We offer you a comprehensive examination of the heart and cardiovascular system. If a disease is detected, we will offer you the help of a therapist, cardiologist, etc. In addition to conducting the study, our specialist will interpret the ECG, ABPM results, etc.
- Methods for studying the cardiac vascular system
- Search for the cause of the disturbance in the functioning of the cardiovascular system
Watch our video about diagnostics of the heart, blood vessels and the function of external respiration
. The heart performs the main pumping function in our body, its task is to ensure adequate supply of blood to the tissues, and with it oxygen and nutrients. With heart diseases (coronary artery disease, atherosclerosis, carditis, etc.), not only the heart itself suffers, but also other organs, including the brain.
In our clinic, research of the cardiovascular system takes place in two directions:
- Study of the structure and function of the heart muscle;
- Vascular examination;
- Search for the cause of the disturbance in the functioning of the cardiovascular system.
Methods for studying the cardiac vascular system
- ECG, Holter-ECG, ECG with stress - determination of the electrical potentials of the heart to clarify the causes of pain in the heart, sensations of “interruptions” in the work of the heart, fainting, tachycardia and other paroxysmal conditions.
- Echo-CG - this method allows you to assess in real time the condition of heart tissue, the contractility of the heart muscle, and the functioning of the heart valves.
- Daily blood pressure monitoring, blood pressure testing under stress – If problems arise with a decrease or increase in blood pressure, the examination of the patient usually begins with a study of daily blood pressure. Daily monitoring provides much more information than a single measurement.
- Coronary radiography – used to diagnose coronary heart disease by visualizing the coronary arteries on coronary radiographs
- Self-monitoring of blood pressure and pulse rate - in many cases, we recommend regularly measuring your pulse and blood pressure to determine the effectiveness of your treatment.
- Polysomnography. Sleep study. Diagnosis of sleep problems - if heart problems occur during sleep, for example, stopping breathing during sleep (sleep apnea), nighttime episodes of palpitations, increased blood pressure associated with snoring, we recommend polysomnography.
- biochemical blood test (lipid profile
- coagulogram
- consultation with a therapist or cardiologist.
Electrocardiography: ECG, Holter-ECG, ECG with stress
Electrocardiography. ECG is the main and mandatory method for studying the heart and its functional state. An ECG helps to determine the cause of pain, shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, to obtain an explanation for the sensations of “interruptions” in the work of the heart, the cause of edema, and to identify hidden heart rhythm disturbances.
A typical routine ECG is performed in the supine position for a few minutes. Sensors are attached to the patient’s chest, arms and legs, from which signals are sent to the recording device, and the doctor describes them. A cardiogram taken within a few minutes does not reflect a complete picture of the condition of the heart and is not a diagnosis . If we are talking about paroxysmal conditions, it is more advisable to carry out daily Holter ECG monitoring.
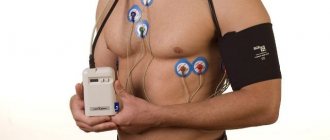
Holter -ECG (Holter monitoring). A method of continuous recording of heart function throughout the day, which makes it possible to identify short-term changes in the rhythm and blood supply of the heart that occur during the day, including at night, thereby identifying hidden and short-term heart problems. The results of Holter monitoring show the heart’s reaction to all events that occurred during the day, including physical activity, stress, sleep, food intake, etc.
How is Holter monitoring performed? ECG recording is carried out using a special portable recorder, the size of a mobile phone, and sensors on the chest, which the patient carries with him under his clothes. After installing the recorder, we recommend that you lead your normal lifestyle with hourly display in the diary of emotional and physical stress received during the day.
ECG with stress. Basically, performing an ECG with stress is required to determine a person’s suitability for various kinds of extreme stress, for example, for pilots, athletes, and before conscription into the army. Carrying out an ECG with stress allows us to identify hidden cardiovascular insufficiency and the threshold of physical activity that the patient can tolerate without harm to his health. Stress ECG is more often performed in young patients.
How is a stress ECG performed? An exercise ECG is performed using a bicycle ergometer (an exercise bike) or a treadmill (a moving treadmill). The doctor installs special sensors on the patient’s body and, in a mode of increasing physical activity, a continuous ECG recording is performed, which makes it possible to determine the threshold of physical activity that does not cause disturbances in cardiac activity.
