and fetus.
I trimester
Most doctors are of the opinion that Nifedipine is completely contraindicated in the first 12 weeks of pregnancy. It is during this period that the formation of the neural tube and the laying of the child’s organs occurs. The slightest failure can provoke severe consequences, fetal malformations. The risk of miscarriage with all the ensuing consequences for the mother is very high.
Important! In the first weeks of pregnancy, Nifedipine is used only in cases of extreme necessity, when there is a serious threat to the life and health of the mother.
II and III trimester
At this stage, the drug is used if there are certain indications for the mother. These include:
- hypertension;
- angina pectoris;
- conditions accompanied by increased uterine tone;
- risk of premature birth;
- late toxicosis.
Typically, the dose of the drug for a pregnant woman is up to 2 tablets throughout the day. Under no circumstances should you exceed the dose prescribed by your doctor. An overdose leads to the development of severe complications and miscarriage.
Side effects
The medicine may cause some side symptoms. To relieve them, your doctor may prescribe additional medications.
Side effects:
- increased heart rate;
- skin redness;
- feeling of warmth or heat on the skin;
- hypotension;
- slight swelling;
- skin rash;
- ventricular tachycardia;
- slow heart rate;
- increased attacks of angina pectoris;
- cardiac arrest, asystole;
- heartburn, nausea, diarrhea;
- swelling of the gums;
- liver dysfunction;
- muscle pain;
- headache;
- sleep disorders;
- tremor of the limbs;
- visual disturbances;
- thrombocytopenia;
- leukopenia;
- renal dysfunction;
- increase in the daily amount of urine excreted;
- sudden enlargement of the breast (gynecomastia).
After an intravenous injection, the patient may feel a burning sensation. After intracoronary administration of the drug, within the first minute the patient’s pulse may sharply increase and blood pressure may drop. These unpleasant sensations disappear after 5–15 minutes.
Contraindications
There are many contraindications that prohibit the use of this drug for some patients:
- collapse;
- severe form of heart failure;
- hypotension, in which systolic (upper) pressure falls below 90 mmHg;
- cardiogenic shock;
- the first 4 weeks after myocardial infarction (acute period);
- aortic stenosis;
- unstable form of angina;
- lactose intolerance, lactase deficiency;
- GGM syndrome - impaired absorption of glucose and galactose;
- increased individual intolerance;
- lactation period;
- pregnancy less than 20 weeks;
- children's age (up to 18 years).
For these diagnoses and conditions, it is necessary to prescribe other medications to the patient. Nifedipine is not suitable for long-term treatment.
Recently, cardiologists conducted a study in which they proved that Nifedipine increases the risk of sudden cardiac arrest, so this medicine must be taken with extreme caution.
Is Nifedipine dangerous during pregnancy?
The question of how negatively Nifedipine affects the fetus is quite controversial. Supporters of one point of view argue that the drug does not pose the slightest danger to the mother and fetus. Proof of this is many years of practice and some medical research. Other sources claim that no research has been conducted on this matter and the effect of the drug on the development of the fetus and the health of the woman during pregnancy can be very negative. Therefore, the use of the medicine during such a delicate period is strictly not recommended.
Information from third sources indicates that studies were nevertheless conducted and their results revealed that Nifedipine has the most negative effect on the fetus. Another point of view is that the medicine is dangerous only in the first stages of pregnancy, but in the second and third trimester the drug does not pose any threat.
It is quite difficult to understand such opposing opinions. Only a specialist can assess the benefits and risks of taking a drug in a particular case. The doctor is obliged to assess the condition of the pregnant woman and child and make a decision individually for each patient.
Carefully
Patients suffering from certain diseases should be extremely attentive to their health. They will have to drink Nifedipine with caution:
- elderly patients;
- hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy;
- severe liver diseases;
- sick sinus syndrome;
- kidney dysfunction;
- mitral valve stenosis;
- chronic heart failure;
- diabetes;
- stenosis of any part of the intestine;
- disturbances in the functioning of cerebral vessels.
Taking the medication in these cases should be strictly under the control and supervision of the attending physician.
Overdose symptoms
You should not take more than 120 mg tablets per day. The maximum dose of intravenous solution is 30 mg.
Signs of overdose:
- a sharp slowdown in heart rate;
- bradyarrhythmia;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- hypotension;
- collapse;
- cardiogenic shock;
- convulsions;
- loss of consciousness;
- hypoxia;
- acidosis;
- slowing of cardiac conduction;
- hyperglycemia;
- coma.
Symptoms appear 3-4 hours after taking the tablets. In case of overdose, the patient's stomach is washed and activated charcoal is administered. He is then given intravenous injections of atropine with calcium gluconate, calcium chloride and norepinephrine to relieve intoxication. Due to proven ineffectiveness, hemodialysis is not performed.
Dangerous consequences
After a certain time, the pressure and pulse will increase as a compensatory mechanism, and if you lower it again, it will be a “swing” (pressure differences over a short period). Such “swings” increase the risk of stroke or heart attack many times more than if the pressure was constant, for example, 150/90.
