Myocardial infarction is a dangerous disease in which the blood supply to the body is disrupted, which leads to the development of tissue necrosis. Official statistics show that in 40% of cases the cause of death is a heart attack.
Thanks to the capabilities of medicine, in most cases the patient can be saved. But he will need to undergo a long course of rehabilitation to restore his functionality and return to a full life.
It is impossible to say exactly how long the recovery process after a heart attack will take, since its duration depends on the severity of the patient’s condition. With a small-focal uncomplicated heart attack, it is possible to return to your previous life within six months. With an extensive heart attack with large areas of necrosis, accompanied by complications, recovery may take 1-2 years.
Rehabilitation after myocardial infarction
Rehabilitation after myocardial infarction (MI) is a whole program for restoring health after a cardiovascular event.
Rehabilitation measures should begin from the moment a patient with a heart attack is admitted to the hospital. Each stage has its own tasks, but they all serve the same goal - to quickly and efficiently restore all functions affected by the disease. This is especially true for the functioning of the circulatory system, restoration of physical activity and ability to work. The most important principles are consistency and continuity. For each patient, a unique set of rehabilitation measures is developed.
The timing and intensity of rehabilitation after a heart attack depend on the speed and quality of first aid, the severity of the disease, the condition of the body, the presence of concomitant diseases, severity class, characteristics of professional activity and other factors. Thus, patients with mild MI and low cardiovascular risk can undergo an accelerated program in 7-10 days (including early discharge within 3-5 days), and with a large heart attack and a high risk of complications, the time period can increase to 28-30 days or more.
Features of heart attack in old age
Older people tend to suffer from serious illnesses. A heart attack is no exception, but do not despair. Even if it happened, there is a good chance of a successful outcome. But you should know what the main features of the course of the disease in older people are:
- the presence of angina over a long period;
- risk of small-focal heart attacks;
- arterial hypertension;
- no pain;
- hidden nature of the pathology, symptoms similar to thoracic radiculitis;
- the course of the disease simultaneously with cerebrovascular insufficiency;
- the risk of cardiogenic shock, which in 90% of cases ends in death;
- diabetes;
- relapses.
It is almost impossible to diagnose a heart attack at an early stage, so doctors recommend being thoroughly examined every year for risks.
Modern medicine has sufficient screening capabilities. You should not neglect them and undergo medical examinations in a timely manner.
Angiography procedure
During medical imaging, the doctor observes the condition of the blood vessels. During the procedure, a dye is injected into the circulatory system, which highlights narrowed areas and areas of blockage in the coronary arteries during X-ray diagnostics. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging are used for the same purpose.
A blood test can detect heart muscle proteins of type I or T troponin 360 minutes after myocardial infarction. This study actually confirms the diagnosis already made. However, you should not delay the tests, since lost time with this diagnosis will work against the patient.
Carrying out an echocardiogram
This diagnostic method is similar to an ECG. It determines the degree of damage to the heart during a heart attack.
Treadmill stress test
While running, the patient's ECG is recorded.
Important ! Even some regularly performed cardiac examinations, for example, angiography, do not completely identify the risk of a heart attack or heart problems, especially in females. The symptoms of the disease in older people are not typical. 40% of patients do not feel any pain. If there is pain, it is much less intense than in young people. In addition, the pain is often localized in different places (back, abdomen, shoulder).
It happens that signs of a heart attack can include neurological symptoms (confusion), gastrointestinal disorders (belching), and nonspecific phenomena (general weakness).
Stages of rehabilitation1
All stages are carried out under the supervision of specialists, starting from the resuscitation team in the intensive care unit (ICU) and ending with a cardiologist in the clinic.
Stage 1.
Inpatient – begins from the moment of admission to the hospital (cardiac intensive care unit, ICU, cardiology department). Main activities: diagnosis, treatment after restoration of patency of the coronary vessels, assessment of the prognosis and risk of complications of MI.
Stage 2.
