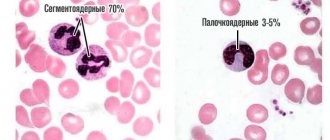
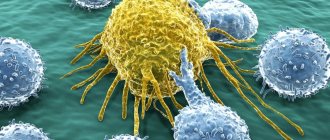
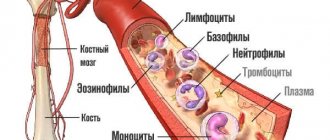
Synonyms: neutrophil granulocytes, NEUT, neutrophil segmented granulocytes, polymorphonuclear neutrophils
There are six types of neutrophils depending on the stage of their maturation. Immature types include myeloblasts, promyelocytes, myelocytes, metamyelocytes and band cells. The final stage of development is segmented neutrophils (mature cells with a formed nucleus, divided into several segments).
Even at the stages of their initial development, neutrophils are able to resist infection, although mature segmented cells cope with this task much more effectively.
In blood tests of people suffering from severe infectious diseases, immature forms of neutrophils can be detected. This is explained by the fact that in the fight against pathogenic microorganisms, segmented cells die too quickly, and therefore the body is forced to use cells that are not fully mature. But in the blood of a healthy person, predominantly mature neutrophils are found, since they cope well with their task with virtually no help from their young brothers.
Figure 1. Phagocytosis. Image: mikrostoker/Depositphotos
Blood test for neutrophils
To determine the level of neutrophils, a complete blood count is used. To designate neutrophils on the analysis form, the Latin abbreviation NEUT is used, which can be expressed either in absolute (cell content per liter of blood, for example 0.04-0.3 × 109) or as a percentage. For general analysis, capillary blood is usually used. The biomaterial is collected from a finger after puncture with a scarifier. Sometimes blood is drawn from a vein - much depends on the methods the laboratory uses.
Additional examinations
Supportive measures are prescribed only by doctors. Among the methods:
- Oral interview with the patient. It is necessary to identify all the symptoms of the pathological process.
- Study of anamnesis.
- General blood and urine analysis. Biochemical methods.
- Allergy tests. Within the framework of which immunological studies are carried out.
- Bone marrow puncture. Quite a risky technique. It is prescribed in extreme cases when there is no other option.
- Immunological tests.
- Chest X-ray.
- Smears from the throat, genitals. From suspected sources of infection.
If neutrophils are low in an adult, this indicates an obvious pathological process: inflammation, poisoning, allergies, disorders of the bone marrow, radiation sickness, or the development of side effects from taking medications.
Indications for analysis
A general blood test is the most common hematological test, so the range of indications for its use is wide. Neutrophils are a type of white blood cell whose main task is to destroy pathogenic microorganisms. Therefore, the main goal of the analysis for the content of neutrophils is to identify potentially dangerous conditions accompanied by infectious and inflammatory processes. In other words, a blood test for neutrophils can be informative both for colds and for kidney or liver diseases.
When is a test ordered?
Band neutrophils can be increased or decreased in patients of different genders and ages.
However, the study is prescribed if there are specific indications in the form of various symptoms and signs of diseases:
- Colds and inflammatory pathologies at the initial stage.
- Increased fatigue and weakness that does not disappear after a long rest.
- Loss of appetite and weight loss for no apparent reason.
- Decreased concentration and memory impairment.
- Dry skin, bleeding gums.
- Indigestion.
- Increased body temperature in the absence of other symptoms of the disease.
- Inflammatory pathologies of the liver, pancreas, gall bladder.
- Kidney diseases in acute and chronic stages.
- Suspicion of acute respiratory tract diseases.
- Oncological diseases in latent form.
- Infectious pathologies of the digestive tract.
- Blood pathologies characterized by a decrease in the level of red blood cells and hemoglobin.
