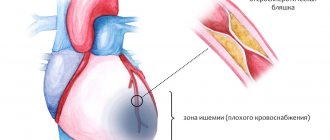
Unfortunately, sudden changes in blood pressure are an unpleasant phenomenon that can first appear in a person at any age. The amount of blood pressure depends on the time of day, fatigue, what a person ate and drank, on his psychological and emotional state, and on weather conditions. And, if the problem of pressure surges has entered the system and become habitual, it is worth sounding the alarm and taking measures to stabilize the pressure.
For a healthy average person, a blood pressure of 120/80 is considered normal. However, for each specific person this figure is quite individual and can fluctuate within certain limits, being considered the norm, if, of course, the person feels cheerful and healthy.
If the pressure constantly fluctuates, this is definitely considered a deviation from the norm. Modern clinical research confirms that even a slight increase in blood pressure, if it occurs regularly, increases the likelihood of cerebral stroke and other serious diseases.
Causes of pressure surges
Probably, more than once, everyone who suffers from hypertension has noticed that their pressure is constantly changing, and at the same time, peculiar “jumps” in pressure occur, that is, it either increases or, on the contrary, decreases.
There are several reasons:
- The first reason is hormonal.
That is, the cerebellum gives a strong signal to the adrenal gland, and it releases a certain enzyme into the blood that causes a sharp jump in blood pressure. To diagnose this, it is advisable to undergo an ultrasound to examine the adrenal glands; - The second reason is psychological or emotional.
If a person is emotional or unbalanced, then this may well affect the stability of blood pressure; - The third reason is physical
. Excessive physical activity, heavy lifting, overexertion during sports; - The fourth reason is atmospheric pressure, as well as the level or strength of magnetic storms.
If a person is very sensitive in this regard, then any jump in atmospheric pressure will have a very adverse effect on his health; - The fifth reason is pharmacology.
Some medications can increase blood pressure; if a person suffers from hypertension, then medications can only be taken after consultation with your doctor. - The sixth reason is lability of the autonomic nervous system
. All our vessels have their own small innervation. Sometimes, the nervous system is overly sensitive than usual, and when excited, these nerve endings can affect vascular tone. With minor disturbances, the pressure can rise excessively high and also decrease.
Of course, there are plenty of reasons for pressure surges, and if a person has hypertension (and other diseases, including chronic ones), it is advisable to be attentive to everything. After all, hypertension is not a battle, but a whole war that will accompany all life, and a person’s goal is not to lose in it!
Possible consequences and complications
Dissonance between pulse and blood pressure is dangerous for the functional state of the body, since with a rapid heartbeat, hypoxia of tissues and organs occurs, which entails the development of irreversible changes in them.
With a simultaneous increase in diagnostic indicators, the following very dangerous conditions may occur:
- disorder of the digestive tract;
- ischemic brain damage;
- necrosis of the cardiomyocyte area;
- arrhythmic shock.
A prolonged and constant increase in heart rate can significantly reduce the performance of a hypertensive patient. The patient experiences a feeling of irritability and complains of causeless weakness and malaise.
Under conditions of excessive load, the myocardium requires more oxygen, which leads to its increased waste. In vessels of small diameter, a deficiency of nutrients occurs, provoking the formation of cardiomyopathy.
Is your blood pressure going up?
To make a diagnosis and provide the necessary assistance, a neurologist will listen to your complaints, conduct an examination and a comprehensive neurological examination, which includes:
- collection of anamnesis of the disease (conversation);
- special neurological tests;
- reflex diagnostics;
- local palpation examination of the spine and musculoskeletal system.
In addition to the main examination, if necessary, the doctor may prescribe:
- MRI;
- Ultrasound;
- X-ray;
- Lab tests;
- EEG;
What symptoms should you pay close attention to (when to see a doctor)?
Dangerous manifestations are diverse, which signs should be especially wary:
- Intense headache for no apparent reason. Accompanied by a squeezing sensation in the back of the head and parietal region.
- Vertigo. Up to complete loss of orientation in space during acute ischemia of the cerebellum, which is responsible for the vestibular apparatus.
- Vomiting without signs of relief after the process.
- Aching pain behind the sternum, acceleration of the heart rate or, on the contrary, its slowdown.
- Problems with heart rate (lack of a clear pattern of the organ’s beating, randomness in its work).
- Sweating (hyperhidrosis).
- Cognitive impairment (decreased memory, mental activity).