Inpatient rehabilitation – takes up the entire acute period of MI (up to 28 days) after the patient is transferred to a specialized rehabilitation or heart attack department, and then to a cardiological sanatorium. This is where more intense physical activity becomes possible.
Stage 3.
Outpatient – carried out in a clinic and at home under the supervision of a cardiologist and a physical therapist. The prevention of recurrent heart attack, coronary heart disease, and treatment of atherosclerosis comes to the fore. Dispensary observation continues for a year or longer.
The division into stages is determined, among other things, by the periods of the disease:
- The most acute period is up to 6 hours,
- Acute MI – up to 7 days after the attack,
- Scarring stage – up to 28 days,
- The stage of a formed scar is from 29 days after the attack.
Rehabilitation covers all aspects of the patient’s health: physical, psychological, social. It includes drug and non-drug treatment methods, such as physiotherapy, lifestyle and diet adjustments, gradual return to physical activity and psychological support.
The effectiveness of rehabilitation affects the survival of patients after MI and quality of life.
OTHER INFORMATION
Please note that if our company (or any part thereof) is sold or placed into receivership, information we hold may be part of the assets transferred; however, such information will continue to be used solely in accordance with the terms of the Policy on the processing and protection of personal data.
For quality control or training purposes, we may monitor or keep a record of your correspondence with us.
•Policy of AstraZeneca Industries LLC in the field of processing and ensuring the security of personal data • Policy of AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LLC in the field of processing and ensuring security of personal data
Physical rehabilitation
At all stages of recovery after myocardial infarction, increasing physical activity is one of the most important components. Of course, certain restrictions make it possible to reduce the load on the myocardium, reduce its oxygen requirements and create conditions for speedy healing. However, unreasonable prolongation of strict bed rest can increase the risk of thromboembolic complications, contributes to the development of congestive pneumonia, disrupts the functioning of the digestive system and leads to muscle weakness. All this affects the terms of rehabilitation and reduces the quality of life.
At the inpatient stage, after acute pain has been relieved and early complications have been dealt with, the severity of the MI is determined. The depth, localization and extent of the heart muscle lesion, the severity of heart failure and the presence of complications are taken into account. It is this indicator that influences what kind of rehabilitation program will be offered to the patient.
Subsequently, depending on the dynamics and performance of the cardiovascular system, the patient is transferred from one level of activity to another. The level of blood pressure, electrocardiogram data, the presence of arrhythmia, as well as individual exercise tolerance are assessed.
Types of rehabilitation
Improvement of health is promoted by:
- drug therapy for circulatory disorders;
- physical therapy and physiotherapy;
- working with a psychologist, gaining knowledge at a health school;
- treatment in a specialized sanatorium.
The attending physician develops the program individually, taking into account:
- the nature of the heart attack and the severity of the condition;
- age;
- severity of heart failure;
- the presence of complications and concomitant diseases;
- physical training.
Drug rehabilitation
Medicines are prescribed during the acute period. After improvement in indicators, you also need to take medications prescribed by your doctor.
When preparing drug therapy, the following are taken into account:
- presence of concomitant diseases;
- causes of thrombosis;
- characteristics of the body.
The condition is kept under control, and the treatment program is adjusted if necessary.
Thanks to regular medication use:
- blood pressure levels stabilize;
- it is possible to prevent the development of arrhythmia and angina pectoris;
- lipid metabolism and blood clotting are normalized;
- the condition of chronic heart failure improves.
Physical rehabilitation
Physical rehabilitation after a heart attack begins during the hospital stay. From the second day, the simplest exercises are shown - you can bend and straighten your toes and fingers, lower your bent legs to the left and right. Between approaches there is a rest - 10-30 seconds are allotted for it.
After transfer to the cardiology department, physical activity increases. Most of the movements are performed in a sitting position. Head turns, raising arms forward and up, and other simple exercises are added. The patient gets up and begins to walk around the room. Then he goes for walks in the corridor. Later he is allowed to go up and down the steps.
After discharge, a gradual increase in activity is indicated:
- A complex of exercise therapy is performed taking into account the physical capabilities of the person. It is selected individually, the loads should be dosed and moderate.
- Simple work around the house and in the garden brings benefits (heavy lifting and other hard work is prohibited).
Shown:
- walks in the open air;
- going up/down stairs;
- cardio exercises;
- Nordic walking;
- jogging and other aerobic exercise.
During classes, indicators are monitored. The initial loads should not be long - a quarter of an hour is enough. Gradually, the duration of classes is increased by five minutes a day and stopped at an hour.
Refusal of physical activity and prolonged bed rest increase the risk of thromboembolic complications and congestive pneumonia. As a result of physical inactivity, the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is disrupted, muscles weaken, and the quality of life deteriorates.
Psychological rehabilitation
After a heart attack, the psychological state seriously deteriorates. The patient feels helpless and fears the next attack and death. Increased nervousness and irritability are common symptoms after illness. If you ignore them, there is a risk of developing neurosis and depression. A psychologist will help improve your psychological mood and form positive thinking. The environment plays an important role - loved ones should provide psychological support.
Stages and approximate terms of physical rehabilitation:
I. On the first day after hospitalization, strict bed rest is most often prescribed, which is expanded from the second day and supplemented with therapeutic exercises, consisting of individually selected exercises. Gradually, the patient can increase the time he can sit, stand, and later walk around the ward. Usually, after 7-18 days, walks of up to 2-3 km at a slow pace and exercise on an exercise bike are allowed.
At the end of the stage, the level of cardiovascular risk is calculated. To do this, a repeat electrocardiographic examination is carried out, the severity of atherosclerotic changes is determined, and the heart’s abilities are assessed using echocardiography (ultrasound examination of the heart).
II. After transfer to a rehabilitation department or sanatorium, tests with physical activity are carried out. Based on their results, the optimal physical activity and its type are selected. They also take into account methods for restoring blood flow in the coronary arteries, the speed of development of various stages of activity at the previous stage, and the general condition.
The complex of physical therapy (physical therapy) gradually includes walking at a faster pace, swimming, and training on exercise machines.
III. At the outpatient stage, the determining factor is the functional class of coronary heart disease (CHD), which is determined using a study that evaluates the increase in oxygen consumption during physical activity (bicycle ergometry, treadmill test - walking on a “treadmill”). This test reflects not only the functioning of the cardiovascular system, but also the respiratory system.
Depending on the functional class of IHD, physical therapy is carried out in a training or gentle mode.
Studies have shown that the longer physical rehabilitation is carried out, the better the long-term results - the risk of recurrent MI and death is reduced to a greater extent.
Physical activity during the rehabilitation period
Physical activity is important not only for maintaining the shape and tone of a healthy person, but also for people who have survived a myocardial infarction. It is important to consider that physical activity during the rehabilitation period should be increased gradually to avoid overwork and negative consequences.
After the attack is relieved, already in the first days, the patient can get up independently, and over time, take short walks, gradually increasing physical activity. During the period of activity, it is necessary to carefully monitor the condition in order to detect possible discomfort in time.
Therapeutic exercise is mandatory in rehabilitation therapy. A set of exercises is prescribed by a qualified physiotherapist and carried out under his supervision. Subsequently, the patient performs the exercises independently.
An important indicator, especially in the initial stages of recovery, is heart rate. At first, even with short walks and little physical activity, it can reach up to 120 beats/min. Subsequently, with proper treatment, its frequency will gradually decrease.
Massage, walking, and swimming are also used as restorative measures.
Psychological rehabilitation
Any disease is stressful. Urgent hospitalization, the need for long-term treatment, and sometimes surgical intervention, and a sharp restriction of activity often become the causes of quite serious mental changes. Therefore, at all stages of rehabilitation, psychological and psychotherapeutic work is carried out with the patient.
A big role in recovery is played by the patient’s attitude, attitude and support of loved ones.
It is also important to overcome the fear of physical activity and form an adequate assessment of your capabilities. Patients feel differently about their condition. There are those who are afraid to make unnecessary movements and delay rehabilitation, and those who underestimate the severity of the disease and too quickly strive to return to their usual rhythm. The doctor’s task is to give an objective assessment, explain the tasks of each stage of rehabilitation and the acceptable level of activity.
At the stage of outpatient observation, it is important to prevent the development of neurosis and depression, which occur in many patients4 and can negatively affect adaptation capabilities.
Stressful situations during the rehabilitation period
After a heart attack, the patient is in a complex psycho-emotional state. There is increased fear, confusion, anxiety, and fear of death. These symptoms can persist for up to six months, in some cases for a longer period. But with the right approach and treatment, negative emotions can be combated and the patient’s psychological state can be stabilized.
Patients with a particularly sensitive psyche are prescribed sedatives and work with a psychologist. The support of loved ones is especially important during this period.
Often after a heart attack, patients fall into a state of depression. In this case, it is imperative to contact a psychologist or psychoanalyst who will help get rid of the depressive state. The specialist will also teach the patient how to properly manage negative emotions and resist stress, thereby preventing subsequent heart attacks.
Fighting bad habits in the post-infarction period
Getting rid of bad habits is an important condition on the path to recovery and preventing possible recurrent heart attacks. A person who has suffered a myocardial infarction must completely give up alcohol and nicotine.
Nicotine has a particularly negative effect on the body - it can lead to a second heart attack. If the patient cannot quit smoking on his own, you can seek the help of psychologists, use acupuncture, or quit smoking with the help of special medications.
Non-drug methods of prevention
After myocardial infarction, atherosclerosis, which most often causes vascular accidents, continues to develop. To prevent its progression and recurrent MI, it is necessary to minimize the effect of risk factors. For this purpose, non-drug and drug methods of secondary prevention of coronary heart disease (CHD) are used.
Non-drug methods, in addition to physical rehabilitation, include lifestyle correction. This concept includes:
- Complete cessation of smoking
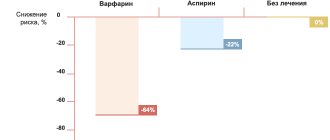
, both active and passive. It has been proven that nicotine and other chemical compounds damage the inner lining of blood vessels (endothelium) and contribute to an increase in the level of “bad” cholesterol, that is, low-density lipoproteins. In addition, smoking leads to vasospasm and an increase in blood pressure, which can provoke new attacks of coronary artery disease. Research data has shown that quitting smoking reduces the risk of death by 36%! - Avoid or minimize alcohol consumption .
The heart primarily suffers from alcoholic drinks: tachycardia, arrhythmia appear, blood pressure increases, the toxic effect of ethanol can lead to another heart attack or sudden death. The permissible dose is 30 g per day for men and no more than 20 g for women. - Weight control and healthy eating.
It is necessary to balance the diet so as to maintain normal body weight and metabolism. Basic principles: reducing animal fats, replacing them with plant foods that do not contain cholesterol. Preference should be given to vegetables, fruits, nuts, lean meats and sea fish, and whole grain cereals. Smoked, canned, fried and salted foods are excluded. It is convenient to control your weight using your body mass index (the result of dividing your weight in kg and height in meters squared). It should be within 25-27 kg/m. In addition, the waist circumference is assessed: for men this figure should not exceed 94 cm, for women – 80 cm.
Who is at risk?
Myocardial infarction develops in people with coronary heart disease, which most often affects older people, especially men. Narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries leads to impaired circulation and necrosis of areas of the myocardium.
The risk of heart attack is higher in patients:
- with a hereditary predisposition;
- diabetes mellitus;
- overweight;
- arterial hypertension;
- rheumatic carditis;
- bad habits (including passive smoking);
- atherosclerosis;
- inflammatory bowel diseases;
- exposed to frequent and prolonged stress.
