Stage 1a uteroplacental blood flow disorder is a phenomenon in which the fetus receives insufficient oxygen. If this problem is ignored, the child may experience hypoxia, which leads to disruption of the development of internal organs or death of part of the cerebral cortex. To prevent the formation of negative consequences, it is necessary to start treatment on time.
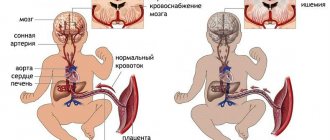
Normal uteroplacental blood flow
Pregnant women often do not even suspect the existence of Doppler ultrasound
. This study helps determine the volume and strength of blood flow using ultrasound radiation. Usually Doppler testing is carried out in the third semester of pregnancy, but in some cases this study can be carried out earlier.
With the help of Dopplemetry, it is possible to identify any pathologies of blood vessels in the uterus or placenta in the early stages. It also helps to identify abnormalities in the fetal carotid and cerebral arteries. Based on the results, the doctor will be able to determine whether the baby is experiencing a lack of blood flow or not.
If a woman’s uteroplacental blood flow is disrupted, her fetus is in constant deficiency of oxygen and nutrients.
Doppler ultrasound examination
, which helps determine blood flow in the pelvis. It can also be used to determine the resistance index, compliance with which is necessary for the normal functioning of the fetus. Having received accurate data from such an analysis, doctors use special mathematical formulas to calculate the speed and volume of blood flow. Based on the results, it can be concluded whether the woman suffers from BMD violations or not.
Violation of fetal blood flow
General information
The bloodstream of the placenta includes two closely interconnected, but not interconnected, blood flow systems: fetal and placental. The Doppler effect is based on a change in the frequency of a sound wave depending on the speed of the observed emitter. In our case, it is a change in the frequency of the reflected ultrasonic signal from an unevenly moving medium - blood in the vessels. Changes in the frequency of the reflected signal are recorded in the form of blood flow velocity curves (BVR). A change in normal KSK indicators is a nonspecific manifestation of many pathological conditions of the fetus, and in many cases preceding the appearance of clinical symptoms; it is important that this also applies to the main pathological conditions during pregnancy, namely:
- NWRP;
- fetal hypoxia;
- gestosis.
Hemodynamic disturbances in the functional system “mother-placenta-fetus” are the leading pathogenetic mechanism of disturbances in the condition and development of the fetus during various complications of pregnancy. Moreover, in the vast majority of observations, hemodynamic disorders are characterized by the universality and uniformity of changes, regardless of the condition of the fetus and the etiopathogenetic factor.
Classification of fetal blood flow disorders
First degree: disturbance of fetal-placental blood flow, not reaching critical values and a satisfactory state of fetal hemodynamics (impaired blood flow only in the umbilical cord artery).
Second degree: compensated disturbance of fetal blood flow (disturbance of the actual hemodynamics of the fetus). A decrease in the maximum speed of blood flow through all valves of the fetal heart in 50% of cases, for the left sections - to a lesser extent. The predominance of the right parts of the fetal heart remains. Pathological spectrum of blood flow in the aorta and/or internal carotid artery of the fetus. Primary changes in the blood circulation of cerebral vessels are much less common (non-placental type of fetal hypoxia). The second degree does not last long and quickly turns into the third degree. Third degree: critical state of fetal blood flow. The functional predominance of the left parts of the heart over the right is a deeper restructuring of intracardiac hemodynamics associated with the centralization of blood circulation. Increased fetal hypoxia - a decrease in transvalvular blood flow by 10.3% for the valves of the left sections and by 23.3% for the right ones. Functional insufficiency of the tricuspid valve in 66.7% of cases (regurgitation flows). Aorta - decrease in diastolic blood flow to its absence (69.6%). Reduced resistance of the internal carotid artery in 57.1% of cases. The combination of simultaneous disorders in the aorta and in the internal carotid artery is more common than in degree 2 disorders (14.3% and 42.3%, respectively).
Stages of fetal blood flow disorders
It is possible to compensate for disturbances in fetal blood flow in various stages, more in the first stage, less in the second. In the third stage, decompensation of fetal hemodynamics occurs. Perinatal losses:
- 1 degree of disturbance of fetal hemodynamics - 6.1% of cases;
- 2nd degree - 26.7%;
- 3rd degree - 39.3%.
Neonatal intensive care:
- 1st degree - 35.5%;
- 2nd degree - 45.5%;
- 3rd degree - 88.2%.
An increase in SDO (peripheral resistance) is a high risk factor for complications in the neonatal period. The most common cause of increased SDO is intrauterine infection. Prolonged spasm of cerebral vessels plays an important role in reducing compensatory capabilities, which leads to disruption of adaptation processes in the early neonatal period.
Treatment of fetal blood flow disorders
Under the influence of therapy, it is possible to improve hemodynamics with mild gestosis . At the same time, circulatory disorders in the utero-placental link are less susceptible to positive dynamics than in the fetal-placental link, which can be explained by the development of morphological changes in the vessels of the uterus due to gestosis. At the same time, normalization of blood flow in 40% of cases in the umbilical cord artery suggests a possible functional nature of changes in fetoplacental hemodynamics.
However, in severe cases of gestosis, fetoplacental hemodynamics did not change significantly after treatment. The appearance of “zero” or retrograde blood flow in the umbilical cord artery, indicating an extreme degree of fetal suffering, dictates the need to abandon therapy in favor of emergency delivery.
Timely correction of the tactics of pregnancy and childbirth, drug therapy, carried out taking into account Doppler indicators, can reduce perinatal morbidity and mortality, but do not exclude a high risk of developing severe neurological complications in the early neonatal period.
A Doppler study conducted in women with grade 3 hemodynamic impairment in the “mother-placenta-fetus” system allowed us to establish the ineffectiveness of the therapy for placental insufficiency. With conservative management of labor, perinatal mortality was 50%. There were no perinatal losses during delivery by cesarean section A comprehensive Doppler assessment of the blood flow of the uterine artery and umbilical cord artery can be considered as an objective indicator of the severity of gestosis, regardless of its clinical manifestations. The outcome of pregnancy and childbirth is determined not so much by the nosological affiliation as by the degree of hemodynamic disturbance in the “mother-placenta-fetus” system. Timely correction of the tactics of pregnancy and childbirth, drug therapy, carried out taking into account Doppler indicators, can reduce perinatal morbidity and mortality, but do not exclude a high risk of developing severe neurological complications in the early neonatal period.
With gestosis, pathological SSCs are detected in 75% of cases. In severe forms of gestosis, changes occur in parallel in the umbilical cord artery. In hypertension, the accuracy of predicting adverse perinatal outcomes during pregnancy significantly exceeds the accuracy of clinical tests (BP, creatinine clearance, urea).
Structure of the uteroplacental blood flow
Mother and child are connected not only by the placenta, but also by a complex system of blood vessels. Therefore, all joint blood circulation is usually divided into levels that cannot exist in isolation, but work only in combination. The central part of the system is the placenta. It ensures the absorption of products from the maternal blood through villi that have grown deep into the wall of the uterus.
At the same time, the blood of mother and child does not mix.
Several rows of special cells form a hematoplacental barrier, which is a serious obstacle to substances unnecessary for the fetus. Through it, the waste blood returns to the mother's venous system. The second part of the blood flow consists of the branches of the uterine arteries. If before pregnancy in the female body they are in a collapsed state and are called spiral, then from the period of 1 month they lose the muscle layer that can cause spasm.
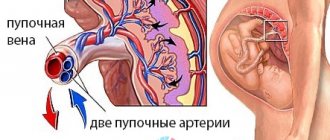
And by four months, the arteries transform into full-fledged trunks, filled with blood and heading to the placenta area. It is this mechanism, useful for feeding the fetus, that can turn out to be fatal during uterine bleeding: the walls of the vessels can no longer contract. The vessels in the umbilical cord form the third pathway of blood flow. There are 2 arteries and a vein here. They connect the baby with the placenta and form the fetal-placental circle. Reduced blood flow at this level causes the most severe damage to the fetus.
What reasons can break the blood flow between the mother, placenta and fetus?
The causes of disruption of the circulatory system between the maternal body and the fetus (fetoplacental insufficiency) have been well studied. Some factors are formed only during pregnancy. The other depends on the woman’s general health.
Pregnancy pathologies include:
- Low attachment of the placenta (obstetricians say - previa, "placentation") - the lower parts of the uterus are distinguished by a thinner muscle layer. Through it, not enough blood flows to the fetus. A similar situation develops in the case of presentation in the area of a postoperative scar (for example, from a cesarean section).
- Late toxicosis is accompanied by damage to small vessels of the uterus; the complication is the most common blood flow disorder.
- Anemia - low hemoglobin levels cause a compensatory increase in heart rate, increasing blood flow through the uterine arteries to compensate for the lack of oxygen. Circulation also changes in the uteroplacental circle.
- Incompatibility between the blood of the mother and the fetus according to Rh - an immune conflict arises with the development of hemolytic disease of the child, anemia. The same situation is possible when transfusion of different blood types from a donor.
- The load on the kidneys due to toxicosis can cause an increase in blood pressure. This helps change blood flow.
- Pathology of the umbilical cord arteries is rarely detected. If there is only one umbilical artery, then there is insufficient blood flow to the fetus.
- Multiple pregnancy - the placenta is increased in size and requires increased nutrition. Sometimes blood flow changes from one fetus to another.
It turns out that the first child is a constant donor for the twin, develops worse, because he transfers blood to his brother, and he himself is “malnourished”
Such changes are called fetotransfusion syndrome. The donor has a lower body weight. And the recipient experiences an increased load on the developing heart. Both kids have problems.
The most dangerous diseases for women are:
- Acute infections during pregnancy - pathogens can penetrate the placental barrier and destroy the vascular network.
- Malformations of the uterus - the most significant is the “bicornuate” uterus. Inside the cavity there is a partition dividing it into 2 parts. Pregnancy is possible only in one of them. The main violation is not the compression factor (the cavity has the ability to stretch sufficiently), but the lack of communication between the uterine arteries, insufficient development of the vascular network, and placental hypoxia.
- Endometriosis is a change in the inner lining of the uterus that occurs after inflammatory diseases (including sexually transmitted infections), frequent abortions, and diagnostic curettages. One of the reasons is smoking and alcohol.
- Uterine tumor - if a woman has even a small fibroid (benign tumor), then pregnancy stimulates the growth of nodes. They take over part of the blood supply, and the fetal blood flow is “robbed.” Failure directly depends on the size of the tumor.
- Diabetes mellitus affects the walls of blood vessels and often occurs in women with risk factors during pregnancy.
Clinical picture of the disorder
The symptoms of blood flow disorders depend on how pronounced the changes in the vascular bed are. On the part of the pregnant woman herself, there may be no signs of pathology at all or only gestosis. Often, hemodynamic disorders are detected due to the fact that a woman is undergoing examination due to the threat of miscarriage or premature onset of labor, which manifests itself:
- pain in the abdomen and groin area.
- the appearance of bloody-mucous discharge from the genital opening.
- Often in pregnant women with a similar pathology, colpitis appears or worsens during gestation.
On the part of the fetus, the symptoms of hemodynamic disorders are more pronounced. With the development of hypoxia, the frequency of the child’s movements decreases. During examinations at an appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist, a specialist may pay attention to an increase or decrease in the child’s heart rate. The doctor may also note that the volume of the abdomen and the height of the uterine fundus are not correlated with gestational age.
How is diagnosis carried out?
The Doppler ultrasound method most accurately helps to make the correct diagnosis and identify the level of impaired blood flow. The method is highly sensitive and very informative. Shows even small changes in the first stage before clinical manifestations. An important advantage is safety for the fetus and the expectant mother.
Using Dopplerography, it is possible to examine blood flow through arteries and veins, obtain a color graphic image, and measure fetal hemodynamics.
This plays a significant role in predicting the course of pregnancy and creates conditions for making decisions on treatment measures.
Indirect diagnostic methods include:
- computed tomography,
- Ultrasound.
The methods allow us to identify lack of fetal weight and placental dysfunction. These signs may be evidence of the development of hypoxia.
Causes of blood flow disorders in the pelvis
A huge number of factors can provoke circulatory failure in the pelvis. Separately, there are those that provoke disturbances during the formation of the placenta, and those that occur at a later date. Thus, it is customary to distinguish between primary and secondary forms of pathology. If the problem is ignored for a long time, the woman’s risk of miscarriage increases, and the fetus cannot develop its endocrine glands, metabolism, and immune functions normally. This phenomenon can be caused by:
- serious infectious diseases;
- genetic abnormalities of the fetus;
- tumors and other diseases of the uterus;
- sudden changes in hormonal levels;
- late toxicosis;
- diabetes;
- heart problems;
- thrombosis and atherosclerosis;
- consequences of surgery on the uterus;
- anomalies of the structure of the uterus on the left and right;
- diseases of the endocrine glands.
The risk of developing uteroplacental insufficiency increases even if one of the above factors is present. If there are several reasons, a woman needs to visit the treating specialist more often in order to identify deviations in time. Your doctor will send you for periodic screenings and other tests.