- Facial distortion, inability to control facial muscles.
- “Disobedience” of half the body. Paresis, paralysis.
- Paresthesia, sensation of goosebumps running on the skin.
- Impaired hearing, vision, and smell (focal neurological symptoms).
The appearance of any of these manifestations is grounds for calling an ambulance. Especially if you suspect a stroke or heart attack.
We use treatment methods such as:
- Manual therapy;
- Osteopathy - treatment by the hands of a doctor, a gentle effect on the musculoskeletal system, nervous and vascular systems, internal organs;
- Medical massage;
- Acupuncture - exposure to biologically active points with microneedles;
- Laser reflexology is a painless effect on reflexogenic zones and points;
- Tsubotherapy is a gentle effect on the body’s reflex points;
- Pharmacopuncture - the introduction of medicinal drugs of natural origin to the source of the problem;
- Plasma therapy is the introduction of the patient’s own purified blood into the site of the disease;
- Isometric kinesiotherapy - individual gymnastic techniques/exercises, according to indications, with elements of joint massage;
- Kinesiotherapy using the Exart installation;
- Kinesio taping;
- Ozone therapy - treatment with active oxygen;
- Physiotherapy;
- Physiotherapy with enzyme preparations;
- Therapeutic droppers;
- Hirudotherapy - treatment with leeches;
- Botulinum therapy is treatment with botulinum toxin preparations.
Archives
O. Y. Zharinov National Medical Academy of Postgraduate Education. P. L. Shupika, Department of Cardiology and Functional Diagnostics
Additionally, the circadian fluctuation of arterial pressure (AT) is a seemingly insignificant physiological phenomenon that, in certain situations, can play a role in fatal cardiovascular diseases. It is well known that the incidence of heart attacks, strokes and cardiac death is highest in the early years, when compared with AT. It is also assumed that the independent form of the development of arterial hypertension (AH) may be a stage of additional AT co-occurrence, assessed by the method of non-invasive AT monitoring (DMAT). In our opinion, it is worth considering the methods for assessing circadian levels of AT and their role for the selection of antihypertensive therapy.
METHODS OF ASSESSMENT OF 1st TYPES OF CIRCADIANIAN CHANGES AT
The introduction of the DMAT method into clinical practice has made it possible to record and evaluate changes in blood pressure over a period of time, and subsequently to understand the rich aspects of the development of hypertension and the ways of differential therapy. ii. We were first able to bring to light the “hypertension of the white market” and to understand why in the majority of patients registered under the hour of polyclinic examination, even high levels of AT do not reveal the same typical for AG organ levels. At the same time, in many patients with hypertension, the level of arterial pressure increases both during the day and at night. Often in patients with “mild” hypertension in the daytime, “night” hypertension itself is the primary factor in the cause of severe organ disorders, swelling, hypertrophy of the pulmonary artery. On the other hand, a marked decrease in blood pressure leads to an increased frequency of acute complications of hypertension, including episodes of myocardial infarction and stroke, in the early years itself (from 6 to 12 years of age). By analogy with the well-known method for assessing heart rate variability, we also added the indicator of the stage of additional colivan AT (SD), using standard methods of variation statistics. By reflecting the relief of blood flow to the average level, it can reflect the severity of changes in the bleeding of vital organs and be an independent predictor of the risk of various complications of hypertension. The obligatory component of the diagnostic conclusion in case of active DMAT is also the “additional AT index” - it is expressed in the hundreds of decreases in AT during the passive period of addition (during the hour of sleep) equal to the active period. The norm is 10–20%.
Based on the remaining European recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of hypertension (2003), the level of AT when measured in the doctor’s office is 140/90 mm Hg. Art. approximately corresponds to the average level of AT 125/80 mmHg. Art. The middle level of AT in the active period produces more than the middle level in the passive period. The recommendations of the Ukrainian Association of Cardiologists (2004) state that the average daily blood pressure is <135/80 mmHg. Art., night <120/75 mm Hg. Art. However, between the same levels of AT, different periods of production vary. However, care is required when programming devices for DMAT and interpreting the results.
Studies using a similar DMAT method show the similarity of changes in AT in patients with normal and hypertensive patients (Fig. 1):
- Rhubarb AT is highest after the 10th day of the morning, reaches the peak of the day, and its plateau can last until the 6th day of the evening.
- In most healthy individuals and patients with hypertension, an increase in blood pressure at the hour of awakening (approximately 6 years of age) by 20/15 mm Hg is expected. Art.
