Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) is a pathology that develops due to a violation of the outflow of blood from the veins of the extremities. Frequent symptoms are changes in skin color, cramps, swelling, pain. The most common is chronic venous insufficiency of the lower extremities.
Often, patients ignore the first symptoms of CVI and turn to a phlebologist with deteriorated health and the condition of the lower extremities. At the earliest stages, the disease is treated conservatively; when pronounced signs of impaired venous circulation appear, complex therapy is required, usually including treatment of varicose veins, nutritional correction, physical activity and wearing compression garments (1, English).
From the article you will learn the causes of chronic venous insufficiency and features of the development of the disease. Classic symptoms and method of diagnosis according to the international classification. Diagnostics and therapy are discussed in detail.
CVI – causes of chronic venous insufficiency
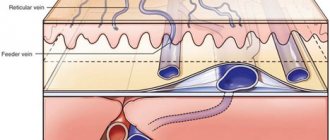
CVI is a symptom complex in which there are problems with the lumen of the veins. Usually the vessels have normal lumen. If there are disturbances, the capacity of the veins is significantly reduced. Overload of the venous system leads to impaired blood return, which is manifested by the appearance of symptoms of chronic venous insufficiency.
Impaired venous blood return leads to symptoms of CVI
Is CVI dangerous? Wikipedia states that CVI actively develops and progresses in women 30-50 years old, especially those with a hereditary predisposition. Often, symptoms of CVI appear during pregnancy, when body weight increases significantly.
Among the factors leading to CVI is weak physical activity.
The appearance of CVI is provoked by:
- travel in transport without changing position;
- long static position at the workplace;
- excess weight;
- tendency to constipation;
- staying in the heat for a long time;
- straining when lifting weights.
In addition, CVI can occur with systematic exercise and taking hormonal contraceptives; CVI often occurs during pregnancy.
CVI - symptoms
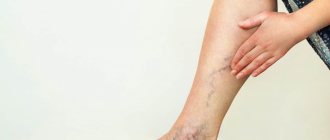
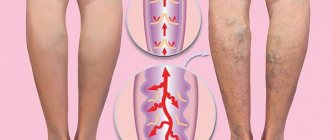
CVI may not manifest itself for a long time, but the symptoms that appear significantly affect the patient’s quality of life. The first symptoms are a feeling of heaviness in the legs, very often swelling of the legs and feet appears. Next comes bursting pain. The calf muscles may cramp at night, and the patient experiences a feeling of heat in the lower extremities.
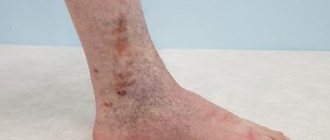
Advanced forms of venous insufficiency - trophic eczema and ulcers
Spider veins and veins begin to appear through the skin, which with varicose veins become noticeable in the form of plexuses, similar to a bunch of grapes. The skin becomes drier and becomes covered with brown “islands” that grow as the disease progresses. Eventually, a trophic ulcer forms in their center.
Classification of the disease
Acute venous insufficiency has no classification by stages. Let's consider the degrees and stages of the chronic form of the disease. To fully describe the patient’s diagnosis, doctors use the CEAP classification, that is, assigning a kind of “code”, for example: C4a, S, Eс, Ad, Pr, 8, 10, 11, 17. It is deciphered based on the following classification characteristics.
C – pathology class:
- C0 – no visible symptoms;
- C1 – spider veins;
- C2 – dilated veins from 3 mm;
- C3 – swelling in the areas of the legs and ankles;
- C4a – dermatitis, pigmentation and other skin lesions;
- C4b – increased pigmentation, thickening of the skin;
- C5 – self-healing skin wounds;
- C6 – non-healing trophic ulcers.
The following index indicates whether the patient has complaints: A – without symptoms or complaints, S – there are complaints.
E – cause of disease:
- EC – congenital;
- Er – etiology unknown;
- Es – the reason is known.
A – localization:
- As – saphenous veins;
- Ar - vessels that connect the deep veins and subcutaneous veins;
- Ad – deep veins;
- Аn – there are no pathologies of the venous system.
P – type of pathology:
- Po – cessation of blood movement through the veins;
- Pr – valve insufficiency;
- Pr,o – both;
- Рn – no disturbances in the movement of blood through the veins were detected.
The number is the area of the venous system where the pathology is detected: from 1 to 18.
CVI - stages of chronic venous insufficiency
The disease has several stages:
- first the venous wall changes;
- valves stop functioning;
- perverted blood flow occurs, leading to venous hypertension;
- varicose veins appear;
- skin pigmentation changes;
- Varicose eczema may appear;
- at this stage, thrombosis often develops, affecting the deep veins;
- complications include thrombophlebitis, pulmonary embolism.
