A burning sensation in the heart area is a typical symptom of a group of cardiological diseases: from coronary insufficiency of varying severity to defects and other disorders. But this is an extremely misleading symptom.
Pathologies of the heart and blood vessels account for no more than 30% of the total number of visits to the doctor.
The remaining situations are associated with endocrine abnormalities, pain syndromes due to disorders of the musculoskeletal system, and other conditions not related to organic abnormalities of the heart.
Instrumental diagnostics puts an end to the issue. Pathologies of cardiac structures are assumed first.
The cost of a mistake will be too high: lost time, health, and sometimes life. Only then can other disorders be diagnosed by exclusion.
The first priority is to contact a cardiologist. After completing the minimum required list of tests, referrals to other specialists are issued, and so on until the cause of discomfort is identified.
Why does a burning sensation appear in the chest?
In the chest cavity there is a complex of mediastinal organs, great vessels, neuromuscular bundles and organs of the respiratory system. A burning sensation in the heart area is the main symptom of damage to these structures. Pain syndrome (cardialgia) accompanies the following diseases:
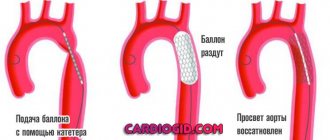
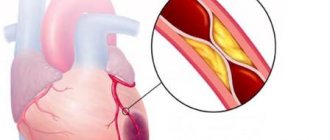
- Myocardial infarction is an acute pathology that occurs when the blood supply to the heart muscle is disrupted due to blockage of the lumen of the coronary arteries. The gold standard of treatment in the early stages is minimally invasive (percutaneous) surgery with placement of a stent in the damaged vessel.
- Angina pectoris is a variant of coronary heart disease, which is characterized by the appearance of pain after physical activity.
- Dissecting aortic aneurysm is an acute pathological violation of the integrity of the vascular wall of the thoracic vessel with the penetration of blood between the inner and outer layers of the wall. The pain syndrome is characterized by high intensity at rest and refractoriness (lack of sensitivity) to taking Nitroglycerin. Most often, the complication occurs against the background of arterial hypertension.
- Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lung tissue that occurs due to the penetration of pathological microorganisms. The disease is characterized by cough, decreased breathing, fever, shortness of breath and weakness.
- Pleurisy is an inflammatory pathology of the membrane lining the walls of the chest cavity. There are dry and exudative variants of the disease with fluid accumulation. Compression of neighboring organs causes dull pain in the chest. Patients acquire a forced position - on the affected side.
- Osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is a degenerative-dystrophic disease of the cartilage and bone tissue of the spinal ridge. The development mechanism determines pathological growths of the vertebral bodies with compression of the nerve roots, which causes pain in the area of innervation. The pain intensifies during movement.
- Diseases of the esophagus - strictures, diverticula, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Disturbances in the passage of the bolus of food or the backfilling of acidic stomach contents cause heartburn, pressing or burning pain in the sternum.
- Pathologies of the abdominal cavity - acute cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder) and gastric ulcer (damage to the integrity of the mucous membrane of the organ). In some cases, the disease is accompanied by painful sensations not only in the upper abdomen, but also behind the sternum. Most often, pain is associated with eating or drinking alcohol.
- Vegetovascular dystonia (VSD) is a functional pathology without a morphological substrate, caused by innervation disorders. Young women with nervous system lability and during pregnancy are more susceptible to the disease. In most cases, symptoms appear after stress.
Other possible causes of burning in the heart are cardiac pathologies of inflammatory and non-inflammatory origin, which include rheumatic organ defects, myocarditis and pericarditis (inflammation of the muscular lining and cardiac sac due to infection).
Intercostal neuralgia
This pathology is characterized by aseptic (non-infectious) inflammation of the peripheral nerves that run along the rib. Most often develops under the influence of local hypothermia.
With this disease, one-sided acute burning, tingling pain and tingling in the chest also occur (if the nerves are affected on the left, patients often characterize them as a burning sensation in the heart).