Diagnostics can be prescribed for preventive purposes, which makes it possible to detect abnormalities at the initial stage. This analysis is a standard examination method, therefore, immediately upon admission of a patient to a hospital in any department, blood is drawn and tested. Thanks to the simplicity and speed of diagnostics, it is possible to identify deviations on the day the biomaterial is submitted.
Preparing for analysis
The study is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach, since food intake causes an increase in the number of neutrophils in the blood. Dinner on the eve of the test is allowed no later than eight o'clock in the evening. 2 days before the study, the patient should follow the following preparation rules:
- stop drinking alcohol;
- limit the consumption of spicy, fried and fatty foods;
- Avoid heavy physical activity and nervous stress.
The morning before the test you should not smoke. It is allowed to drink pure still water.
Figure 2. Preparation for donating blood for analysis.
Methods for counting quantities
Band neutrophils, like all blood cells, are counted in the finished smear after staining. They react to both acidic and alkaline reactions of paints. That's why they are called neutrophils.
A total count of cells of each type contained in a unit volume is carried out. For “rods” the absolute amount is normal from 1.8 to 6.5 x 109/liter of blood.
A more important indicator is the percentage of band forms in the total number of leukocytes. A detailed calculation of all types is the leukocyte formula.
On the right are the final cells: all with “freckles”, which means “granulocytes”, in the middle row the penultimate one is a band neutrophil
Normal levels of neutrophils in the blood
The number of neutrophils in the blood is approximately 40-70% of the total leukocyte mass in both men and women.
When conducting research, experts primarily pay attention to the content of neutrophils at the middle and full stages of maturation, that is, band and segmented forms. Young cells are of interest if the development of the spread of inflammatory processes is suspected. The table shows the leukocyte formula, which reflects, among other things, the number of neutrophils. Table 1. Leukocyte formula with the number of neutrophils
| Index | × 10x9/l | Share as a percentage of the number of leukocytes | |
| Neutrophils | segmented | 2.0 – 5.5 | 40 — 70 |
| stab | 0.4 – 0.3 | 1 — 5 | |
| Basophils | Within 0.062 | Within 1.0 | |
| Eosinophils | 0.02 – 0.3 | 0.5 — 5 | |
| Lymphocytes | 1.0 – 3.2 | 17 — 38 | |
| Monocytes | 0.07 – 0.5 | 3 — 12 | |
In children of the first year of life, the number of band neutrophils can reach five, then the maximum value is limited to four, as in adults. The smallest number of segmented neutrophils is observed in children 4-5 years old (35-55%). In other age groups it varies between 40-70%.
If segmented neutrophils are increased
The growth of cells of the neutrophil species is called neutrophilosis. The level of segmented neutrophils exceeds 75%.
Both segmented and rod cells increase.
Sometimes earlier forms appear in a blood test - myelocytes, but segmented ones do not change. In the leukocyte formula, this looks like a shift to the left (according to the location of cells in the list of leukocyte forms). At the same time, granularity is detected in neutrophils.
The causes of neutrophilia can be:
- infection with acute bacterial, fungal infection, spirochetes;
- exacerbation of the inflammatory process in rheumatism, pancreatitis, polyarthritis;
- the presence of a dead area in the body, for example, in acute myocardial infarction;
- recent vaccination;
- severe alcohol intoxication;
- disintegrating tumor;
- damage to the kidney tissue, especially with diabetic nephropathy;
- treatment with steroid hormones, heparin.
Vaccination of the adult population is carried out according to epidemic indications.
A shift to the right is detected when a high level of segmented forms predominates over younger band forms. It's possible:
- Segmented neutrophils are increased in the child’s blood and nasal smear. Reasons what to do
- after acute blood loss;
- as a reaction to blood transfusion;
- for some types of anemia.
The cause of a temporary increase in neutrophils may be:
- condition before menstruation in women;
- long-term stress associated with increased workload;
- physical stress.
Pregnancy causes a general increase in white blood cells by 20%. This is the protection of the mother and fetus from unwanted influences. During pregnancy, the absolute number of segmented neutrophils is increased (more than 6 x 109/l), and their relative level in the formula remains unchanged.