We recommend that you take with you to the clinic the results of previously conducted ECG studies, which may be useful for more accurately determining the dynamics of pathological processes in the heart muscle.
Main indications for ECG, Holter-ECG, ECG with stress:
- Pain in the heart area
- Cardiac ischemia
- Shortness of breath of unknown origin
- Cardiopalmus
- Feeling of interruptions in the heart
- Edema of unspecified nature
- Increased or decreased blood pressure
- Preventive examination
Echocardiography / Echo-CG / Ultrasound of the heart
Echocardiography or Echo-CG, cardiac ultrasound is a method of ultrasound diagnostics of the functional and anatomical state of the heart muscle and the valvular apparatus of the heart. Ultrasound of the heart is relatively simple to perform, does not have a harmful effect on the patient, and is highly informative. As a rule, we perform echocardiography to diagnose coronary heart disease, when examining for heart pain, heart failure, heart defects and inflammatory diseases (carditis).
How is Echo-CG performed: Ultrasound of the heart is performed using an ultrasound machine equipped with a cardiac sensor and an appropriate program with the patient lying on the couch. Ultrasound freely penetrates the intercostal spaces and, reflected from the heart and moving blood, returns to the sensor. The doctor, using a sensor, receives an ultrasound signal that displays the anatomical state of the tissues of the heart muscle and valve apparatus, then, using a set of programs, processes the resulting image and calculates the parameters of the heart.
We recommend that you take with you to the clinic the results of previous echocardiography studies, which may be useful for comparison with the new echocardiography data obtained. This way you can judge the effectiveness of the treatment and the improvement/deterioration of the heart condition.
Main indications for Echo-CG:
- Pain in the heart area
- Fainting during exercise
- Cardiac ischemia
- Anatomical malformations of the heart
- Heart valve insufficiency or stenosis
- Impaired cardiac hemodynamics
- Inflammatory processes in the heart - carditis
- Swelling of the legs
- Resolving the issue of indications for surgical treatment
24-hour blood pressure monitoring, blood pressure testing under stress
Daily blood pressure (BP) monitoring reflects its true values during the day during your normal lifestyle. These data cannot be obtained with a single blood pressure measurement. In some cases, it is advisable to simultaneously monitor an ECG (electrocardiogram) and blood pressure.
Daily monitoring of blood pressure with high blood pressure allows for early diagnosis of arterial hypertension, its connection with emotional and physical stress, and optimization of the time of taking medications. This method allows you to identify patients with nocturnal hypertension, when the increase in blood pressure is invisible and therefore dangerous, as well as for assessing blood pressure during nocturnal angina and respiratory failure.
Daily monitoring of blood pressure with low blood pressure allows you to find the cause of fainting and semi-fainting states, attacks of weakness.
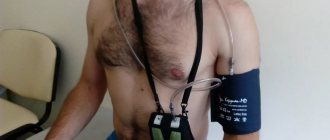
How is daily blood pressure monitoring performed? The patient is given a cuff on his left arm, which is then placed on the arm for 24 hours, and a small compressor with a recorder, which pumps air into the cuff at a certain frequency and measures blood pressure. It is important to lead an ordinary lifestyle with an hourly display in the diary of the emotional and physical stress received during the day.
Study of blood pressure under load. The study of blood pressure under load makes it possible to assess the direction and severity of shifts in basic hemodynamic parameters under the influence of different types of physical activity, as well as the speed of their recovery.
How is blood pressure tested under stress? The patient's blood pressure is measured at rest and its value is compared after exercise on a bicycle ergometer or physical exercise. When carrying out 24-hour blood pressure monitoring, you can conduct test stair climbs (to be agreed with your doctor). We recommend that you take with you to the clinic the results of previous blood pressure tests, which may be useful for the early diagnosis of arterial hypertension and optimize the timing of taking medications.
Main indications for daily blood pressure monitoring:
- Unstable blood pressure readings
- Frequent headaches of unspecified nature
- Swelling in the legs
- To clarify the degree of arterial hypertension and individual rhythms of blood pressure fluctuations during ducks
- To select adequate therapy for hypertension
- To control the treatment
- Fainting
The main indications for performing a blood pressure test under load:
- Prolonged stress conditions
- Unstable blood pressure readings
- Feeling worse during physical activity
- Examination before stress loads (pilots, athletes, military personnel)
Coronary angiography – diagnosis of coronary heart disease
Coronary angiography is a contrast X-ray examination of the vessels of the heart, performed on an outpatient basis without hospitalization. Coronary angiography allows you to determine the nature, location, extent and degree of narrowing of the coronary vessels of the heart. This study is performed to determine the feasibility of surgical treatment of coronary heart disease.