However, unlike angina:
- discomfort spreads only along the intercostal arch;
- there is no irradiation to the shoulder or arm;
- pain intensifies with breathing, movements in the spine;
- unpleasant sensations are well relieved by taking NSAIDs (Ibuprofen, Ketanov).
How to find the source
Determining the source of a burning sensation in the heart area consists of several stages. Diagnostic criteria take into account concomitant diseases, characteristics of pain and other symptoms, and the effect of medications.
If the cause of the pain is associated with cardiac pathology, there is a history of coronary heart disease or hypertension (persistent increase in blood pressure). The pain syndrome during a heart attack is characterized by high intensity, compression in the chest, irradiation to the left shoulder, scapula and lower jaw. An attack of angina pectoris is accompanied by a lack of air and acute stabbing pain.
Infectious pathologies of the lungs are characterized by fever and symptoms of respiratory failure (rapid shallow breathing, participation of additional muscles). The pain syndrome with severe exudative pleurisy and rib fractures intensifies during inspiration. Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract are distinguished by the following symptoms: defecation disorders, nausea and vomiting. Pain in acute cholecystitis is most often localized in the right hypochondrium with irradiation to the right shoulder and scapula.
An attack of vegetative-vascular dystonia is characterized by a variety of symptoms: from dizziness to increased heart rate and loss of consciousness. A burning pain in the heart area is possible as a manifestation of a psychosomatic disorder.
Plan of instrumental and laboratory examination:
- Measure the temperature - high values throughout the day indicate an infectious or acute inflammatory process (pneumonia, pleurisy).
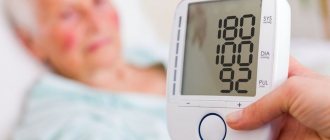
- Blood pressure - dissecting aortic aneurysm occurs against the background of a hypertensive crisis (level of indicators - 210/120 mm Hg).
- Complete blood count - an increase in ESR and leukocytes indicates inflammation.
- Electrocardiography (ECG) - to determine changes in heart rhythm during a heart attack. Tachycardia (increased heart rate), bundle branch block, and atrial fibrillation are more often recorded.
- Chest X-ray - performed to exclude the diagnosis of pneumonia, pleurisy, rib fractures, osteochondrosis and changes in heart size (with effusion pericarditis).
- Ultrasound examination of the heart and blood vessels (echocardiography - EchoCG) - determines focal changes in the myocardium during infarction, rheumatic defects and myocarditis.
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy is an endoscopic method for diagnosing diseases of the upper gastrointestinal tract. Used to detect gastric ulcers and esophageal pathologies.
- Ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs to exclude acute cholecystitis.
- Biochemical blood test - increased bilirubin indicates cholecystitis.
- Markers of myocardial necrosis (troponins I and T, CPK-MB) are used to diagnose the acute stage of a heart attack.
If, after all the studies, no organic pathology is found, and the patient continues to complain that he is in pain, the doctors write in the card “vegetative-vascular dystonia.” For information on how to act for a patient with such a “diagnosis,” see our video at the link below.
Viral diseases
Painful sensations in the chest area are also a symptom of viral diseases. Distinctive signs include high body temperature, fever, lethargy, nausea, vomiting, etc. With such signs, you should immediately call an ambulance, since many viruses are dangerous to the life and health of the patient. Whatever the cause of your pain and burning, you should know that there are no unimportant signals from the body. You need to listen to him and, if necessary, contact a specialist.
Treatment and prevention of recurrent episodes of pain
Depending on the diagnosis, the patient is prescribed treatment. The main preventive measures include compliance with medical prescriptions.
More often, for aching pain associated with diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, it is recommended to follow a diet (no fatty, fried foods, limit the consumption of salt, alcohol, coffee and strong tea). Prescribed drugs that reduce the secretion of hydrochloric acid in the stomach, which injures the compromised mucous membrane:
- antacids (“Almagel”, “Phosphalugel”);
- histamine blockers (“Famotidine”, “Ranitidine”);
- proton pump inhibitors (Omeprazole, Pantoprazole).
To prevent the development of acute coronary syndrome (a feeling of intense pressing pain in the heart area associated with impaired blood supply to the myocardium), drugs are prescribed that reduce blood viscosity and prevent the development of blood clots:
- antiplatelet agents - acetylsalicylic acid (“Aspirin”);
- indirect anticoagulants - "Warfarin".
Emergency help for acute chest pain with numbness of the left arm, shoulder girdle and neck is to take Nitroglycerin tablets. The drug expands pathologically narrowed coronary arteries and restores impaired blood flow. With angina pectoris, three to five minutes after taking the medicine, the patient feels an improvement in his condition. If the effect does not occur within 20 minutes, there is a risk of developing a heart attack, so you need to call an ambulance.
Patients with vegetative-vascular dystonia, who have pain in the chest or heart area, are recommended to use sedatives (calming agents). For weakness, dizziness, and decreased ability to work, nootropic and restorative drugs (vitamin and mineral complexes) are prescribed.
Hormonal disbalance
Endocrine disorders are another common cause of pathology. First of all, this symptom is characteristic of hyperthyroidism - increased hormonal activity of the thyroid gland.
In addition to chest pain, patients with this disorder are concerned about:
- tachycardia;
- sudden weight loss due to increased appetite;
- irritability, anxiety;
- increased sweating;
- trembling in hands;
- stool disorders, diarrhea;
- bulging eyes, swelling of the eyelids;
- brittleness of nails and hair;
- in women - cycle disorders, in men - impotence.
A burning sensation behind the sternum is one of the signs of hormonal imbalance during menopause.
Also, premenopausal women often:
- headache and dizziness;
- hot flashes and severe sweating are observed;
- worries about irritability, tearfulness;
- sleep deteriorates;
- the skin itches (itches), the number of wrinkles increases;
- fingertips go numb;
- the level of sexual desire decreases;
- body weight increases.
conclusions
There are many reasons why the heart burns. Most of them are associated with chronic pathologies that require complex and long-term treatment.
However, other sources of intense pain include pathologies that directly threaten human life. Therefore, at the first symptoms, which are accompanied by disorders of the nervous system (arms or legs begin to go numb), expressed by respiratory failure (shortness of breath, debilitating cough), consult a doctor for qualified help.
Spinal diseases
Very often, a burning sensation in the area of the heart indicates disorders in the spine, because the condition of the skeletal system has a significant impact on various organs. Such sensations occur after lifting heavy objects, bending over, or making sharp turns. A burning sensation is most often observed with osteochondrosis, displacement of intervertebral discs.
All symptoms are similar to those of angina pectoris, except for the lack of a cause-and-effect relationship with physical activity. To reduce pain, you don’t need to do anything, just change your body position. If you have such symptoms, you should consult a therapist or neurologist and begin the prescribed treatment.
Pain in the heart area radiates to the shoulder blade. Diagnostics
If your heart hurts and radiates under your shoulder blade, then you should consult a specialist as soon as possible. At the KDS Clinic, patients undergo a comprehensive examination using modern equipment and new technologies. After the initial examination, the patient informs the doctor about the nature and frequency of pain. The patient is referred for tests and examinations. When your heart hurts and radiates to your shoulder blade, visit a cardiologist, neurologist and orthopedist. Undergo ultrasound diagnostics, electrocardiogram and Holter examination. Call the clinic at number.
Paraesophageal hernia
Since topographically most of the stomach is located in the epigastrium, problems of the digestive system often mimic cardialgia.
Burning pain is observed with paraesophageal hernia - a pathological displacement of the cardiac part of the stomach into the chest cavity. This condition is accompanied by heartburn, difficulty swallowing, and hiccups. Patients also feel sick after eating a large meal.