The walls of the veins become more permeable, lymph enters the blood, trophism is disrupted and inflammation occurs (10-15% of cases). The last stage of CVI is a venous trophic ulcer (4% of cases)
Preparation for surgery and anesthesia
Preparation for intervention on deep vein valves includes bowel cleansing and shaving the hair in the area of surgical access. The night before surgery, the patient is given a mild sedative. Immediately before entering the operating room, premedication is performed with a mild sleeping pill and analgesic.
In the operating room, a catheter is installed in the bladder and a subclavian intravenous catheter for infusion of solutions during surgery. For the purpose of anesthesia, we usually use an epidural catheter - an injection into the spine and prolonged administration of painkillers.
To monitor blood pressure and ECG indicators, a special monitor is connected to the patient.
CVI - Diagnostics
Typically, patients turn to a phlebologist when obvious signs of CVI are visible to the naked eye, and the diagnosis is easy to make. Specialized clinics use ultrasound methods to diagnose CVI:
- the condition of blood vessels is studied;
- assesses how blood flows through them;
- Disturbances in the functioning of venous valves are considered.
Ultrasound scanning gives a complete picture of the causes of CVI
With an ultrasound examination, the doctor receives a three-dimensional image of the vessel, reliable information about its functioning, and can make an objective diagnosis.
Direct valvuloplasty
It involves dissection of the venous wall above the valve and direct elimination of the anatomical and functional defect. The advantage of the method is the clear identification of the defect, ideal opportunities for restoration of the venous valve leaflets under visual control.
The disadvantages are the risks of damage to the valve apparatus during vein dissection, which can be eliminated by preliminary transverse venotomy followed by dissection of the vein above the valve under visual control. Direct valvuloplasty is a complex surgical procedure, which prevents its widespread use and must be performed under a microscope.
CVI – complications of chronic venous insufficiency
Many patients have a common belief that CVI is not too dangerous, that it is just cosmetic. In fact, disturbances in the venous blood flow of the legs provoke the formation of blood clots. Therefore, CVI has two main complications: thrombosis and thrombophlebitis. In the first disease, the deep veins suffer:
- the affected area acquires a bluish tint,
- tissues swell
- movements are accompanied by pain.
With thrombophlebitis, blood clots form in the superficial veins. Wherein
- the skin turns red;
- Painful lumps form under the skin
- When walking, the patient experiences sharp pain in the legs.
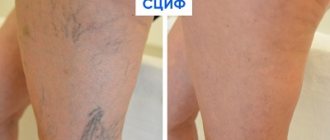
A detached blood clot can clog a large vessel and cause death. Acute manifestations of these diseases are treated only in a surgical hospital. You can see the danger of CVI - photos, the results are on websites on the Internet.
External valvuloplasty
It involves narrowing the vein around the valve in order to achieve closure of the valves. This operation has only two advantages: there is no need to cut the vein and it is easy to perform. It is significantly less effective than direct intervention.
The technique of such an operation can be different:
- Using an outer ring or coil on a vein (Vvedensky method)
- An enveloping suture of the vein above the valve without opening the lumen (extravasal valve correction)
- Wrapping the vein with bovine pericardium or a flap from a vascular prosthesis
The main disadvantage of this technique is the uncontrolled effect and the possibility of persistent narrowing of the vein.
CVI. How to treat the disease with creams?
Treatment with all kinds of ointments is very common at the household level. Many patients stop treatment at this point. Most ointments only temporarily relieve swelling and pain. CVI – how to treat it? This question is asked by all patients. Such popular remedies as heparin ointment, venoruton, venitan, hepatrombin cope well with the external manifestations of CVI at an early stage, but cannot eliminate its cause. For effective treatment that will give long-term results, a visit to a phlebologist or vascular surgeon is mandatory.
Observation after surgery
The patency of the restored venous segment must be monitored after surgery before discharge from the hospital using venous ultrasound.
Subsequently, examinations by a vascular surgeon with ultrasound should be performed at least once every 6 months. After a year, it is advisable to perform MRI venography.
The patient will be prescribed medications to reduce the likelihood of blood clots. Most often it will be warfarin (under the control of an INR analysis), sometimes we prescribe Prodaxa. It is unacceptable to stop taking these medications on your own without consulting your doctor.
CVI - how to cure without consequences?
This can be done even in difficult cases; treatment of CVI in Moscow can be carried out at a high level. True, then surgery will be needed to restore blood flow in the veins. But in the early stages, conservative treatment of CVI without surgery is sufficient. In particular, elastic compression is used. For this purpose, special medical knitwear is used in the form of stockings, golf, tights (conservative treatment).
When treating CVI, it is very important not to waste time using various ointments that give a local and short-term effect, but to seek help from a qualified specialist.
CVI - treatment at home
Don't be afraid if you are diagnosed with CVI. Treatment with folk remedies will alleviate the situation. For example, venotonic drugs will help. They strengthen the walls of blood vessels, stimulate microcirculation, and quickly relieve the feeling of tired legs and swelling. Patients are also treated with blood thinning medications.