After the pressure decreases, the patient's behavior changes dramatically. He does not orient himself in time and space, sometimes his limbs become more numb due to impaired blood circulation in the brain due to decreased pressure.
Interaction with other drugs
Blood pressure drops sharply when Nifedipine is taken simultaneously with other antihypertensive drugs, as well as diuretics, diltiazem, and drugs based on phenothiazine and its derivatives.
Attention and memory may be affected when Nifedipine is used with anticholinergic medications.
This medicine should not be combined with beta-blockers, otherwise severe hypotension and even heart failure may occur.
In combination with magnesium salts, the patient experiences severe muscle weakness.
The effective effect against angina pectoris is enhanced when the drug is combined with nitrates.
Due to the intake of digoxin and theophylline, the amount of these substances in the blood increases.
You should not take Nifedipine together with medications containing calcium. These substances have opposite properties, which reduces their effectiveness. Side effects of the drug are enhanced in combination with fluoxetine and vincristine. Also, the effect of Nifedipine is reduced in combination with rifampicin, so these two drugs are incompatible with each other.
The level of nifedipine in the blood decreases if you take the medicine together with phenytoin, phenobarbital or carbamazepine. Conversely, concentrations increase in combination with itraconazole, cimetidine, fluconazole and ranitidine.
The QT interval on the ECG is prolonged when Nifedipine is taken simultaneously with quinidine. This occurs because the amount of quinidine in the blood decreases sharply, and when it is discontinued, it suddenly increases.
Severe hypotension, dizziness and other unpleasant symptoms occur if the patient drinks Nifedipine and drinks containing ethyl alcohol. This drug should not be combined with grapefruit juice.
What to do with high blood pressure and a hangover
We, narcologists, can apply this standard only after we introduce sleeping pills. Only after this we begin symptomatic treatment if necessary, but not earlier.
In most cases, sleeping pills reduce blood pressure as a side effect, and a well-chosen drip composition that will nourish all organs will cause the symptoms to go away on their own.
Magnesium sulfate or hot injection!
At the moment, one of the best drugs that serves to relieve pressure, even in withdrawal syndrome, is Magnesium sulfate. This drug is used because of its positive properties:
- Reduces blood pressure in the proportion as necessary and is not a dose-dependent drug;
- Relieves convulsions, spasms, epileptic condition;
- Protects nerve cells from death;
- Normalizes heart function;
- Dilates blood vessels;
- Narcologists almost always use this drug, even for slightly high blood pressure. Unfortunately, people are often allergic to it.
The article is for informational purposes only! If you want to receive professional medical assistance, please contact us. We also recommend reading other articles on this topic on our website.
special instructions
Nifedipine should be taken only under the strict supervision of doctors. Elderly patients are advised to reduce the dose. The medicine causes withdrawal symptoms, so it is discontinued gradually. It is necessary to discontinue the drug if the patient experiences chest pain.
If a person has stenosis of two coronary vessels, then the medicine cannot be administered intracoronarily into the third.
During the course of treatment it is forbidden to drink alcohol. It is advisable to refrain from working with machinery, driving a car or other types of transport, and also avoid dangerous work that requires great concentration.
Analogs
The following drugs are complete or partial analogues of Nifedipine:
- "Calcigard Retard".
- "Cordaflex".
- "Cordipin Retard."
- "Kordipin HL".
- "Corinfar".
- "Corinfar Retard".
- "Nifecard HL".
- "Phenigidine."
The doctor may prescribe these drugs instead of Nifedipine. They have similar properties.
What does this standard mean?
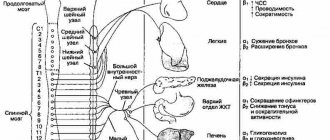
It leads to taking emergency cardiac medications to lower blood pressure (capoten, captopril, nifedipine). They act immediately and relieve pressure as a symptom!
Also, according to the Standard, it is necessary to take diuretics (diuretics)! After drinking alcohol, the water-salt balance is always disturbed, so the bloodstream is dehydrated, even if there is swelling in the legs and face, this liquid is outside the bloodstream, and diuretics will primarily remove fluid from the vascular bed and provoke an increase in blood viscosity - the load will increase sharply on the heart and increases the chance of blood clots.
Taking accumulative drugs for the treatment of hypertension - for example, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, antirelapse inhibitors - they begin to work only after constant use for at least a week - there is no point in drinking them.
With high blood pressure, the pulse is almost always increased, so drugs from the group of B-blockers (metoprolol, atenolol, propranolol, anaprilin) are also used to slow down the heartbeat.
These methods will, of course, lead to a decrease in blood pressure and normalization of the pulse, but despite the normalization of indicators, the patient gets worse! These drugs act for a certain number of hours, and the main criterion for the treatment of alcohol withdrawal is sleeping pills, which were not used, so the nervous system continues to be deficient in nutrients and agitation increases, which will lead to: