Do not self-medicate. At the first signs of illness, consult a doctor.
This test has some distinctive features from other methods used to study the clotting time of the main biological fluid of the human body. For example, such a blood test involves the use of capillary blood, while others involve the study of venous material.
It is also worth noting that no specific preparation is required from patients. However, there are several factors that influence the determination of blood clotting in this way.
These include:
- age category - in infants, as a result of the lack of certain substances and features of the functioning of internal organs, the indicator may be increased, that is, coagulation will take longer;
- poor nutrition, namely, insufficient intake of vitamins and nutrients into the body provokes a decrease in coagulation;
- Excessive physical activity also negatively affects the period of time that should be spent on clotting.
The essence of the analysis
As mentioned above, a coagulogram method such as blood clotting according to Sukharev does not require taking blood from a vein, but involves studying capillary biological material, that is, taken from a finger.
Such a test is carried out to assess the state of enzymes that are part of the main fluid of the human body. However, the data from this study are not enough to identify the cause of the violation.
Such an analysis indicates the patient’s body’s ability to protect itself from heavy blood loss. It should be noted that the quality and speed of coagulation are directly related to the functioning of the endocrine and nervous systems, therefore significant deviations from the norm in women, men and children may be associated with the functioning of these organs.
This study is part of a coagulogram designed to assess hemostasis. This means that the Sukharev method allows you to establish the time interval between blood sampling and the beginning of the formation of a fibrin clot.
The essence of the technique is that the biological material being studied is placed in a special vessel called a “capillary”. Over a period of time, he leans left and right in the same rhythm. In this case, the specialist uses a stopwatch to record the period of time that passes from the moment the device begins to move until the blood clot appears.
Blood clotting according to Sukharev
Blood clotting time (according to Sukharev) is a fairly simple blood test that is taken from a finger prick. The coagulation indicator itself is needed to assess the state of enzymes, but it does not provide information about the mechanisms of its disruption.
In general, the clotting process shows how much the body can protect itself, including from blood loss. Coagulability directly depends on the functioning of the endocrine as well as the nervous system. To determine the state and assess hemostasis (the general coagulation system), a coagulogram is prescribed, as well as blood clotting time (according to Sukharev).
In essence, Sukharev’s method allows you to estimate the interval between blood sampling and the beginning of its thickening, or more precisely, the appearance of fibrin (clot) in it.
Previously, more than thirty methods for determining coagulability were used in medicine; today laboratories use only two, the most reliable and informative ones - according to Sukharev and the Lee-White method. The Sukharev method determines the clotting time of capillary blood only, and the Lee-White method determines only venous blood. This is their difference, but in general both of these methods are quite informative; without them it is impossible to obtain a complete homeostatic picture.
No preparation is required for this analysis, except that the material is collected in the morning and on an empty stomach. Of the liquids, you can only drink water, since all kinds of juices, as well as tea or coffee, can distort the picture of the coagulogram. The procedure itself takes very little time.
How is the research conducted?
The material for the study is a small amount of blood from the patient’s finger. The blood is placed in a special stand, the so-called Panchenkov apparatus. Since the very first drop may contain tissue fluid, only subsequent portions are examined, and the first drop is blotted and wiped off the finger.
The material is collected into a special vessel - a capillary, which tilts in a given rhythm, either left or right at a certain angle. The stopwatch measures the time when the blood stops moving freely inside the vessel, that is, it begins to clot. The normal blood clotting time (according to Sukharev) is: the beginning of fibrin formation is from 30 to 120 seconds, the end of the process is from 3 to 5 minutes.
It should be noted that the results, that is, blood clotting time (according to Sukharev), may vary depending on what medications the person being examined takes. For example, the period from fibrin formation to the end of the coagulation process may be increased due to the use of anticoagulants (warfarin, fraxiparin and others). Liver pathologies or more severe diseases such as hemophilia also increase clotting time.
The blood clotting time (according to Sukharev) can be much lower than normal, as a rule, this happens in women taking oral contraceptives, and this is also possible with large blood loss.
