AMPP usually does not pose a threat to the baby’s life; such children develop normally, and over time this disease can go away on its own. But in cases where the child’s pathology is not limited to one aneurysm, but is combined with another heart defect, then this is, of course, a cause for concern for parents. A good ultrasound specialist in Makhachkala can detect heart abnormalities in a newborn during an ultrasound examination already in the first days of the baby’s birth.
1.General information
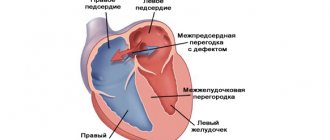
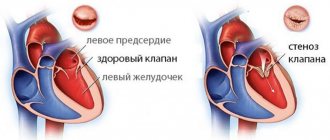
An aneurysm (the less correct term “aneurysm” is sometimes used) is a local bulge, a protrusion of any boundary surface in the form of a stretched sac, or a spindle-shaped expansion of the walls of a blood vessel (saccular aneurysms are also found on vessels, but much less frequently). Thus, an atrial septal aneurysm (ASA) is a curvature of the membrane separating the right atrium from the left. Normally, this septum is sealed, relatively straight and does not bend, at least significantly, in any direction.
Many authors qualify an MPP aneurysm as a pathology only if the protrusion in any direction (to the right atrium, to the left, or S-shaped) exceeds 10 mm and is combined with prolapse (sagging) of the mitral valve. In terms of the general population, such an anomaly is rare; more often it accompanies congenital connective tissue diseases. An MPP aneurysm is called a “minor cardiac anomaly” or “small heart defect”, since in most asymptomatic cases it does not pose a real danger and does not require treatment, and is usually discovered by chance. However, it does not at all follow from this that this anomaly can be forgotten without attaching any significance to it: the situation can sharply worsen with the onset of enlargement of the aneurysm, thinning of the aneurysm and its spontaneous breakthrough, after which the dynamics become unpredictable.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Mechanisms of aneurysm formation
Patent foramen ovale
During the prenatal period in the fetus, the oval window is located in the septum between the atria. Through this window, blood is discharged from the left atrium to the right. Thus, the blood flow does not involve the pulmonary circulation, since during this period there is no need for the lungs to work.
After birth, the baby's lungs begin to function and the oval window closes (overgrows). If the window does not close completely, thin connective tissue forms in this place, or a communication remains between the atria.
- Aortic aneurysm: symptoms and treatment
3. Symptoms and diagnosis
In early childhood, the course is usually asymptomatic. However, the reason for a thorough examination, incl. cardiological, where an aneurysm is usually detected - should be a child’s lagging behind in psychophysical development, insufficient body weight, frequent acute respiratory viral infections; at later stages - signs of infantility of the reproductive system, constant pallor, fatigue from the slightest physical exertion, pain in the heart, sometimes noticeable protrusion of the chest in the cardiac zone.
The severity of this symptom complex varies widely - from severe to insignificant, not significantly affecting the quality of life and overall development. The greatest danger is rupture of an aneurysm with the formation of an interatrial defect (message), as a result of which the normal, natural hemodynamics of the myocardium are disrupted. However, it is no coincidence that this development of events is called unpredictable above: in some cases, the acquired defect allows you to lead a completely normal lifestyle for decades, in others it creates the threat of a stroke or the so-called. sudden cardiac death. After 40 years of age, a patient with a defect in the bladder, formed as a result of a rupture of an aneurysm, often has to be disabled due to increasing hemodynamic disturbances and risks.
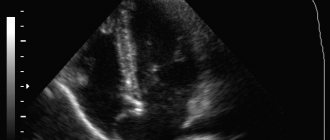
In diagnosis, in addition to anamnesis, the results of clinical examination and observation, ultrasound echocardiography (EchoCG) is of greatest importance, which has virtually no contraindications, allows repeated studies over time and allows for visualization of the aneurysm with an accurate assessment of its characteristics. As a clarifying diagnosis, usually to identify and study associated anomalies and defects, transesophageal ultrasound, CT, and cardiac catheterization may additionally be prescribed.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Why pathology may occur
Scientists have still not come to a consensus on why a child’s heart aneurysm develops. Although such a developmental anomaly is not new in medicine. Scientists have known about this pathology for a long time, but due to insufficient diagnostic capabilities, it was detected much later, when the process of various kinds of complications began. Today everything has changed. Doctors can make a preliminary diagnosis at the stage of intrauterine development, and then confirm or refute it using ultrasound when the child is born.