- In the late evening, blood pressure level normally decreases by 10–20%, equal to the active period (profile of the “deeper” type, which is optimal); The lowest level of AT is recorded around the 3rd night.
Rice. 1.
A schematic representation of the history of systolic AT over a period of 24 years, especially with normal levels of AT (lower curve) and AG (upper curve). Rectocutnik saw the period of maximum risk of cardiovascular processes, the dotted line shows the “non-deeper” profile (without an adequate night-time decrease in AT).
The nature of the pain in the body depends on the triviality and terms of the active period of pain, the level of physical stress and the evidence of anxiety (for example, with hypertension of the “white market”). In some patients with hypertension, the following features of the AT profile can be observed:
- The number of nightly decreases in blood pressure results from a decrease of 0–10% (profile of the “non-deeper” type, so there is insufficient decrease in blood pressure) or an increase in blood pressure during the passive period (profile of the “night-picker” type, then there is an increase in blood pressure). Nya AT night). These types of AT profile are associated with an increased risk of target organ damage (hypertrophy of the left sac, microalbuminuria) and cardiovascular diseases (hemorrhagic stroke).
- The decrease in AT at night is greater than 20% (profile of the “hyper-deeper” type, meaning an extreme decrease in AT). It is assumed that this type of AT profile may be associated with an increased risk of ischemic stroke.
- Above-world rank advancement of AT (at the same rate as the rate of growth of the achieved level of AT) (Fig. 2). When selecting optimal antihypertensive therapy, one should take into account that an additional AT profile of the “hyper-hyper” type may result in both significant decreases in AT at night and significant elevations in AT in the early years.
Rice. 2.
Graphic depiction of the results of DMAT and changes in heart rate soon (dashed line below) in patient K., 56 r. The abscis axis shows the year of progress, and the ordinate axis shows the levels of AT and heart rate. Additional AT profile of the “deeper” type (additional AT index 15/19 mm Hg), due to persistent 2-3rd stage BP shifts, increased level of systolic BP (SD 17/12 mm Hg) and expression increase in the level of AT in the wounded year. Cream of stagnation of drugs with a persistent and persistent antihypertensive effect (probably, fixed combinations), in which it is necessary to correct the expression of the wound level of the AT level.
There is still no clear idea about the normal indicators of the stage of Kolivan AT stretching to achieve. The recommendations of the Russian Cardiological Scientific and Viral Complex of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation on the basis of a large number of healthy individuals indicate the following reference level of blood pressure level (SD): for systolic blood pressure - 15 mm Hg. Art. in active i 15 mm Hg. Art. - during the passive period, for diastolic AT - approximately 14 and 12 mmHg. Art. When any of the indicated four indicators grow, learn about the supernal stage of AT. In this type, it is especially important to treat antihypertensive measures with a thorough and stable pharmacological action.
In addition to the way of life, the nature of the benefits of AT depends on many factors, such as age, and ethnicity. For example, the recent decrease in AT is less pronounced in summer individuals, men, and black patients. In addition, insufficient reduction in blood pressure in the early years is avoided in case of rich pathological conditions and illnesses, for example, symptomatic hypertension (renovascular hypertension, primary aldosteronism, Cushing’s syndrome, pheochromocytoma), obesity, diabetes, disturbed sleep.
MECHANISMS OF CIRCADIANIAN COLIVAN RIVNYA AT
The main “regulator” of circadian rhythms in the human body is located in the suprachiasmatic nucleus in the anterior part of the hypothalamus, and the most important endocrine “messenger” is the pituitary hormone melatonin. At the same time, due to changes in melatonin levels, the level of additional hemodynamic parameters changes with age. Previous results allow us to assume that the stagnation of exogenous melatonin directly reduces the decrease in AT levels.
More consistent are the data on the importance of the autonomic nervous system, as well as the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, in shaping circadian levels of hemodynamic parameters. Zokrema, the rate of sympathetic impulses and catecholamines advance at the moment of awakening or immediately thereafter, as the activity of the parasympathetic nervous system changes simultaneously and is at its greatest. at night. Changes in the activity of the renin-angiotensin and sympathetic nervous systems occur in parallel. It’s not surprising that the fragments of the awakening of adrenergic receptors in the liver are absorbed by the established renin. At the same time, a modulator of the secretion of various hormonal substances can help change AT. Obviously, the peak of renin activity reaches approximately the 8th year of the morning, angiotensin II and aldosterone - even later. It is also evident that the increase in renin activity is observed during the hour of sleep, reaching maximum levels during the phase of normal sleep. However, the significance of circadian changes in these parameters in the pathogenesis of essential hypertension has not yet been established. Obviously, the early development of hypertension is associated with increased activity of other neurohumoral substances (adrenocorticotropic hormone, cortisol, natriuretic peptides, opioids, endothelins), blood thinning factors i, activation of platelets and suppression of fibrinolysis. These mechanisms may be important specific “targets” for the prevention of cardiovascular complications of hypertension.
