High blood pressure, a problem that everyone has heard of. But low blood pressure also occurs quite often, even in young people. If with hypertension everything is more or less clear, there is a clear gradation of numbers, then with hypotension it is not possible to focus only on numbers. One person feels great with a blood pressure of 90/60, but feels unwell when the pressure rises to 120/60. Another person with low blood pressure feels weak and lacks strength.
What it is
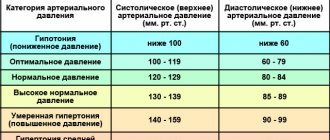
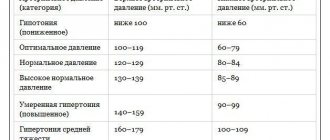
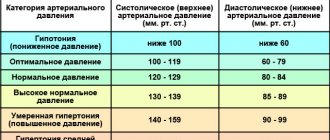
Reduced blood pressure is considered to be less than 100/60 mmHg. Art. Sometimes this may be physiological hypotension, which does not cause deterioration in well-being. Such individual characteristics can be caused by heredity and a person’s physique. They are also found among residents of high mountain regions, tropics, and athletes. A person usually finds out about this by accident and has no complaints1.
If low blood pressure is accompanied by symptoms of malaise, we can talk about pathology. Often, episodes of low blood pressure begin in childhood and adolescence as manifestations of neurocirculatory dystonia. Then they become regular and can develop into chronic arterial hypotension2.
If arterial hypotension is a consequence of other diseases, it is necessary to carry out treatment aimed at these problems. What can cause low blood pressure:
- anemia;
- chronic diarrhea;
- severe varicose veins, which leads to retention of a large volume of blood in the lower extremities;
- consequences of taking diuretics, antihypertensive drugs, barbiturates, antidepressants;
- adrenal insufficiency;
- tonsillitis;
- gastritis, peptic ulcer;
- diseases of the liver and biliary tract;
- heart diseases.
There are many reasons, so a medical examination and examination is required to establish the correct diagnosis.
Sometimes such an unusual combination of hypotension in an upright position with hypertension in a supine position is detected. Since blood pressure is usually measured while sitting, hypertension may not be detected immediately.
To establish a correct diagnosis, a medical examination and examination is required.
Welcome to the website of the State Health Institution “City Clinic No. 5”!
Details Published 08/19/2020 07:15 Why blood pressure drops: seven possible causes of hypotension
Low blood pressure is often a symptom of cardiac failure, when the heart pumps blood worse and vascular tone is weakened
Is it normal for it to increase with age? Experts talk about the real causes of blood pressure problems.
Hypotension (scientifically called arterial hypotension) is a condition when, when measuring pressure, the tonometer shows numbers below 105/70 mm Hg. Art. As a rule, it is accompanied by weakness, dizziness, headaches, and nausea.
1. There are people who have LOW BLOOD PRESSURE as an innate feature of the autonomic nervous system. These are people of the so-called asthenic type (as a rule, they have a fragile physique, light or brown hair, pale skin), they make up about 7% of the population. They are not distinguished by great endurance and performance, but they live quite active lives and do not feel
your low blood pressure. But an increase in pressure even to the normal limits (120/80) is tolerated very poorly.
2. Low blood pressure is often a symptom of cardiac failure, when the heart pumps blood worse and vascular tone is weakened. Often this condition occurs against the background of inflammatory heart diseases - endo- and myocarditis, which in half of the cases develop as complications after tonsillitis and flu. Hypotension also accompanies diseases associated with impaired nervous regulation of the heart (various arrhythmias and blockades). All these disorders are clearly visible on the ECG.
3. Vegetative-vascular dystonia of the hypotonic type (scientifically called neuro-circulatory dystonia). Because there are two types of reactions in this condition: sympathoadrenal and parasympathetic
Psychiatrists joke that a person’s soul is not in the heart, but in the kidneys - after all, stress hormones are produced in the adrenal glands:
- Adrenaline (“aggressive hormone”) excites, causes a feeling of heat, a rush of blood to the head, increased blood pressure, sweating, aggressive irritability, dysphoria (an irritable-sullen mood).
- Acetylcholine (“weakness hormone”), on the contrary, lowers blood pressure, causes cold sweats, chills, irritable weakness, a feeling of melancholy and weakness.
— And some people have mixed attacks, when acetylcholine and adrenaline reactions alternate. This gives rise to pressure surges, a person literally throws himself into the heat, then into the cold, says psychiatrist, psychotherapist, psychosomatics specialist Anatoly German.
