General description of the disease
The term angina pectoris refers to a form of ischemic heart disease (coronary heart disease) that occurs due to an insufficient amount of blood in its cavity. Angina pectoris differs from myocardial infarction in that during an attack of pain in the sternum, no changes occur in the heart muscle. While during a heart attack, necrosis of cardiac muscle tissue is observed. The popular name for angina is angina pectoris.
Causes of angina
- Insufficiency of cardiac circulation at any given moment, for example, when performing physical activity.
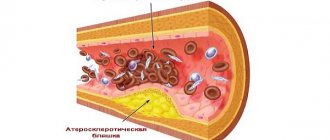
- Atherosclerosis of the heart arteries, that is, narrowing of the arteries, due to which they are not able to pass the required volume of blood through themselves.
- Arterial hypotension is a decrease in blood flow to the heart.
Symptoms
The surest sign of angina is a pulling, squeezing or even burning pain in the sternum. It can radiate (give) to the neck, ear, left arm. Attacks of such pain can come and go, although usually their occurrence is determined by certain circumstances. Patients may also experience nausea and heartburn. The difficulty of making a correct diagnosis lies in the fact that people who experience pain in the ear or other parts of the body do not always associate it with angina attacks.
It is important to remember that angina is not pain that goes away on its own after half a minute or after a deep breath or a sip of liquid.
General rules
Angina pectoris is a variant of the course of coronary heart disease , and is characterized by the appearance of discomfort or pain in the chest. Attacks of pain are associated with transient myocardial ischemia that occurs at the height of the load. At this time, the myocardial need for oxygen increases, but due to the narrowing of the coronary vessels, its delivery deteriorates. Narrowing is most often associated with atherosclerosis . In the coronary arteries, lipidosis (the initial stage of atherosclerosis) develops already at 10-15 years of age.
Angina symptoms, treatment and nutrition
In most cases, attacks appear against the background of physical stress (emotional), after eating or in cold weather, when walking against the wind, leaving a warm room in the cold. In addition, certain conditions ( hypertension , hypertrophic cardiomyopathy , aortic stenosis ) can also cause attacks.
The main symptom of angina is chest discomfort or pain, which can be mild and not cause concern, or severe, manifested as intense compression in the precordial area. The pain may radiate to the shoulder and left arm. You may experience pain in the lower jaw, back, or throat. Sometimes the discomfort is localized in the abdomen (in its upper part) and shortness of breath occurs.
Some patients experience atypical symptoms: bloating, dyspeptic symptoms , gas formation . At the height of the attack, an increase in heart rate and pressure are observed. Typically, attacks resolve with rest or after taking nitroglycerin .
Treatment may include antiplatelet drugs, nitrates, calcium channel blockers, beta blockers, and statins. Nutrition is of no small importance in this disease. An increase in cholesterol and LDL fractions in the blood leads to the progression of atherosclerosis and narrowing of the lumen of blood vessels.
The diet for angina pectoris is aimed at slowing the progression of atherosclerosis. It is aimed at eliminating lipid metabolism disorders, weight loss and improving blood circulation.
General principles of nutrition:
- Reducing animal fats and carbohydrates (easily digestible). When cooking, you need to trim off the fat, remove the fat rendered during cooking and remove the skin from the bird. The degree of restriction of fats and carbohydrates depends on the patient’s weight.
- Normal protein content.
- Restriction of salt (4 g), cholesterol (0.3 g) and extractives.
- The content of linoleic acid, lipotropic substances, dietary fiber, potassium and magnesium has been increased due to an increase in vegetable oils, seafood, vegetables, fruits and cottage cheese in the diet.
- Increasing the proportion of products containing iodine (seaweed, mussels, sea fish, squid, shrimp).
- Exclusion of products that stimulate the cardiac and nervous systems (coffee, tea, alcohol, cocoa).
- Meals 5 times a day, in small portions.
All products of animal origin contain cholesterol, but there are products with a high content of it, so-called “cholesterol concentrates”: brains, mayonnaise, margarine, offal, egg yolk.
As it turned out, the danger is not the cholesterol that comes with food, but the lack of the required amount of fiber in food (vegetables, fruits, bran). In this regard, the diet provides for an increase in the proportion of plant foods in the diet. Refined carbohydrates (sugar, flour products, sweets, potatoes and any baked goods) contribute to the progression of atherosclerosis, so they are strictly limited.
general characteristics
The diet helps improve blood circulation, function of the cardiovascular system, liver and kidneys, normalize metabolism, and spare the cardiovascular system and digestive organs.
General characteristics:
a slight reduction in calories due to fats and partly carbohydrates. Significantly limiting the amount of sodium chloride, reducing fluid intake. The content of substances that excite the cardiovascular and nervous systems, irritate the liver and kidneys, unnecessarily burden the gastrointestinal tract, and promote flatulence is limited. The content of potassium, magnesium, lipotropic substances, and products that have an alkalizing effect has been increased. Cooking with moderate mechanical gentleness. Meat and fish are boiled. Avoid hard-to-digest foods. Food is prepared without salt. The food temperature is normal.
Chemical composition and calorie content:
- carbohydrates - 350-400 g,
- proteins - 90 g (55-60% animals),
- fats - 70 g (25-30% vegetable),
- calories - 2500-2600 kcal,
- table salt - 5 g (on hands),
- free liquid - up to 1.5 l.
Diet:
5 times a day in relatively even portions.
Authorized Products
- Wheat bread, grade II, grain, with bran, rye. Homemade baked goods with wheat bran and no salt.
- Refractory fats are excluded and half the amount of fats is replaced with vegetable oils.
- Vegetarian soups, you can prepare cabbage soup, beetroot soup, fruit soup and limited cereal soup, excluding rice and semolina.
- Meat, fish and poultry only of low-fat varieties, boiled or baked. Baking is done after preliminary boiling. Preference is given to fish and seafood dishes. Be sure to eat seaweed every day.
- Cabbage of all types, carrots, beets, zucchini, pumpkin, eggplant, potatoes (limited due to carbohydrate content) and green peas. You need to eat a large amount of vegetables fresh, and in case of gastrointestinal pathology, boiled and baked.
- Low-fat dairy products and fermented milk drinks, sour cream - limited for dressing dishes.
- Cereals (it is advisable to limit or exclude rice and semolina) are boiled in water and milk; you can make puddings and cereals with cottage cheese and vegetables. If you are overweight, avoid pasta.
- Eggs up to 3 per week (whole) and an egg white omelet.
- Any fruits and berries in raw form, in compotes, jellies, to which it is allowed to add a minimum of sugar or replace it with xylitol.
- Weak tea with milk, chicory drink, coffee drinks, vegetable juices, diluted berry and fruit juices. Daily use of rosehip infusion and wheat bran decoction.
- Low fat butter and vegetable oils.
- Any nuts in their natural form, but their high calorie content should be taken into account.
Table of permitted products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| greenery | 2,6 | 0,4 | 5,2 | 36 |
| eggplant | 1,2 | 0,1 | 4,5 | 24 |
| beans | 6,0 | 0,1 | 8,5 | 57 |
| zucchini | 0,6 | 0,3 | 4,6 | 24 |
| cabbage | 1,8 | 0,1 | 4,7 | 27 |
| broccoli | 3,0 | 0,4 | 5,2 | 28 |
| boiled cauliflower | 1,8 | 0,3 | 4,0 | 29 |
| bulb onions | 1,4 | 0,0 | 10,4 | 41 |
| carrot | 1,3 | 0,1 | 6,9 | 32 |
| cucumbers | 0,8 | 0,1 | 2,8 | 15 |
| salad pepper | 1,3 | 0,0 | 5,3 | 27 |
| salad | 1,2 | 0,3 | 1,3 | 12 |
| beet | 1,5 | 0,1 | 8,8 | 40 |
| celery | 0,9 | 0,1 | 2,1 | 12 |
| soybeans | 34,9 | 17,3 | 17,3 | 381 |
| asparagus | 1,9 | 0,1 | 3,1 | 20 |
| tomatoes | 0,6 | 0,2 | 4,2 | 20 |
| Jerusalem artichoke | 2,1 | 0,1 | 12,8 | 61 |
| pumpkin | 1,3 | 0,3 | 7,7 | 28 |
| beans | 7,8 | 0,5 | 21,5 | 123 |
| garlic | 6,5 | 0,5 | 29,9 | 143 |
| lentils | 24,0 | 1,5 | 42,7 | 284 |
Fruits | ||||
| avocado | 2,0 | 20,0 | 7,4 | 208 |
| oranges | 0,9 | 0,2 | 8,1 | 36 |
| pomegranate | 0,9 | 0,0 | 13,9 | 52 |