ADDITIONAL CONTINUATION FOR THE EFFECT OF ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DISEASES
The existing findings about circadianity and the stage of additional AT activity allow for the development of various approaches to the differential stasis of antihypertensive factors. In addition to the obvious, there is a need for balanced AT during the passive period of extraction and “infusion” of the wound year:
- In addition to the importance of nighttime blood pressure in the development of severe hypertension, it is important to normalize blood pressure levels before bedtime. In patients with additional AT profiles of the “non-deeper” and “night-picker” type, in order to achieve the goal, you need to selectively adjust the AT level at the beginning of the year.
- Another purpose of antihypertensive therapy lies in the prevention of supra-morbid wound displacement of AT. Considering the key power of the optimal antihypertensive drug, it may be possible to preserve the effect of lowering AT, which makes it possible to “harvest” the wound with a one-time wound or evening use of medications. This very aspect of pharmacotherapy of hypertension has become the main leitmotif for the development of many daily long-acting drugs.
- In patients with persistently displaced AT levels (Fig. 3), the required treatment is not lower than the average AT levels, but rather an increase in the optimal AT level profile. Obviously, to achieve this goal, specific “chronotherapeutic” approaches are needed to determine the optimal time for the recognition of antihypertensive functions.
Rice. 3.
Graphic representation of the results of DMAT in patient B., 44 r. Additional AT profile of the “non-deeper” type (additional AT index 9/5 mm Hg), with persistent elevations of the 3rd stage AT and a normal level of systolic AT increase (SD 13/9 mm Hg). These particularities indicate the high prevalence of symptomatic hypertension.
One of the most important characteristics of current antihypertensive agents is the level of preservation of their concentration in the blood and the effect of reducing AT during the dosing period, before taking the intended dose. Actions with a wide variety of short-acting drugs can be saved until the time of administration. However, at the peak concentration of the drug, you can avoid an extreme decrease in the level of AT. In order to assess the extent of the antihypertensive effect and avoid excessive doses of drugs, a standard was developed - the so-called minimum/maximum coefficient (trough/peak, T/P), which is optimally responsible for exceeding 50–60%.
A high T/R coefficient is associated with the use of trivala and a stable antihypertensive drug, which means a shorter response to the crust and the risk of treatment with trivalent treatment of hypertension, compared with short-acting drugs, will ensure effectiveness This effect extends the strength of the drug with a one-time dose and allows you to eliminate “wheeze syndrome” if you accidentally skip a dose. . In addition, an adequate level of T/R indicates a decrease in the number of side effects of antihypertensive disorders and an increase in the compliance of patients before treatment. Drugs with a T/R coefficient of less than 50%, which significantly contribute to the effect of reducing AT (for example, nifedipine and captopril), generally meet the needs of treating hypertensive crises, as well as in case of trival Extensive therapy may help to advance the level of AT. In this case, the bleeding of vital organs often and clearly changes and the lack of therapy can cause the risk to become overweight. In view of the limited potential for saving the effect of reducing AT, the prescribed drugs need to be taken 3 times a day. In our opinion, it is due to the low sensitivity of patients to the trivial treatment of hypertension with one-time dosing.
There is still a lack of monitoring of the effectiveness of antihypertensive treatment based on a comprehensive antihypertensive profile. It appears that all groups of antihypertensive agents are of the first line (diuretics, beta-blockers, calcium antagonists, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, receptor antagonists) in angiotensin II) - drugs that will ensure gentle and stable control of AT for 24 years. However, their stagnation will not always allow you to avoid the wound infection of the AT. Most often, antihypertensive effects with one-time dosing are attributed to the drug. The problem lies in the fact that after 24 years after taking these drugs, the excessive effect of lowering AT remains, so in order to effectively overcome the complications of the wound, it is necessary to achieve the maximum antihypertensive effect of therapy at this time ї. In clinical practice, there are different ways of dealing with the above problem:
- Consider fixed combinations of antihypertensive agents, such as drugs with different effects, to preserve the effect of reducing blood pressure in adequate doses. Typically, such combined drugs contain a diuretic component, which induces a more stable vasodilation, potentiating the effect of drugs from other groups and inducing a safer pharmacological action. In Ukraine, a fixed combination of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or beta-blockers with diuretics is often preferred. It is significant that the inclusion of neurohumoral modulators in antihypertensive therapy regimens is justified based on the mechanisms of circadian AT.