Do you need to relieve the pain of CVI? Treatment with traditional methods:
- Apple vinegar. Twice a day for 30 minutes. Apply gauze soaked in vinegar to your feet for 30 minutes. Keep your legs higher. Reviews about the product are contradictory, but the majority note a positive, weak effect.
- Bell pepper. Dilute a teaspoon of pepper powder in a glass of hot water and drink three times a day. The product stops leg pain and improves blood flow. But CVI does not go away that easily, treatment, the results are still not the same as when treated by a professional phlebologist.
Prevention of chronic venous insufficiency
If you perform simple activities every day, the risk of developing CVI is reduced significantly. Even if CVI is discovered, treatment will not be so serious, especially in the early stages.
- You should lead a healthy lifestyle and play sports.
- Follow a diet.
- Wear comfortable shoes and use orthopedic insoles.
- Use elastic compression.
If the first signs of CVI still appear, you cannot postpone a visit to a phlebologist. He diagnoses the degree of CVI. Any delay in time is fraught with complications. Some of them are fatal. If the disease has nevertheless developed to a complex stage, you should not despair. Even complex cases can be cured using modern endovascular surgery, see the photo on our clinic’s website.
Frequently asked questions from our patients on the Internet
My legs are constantly swollen, how can I restore blood circulation in my legs? Maria from Arkhangelsk asks:
Dear Maria! To restore blood circulation in the legs, you first need to find out the cause of the swelling. As a rule, from a modern point of view, you need to start with an ultrasound duplex scanning of veins and consultation with a phlebologist.
How to identify blood clots in the legs? Oksana from Vladimir is interested in:
Dear Oksana! If you have the slightest suspicion of thrombosis, you should urgently seek medical help. A good diagnosis begins and always includes vascular ultrasound. This technique allows you to accurately determine not only blood clots in the legs, but also the cause of their occurrence. However, the method has a pronounced operator dependence, and it is better to trust professionals in their field.
How to understand that there are blood clots in the veins? Maxim from Yekaterinburg is interested in:
Dear Maxim! Only a specialist can reliably understand that there are blood clots in the veins, or exclude this situation. Thrombosis can be suspected based on the following signs:
- Swelling of the limb.
- Pain and/or redness.
- Feeling of heaviness and fullness in the limb.
- Vein thrombosis has already been previously diagnosed, since blood clots in the veins often recur.
The best solution would be to consult a phlebologist with an ultrasound scan of the venous vessels. You can make an appointment at our center for a consultation at any time convenient for you by phone.
How to check veins for blood clots in the legs? Asks Valentina from Smolensk:
Dear Valentina! You can check the veins for the presence of blood clots in the legs using ultrasound duplex or triplex scanning of the veins of the lower extremities at an appointment with a phlebologist.
How to treat chronic venous insufficiency at home? Zinaida from Tambov asks:
Dear Zinaida! Chronic venous insufficiency should be treated at home only after a good consultation with a specialist who will diagnose and give recommendations. Otherwise, you have a good chance of getting complications from the disease. When you find yourself on websites that colorfully describe how and what to treat at home, remember that most often professional doctors have nothing to do with such recommendations.
How to deal with the symptoms of chronic venous insufficiency? Nellie from Ufa asks:
Dear Nelly! It is better to start fighting the symptoms of chronic venous insufficiency in the legs before these symptoms appear, that is, with prevention: regular physiological exercise, a balanced diet, the use of compression hosiery for excessive loads, air travel. If signs of CVI appear: swelling, heaviness, varicose veins, you should consult a good specialist. This is the only way you can count on success.
PS I do not advise you to treat the symptoms of CVI at home via the Internet.
How to relieve pain from chronic venous insufficiency at home quickly? Asks Alexandra from Tyumen:
Dear Alexandra! The appearance of pain with varicose veins is most often a symptom of a developed complication, varicothrombophlebitis or deep vein thrombosis. If pain occurs due to varicose veins, stopping it at home is an extremely dangerous undertaking. It is necessary to quickly seek medical help, possibly calling an ambulance. You can quickly relieve pain with any NSAID, for example, ketoprofen or meloxicam (Movalis). But this is purely a temporary measure.
Varicose veins have started, what should I do? Maria from Nizhny Novgorod asks:
Dear Maria! If you have developed varicose veins or there are pronounced signs of varicose veins, you need to contact a professional. The most competent diagnosis and subsequent treatment can be provided to you by specialized centers for the treatment of venous pathology. After the examination, the center specialist will explain to you in detail what and how to do.
What is a good prevention for varicose veins on the legs? Nadezhda from Orenburg is interested in:
Dear Nadezhda! Prevention of varicose veins on the legs includes the following aspects:
- The closest to physiological load on the lower extremities, the involvement of the calf muscles, reducing the time of static load.
- Complete, balanced nutrition.
- For long-term static conditions and air travel, wear compression hosiery of I-II compression class.