To determine the severity of the disease, neutrophilia is divided into forms:
- moderate - the number of cells is not higher than 10 x 109/l;
- pronounced - absolute content from 10 to 20 x 109/l;
- severe - cell count above 20 x 109/l.
Causes of increased neutrophils in the blood
Elevated neutrophil levels can indicate a wide range of illnesses and injuries. Very often, the cause of an increase in neutrophils in the blood is infectious processes of bacterial origin, which can be either focal or generalized (spread throughout the body).
Reasons for increasing the level of neutrophils in the blood:
- upper respiratory tract infections (laryngitis, pharyngitis, sore throat);
- pneumonia;
- kidney diseases;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- local purulent-inflammatory foci (abscesses, abscesses);
- viral diseases (measles, mumps, chickenpox, rubella, etc.);
- oncological diseases;
- taking hormonal medications;
- infections of bacterial origin (dysentery, tuberculosis, cholera, anthrax, etc.);
- poisoning with toxic substances;
- processes of tissue necrosis (gangrene, myocardial infarction, major burns);
- injuries of large organs;
- fractures;
- damage to the skin (cuts, abrasions, etc.);
- gout;
- sepsis (blood poisoning).
Eating canned foods can also cause an increase in neutrophils. This applies to those products in which there are no longer living bacteria left, but the toxic products of their vital activity have been preserved.
Indicator 0
There is an indicator of 0 – what does this mean? Indicator 0 in a child and 0 in an adult can most often be provoked by the following factors:
- Bacterial infections such as typhus, tularemia or chronic brucellosis.
- Viral infections that can lead to a decrease in neutrophils. In such a situation, the patient may become ill with rubella, influenza, scarlet fever, measles, diphtheria or viral hepatitis.
- Toxic effects of medications.
- Anemia can cause a lack of neutrophils in an adult or child.
- Because of radiation.
Causes of low levels of neutrophils in the blood
A decrease in the level of neutrophils in the blood is called neutropenia. The cause of this phenomenon can be diseases of various natures, as well as taking various medications.
Reasons for decreased neutrophil levels:
- infectious diseases (viral hepatitis, typhus, influenza, mononucleosis, etc.);
- autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic vasculitis, Crohn's disease, etc.);
- radiation sickness;
- blood diseases (leukemia, hemolytic and dyserythropoietic anemia).
Separate mention should be made of medications: taking them can also cause neutropenia. This is a very broad group of medications, which includes:
- NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: analgin, amidopyrine);
- antibacterial drugs (cephalosporins, penicillins);
- drugs to lower sugar (chlorpropamide);
- thyreostatic agents (propylthiouracil, Mercazolil);
- antimalarial drugs of synthetic origin (hydroxychloroquine);
- sulfonamides (sulfapyrazone; sulfasalazine);
- cytostatics (chlorambucil, methotrexate);
- antivirals (ganciclovir, zidovudine).
Figure 3. Blood cells in a healthy person and with neutropenia. Image: Sakurra/Depositphotos
Why are neutrophils low?
The reasons for the low level may vary. Among the main ones we can list the following:
- Viral infections (rubella, influenza, measles, hepatitis, etc.).
- Protozoal infections (toxoplasmosis, malaria, leishmaniasis).
- Rickettsial (typhoid fever).
- Some bacterial infections (typhoid fever, brucellosis, paratyphoid fever).
- Consequences of taking certain medications (analgesics, cytostatics, sulfonamides).
- Anemia (aplastic, hypoplastic).
- Agranulocytosis.
- Consequences of radiation therapy.
- Radiation exposure.
- Unfavorable environmental conditions.
- Some hereditary diseases.
- Inflammatory diseases that have acquired a generalized course.
- Hypersplenism.
- Ulcer of the duodenum and stomach.
- Anaphylactic shock.
