With atherosclerosis, the issue of nutrition is acute: what can you eat without harm to your well-being if there is a metabolic disorder in the body. There is no cholesterol in vegetable oil because it is contained in animal products; they contain fats with “harmful” lipids that settle in the form of atherosclerotic plaques. Experts clarify that consuming plant products does not pose any danger and you can eat them without fear - they do not increase cholesterol.
Studies have shown that with regular consumption of olive fat, the concentration of low-density cholesterol decreases due to an increase in the content of substances that destroy cholesterol plaques.
Difference between vegetable and animal fats
Fats are foods that contain a high percentage of fatty acids.
- Unsaturated fatty acids are capable of attaching various chemical elements to their molecule, becoming “saturated” with them, changing and regulating the metabolism of almost all substances. In addition, they act as cleaners, removing free cholesterol from the blood and washing away the already deposited cholesterol from the vascular wall. Animal and human cells do not synthesize polyunsaturated fatty acids; they enter their bodies only with plant foods, which is why they are called essential.
- Saturated fatty acids interact weakly with other substances. They are the main energy source awaiting command in fat depots; they are partially involved in hormonal synthesis and ensure the elasticity of cell membranes. Saturated fats are produced by the tissues of the human body in sufficient quantities and may not be present in the diet.
Fatty foods contain all types of acids, just in different quantities. Animal fats contain more saturated fats , which have a dense consistency with a low melting point.
In most vegetable fats, unsaturated fats predominate - they are liquid and begin to solidify only in the cold.
In order to reduce cholesterol, you need to learn how to create a menu with a low concentration of saturated fatty acids. Otherwise, they will remain unclaimed and will circulate in the bloodstream, dangerously coming into contact with the vascular walls.
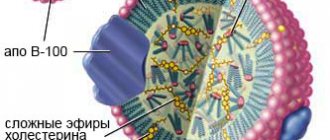
Unspent saturated fats are converted into cholesterol as a result of chemical reactions. The process occurs with varying intensity in almost all tissues of animals and humans, but its main supplier is the liver. Synthesized cholesterol is carried by the blood throughout the body, penetrating every cell. This means that animal fats contain both fatty acids and their own cholesterol. There is a lot of it in butter, pork, beef and lamb fat, and cold-water fish.
Plants do not have organs like animals, therefore, it is not for nothing that companies producing vegetable oils write “cholesterol-free” on their labels. After all, this is a product of pressing oilseeds (seeds, nuts, some fruits and herbs) with subsequent industrial processing of raw materials:
- olives;
- corn;
- peanuts;
- soy;
- sesame;
- buckwheat;
- sea buckthorn;
- milk thistle;
- flax;
- rapeseed;
- walnuts, almonds, pine nuts;
- grape seeds, cherries, apricots...
But in our country, sunflower is , and it is advisable to know everything about it.
What does imbalance lead to?
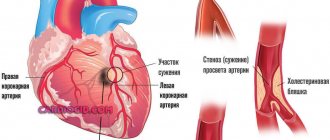
Unused cholesterol (that which has not been converted into bile and is not used for the synthesis of hormones and vitamins) is excreted from the body. Every day, approximately 1000 mg of cholesterol should be synthesized in the body, and 100 mg should be excreted. In this case, we can talk about cholesterol balance. In cases where a person receives more of it from food than necessary, or when the liver is not in order, free low-density lipoproteins accumulate in the blood and on the walls of blood vessels, narrowing the lumen. Disruption of the normal process of production, absorption and excretion of cholesterol leads to diseases such as obesity, hypertension, atherosclerosis, cholelithiasis, liver and kidney diseases, diabetes mellitus, etc.
Cholesterol in sunflower oil
Sunflower seed fat is a cheap and accessible food product, unlike its relatives, which are produced mainly abroad. For us, it tastes more familiar, we have learned to use it rationally in the preparation of cold and hot dishes, in cooking and canning. Is it possible to include such food in the diet for atherosclerosis? Is there cholesterol in our native sunflower oil, and how harmful is it?