4.LOCKED PRESSURE can be a side effect of some medications. The pressure can be “dropped” by:
- heart medications (nitroglycerin preparations, beta-blockers),
- large doses of antibiotics,
- antispasmodics and painkillers,
- large doses of “simple” sedatives (Corvalol, Valocordin, tinctures of peony and motherwort). Valerian has a milder effect.
5. A sudden drop in pressure occurs during an exacerbation of a stomach ulcer or an attack of pancreatitis. Usually this condition, in addition to pain in the stomach, is accompanied by general weakness and cold sweat. This is symptomatic hypotension and will go away once you heal your stomach.
Also, pressure always drops with any bleeding: nasal bleeding, hemorrhoidal bleeding.
6. Hypotension almost always accompanies some types of depression:
- asthenic - depression of exhaustion. With it, a feeling of fatigue prevails, outwardly there is a hint of exhaustion, a person can even seriously lose weight.
- apathetic. She is characterized by complete indifference to her surroundings, she doesn’t want anything, “nothing pleases, nothing hurts...”
- anhedonic. This is a loss of joy. Saturation with emotions, a feeling of mental impasse. Depression of great emperors and successful businessmen.
7. In completely healthy people, pressure can drop sharply after procedures that cause vasodilation - Russian baths, saunas, thermal baths, body wraps. So everyone, and especially older people, need to monitor their blood pressure very carefully if you go to the sauna. You should not stay in the steam room for more than 5-7 minutes at a time. Even if you are a fan of bath procedures, you need to take breaks and under no circumstances drink alcohol either before or after the bath.
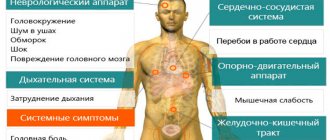
Symptoms of hypotension
The symptoms that occur are usually caused by a lack of blood supply to the brain and heart. Here are typical manifestations1:
- headache;
- dizziness, imbalance;
- nausea;
- severe weakness;
- memory impairment;
- decreased performance;
- intolerance to bright light, harsh sounds, stuffiness.
Deterioration in health is accompanied by pain in the heart, rapid or slow heartbeat, and rhythm disturbances.
As soon as such a person gets out of bed in the morning and starts walking, he feels worse due to an even greater decrease in blood pressure, so he wants to go back to bed. Additional symptoms:
- coldness and impaired sensitivity of the extremities (fingers);
- symptoms worsen due to fatigue, stress, lack of sleep, acute infections and exacerbation of any chronic diseases.
Low blood pressure: symptoms and causes
Low blood pressure or hypotension is a pathological change in the human body in which blood pressure drops below generally accepted norms (120/80 mm Hg). Low blood pressure is considered to be reduced to 90/60 mmHg. Art. and below. The disease is treated only if it has a negative impact on the human body.
Physiological norms of hypotension:
- a feature of the body, low blood pressure is the norm for the structure of a certain individual;
- compensatory, adaptive, typical for a person living in the mountains;
- orthostatic hypotension - a sudden change in body position;
- Postprandial hypotension is a decrease in blood pressure after eating food.
Low blood pressure - causes:
- diseases of the cerebral vessels, mainly central;
- stress;
- thyroid diseases;
- cancer;
- anemia;
- hepatitis;
- inflammation of heart tissue;
- brain injuries;
- rheumatism;
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- gastrointestinal ulcer;
- taking certain medications;
- strong physical activity. Acts as a protective reaction of the body;
- change of place of residence to a different climate zone or sudden change in weather;
- change in electromagnetic field;
- exposure to radiation;
- heredity;
- VSD (vegetative-vascular dystonia).
Quite often, hypotension is a symptom of VSD. Vegetovascular dystonia is a disruption of the human body by the autonomic nervous system. This symptom causes disturbances in the functioning of: cardiovascular system (cardiovascular system), heart rate (heart rate), endocrine system, thermoregulation, etc.
Causes of VSD: chronic stress, tension, neurosis, psychological trauma, negative habits, occupational hazards, heredity.
Symptoms of low blood pressure:
- Decrease in pressure to 90/60 mm Hg. and below.
- Weakness.
- Cardiopalmus.
- Sleep disturbance.
- Cold hands and feet.
- Frequent mood swings, aggression.
- Increased sweating.
- State of drowsiness.
- Frequent dizziness.
- Headache in the forehead and temples.
- Shortness of breath after slight exertion.
- Fainting.
- Nausea.
Complications:
- problems with the cardiovascular system, due to rapid heartbeat there is a strong load on the heart muscle;
- Pregnant women experience oxygen starvation of the fetus and disruption in its development. Also, pregnant women with hypotension often experience severe toxicosis and gestosis.