Consequences of deviation of neutrophils from the norm
A change in the level of neutrophils in the blood is a signal from the body about the presence of inflammatory diseases, injuries or poisoning. Therefore, it is necessary to accurately determine the cause of the increase or decrease in neutrophils in order to begin treatment in time or eliminate the provoking factor. If this is not done on time, the consequences can be severe (even death). The greatest danger among possible causes is infectious diseases of a bacterial nature, as well as processes of local suppuration and necrotization (death) of tissue.
Segmented neutrophils are increased
If neutrophils in the blood are elevated, what does this mean and what is the reason – doctors cannot immediately answer for sure. The only correct statement is the presence of an infection, a pathology complicated by the penetration of pathogenic microbes into the body. In order to accurately establish a reliable cause, a thorough, comprehensive examination of the entire body is required.
However, in most cases, increased segmented neutrophils in the blood are recorded when:
- development of bacterial infection;
- the appearance of a fungal infection;
- mild inflammatory process.
Segmented neutrophils are increased - reasons
An increase in segmented neutrophils is always a reason to examine the body. In such cases, they speak of a shift in the leukocyte formula to the right.
Among the common situations accompanied by this symptomatology, it is necessary to highlight:
- Not related to pathology: physical activity, food intake.
- Pathological: purulent abscesses, burns, trophic ulcers, leukemia, acute inflammatory diseases (pneumonia, tonsillitis, otitis, sepsis, peritonitis), the formation of malignant or benign tumors.
Segmented neutrophils are increased - what to do?
The main task in this case is to determine the reason why increased segmented neutrophils are detected.
The patient is indicated for additional examination, including consultations with the following specialists:
- therapist;
- infectious disease specialist;
- hematologist.
The patient must strictly follow the doctor's instructions and prescriptions. If neutrophilia is caused by a certain pathology, therapy is aimed at its complete cure.
- Reduced neutrophils in the blood
To help your body recover faster, doctors recommend following the following rules:
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Healthy eating.
- Seasonal therapy using multivitamins.
How to reduce the number of neutrophils in the blood
To reduce the number of neutrophils in the blood, it is necessary to influence the cause of this phenomenon, since there are no separate ways to eliminate it. If the increase in neutrophil levels is caused by short-term stress or increased physical activity, then no specific correction is required.
For persistent neutrophilia, depending on the disease that caused it, the following treatment methods are used:
- antimicrobial therapy - antibiotics are used for infections (amoxicillin, cefixime);
- antiplatelet therapy - in case of heart attack and a tendency to blood clots, acetylsalicylic acid and alteplase are prescribed;
- anti-inflammatory therapy - glucocorticosteroids (prednisolone) are used to reduce inflammation that provokes neutrophilia;
- chemotherapy – aimed at combating malignant tumors (cytostatics, antimetabolites).
If there is a local focus of inflammation, surgical treatment can be used. For example, it is relevant for appendicitis or abscesses. The menu should limit the amount of meat products, canned and smoked. The diet should be rich in vegetables and fruits.
To normalize the level of neutrophils in the blood, it is recommended to eat more vegetables and fruits. Photo: sommail / freepik.com
How to increase the number of neutrophils in the blood
To correct neutropenia, it is necessary to identify its cause. If a decrease in neutrophil levels is caused by taking medications, you should first weigh the possible risks of a decrease in neutrophil levels with the importance of the therapeutic effect of the drugs used. In extreme cases, the drug can be replaced with an analogue that does not affect the level of neutrophils in the blood. The underlying diseases that cause neutropenia are treated with antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and antiviral drugs.
It is recommended to consume the following products:
- any meat dishes (it is important that they are all well thermally processed);
- hard boiled eggs;
- pasteurized milk;
- cheese (except for varieties with mold);
- potato;
- rice;
- pasta;
- fruits and vegetables;
- alcohol only in consultation with a doctor.
Careful heat treatment of meat and eggs is necessary in order to exclude the possibility of bacteria and microbes entering the body, which actively multiply in poorly fried or undercooked protein dishes.