- Do not hesitate to take drugs once at a time and take another drug late in the evening to maintain reliable control of AT after 6–8 years, otherwise it’s too early. For example, if you are suffering from congestion of Enap-HL (10 mg enalapril + 12.5 mg hydrochlorothiazide), you can add a calcium antagonist (amlodipine) or an alpha-blocker (doxazosin) in the evening. This approach is especially indicated for patients with advanced AT profiles of the “non-deeper” or “night-picker” type. It is clear that fixed combinations of antihypertensive agents, which replace a diuretic, are often prescribed in the early stages, often before drinking.
- Increase the dose of the non-diuretic component of the fixed combination. For example, if the drug Enap-HL is given a partial effect of reducing AT, do not completely increase the dose of both components of the combination for the same amount as another Enap-HL tablet in the evening, but increase the dose of enalapril in any way. for Enap 20-HL (20 mg enalapril + 12 .5 mg hydrochlorothiazide). Indications of the approach may be limited in rich patients with stage 2 or 3 hypertension and an optimal additional AT profile. Considering that Enap-HL replaces a therapeutic dose of hydrochlorothiazide (12.5 mg), an increased dose of the diuretic component is not sufficient. In addition, it is unjustified to use a diuretic in the evening, including as a component of a fixed combination.
- Stabilize the forms of medicines that can be taken once a day, using the appropriate vocabulary or using drugs with high T/R ratios. This approach meets the needs of treating most patients with persistent hypertension, but not associated with advanced symptoms of treatment (for example, with telmisartan, which is considered a promising method of treatment). circumventing the wound movement of AT). It is significant that the indications for this approach are not always valid in patients with an additional AT profile of the “hyper-hyper” type, as this may cause an abnormal decrease in the AT level in the last year.
Thus, the nature and level of expression of circadian hypertension levels is the primary factor responsible for the development of hypertension. The DMAT method is an informative tool for clinical assessment of AT changes. Adequate antihypertensive therapy follows the regulation of circadian levels of AT, and can include selective correction of the level of AT during the period of addition.
First aid for an attack of hypertension
A significant increase in blood pressure levels requires urgent medical attention. You should call an ambulance. Before the doctors arrive, you will need to take a horizontal position, calm down and not panic. This will only worsen an already serious condition.
Showers, baths and other dubious methods should be left aside. This is harmful advice that can cost the patient’s life.
Before the ambulance arrives, you should take the prescribed drug (if treatment has already been prescribed) or a medicine based on herbal components, phenobarbital (Corvalol, Valocordin, Motherwort and Valerian, but not in the form of an alcohol tincture: ethanol is the enemy of hypertension).
Capoten, Captopril, vasopressors (dopamine) and other medications should not be taken: it is impossible to calculate the dose yourself, so there is a risk of a sharp drop in blood pressure with the development of a heart attack or stroke.
Upon arrival of the team, the issue of possible transportation to a hospital is decided. Whether to go or not is up to the patient himself. But there is no point in refusing: it is not known what we are talking about. It is better to understand and establish the root cause.
Therapeutic measures
Specific therapy, using drugs of several groups:
- Beta blockers.
- Calcium channel blockers.
- Diuretics.
- ACE inhibitors.
- Vitamin and mineral complexes.
- Food supplements with microelements.
Statins are used to eliminate lipid deposits.
Tonics are not used as they are dangerous and ineffective in the fight against high blood pressure.
Herbal sedatives based on motherwort and valerian, and barbiturates in small dosages are prescribed.
If necessary, surgery is indicated (heart defects, vascular defects, development of malformations, benign and malignant tumors in anatomical structures, aneurysms, cholesterol plaques).
Given the physiological nature of the condition, a change in schedule and lifestyle is indicated. You need to sleep at least 8 hours, avoid exercise, smoking, alcohol, especially psychoactive substances, use drugs in a strictly designated dosage after consultation with a specialized specialist.
Systematicity and complexity are important in treatment.