Low blood pressure - diagnosis:
- taking anamnesis;
- inspection;
- blood pressure measurement and daily monitoring;
- examination by doctors: neurologist, cardiologist, endocrinologist;
- blood analysis;
- Analysis of urine;
- Ultrasound of the heart;
- load tests;
- CT;
- MRI;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys, adrenal glands, thyroid gland.
Treatment.
If a concomitant disease causing hypotension is detected, it is treated. In the absence of other diseases, medications are prescribed to normalize blood pressure. Strictly follow the daily routine and proper nutrition. Stop smoking and minimize alcohol consumption. Regular walks.
Prevention:
- giving up bad habits (smoking, minimizing alcohol);
- sleep at least 7-8 hours;
- active lifestyle;
- body weight control;
- blood pressure control.
How to raise blood pressure
Oddly enough, drinking coffee and tea in the morning is not recommended, but it is better to avoid it altogether. The desire to get a “charge of vigor” in the morning first becomes a habit, and then turns into doping and requires a constant increase in the dose1.
Moderate loads with a smooth increase in duration have a positive effect. For example, walking, exercise bike, gentle jogging, skiing, swimming.
Static loads with a forced posture (working at a computer), tilting the head, lifting heavy objects are best avoided. If it is impossible to alternate them with physical activity.
In the morning, you need to learn to get up slowly so as not to cause a drop in blood pressure. Compression stockings on your legs may also help. It will reduce the amount of blood in the veins of the lower extremities. For training, you can sleep with the head of the bed elevated.
It is better to avoid static loads with a forced posture
Pathological factors of low pressure
If hypotension leads to insufficient blood circulation, hypoxia, heart rhythm disturbances, headaches and fainting, you need to sound the alarm. The critically low blood pressure limit is 85/55, which may be followed by loss of consciousness and vascular collapse. And regular attacks can lead to a stroke or heart attack.
Primary pathological hypotension is rare. Its cause is a special form of cardioneurosis, usually congenital. Secondary is not an independent disease, but a symptom of deeper health problems. The most common:
- Hypovitaminosis. Low blood pressure may be a sign of a lack of ascorbic acid, vitamins B12, A and E.
- Difficult pregnancy: with frequent attacks of toxicosis, dehydration, decreased hemoglobin levels.
- Inadequate nutrition: strict diets, fasting.
- Dystonia often causes a sharp drop in blood pressure, accompanied by tremor, dizziness, bradycardia, and loss of strength.
- Iron deficiency anemia: leads to hypoxia and systemic disorders, including a decrease in vascular tone.
- Diseases of internal organs: pancreatitis, hepatitis, stomach ulcer.
- Endocrine diseases. Hypotension is often accompanied by insufficiency of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland.
- Traumatic brain injuries. Damage to the central nervous system often manifests itself as a persistent decrease in blood pressure.
Vascular tone decreases in various acute conditions: massive blood loss, toxic shock, severe poisoning.
Physiotherapeutic procedures
- Cryochamber.
- Rubbing with warm water with a gradual decrease in temperature to 10-15*C.
- Charcot/rain/circular shower.
- Turpentine, carbon dioxide, mineral baths.
- Other tonic effects.
It is most convenient to receive a set of procedures during sanatorium-resort treatment. This allows you to take your mind off the stress of everyday life, normalize your sleep and diet. Walking and a good emotional background will make an important contribution to the healing process.
Symptoms of Low Blood Pressure
The hypotonic state is characterized by:
- dizziness, dull headaches, squeezing the back of the head and temples;
- the appearance of dark circles before the eyes;
- muscle weakness, decreased sensitivity, numbness or tingling of the fingers;
- asthenia: irresistible drowsiness, apathy, absent-mindedness;
- excessive chilliness of the hands and feet.
During a sudden attack, most hypotensive patients feel lightheaded, may lose their balance, or faint. Another deterioration in health is provoked by severe stuffiness, physical fatigue, hunger, and dehydration.
Drugs
To normalize tone, it is possible to take adaptogens in courses1:
- Eleutherococcus;
- ginseng;
- Aralia;
- pantocrine;
- lemongrass
If arterial hypotension is a consequence of other diseases, it is necessary to carry out treatment aimed at these problems.
In case of adrenal insufficiency, lifelong replacement therapy may be prescribed. Depending on the type of violation, the following is used:
- glucocorticoids (cortef);
- mineralocorticoids (cortineff).
A special case and difficulty for the doctor and the patient is the combination of arterial hypotension and hypertension. Since the treatment methods are radically opposite, choosing the right treatment method is not easy.
In any case, the prescription and correction of treatment should be made by a doctor. At the same time, success in treatment cannot be achieved without the patient’s efforts.
Pressure, don't drop!