The likelihood of relapse is especially high in people who have already had a myocardial infarction. It is advisable for an at-risk patient with coronary artery disease to be cared for by an experienced caregiver, for example in a nursing home. She will be able to recognize the signs of myocardial infarction in time, provide proper first aid and organize care after the attack.
Main groups of drugs:
1. Beta blockers
. Prescribed to almost all patients after MI, regardless of the presence or absence of heart failure. They reduce the myocardial oxygen demand and reduce the risk of sudden death, and also help to increase life expectancy.
2. Antiplatelet agents.
They prevent the formation of blood clots in blood vessels, reduce inflammation in the inner choroid, and reduce the risk of developing vascular accidents (heart attacks, strokes).
3. Statins.
They reduce the level of atherogenic cholesterol (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol - LDL-C), preventing the progression of atherosclerosis and the formation of new atherosclerotic plaques in blood vessels. It has been proven that reducing the concentration of LDL cholesterol by 1 mmol/l reduces the risk of death from coronary artery disease and its complications by 34%, as well as the need for surgical treatment.
4. Nitro drugs.
They are used if the patient continues to have angina attacks, or signs of silent ischemia are recorded on the electrocardiogram.
5. Antiarrhythmic drugs.
Prescribed if necessary for the treatment of various types of arrhythmias, which sometimes occur in patients who have had a myocardial infarction.
6. Antihypertensive drugs.
Prescribed if it is necessary to treat hypertension, usually several drugs are selected, the combination of which gives the optimal result for each patient.
Drug therapy is carried out under the supervision of a cardiologist. Before discharge, patients meet with the doctor daily, then 1-2 times a month in the first year and once every three months in the second. Periodically, you need to repeat an ECG, blood lipid test, exercise testing and other examinations as necessary.
A comprehensive rehabilitation program, subject to all principles, helps patients recover in a shorter time, improve their quality of life, and prevent recurrent heart attacks and other complications.
SARU.CLO.19.05.0797
Rehabilitation at home
However, if you do not end up in a sanatorium, physical rehabilitation can and should be carried out independently. The easiest way is to walk every day. You need to choose a rhythm that is comfortable for you, slow or moderate, and go for walks at least 5 times a week for 30-60 minutes. If you feel tired or weak, sit down to rest or return home. In just a few days you will be able to walk further.
The load should not lead to the development of an attack of angina pectoris
or severe shortness of breath and palpitations, only mild shortness of breath is acceptable.
Monitor your pulse;
during exercise, your heart rate should definitely increase. At the first stage, achieve a small increase of 20-30% (for example, 15-20 beats per minute). In the future, if you have good exercise tolerance, continue to monitor your pulse and do not allow the value to exceed 200 - your age (for example, you are 56 years old: it is not advisable for your pulse to exceed 200-56 = 144).
According to the recommendations of Russia’s leading specialist in the rehabilitation of patients with heart disease, Professor D.M. Aronova, depending on the severity of angina manifestations (functional class), there are different acceptable types and volumes of physical activity.
Below are tables developed by prof. D.M. Aronov, by which you can determine the physical activity possible for you. We remind you that angina is divided into 4 functional classes, I f.k - the mildest, when angina attacks develop only during high-intensity loads, IV f.k. the most severe - an attack can develop at the slightest physical exertion and even at rest. The sign (-) indicates loads that are not permitted. (+) – activity is allowed, the number (+) reflects the volume or intensity of the load performed.
Caring for an elderly patient after a heart attack
Despite all the advances in medicine, many systems decline with age. One of the most important systems - the heart - can fail at the most inopportune moment if you do not monitor your blood pressure and do not take preventive measures (healthy lifestyle, healthy diet, sports) to reduce risks. One of these unexpected illnesses may be myocardial infarction.
A heart attack can happen at any age, but older people aged 40 to 70 are at particular risk. Most often, myocardial infarction occurs in men, but after 70 years of age, the risk is equal for both men and women.
What is myocardial infarction?