Some technologies for the production of edible fats insist on the presence of cholesterol in sunflower oil, although no one specifies where it came from. A natural question arises: how much cholesterol does it contain? Author of a manual for food industry specialists “Fats and Oils. Production. Composition and properties. Application" Richard O'Brien claims that it contains 0.0008-0.0044% cholesterol. In terms of the daily dose of the product, this amounts to 0.0004-0.0011 g. The dose is so small that it can be ignored.
Sunflower oil is actually 100% fatty acids , among which mono- and polyunsaturated ones occupy the leading place. The share of saturated ones accounts for up to 10%. The content of microelements and vitamins A, D, E and K is calculated in milligrams, and the more intensive the processing of the product, the less of these substances remains.
- First pressing is the most environmentally friendly method of oil production, in which the original chemical compounds are preserved and new ones are not formed. After cold pressing, the oil is settled and filtered. In essence, it is raw vegetable fat, which cannot be stored for a long time and is unsuitable for heat treatment of foods, but it has the aroma and taste of roasted seeds.
- During hot pressing, it is heated to 110°, and the constituent components react with each other. As a result, the color becomes richer, and the taste and smell are brighter. On the labels of products obtained only by pressing, “first pressing” is indicated. It is completely absorbed by the body and is considered the most useful.
- Extraction is the next production stage, which involves extracting oil from the cake after pressing the seeds. The cake is mixed with organic solvents, which draw out the oily liquid to the maximum and leave a fat-free residue. The resulting mixture is sent to the extractor, where the solvents are separated back. The final product, as in the first stage, is settled and filtered. In stores it can be found marked “unrefined.”
- Refining is necessary for bleaching, removing pesticides and heavy metals, extending shelf life, and separating free fats that give off an unpleasant taste and smoke when fried. If sunflower oil goes on sale after this purification step, it is called “refined non-deodorized.” With partial refining, the product loses its vitamin composition and microelements.
- Deodorization is a stage of deep refining during which odorants are removed from the product. It is deodorized refined oil that we use most often, as it is universal for preparing any dishes.
- Freezing completely removes all the additives and leaves only the fatty acids. In freezing sunflower oil, there is either a refining stage or it is not. In the first case, refined, deodorized and frozen oil becomes impersonal: without color, smell and taste. Its inability to change the taste of cooked foods is used in the food industry. Unrefined frozen butter is also used in the home kitchen.
A little about margarine
What about margarine? This product does not contain cholesterol, but for some reason doctors are extremely unfriendly towards it.
The fact is that margarine, which is made from a mixture of vegetable and, less often, animal fats, contains trans fats. These substances are lipid molecules chemically modified during production, which have an extremely negative effect on the metabolic state. 100 g of product with a calorie content of 717 kcal contains 81 g of fat, of which 15 g are saturated and 15 g are chemically transformed.
Therefore, margarine and its analogues (cooking fat, edible lard, etc.) are not recommended for consumption even by healthy people. And such products should be completely excluded from the diet of patients with atherosclerosis.
A cholesterol-lowering diet is an important stage in the treatment of atherosclerosis. In this case, the doctor’s task remains to explain the general rules of nutrition and draw up individual recommendations, and the patient will have to apply the acquired knowledge in practice. Above we looked at how butter, vegetable oil and margarine affect fat metabolism in the body, as well as what beneficial and harmful properties these products have. Any oil for lowering cholesterol should be used according to the rules of a healthy diet and be beneficial to the person.
The benefits and harms of different types of vegetable oils
The benefits of any product are assessed by the ratio of substances necessary for the body and harmful. From this point of view, almost all vegetable oils are healthy: they contain few saturated fatty acids and many unsaturated and polyunsaturated ones. The exceptions are coconut and palm, and cholesterol has nothing to do with it: they are overloaded with saturated fats.
Sunflower, corn and olive oils are the main suppliers of polyunsaturated and unsaturated acids, since the taste allows them to be added to dishes in sufficient quantities. Their regular use helps improve brain function, normalize intestinal motility, strengthen the heart muscle and vascular walls, cleanse the skin, and get rid of bad cholesterol. Their role has also been proven in accelerating metabolism, preventing osteoporosis, improving visual acuity and coordination of movements. And with proper use of olive oil, the risk of developing breast cancer is also reduced.
Mustard oil, although not actually bitter, has a noticeable antiseptic and bactericidal effect. Sesame, in addition to unsaturated fat, contains phosphorus and calcium - the main microelements of bone tissue. Soybean and rapeseed (canola) are leaders in the fight against high cholesterol. The medicinal properties of sea buckthorn and flaxseed oils are more used in the manufacture of topical medicines for dermatological and gastroenterological patients.
Nut oils have a specific taste and are used in small quantities, although their qualities are not inferior to other vegetable fats. They lower cholesterol levels and also thin the blood, preventing thrombosis.
Creamy
But butter consists of animal fats, so it increases cholesterol in the blood. It is made from heavy cream.
Interestingly, its calorie content is slightly lower than vegetable oils (717 kcal/100 g), but in the lipid formula there is a significant bias towards saturated fats. 100 g of butter contains:
- saturated fat – 51 g;
- poly-NN ZHIK–3 g;
- mono-NN ZHIK – 21 g;
- cholesterol – 215 g.
Note! The rate of consumption of exogenous cholesterol is up to 300 g. With atherosclerosis, this figure decreases to 150-200 mg.
Among the beneficial properties of the product are:
- positive effect on the gastrointestinal mucosa: oil heals cracks and small ulcers located in the stomach or intestines;
- reducing the risk of developing cancer;
- improved metabolism;
- activation of the nervous system.
However, this product, rich in “bad” lipids and saturated fats, can worsen the course of atherosclerosis, so it is not recommended to consume butter if you have high cholesterol. It is better to replace it with vegetable oils that reduce OX levels. Even a healthy person is recommended to eat no more than 15 g of butter per day.
Is there cholesterol-free oil?
To summarize, we can say with complete confidence: there is cholesterol-free oil, and this is any vegetable oil. Even if someone has proven its presence in microdoses, it will in any case get lost somewhere in the gastrointestinal tract and will not affect the blood test in any way. But to the question whether vegetable oil contains substances that affect plasma cholesterol levels, the answer is positive.
Other characteristics
You can distinguish a product that has undergone minimal processing by the smell of the seeds and the formation of smoke during cooking or frying. Despite the fact that sunflower or other vegetable oil is recognized as a cholesterol-free product, it must be consumed very carefully:
- Firstly, 100 g of product contains 900 kcal.
- Secondly, it cannot be used frequently to cleanse the body, so that diseases of the stomach and intestines do not develop.
- Thirdly, it should be used only within the period indicated on the package.
- Fourthly, it must be stored in a dark place where the temperature does not exceed +20 ºС, but it should not be less than +5 ºС.
- Fifthly, after purchasing the product, you need to pour it into a glass jar, which is placed in the refrigerator.
The level of cholesterol (lipophilic cholesterol alcohol, TC) in the blood is an important laboratory indicator of the state of the cardiovascular system and metabolism. Increasingly, patients are faced with an increase in “bad” fats in the body and require careful diagnosis and treatment of this condition. One of the methods for correcting dyslipidemia is following a diet that limits the consumption of animal fats. What about the cholesterol content of butter? Can patients with atherosclerosis eat this product?
Fatty foods as one of the causes of disease
An increase in “bad” cholesterol is often associated with dietary errors. What foods contain cholesterol and what should be on your “stop list”? First of all, these are offal - brains, kidneys, liver, chicken gizzards. Cholesterol is also contained in fatty meats and poultry, semi-finished meat products, smoked meats, sausage products, pates, canned food, shrimp, caviar, various sauces, and egg yolks. Unfortunately for those with a sweet tooth, confectionery, baked goods, and low-grade chocolate can also increase cholesterol. Finally, high-fat dairy products cannot be part of a healthy diet. We are talking about butter, sour cream, cheeses, cream, cottage cheese. Of course, if you consume the listed products in moderation and prepare them correctly, then there will be no harm from them. But if you regularly, and even in large quantities, eat, say, fatty meat as a snack with a salad dressed with mayonnaise, then there is no doubt that over time the body will react to this by increasing LDL.