It should be taken into account that clotting may be increased due to the fact that prothrombinase has begun to form in large quantities in the body. All information about the time and speed of blood flow clotting is needed, first of all, by the doctor to clarify the diagnosis and monitor the effectiveness of therapy. In any case, the interpretation of such a complex indicator is the task of a specialist, and not the patient himself.
Norm and possible reasons for deviation
Normal blood clotting according to Sukharev
According to Sukharev, the blood clotting norm will be common for all people, regardless of gender, age category or period of gestation.
Thus, the generally acceptable blood clotting time varies from 2 to 5 minutes. In particular, the beginning of coagulation is from 30 seconds to 2 minutes, and the completion of such a process is from 3 to 5 minutes.
Hypercoagulability, or rapid fibrin clot formation, may indicate health problems such as:
- autoimmune diseases;
- the beginning of progression of DIC syndrome;
- genetic pathologies;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- disruption of the functioning of the endocrine system;
- diseases of infectious nature;
- severe intoxication of the body;
- increased platelet production;
- disruption of fibrinogen formation;
- liver damage;
- long-term treatment with heparin.
A low blood clotting index according to Sukharev or hypocoagulation is often provoked by:
- thrombocytopenia;
- leukemia;
- severe DIC syndrome;
- congenital clotting problems;
- anemia of any form;
- liver failure or other pathologies of this organ;
- deficiency of vitamin K and calcium in the body;
- overdose of drugs that have an anticoagulant effect.
However, to accurately determine the provoking factor, you will need not only such a blood test, but also:
- more extensive laboratory tests;
- a wide range of instrumental examinations;
- consultation with specialists from various fields of medicine.
Blood clotting indicators during pregnancy
Every pregnant woman registered at the antenatal clinic is necessarily referred by a gynecologist for an analysis called a hemostasiogram. The results of a hemostasiogram make it possible to determine the presence of disorders in the blood coagulation system, if any.
The role of hemostasis during pregnancy
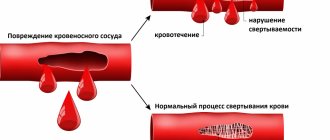
Hemostasis acts as a “thickener” of blood; thanks to this system, a person avoids significant blood loss in cases of vascular damage. In tandem with the coagulation system, an anticoagulant acts in the body - a “thinner” of the blood. When the balance is disturbed, the systems malfunction, as a result, the blood can become too viscous, which leads to the formation of blood clots, or too liquid, in both cases the blood clotting time changes.
What are the dangers of impaired hemostasis for pregnant women?
Increased blood clotting during pregnancy can provoke disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome, in which thickening blood in the vessels causes disruption of placental blood flow. The condition is dangerous for the baby, as he cannot receive adequate nutrition, which immediately affects his development. In severe cases, pregnancy may stall, and ultimately the fetus dies. Timely testing for hemostasis gives a great chance to avoid such complications.
Disorders of the coagulation system can cause premature separation of the placenta, even if it is in a normal location.
When is it necessary to take a blood clotting test?
It is recommended to perform a hemostasiogram before the expected pregnancy. In case of poor performance, you can undergo a course of therapy, which the doctor will select individually. The risk group that requires mandatory preliminary screening for coagulation includes women:
- having relatives who have suffered a stroke, heart attack, thrombosis, varicose veins;
- suffered a miscarriage or frozen pregnancy;
- athletes and those working in heavy work.
During pregnancy, it is also necessary to undergo diagnostics, especially if the doctor diagnoses:
- recurrent miscarriage - the presence of two or more unsuccessful pregnancies (miscarriage, fading);
- gestosis - swelling of the extremities, protein in the urine, high blood pressure;
- threat of miscarriage.
If there is gestosis during pregnancy, blood clotting increases in 70% of cases, which aggravates treatment. You can also prevent the situation by taking a timely test and undergoing therapy.