Probably every adult has heard or knows firsthand how arterial hypertension negatively affects the body when blood pressure is above normal 120/80 mm Hg.
But not everyone knows how dangerous the opposite condition is - hypotension. Moreover, it is not entirely clear what indicators correspond to it.
The conversation will be about where the border between normal and pathological is, and what to do when the Rubicon is behind us.
Arterial peak
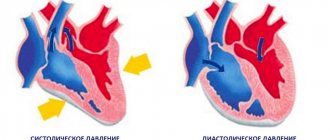
The blood pressure value is reflected in two numbers. The first demonstrates the level of pressure blood exerts on the walls of blood vessels during contraction of the heart muscle. This pressure is called systolic.
The second indicator is diastolic, it reflects the blood pressure on the vessels at rest, between heartbeats.
A normal blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg. However, this does not mean at all that 110/70 already indicates hypotension. There is some “play” in indicators that differ from the average statistical norm, both smaller and larger.
This is due to the fact that even in healthy people, blood pressure is not a constant constant. It decreases during sleep and increases when awakening or activity. Sometimes indicators can fluctuate between 30-40 mmHg. during the day!
Have you ever felt a momentary feeling of dizziness and weakness when you suddenly got out of bed? They appear due to excessive blood flow to the extremities and, accordingly, outflow from the brain. A healthy body with orthostatic hypotension—that’s what this condition is called—reacts very quickly by narrowing blood vessels and increasing pressure.
Sometimes low blood pressure (that is, lower than 120/80) becomes permanent and is not accompanied by unpleasant symptoms. This often happens at a young age. This is a variant of the norm.
However, if pressure readings reach 90/60 mm Hg. or fall even lower, we are talking about arterial hypotension.
Causes and signs of hypotension
There is an impressive list of factors that do not allow the body to independently normalize blood pressure. By the way, such a popular diagnosis as vegetative-vascular dystonia does not apply to them. Moreover: such a diagnosis does not exist, but that is a completely different story.
Returning to the real causes of hypotension, we list the most common:
- Decreased blood volume, or hypovolemia, is the most common cause. It may result from insufficient fluid intake, fasting, or excessive water loss through vomiting or diarrhea.
- Heart disease - if the heart muscle cannot pump enough blood, blood pressure drops. This happens with myocardial infarction and heart failure.
- Hormonal imbalance, primarily thyroid dysfunction
- Blood diseases - decreased hemoglobin levels (anemia).
- Taking a number of medications, in particular diuretics (can help reduce blood volume), antihypertensive drugs of various groups, including calcium channel blockers, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II blockers, beta blockers, and nitrates (nitroglycerin).
Characteristic signs of hypotension: • Dizziness, weakness • Blurred vision • Fatigue • Nausea • Pale, cool skin.
The main danger of hypotension is a decrease in quality of life and a high risk of injury in situations where loss of consciousness occurs against the background of low pressure. In severe, critical cases, hypoxia can develop, and then the brain, heart and other organs suffer from lack of oxygen. To prevent this from happening, it is important to control your blood pressure. If it drops below 90/60 mmHg, you should consult a doctor. It will help you find out why the body cannot cope with blood pressure regulation and offer a way out of the situation.
How to treat?
Let's start with the fact that, alas, there is no magic pill that would increase blood pressure. Therapy is selected individually depending on the cause of hypotension. If the problem is based on a disease, you need to start correct treatment. As soon as the cause is eliminated, the effect will also disappear. When hypotension is associated with other factors, the approach to its correction is completely different.
There is no need to treat simply “low blood pressure”, at which you feel great. Measures should be taken only in cases where hypotension is accompanied by symptoms. And you need to start with simple lifestyle changes. To prevent your pressure from falling below critical levels: • Drink plenty of water • Give up alcohol or minimize its consumption • When changing the position from horizontal to vertical, take your time - get out of bed slowly • Unlearn sitting with your legs crossed • Increase physical activity • Try not to sit and do not stand in one position.
Among the most accessible and effective remedies that help to quickly increase blood pressure are a cup of good strong coffee and adaptogens - tincture of ginseng, lemongrass, aralia, and eleutherococcus extract.
However, you shouldn’t get carried away with them: both caffeine and general tonics can be used in doses, in the first half of the day. Otherwise, the problem with hypotension may result in new troubles, such as insomnia, tachycardia and increased nervous excitability.
And to avoid the temptation to drink a couple of “extra” cups of coffee or another dose of ginseng tincture, take a radical approach to solving the problem - change your lifestyle and allow your body to bring the pressure in order on its own.
Marina Pozdeeva
Photo depositphotos.com
The opinion of the author may not coincide with the opinion of the editors