A cardiac aneurysm in a child is considered a fairly rare structural disorder. According to scientists from the Yaroslavl State Medical Academy, it is observed in 2.5% of full-term newborns. It is distinguished from severe heart defects by the minimality of the defect, the absence of disturbances in the contractility of the organ, the closure of the heart valves and the flow of blood through the vessels.
Scientists have been closely studying MARS syndrome for more than 35 years and cannot yet accurately predict what problems such a disorder may result in in each specific case, whether it threatens the future life of the baby or will not manifest itself in any way.
4.Treatment
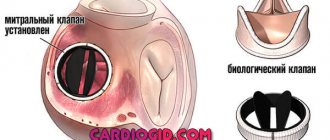
With an uncomplicated aneurysm, there is no need for either conservative or cardiac surgery (for obvious reasons, any surgical intervention on the heart is in itself risky and is used only as a last resort measure with no alternatives). However, observation and regular follow-up examinations by a cardiologist are strictly necessary: the condition and size of the aneurysm must be monitored. In cases of threatening development of the clinical situation, the patient is immediately hospitalized, and in the cardiac surgery hospital the defect or plastic suturing of the MPP is performed using bioinert materials.
complication
Many parents are afraid that their child's heart aneurysm will simply rupture. However, in most cases their fears are completely unfounded. This pathology does not pose a serious threat to its carrier, but in some cases there is still a risk of progression of negative consequences. The most common complications of this structural disorder include:
- Increased or decreased heart rate.
- Rupture of a protrusion that occurred during intrauterine development. It occurs rarely and leads to a sharp deterioration in intracardiac hemodynamics.
- Decreased blood pressure – hypotension.
- Heart failure.
- Circulatory failure.
- Increased risk of developing endocarditis, thromboembolism, etc.
- An abnormality in the structure of the septum makes it vulnerable to bacterial infections.
Why is a cardiac aneurysm dangerous?
A cardiac aneurysm is dangerous due to the formation of blood clots. Echocardiography often reveals blood clots in a distended cavity. A blood clot can break off at any time and lead to serious consequences.
Common complications of cardiac aneurysm include:
- ischemic stroke - a violation of cerebral circulation with damage to brain tissue;
- thromboembolism (blockage) of the pulmonary artery;
- kidney infarction - an acute circulatory disorder leading to the death of organ tissue;
- gangrene – necrosis of body tissues, accompanied by their rotting;
- repeated myocardial infarction is an acute disturbance of blood circulation in the heart muscle.
In addition to the risk of blood clot rupture, a cardiac aneurysm contributes to the development of heart failure with characteristic symptoms: shortness of breath, interruptions in heart function, chest pain, and swelling.
Disease prognosis
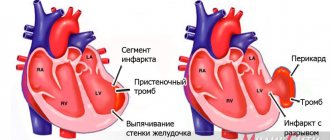
The prognosis for cardiac aneurysm depends on many factors. First of all, it depends on the size and location of the protrusion, the state of the cardiovascular system, concomitant pathologies, and the person’s age. If the aneurysm is small in size and you see a doctor in a timely manner, the prognosis for the disease is favorable. An aggravating prognostic factor is the addition of heart failure. Lack of treatment for extensive post-infarction aneurysms also significantly worsens the prognosis. Uncomplicated flat cardiac aneurysms occur most easily; saccular protrusions are often complicated by intracardiac thrombosis.
How to make an appointment with a specialist?
JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg) is located in the center of Moscow in the Central Administrative District at the address: 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane, building 10 (Mayakovskaya metro station).
Our medical center employs doctors of the highest qualifications and extensive experience. All diagnostic measures are carried out with maximum efficiency. Especially when it comes to emergencies. All procedures are carried out on modern equipment using the latest technologies.
Doctors, having received the examination results, prescribe the optimal treatment method, which will be aimed exclusively at a positive result. Patients are always under the strict supervision of doctors. This allows you to quickly react if the child’s condition worsens.
If you have questions, you can make an appointment by phone.
Classification of cardiac aneurysms
Cardiac aneurysms are classified according to many criteria: the cause and course of the disease, cellular structure and mechanism of formation, shape and size. A detailed classification of cardiac aneurysms is given in the table.