| grapefruit | 0,7 | 0,2 | 6,5 | 29 |
| pears | 0,4 | 0,3 | 10,9 | 42 |
| kiwi | 1,0 | 0,6 | 10,3 | 48 |
| lemons | 0,9 | 0,1 | 3,0 | 16 |
| mango | 0,5 | 0,3 | 11,5 | 67 |
| tangerines | 0,8 | 0,2 | 7,5 | 33 |
| nectarine | 0,9 | 0,2 | 11,8 | 48 |
| peaches | 0,9 | 0,1 | 11,3 | 46 |
| apples | 0,4 | 0,4 | 9,8 | 47 |
Berries | ||||
| gooseberry | 0,7 | 0,2 | 12,0 | 43 |
| Red currants | 0,6 | 0,2 | 7,7 | 43 |
| black currant | 1,0 | 0,4 | 7,3 | 44 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| nuts | 15,0 | 40,0 | 20,0 | 500 |
| cashew | 25,7 | 54,1 | 13,2 | 643 |
| sesame | 19,4 | 48,7 | 12,2 | 565 |
| flax seeds | 18,3 | 42,2 | 28,9 | 534 |
| fenugreek seeds | 23,0 | 6,4 | 58,3 | 323 |
| sunflower seeds | 20,7 | 52,9 | 3,4 | 578 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| buckwheat (kernel) | 12,6 | 3,3 | 62,1 | 313 |
| oat groats | 12,3 | 6,1 | 59,5 | 342 |
| cereals | 11,9 | 7,2 | 69,3 | 366 |
| millet cereal | 11,5 | 3,3 | 69,3 | 348 |
| barley grits | 10,4 | 1,3 | 66,3 | 324 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| honey | 0,8 | 0,0 | 81,5 | 329 |
Dairy | ||||
| skim milk | 2,0 | 0,1 | 4,8 | 31 |
| natural yogurt 2% | 4,3 | 2,0 | 6,2 | 60 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cottage cheese 0.6% (low fat) | 18,0 | 0,6 | 1,8 | 88 |
| curd tofu | 8,1 | 4,2 | 0,6 | 73 |
Meat products | ||||
| beef | 18,9 | 19,4 | 0,0 | 187 |
| rabbit | 21,0 | 8,0 | 0,0 | 156 |
Sausages | ||||
| boiled diet sausage | 12,1 | 13,5 | 0,0 | 170 |
Bird | ||||
| chicken fillet | 23,1 | 1,2 | 0,0 | 110 |
| turkey | 19,2 | 0,7 | 0,0 | 84 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| fish | 18,5 | 4,9 | 0,0 | 136 |
| squid | 21,2 | 2,8 | 2,0 | 122 |
| mussels | 9,1 | 1,5 | 0,0 | 50 |
| seaweed | 0,8 | 5,1 | 0,0 | 49 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| butter | 0,5 | 82,5 | 0,8 | 748 |
| linseed oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| olive oil | 0,0 | 99,8 | 0,0 | 898 |
| sunflower oil | 0,0 | 99,9 | 0,0 | 899 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| mineral water | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| green tea | 0,0 | 0,0 | 0,0 | — |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Feed your heart right. Rational nutrition for cardiovascular diseases.
Today, heart disease has become a real disaster. But you can prevent and even cure angina pectoris, ischemia, arrhythmia, hypertension, and prevent heart attack and stroke with the help of proper nutrition. Rational nutrition is nutrition that fully satisfies the physiological needs of the body for nutrients and energy, which in turn helps to maintain and strengthen health and prevent diseases.
Nutrition for cardiovascular diseases is based on the following principles: food should be varied, energy consumption should be optimal to maintain ideal weight; the diet should contain a certain amount of nutrients in an optimal ratio (proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins, macro- and microelements), taking into account age, gender, climatic and other characteristics; the total fat content in the diet should not exceed 30% of the total energy composition, and the saturated fat content should not exceed a third of all consumed fats; the amount of dietary cholesterol consumed is less than 300 mg/day; the ratio between saturated, mono- and polyunsaturated fats should be 1:1:1; preventive diet; compliance with the diet.
What misconceptions about healthy and unhealthy nutrition do we most often encounter?