Myocardial infarction is an acute, severe pathological condition associated with the death of the heart muscle. Necrosis of the myocardium (heart muscle) occurs due to oxygen deficiency.
A heart attack can occur not only in the heart, but also in other organs and tissues. There is a heart attack of the brain, lung, etc. However, the most famous heart attack - myocardial infarction - is also the most dangerous.
Medical classification of myocardial infarction
In total, there are two types of myocardial infarction: small-focal and large-focal . Small-focal infarction is widely considered a mild form of pathology and work ability is usually preserved.
A large-focal heart attack can lead to complete disability, as it entails very serious consequences.
Both types of heart attack require immediate surgical intervention. In the future, inpatient treatment and a long period of rehabilitation are indicated.
Main risk factors for myocardial infarction
- Smoking and drinking alcohol
- Diabetes
- Hereditary predisposition
- Exhaustive physical labor
- Obesity, overweight
- Stress
Types of heart attack
In everyday life, many are not aware of the existence of different forms of myocardial infarction. These forms may have different manifestations, so each symptom that worries your elderly relative should be treated with attention:
- Form 1
Painless. Usually occurs against the background of the extreme stage of arterial sclerosis. Accompanied by a feeling of lack of air, cardiac asthma, gastrointestinal disorders, sweating, a sharp drop in blood pressure, and weakness.
If such a heart attack is suffered without proper hospitalization or treatment, it can lead to scarring of the heart tissue, chronic heart failure and other problems.
- Form 2
Abdominal (atypical). The main symptom is unbearable abdominal pain.
- Form 3
Cerebral. Usually accompanied by cognitive disorders, mental confusion, headaches, and dizziness. May also be a symptom of a stroke.
- Form 4
Classic. Usually accompanied by chest pain that radiates to the left forearm, shoulder and shoulder blade.
What about work ability?
Each myocardial infarction survivor is usually assigned a specific functional class. Usually it indicates the severity of the condition, what the consequences are, what limitations there are. With the help of FC, you can determine a set of therapeutic exercises and the level of workload.
Functional class 1: patients who suffered a small focal infarction with minor impairments.
Functional class 2: patients with minimal complications.
Functional class 3: patients with frequent attacks of angina (up to six attacks per day).
Functional class 4: patients with serious complications (for example, after clinical death)
- The disability group is assigned to patients with functional class 3-4. This means that any physical activity is contraindicated for them. If your elderly relative’s FC is 1-2, then usually he can do light work.
- All survivors of myocardial infarction are prohibited from engaging in heavy physical labor, working in shifts, or working 12- and 24-hour shifts.
- All patients who have experienced a heart attack must be under constant observation at the clinic. After a year, the patient can count on sanatorium treatment.
Manifestations of myocardial infarction
The most common complaint is chest pain lasting more than 15-20 minutes. The pain “radiates” to the left arm, a tingling sensation appears in the left arm and fingers. Pain can also radiate to the muscles of the shoulders, neck, and jaw.
Usually the pain is characterized as a “knife in the heart”, very sharp, cutting, burning. Sometimes the patient may start screaming in pain. However, in some cases the pain may not be so severe. It may feel like “discomfort” and “tightness” in the chest. This sensation may be accompanied by a dull ache and numbness in the limbs.
The attack may begin suddenly, most often at night or before dawn. The pain develops in waves, sometimes subsiding, sometimes intensifying, but the pain does not stop.
The most important thing: remember the main sign of a heart attack - prolonged, unremitting pain that lasts more than 15 minutes.
What to do in case of an attack?
- Immediately stop any activity, sit or have the victim sit down and lower their legs down;
- If pain occurs to you or your loved one while lying down, sit down and put your legs down or sit the patient down with your legs down
- Open a window or get rid of tight clothes, unbutton the patient’s clothes;
- Place one nitroglycerin tablet under your tongue, repeat after three minutes if there is no effect;
- Call an emergency doctor. Before arriving, the victim needs to chew a quarter of an aspirin tablet.