How coronary angiography is performed: Under local or general anesthesia, the doctor installs a special catheter through the femoral artery or through the artery of the forearm, which is passed through the bloodstream through the upper part of the aorta into the vessels that supply the heart. A radiopaque substance is injected through the catheter, which is carried through the bloodstream through the coronary arteries that supply the heart muscle. Using a special device, an angiograph, areas of obstruction in the patency of the bloodstream are recorded. Upon completion of the study, the doctor makes a conclusion on the choice of treatment method.
Preparation for coronary angiography: Before performing coronary angiography, it is necessary to take a general blood test, determine the blood group and Rh factor, and test the blood for hepatitis and HIV infection. The issue of the need for coronary angiography is decided after consultation with a cardiologist.
Main indications for coronary angiography:
- Coronary heart disease with risk of developing myocardial infarction
- Heart failure
- Unstable angina not amenable to drug correction
- Left ventricular dysfunction accompanied by arterial hypotension or pulmonary edema
- Establishing the degree of risk of complications during planning heart surgery for valve replacement and correction of congenital heart defects
Self-monitoring of blood pressure and pulse rate
The easiest way to monitor heart function and blood pressure is to take self-measurements and record the data in a diary. We recommend regular blood pressure and pulse measurements for 10 days: this period is usually sufficient to obtain a statistically reliable result. Such control, among other things, makes it possible to assess the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment.
How to independently monitor blood pressure and pulse rate: We recommend performing the measurement procedure while sitting on a chair with a backrest, placing your hands on the table at chest or stomach level.
Measurements are taken in the morning immediately after waking up from sleep and in the evening before going to bed in a quiet environment. It is not recommended to walk up the stairs, drink hot drinks, eat heavily or take a shower before measuring blood pressure and pulse. It is allowed to carry out the measurement procedure at intervals of 15–20 minutes after these moments. All results of measurements of pulse number and pressure are recorded on a tablet with which after 5 - 10 days you need to come to the doctor or send it by e-mail.
Nikolay Amosov test
The creator of the artificial heart valve has proposed an even simpler ladder test that does not require outside help. You can do it on the way home.
- Before you start, you need to measure your pulse. At rest, its norms are: 60–80 beats per minute in women and 50–85 beats in men.
- Slowly walk up the stairs of the 4th floor.
- Measure your pulse again. If it doesn't exceed 100 hits, great. At 100–120 blows: satisfactory, 120–140 blows: the result is alarming. If it is more than 140, accompanied by severe shortness of breath, you must stop the test and see a doctor.
Next stage: climbing stairs for 4 minutes:
- managed to climb 15 floors: excellent;
- no more than 12 floors: good;
- 10–11 floors: something to worry about;
- 9 floors or less: time to see a doctor.
If there are no high-rise buildings nearby, you can modify the test: when you reach the top floor, go back down. In this case, descending 3 floors is equal in load to ascending 1.
Search for the cause of the disturbance in the functioning of the cardiovascular system
- Vascular examination If the cause of heart muscle suffering is atherosclerosis, we will offer you to conduct an ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the vessels of the brain and neck, ultrasound examination of the vessels of the arms and legs because with atherosclerotic damage to the vessels of the heart, there is a high probability that some other vessels are involved in the process.
- Biochemical blood test (lipid profile study, i.e. the ratio of harmful and good cholesterol);
- Immunological and microbiological studies (bacteriological cultures, PCR, determination of antibodies to infections). These studies may be useful for selecting targeted treatments for carditis.
- An immunogram can be useful to find the reason why the causative agent of carditis was able to enter the body. Typically, the immune system prevents any foreign agent (bacteria, virus, etc.) from entering the body. Our task is to find the dysfunctional link in the immune system and prevent the development of carditis in the future.
When there is an imbalance in various forms of cholesterol, atherosclerosis develops.