Types of cardiac aneurysms
| Classification sign | Type of aneurysm | Decoding |
| Cause of the disease | congenital | are formed due to disorders of intrauterine development of the fetus |
| acquired | in the vast majority of cases occur after a myocardial infarction | |
| Flow | spicy | form within one to two weeks after a heart attack |
| subacute | are formed from the third to the eighth week after a heart attack | |
| chronic | occur later than the eighth week after myocardial infarction | |
| Cellular structure | muscular | made up of muscle fibers |
| fibrous | the walls of the aneurysm are formed by fibrous tissue | |
| fibromuscular | include muscle and fibrous tissue | |
| Education mechanism | true | have a three-layer structure, consist of dead scar tissue |
| false | are formed when the myocardium ruptures and the formation of a cavity limited by the pericardium (the outer lining of the heart) | |
| functional | areas of viable myocardium that protrude during ventricular contraction | |
| Form | diffuse | have a flat shape |
| saccular | characterized by the presence of a “neck”, which, when expanded, forms a sac-like cavity | |
| delaminating | are formed due to rupture of the endocardium (the inner lining of the heart) |
Cardiac aneurysms can come in different sizes. There are significant aneurysmal protrusions - more than eight centimeters, medium - from three to seven centimeters in size, and small (hidden) aneurysms - less than three centimeters.
Therapy
Before treating a child, he must undergo certain diagnostic procedures:
- Auscultation is listening to the heart using a stethoscope. This device will allow you to hear noises if there is a possibility of an anomaly;
- ECG. Performed to check the functioning of the heart, it makes it possible to identify rhythm disturbances;
- Ultrasound. This diagnostic method is safe and quite informative. It allows you to detect bulging of the interatrial septum, as well as determine fluctuations in the cardiac cycle.
Treatment depends on the growth rate and increase in the size of the formation. As the disease progresses, the patient is indicated for surgical intervention, which involves replacing the damaged area of the vessel with an artificial graft.
Small aneurysms rarely lead to rupture of a heart vessel, so they can be treated with medications. Drug therapy includes antihypertensive drugs, which are also used to stabilize blood pressure. Therapeutic measures should be aimed at normalizing the functioning of the heart muscle, adjusting the rhythm, and improving metabolic processes in the myocardium.
Treatment is not complete without magnesium supplements. The role of this microelement in the formation of collagen fibers is difficult to overestimate. Magnesium has an antiarrhythmic effect, promotes contraction and relaxation of heart cells. That is why it is included in complex therapy for rhythm disturbances.
Treatment with magnesium preparations consists of taking Magnerot three times at a dosage of 0.5 g at a time. The duration of such therapy is 1 week. After this, take 25 g of this drug for 5 weeks. The use of Magne B6 is also required. The course of treatment is 1.5-2 months. The dosage depends on the child’s weight.
For antioxidant protection and membrane-stabilizing effect, L-carnitine, Cyto-Mac, and Coenzyme Q10 are used. Metabolic therapy can last about 1.5 months. Moreover, it must be repeated several times a year, as a rule, two or three are enough.
To improve metabolism, it is recommended to take PP and B vitamins. Vitamin therapy is carried out over a two-month course, repeated up to 3 times a year.
It is also possible to use beta blockers, glycosides and anticoagulants. The former help reduce heart rate. Glycosides and anticoagulants can be prescribed at the preoperative stage.
Additionally, you should adhere to non-drug treatment, the essence of which is as follows:
- It is necessary to properly organize the child’s daily routine, ensure normal sleep, walks in the fresh air, and proper rest.
- Particular attention should be paid to the baby’s nutrition; it should be balanced and as healthy as possible.
- It will be useful to carry out hydrotherapy or balneotherapy.
- Different types of massage have a very good effect.
- Physiotherapy will also be beneficial, especially if we are talking about electrophoresis using magnesium.
Small aneurysms can be treated with folk remedies. But they should only be used under the supervision of a physician. Under no circumstances should you conduct experiments on your own, especially if the pathological formation has reached a large size.
Among traditional medicine recipes, a collection of herbs such as rose hips, valerian officinalis, hawthorn and calamus has proven itself to be excellent. To prepare the product you need to take 1 tbsp. spoon of each component, and pour boiling water (0.5 l) over the raw materials. After the infusion has stood for 2-3 hours, it is filtered and 1 teaspoon of the decoction is diluted in a glass of water. Treatment is carried out three times a day.
When should you see a doctor?
A visit to a pediatric cardiologist, pediatrician, and vascular surgeon is recommended if you have the following signs of an aneurysm in children:
- frequent and severe headaches in a child;
- a feeling of discomfort and unpleasant sensations in the chest;
- periodic loss of consciousness and frequent dizziness;
- shortness of breath even with mild physical exertion;
- pallor and some swelling of the skin.
An experienced pediatric cardiologist at Meditsina JSC (academician Roitberg’s clinic), located in the central district of Moscow, will carefully examine the child and record all his complaints. The specialist will talk with the parents and carefully study the provided medical documents. Based on the results, the necessary studies will be prescribed and appropriate treatment procedures will be carried out.