Stages of recovery after a heart attack
- Stationary
The first stage of recovery takes place in the hospital. It usually lasts from one to three weeks, depending on the severity of the attack. At this time, the main emphasis is on drug treatment, feasible therapeutic physical activity and psychological support.
- Post-inpatient
It takes place either at home or in a special rehabilitation center, sanatorium or boarding house for the elderly. Lasts from six months to a year. Of all the listed options, the most difficult is to organize home care, since during this period the patient must undergo regular examinations by a number of specialists, primarily a cardiologist, and must also undergo a course or several courses of sanatorium-resort treatment.
- Supportive
This stage is usually lifelong. The patient should adhere to the healthiest lifestyle possible and a balanced diet, engage in exercise therapy, give up bad habits, be observed by appropriate specialists and take prescribed medications.
Exercise therapy
You can find out more about the benefits of physical therapy here.
Psychologist support
Patients who have suffered a heart attack are strictly forbidden to be nervous and worried. That is why it is so important to pay attention to the psychological state of the patient and consult a specialist.
An elderly patient may feel helpless in this state, experience fear of the return of the pathology, and this fear, paradoxically, can lead to tragedy. A professional psychologist will help the patient accept the situation and look into the future with confidence.
What is excluded from the diet?
- Fried, spicy, fatty, salty foods.
- Semi-finished products, highly processed products
- Fast food
- Store baked goods and sweets
- Sauces
- Sweet soda, strong tea and coffee
- Dishes and products with added sugar
- High calorie dishes
What should you include in your diet?
- Lean meat, poultry, fish (boiled or steamed)
- Vegetables, fruits, berries
- Nuts
- Legumes
- Whole grain homemade baked goods
Patients should monitor excess weight, but they are prohibited from losing more than 5 kg per month. Losing weight should be smooth.
You should also divide your meals into 5-6 meals a day (breakfast, lunch, dinner, two snacks between them). It is better to eat little and often than rarely and a lot. You should chew your food thoroughly in order to feel full in time. You should drink no more than 1.5 liters of water per day to avoid swelling.
What should a sick person's plate look like?
- For breakfast/lunch/dinner: any lean boiled/steamed meat (the size of a fist), durum wheat cereals/pasta (a handful), vegetable salad (a fist).
- For a snack: vegetable salad, fruits, nuts.
At night, you can drink a glass of low-fat milk (ryazhenka, kefir, yogurt).
What other features of caring for a patient who has had a heart attack?
- In the first ten days after an attack, it is strictly forbidden to break bed rest.
- The formation of bedsores and other complications should be closely monitored. You can find out how to do this here.
- It is forbidden to make sudden movements. After completing bed rest and with the doctor’s permission, you need to help the patient take a sitting position smoothly, without jerking.
- The patient can take a vertical position only in the presence of a specialist or nurse.
- Be sure to monitor your blood pressure.
- Make sure you take your medications on time.
- Sanatorium treatment after discharge from the hospital is recommended.
If your relative suffered a heart attack and you feel confused, don’t worry! We work with older people with different health conditions and are ready to provide maximum comfort for your loved one. We offer each of our guests a cozy space, attentive staff, balanced nutrition and supportive procedures.
Don't know how to provide quality care for a loved one?
We will help!
8
In the network of boarding houses "Vita" we guarantee you complete care.
We help with transportation to the boarding house.
We offer
- Accommodation in a room for one, two, three or four guests to choose from.
- Dietary balanced nutrition. Only high-quality and fresh products.
- Games, sports, outdoor walks, concerts and much more.
- Monitoring your well-being and taking medications prescribed by your doctor.
- Full medical care and health monitoring 24 hours a day (accompaniment, assistance in eating, carrying out hygiene procedures).
- Providing specialized equipment and technical care.
- Regular change of bed linen, washing of clothes.
- Assistance in carrying out hygiene procedures.
- Optimal price-quality ratio for you and your loved ones.