Atherosclerotic cholesterol plaques block the lumen of blood vessels, impair blood circulation, and can cause myocardial infarction and heart pain. We recommend regular heart examinations, namely bicycle ergometry, Echo-CG (ultrasound of the heart), ABPM and others. This will help identify problems with the cardiovascular system before obvious symptoms appear. Bicycle ergometry is an indispensable study to check how the myocardium (heart muscle reacts) to physical activity or stress; ultrasound of the heart shows the contractility of the myocardium. Daily blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) will help identify trends in blood pressure changes and help in identifying factors that contribute to a rise in blood pressure.
Squat test
Here you don’t even need a ladder; you can check your heart function at home. You will need a little more than 1 m² of free space, a stopwatch or timer. No preparation for the study is needed:
- Measure your pulse per minute while at rest. Remember the result.
- Time yourself for 30 seconds and try to do 20 squats during this time. As you lower, stretch your arms forward, and as you rise, press them to your hips.
- After finishing the exercise, immediately repeat the heart rate measurement.
- Rest for 3 minutes and measure the beat frequency again.
A comparison of three results: at rest, after exercise and after rest shows whether everything is fine with the heart:
- the pulse after squats increased to 25% and recovered to the initial result: excellent;
- the frequency increased by 25–50% after exercise, and after rest remained increased by 20–30%: the result is good, but you need to monitor your health;
- the load caused the heart rate to increase by 50–75%, after rest it remains just as high: there are violations and reasons to consult a doctor;
- The pulse fluctuates after exercise, becoming 76% higher or higher, there was not enough rest for recovery, it quickly returned to normal: diagnostics and medical assistance are urgently required.
References
- Diagnosis and correction of lipid metabolism disorders for the prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis. Eurasian Association of Cardiologists. National Atherosclerosis Society. Moscow, 2021.
- Boytsov S.A. and others. Cardiovascular prevention 2021. Russian national recommendations. Russian Society of Cardiology, National Society of Preventive Cardiology, Russian Society for the Prevention of Non-Infectious Diseases // Russian Journal of Cardiology 2018; 23(6): 7–122.
- Sigurdardottir FD et al. Relative Prognostic Value of Cardiac Troponin I and C-Reactive Protein in the General Population (from the Nord-Trøndelag Health [HUNT] Study) // Am J Cardiol. 2018;121(8): p. 949-955.
- Ford I et al. Ticagrelor for Prevention of Ischemic Events After Myocardial Infarction in Patients With Peripheral Artery Disease // J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016; 68(25), p. 2719-2728
- Naess IA, Christiansen SC, Romundstad PR et al. Prospective study of homocysteine and MTHFR 677TT genotype and risk for venous thrombosis in a general population—results from the HUNT 2 study. // Br. J. Haematol., 2008, v. 141, p. 529–535.
- Moat SJ Plasma total homocysteine: instigator or indicator of cardiovascular disease? //Ann. Clin. Biochem., 2008, v. 45, p. 345–348.
Diagnosis of CVD
The level of modern diagnostics makes it possible to identify most diseases of the cardiovascular system at an early stage, when the pathological process is reversible and responds well to therapy.
Methods for studying heart disease are divided into physical, laboratory and instrumental.
Physical examination methods performed by the doctor at the first appointment include:
- examination of the skin and mucous membranes;
- palpation - palpation;
- percussion - tapping;
- auscultation - listening.
Despite their simplicity, physical examination methods allow the doctor to make a preliminary diagnosis and outline the range of necessary laboratory and instrumental tests.
- During the examination, changes in the color of the skin (pallor, cyanosis, yellowness) are noted; the presence or absence of pastiness or swelling of the extremities, pulsation of the cervical arteries.
- Using percussion, the boundaries of the heart are determined, which, in case of myocardial pathologies, go beyond normal limits.
- Using a phonendoscope, auscultation is performed - listening to heart sounds and noises and assessing their sonority and rhythm.
- Blood pressure is measured.
Currently, these methods are relegated to the background, since there are modern, faster and more effective ways to detect pathologies of the cardiovascular system.
Computed tomography of cardiac vessels
Computed tomography of the blood vessels of the heart (CT angiography) is performed using a computer tomograph, which contains an X-ray tube inside. Rotating, it provides a three-dimensional image of the vascular bed being examined, helping the doctor identify various vascular diseases. Before the procedure, a radiopaque contrast agent is injected into the patient’s vein, after which he lies down on the tomograph table. It is not advisable to move during the procedure, as this may distort the data. CT is significantly inferior in information content and reliability to coronary angiography.