Classification
These deviations have varying degrees of damage and development. Mainly the following are distinguished.
| Failure of blood flow 1a degree | Accompanied by the presence of abnormalities in the uterus and placental arrangement of blood vessels. The fruit is not affected. At this stage, the pathology is not significant. Therefore, it can be easily eliminated. After timely diagnosis, you should definitely undergo a routine examination |
| Violation 1b degree | The child’s condition with this pathology remains satisfied. But the risk of danger increases |
| Development of stages 2 and 3 of the disease | Severe abnormalities in all systems. Serious complications can lead to fetal death |
Symptoms of uteroplacental disorder
Like any other pathology, BMD disorder has a number of features in its manifestation. If you know exactly the signs of this deviation, a woman will be able to identify the disease in the early stages, which will allow her to consult a doctor in time. The main danger of stage 1a uteroplacental blood flow disturbance is that the fetus experiences oxygen starvation. Such hypoxia interferes with the normal development of its internal organs and can cause miscarriage or fading of pregnancy. Pathology can be recognized by the following changes:
- the child's heart rate increases significantly;
- the fetus periodically becomes either active or lethargic;
- the volume of the abdomen does not correspond to normal readings - it is ahead of them.
Signs of degree 1a BMD impairment usually appear in the decompensated form. However, in some cases there are no manifestations of this pathology at all. It is possible to find out about its presence only after the next examination.
How does insufficient placental blood supply threaten the fetus?
All disorders of both uteroplacental and fetoplacental nature lead to oxygen deficiency of the fetus (hypoxia). Complications are caused precisely by this mechanism:
- the formation of the internal organs of the fetus is disrupted, there is a lack of weight, this is called “intrauterine growth retardation”;
- the heart reacts with rapid contractions (tachycardia) or arrhythmias, bradycardia;
- the composition of electrolytes and acid-base balance are disrupted;
- the functioning of the endocrine system is disrupted, the fetus experiences a hormonal imbalance;
- fat depots are not formed.
The most severe complications are fetal death and threatened miscarriage.
Myomatous nodes take away part of the vascular network from the fetus for its growth
Detection of blood flow disturbances
Determining uteroplacental circulatory disorders is quite simple. To do this, the doctor uses modern diagnostic methods that make it possible to identify pathology without harm to the child. Before the specialist sends you for examination, he will collect a detailed medical history and assess the degree of manifestation of the BMD violation. In general, diagnosing this problem looks like this:
- physical examination of the pregnant woman;
- ultrasound examination of the pelvis and abdominal cavity;
- ultrasound fetometry;
- Dopplerometry;
- cardiotocography;
- assessment of fetal activity;
- General, biochemical and hormonal blood tests.
An experienced specialist can easily identify this pathology based on the patient’s complaints alone. To do this, he needs to collect information about her obstetric past.
, assess the general condition of the body. Based on the results of functional tests, the doctor will be able to identify the most optimal and effective treatment that will help quickly relieve the fetus from oxygen starvation.
Treatment of uterine blood flow disorders
- Almost all degrees of blood flow disorders require mandatory treatment. The question is what degree of blood flow disturbances is detected, and whether it is accompanied by fetal growth retardation. Basic methods of treating fetal blood flow disorders:
- Normalization of the lifestyle and nutrition of a pregnant woman. It is important to walk a lot in the fresh air, sleep at least 8 hours at night and try to rest for at least an hour during the day, avoid sitting for long periods in an uncomfortable position, move a lot, eat normally and nutritiously.
- Blood pressure control is one of the most important parameters determining uterine blood flow. If you have arterial hypertension, you must constantly take medications prescribed by your doctor and independently monitor your blood pressure readings.
- Treatment of intrauterine infection with antiviral drugs and antibiotics.
- The use of antispasmodics - No-shpy, Drotaverine, Papaverine. These drugs relax the wall of the uterus and spiral arteries, increasing blood flow.
- Taking magnesium supplements - magnesium has a relaxing effect on the uterine wall and a powerful protective effect on the central nervous system of the fetus. The last factor is important in the development of hypoxia.
- The use of vascular drugs is a large group of disaggregants, angioprotectors and drugs that improve microcirculation and tissue trophism. The most common drugs in obstetrics are Pentoxifylline, Dipyridamole, Actovegin and their derivatives.
- In case of Rh conflict, plasmapheresis is prescribed - purification of the mother's blood using a special device to reduce the amount of antibodies damaging the fetal red blood cells.
Drug treatment
Most often, grade 1 A blood flow disturbances during pregnancy are corrected with the help of medications. When initial signs of a disorder are identified, treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis. More severe circulatory failure requires hospitalization in a hospital.
The following drugs are used for treatment:
- antispasmodics – “Eufillin”, “No-shpa”;
- vascular – “Actovegin”;
- antiplatelet agents – “Curantil”;
- vitamins and microelements – “Ascorbic acid”, “Magne B6”;
- hepatoprotectors – “Hofitol”, “Essentiale”;
- tocolytics – “Partusisten”, “Ginipral”;
- improving blood microcirculation - “Trental”;
- antihypoxants – “Instenon”;
- metabolic – “ATP”.