Methods for treating hemostasis disorders in pregnant women
With timely diagnosis of hemostasis disorders, many complications of pregnancy can be avoided. In European medical practice, DIC syndrome is treated with low molecular weight heparins, which are absolutely safe for the fetus. Treatment can be done at home with the permission of a gynecologist, subject to control tests (every 2 weeks). At the same time, doctors prescribe antioxidants, aspirin-containing drugs, folic acid, and vitamin B.
If the patient does not have the opportunity to buy expensive low molecular weight heparins, the specialist can replace them with regular heparin. In this case, strict monitoring of the results and condition of the pregnant woman is necessary, since the dose of an unfractionated drug is very difficult to select immediately; you will have to visit the clinic twice a week. For control, you need to periodically take a blood clotting test.
Decoding the results
Studying blood for clotting using Sukharev’s method can give the following results:
- normal coagulation time - this means that the person has no signs of pathologies that could cause a disruption in the coagulation process;
- a decrease in time - indicates a fairly high probability of the formation of complications such as the formation of blood clots or thromboembolism (the fact that the blood clots very quickly may be a sign of serious disorders);
- an increase in the segment indicates a disruption in the functioning of prothrombins, against which the development of life-threatening hemorrhages is possible.
It follows from this that such a blood test allows clinicians to fully and from all sides assess the condition of not only the blood itself, but also assess the functioning of all internal organs and systems.
Indications for testing
The time interval for blood clotting is determined in preparation for surgery on internal organs.
The following pathologies are considered indications for a hematological test:
- drug, chemical or alcohol intoxication of the liver;
- hepatitis;
- cirrhosis;
- stomach ulcer;
- gastritis;
- erosive-perforative processes in the intestines;
- varicose deformation of venous beds;
- tendency to thrombosis;
- diabetes;
- endocrine disorders;
- metabolic and metabolic disorders.
This study is prescribed before using anticoagulant drugs.
Determination of blood clotting is indicated for women:
- For menstrual irregularities. The test is prescribed as part of differential diagnosis.
- Before childbirth. Diagnostic information about the rheological properties of blood allows you to avoid numerous complications.
- For the procedure of artificial abortion. Surgical intervention is traumatic and associated with massive blood loss.
- Before a caesarean section. Determination of hemostatic characteristics plays a significant role in ensuring the safety of mother and child.
- For hypermenorrhea. Dysfunctional-pathological uterine bleeding requires clarification of the cause and selection of adequate treatment tactics. A coagulogram using the Sukharev method is carried out as part of a comprehensive laboratory and hardware diagnostics.
- In preparation for artificial conception. Hemostatic disorders can provoke bleeding during in vitro fertilization, during embryogenesis, and subsequent labor. Excessive thrombus formation causes blockage of the blood vessels of the placenta, which leads to fetal death and miscarriage.
A coagulogram using the Sukharev method is used in the selection of oral contraceptives, many of which affect the rheological properties of blood. The study is indicated for patients taking Heparin for a long time.
A hematological test is carried out to clarify the clinical picture of DIC syndrome - a pathological process with nonspecific physiological characteristics, which is characterized by the formation of disseminated blood clots. Among the numerous indications for laboratory testing of blood clotting time are autoimmune diseases, cardiovascular dysfunctions, and genetic pathologies.
The test is performed if excessive viscosity of the hematological fluid is suspected, due to excessive concentration of fibrin protein or increased secretion of platelets. A coagulogram is prescribed during a comprehensive examination of patients prone to spontaneous nosebleeds.
Preparing for the test
Blood sampling for study by laboratory methods is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach. The procedure is extremely simple and quick. No special preparation is required for the test. Before the test, you are allowed to drink a small amount of liquid without sugar or gases.
3 days before the scheduled date, you must stop taking medications that affect the rheological properties of the blood. Women are not recommended to take the test during menstruation. 24 hours before taking blood from your finger, you should not eat fried, salty, or hard-to-digest foods.
To obtain an accurate result, you should not take the test against the background of heavy physical exertion, nervous strain, or strong emotional excitement. Within 30 min. You should not smoke before the procedure.