Usually, to improve the condition, two courses of therapy are carried out - immediately after the diagnosis is made and at 32-34 weeks. After this, the doctor decides on the method of delivery. This is especially important if the circulatory disorder is severe. If blood flow is impaired to the 1st degree, childbirth is carried out naturally.
How to help the body?
Treatment of uteroplacental disorders should be started in a timely manner to avoid negative consequences. If a woman is at increased risk of developing this pathology, then she should visit the gynecologist more often. The treatment method depends on the reasons that provoked this phenomenon. In most cases, medications that relieve uterine tone or improve blood clotting help improve blood circulation.
When the first signs of changes in blood circulation in the pelvis appear, a pregnant woman should immediately consult a doctor.
If a woman is diagnosed with a violation of the fetal-placental blood flow, she is immediately hospitalized at 36 weeks
. She will have to stay in the hospital until she gives birth. It should be noted that labor activity with such pathology requires special care. If a woman did not take any medications during pregnancy, she is prescribed a cesarean section, which means that a natural birth is impossible.
Features of blood circulation between mother and child during pregnancy
Disturbance in the blood flow of the placenta causes a lack of nutrition and oxygen in the child and causes his death.
The state of placental-uterine blood flow requires close attention during pregnancy. To assess his condition, routine diagnostics are carried out, and preventive and therapeutic measures are taken. The work of blood circulation between mother and baby is based on the functioning of the umbilical artery, veins, and placenta. The uterine arteries are able to contract, blocking the flow of blood due to the thickness of the muscle layer they have. This structure of the uterine arteries is designed to reduce blood loss during menstruation.
During pregnancy at 4-5 weeks, during the gestation of the egg, the muscle layer in the arteries disappears under the influence of hormones. At 16 weeks, another transformation of the arteries occurs, during which they open to constant filling with blood.
What happens in the arteries:
- connection of two flows of different directions;
- diffusion of substances necessary for a growing baby;
- enrichment of the fetal bloodstream with oxygen and beneficial substances brought by the maternal circulation.
Part of the work of blood circulation falls on the arteries and veins of the umbilical cord. Blood flows through the arteries to the baby, and through the veins it returns to the placenta. Violation of the fetal-placental blood flow leads to inhibition of the growth of the child’s organs and poses a threat to his health.
Prevention of uteroplacental pathology
To give birth to a healthy baby, a pregnant woman needs to be more careful and listen to her body. Try to watch your diet: it should be nutritious, rich and healthy. You can also take vitamin complexes or Ginipral, which will eliminate the deficiency of any element.
Also try to drink as much clean water as possible - at least 2 liters per day. Do not forget to control your body weight - during pregnancy it should not increase by more than 10 kg.
Doctor's recommendations will help you get rid of BMD level 1a violation
. Do not forget to regularly visit your treating specialist to monitor the development of this pathology. If normal blood flow is disrupted, the woman may be placed on preservation. Remember that you should not prescribe treatment for yourself based on the advice of friends or information from the Internet. This will lead to the development of serious complications.
Symptoms
At the first stage of development, symptoms practically do not appear. Deviations can only be noticed during a special ultrasound examination.
After 28 weeks of gestation, a woman feels the baby’s movements up to 10 times a day. If activity decreases, you should immediately contact a gynecologist. It is very difficult to detect the signs on your own.
These include:
- slow abdominal growth;
- insufficient or excessive amount of amniotic fluid;
- gestosis;
- high blood pressure;
- swelling;
- sudden weight gain;
- bloody issues.
Considering the risks, doctors regularly monitor the woman’s condition and the baby’s development. At each examination, he takes measurements and prescribes tests. This makes it possible to timely detect even minor deviations and disturbances of the gestational period.
Prevention of pathology
In order to avoid problems with blood flow, it is important for a woman to eat well. The diet should be enriched with vitamins to the maximum, contain the necessary microelements, as well as the right amount of proteins, fats and carbohydrates. It is important to drink enough fluids if there is no swelling.
Women from the most vulnerable groups - those under 18 years of age and over 35 years of age, those with bad habits, those suffering from chronic diseases - should take the necessary medications prophylactically to prevent problems with blood flow.
A woman should monitor her body weight. A total weight gain of more than 10 kilograms by the end of pregnancy is considered a risk factor.
In conclusion, it should be noted that placental insufficiency is a serious problem, sometimes fraught with fatal complications for both the mother and the unborn child. Therefore, it is important already at the planning stage to analyze your lifestyle and eliminate possible risks, and during pregnancy to monitor your condition and not neglect medical recommendations.