Most often, people suffering from cardiovascular diseases believe that a diet that is good for blood vessels, such as the Mediterranean diet, is very expensive, especially now, during a protracted economic crisis. In fact, you can choose products that are good for the heart and blood vessels and are not burdensome on the wallet, even with limited funds. Because the main thing is to eliminate salt and animal fat, switch from expensive lamb, pork, beef, cheese to cheaper and lean chicken, fermented milk products - kefir, cottage cheese. Buying fish doesn't have to be expensive. Vegetables - cabbage, potatoes, zucchini and dried fruits also cost no more than harmful sausages, sausages, baked goods, butter and other products that cause irreparable harm to the entire cardiovascular system.
What dietary restrictions and consumption of healthy foods can be taken to prevent cardiac diseases?
In some cases, we have to enrich the diet with biologically active food additives that compensate for the lack of consumption of certain essential nutrients. Most often these are sources of polyunsaturated acids of the omega-3 family, a number of microelements, such as selenium, and vitamin and mineral complexes. This is necessary for all those who cannot afford to eat sea fish at least twice a week or eat a mostly poor and uniform diet, since these people are at the highest risk of developing a deficiency of much-needed nutrients and associated diseases. In addition, the vast majority of cardiac patients require increased amounts of heart-protective micronutrients. It is important to remember here that for prevention you need to take, for example, at least 200 – 400 mg of omega-3 PUFAs per day.
How does the diet depend on the age and gender of patients?
The older a person gets, the less calories they spend. Firstly, metabolism slows down with age, and secondly, physical activity decreases. Often people do not notice that muscle mass has partially been replaced by fat mass, because the arrow on the scale remains in place. To do this, you need to conduct special studies that will show the ratio of bone, muscle and fat tissue in the body, and adjust the diet based on the results. As a rule, after 50 years you need to reduce your total caloric intake. A lower calorie diet is recommended for women, since energy expenditure in men is initially higher.
How should cardiac patients eat in the summer, in the heat?
Even among cardiologists, there is an opinion that it is necessary to limit fluid, since excess fluid causes swelling and provokes an increase in blood pressure. This is partly true, but there is a mistake here. It is important to limit salt, which retains fluid in the body, not water. Excessive fluid restriction can lead to blood clots. The number of these diseases doubles on hot days precisely because patients drink little fluid. People with diseases of the cardiovascular system need to drink one and a half liters of water daily, and in hot weather - two to two and a half liters. Sometimes sensations can be deceiving; many people mistake thirst for food, overeat, but never get water. Therefore, you need to watch how much you drink. The water should be still. It is worth limiting mineral water to 0.5 liters per day, as it contains a lot of salts that retain water in the body. But you shouldn’t give it up completely, as it contains microelements necessary for the heart.
What is the role of fermented milk products, in particular those enriched with bifidobacteria and lactobacilli?
Microbiocenosis, that is, the totality of all beneficial intestinal bacteria, is of enormous importance for the proper functioning of not only the intestines, but also the heart. Metabolic processes occur daily in the human body, striking in their scale. For example, every day in the human body, about 400 g of protein is normally broken down into amino acids and synthesized again - mainly muscle and blood plasma protein. Many people do not know that there is a so-called muscular-intestinal circulation of amino acids, in which amino acids formed during the natural breakdown of protein enter the intestinal cavity, and are then reabsorbed and used to build new muscle proteins. I would like to remind you that the heart is also a muscular organ in which the same processes of protein self-renewal take place. Therefore, it becomes clear how much the condition of the heart depends on the ability of the intestines to fully perform their work and, not least of all, on the state of the intestinal microflora. If protein breakdown for a long time prevails over its resynthesis, that is, restoration, then gradually this can lead to dysfunction of the muscular system and heart failure. This is especially dangerous if a person has already suffered a myocardial infarction. Intestinal dysbiosis is also dangerous because it is a factor that provokes angina attacks. Accumulated gases cause discomfort and pain, which can reflexively cause coronary spasm and an attack of angina. In addition, the absorption of vitamins, minerals and other beneficial substances depends on the state of the microflora. Therefore, it is imperative to introduce fermented milk products into your diet, preferably additionally enriched with beneficial bacteria. A rational, balanced diet allows for effective prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases, and also greatly enhances the therapeutic effect of medications. The diet of patients with heart and vascular diseases should contain a minimum amount of table salt, limited in the content of dietary cholesterol and animal fat, with normal or reduced calorie content. At the same time, the diet of patients should contain a sufficient amount of foods rich in dietary fiber, potassium and magnesium, polyunsaturated fatty acids of the omega-3 and omega-6 families. Such nutrition will slow down the development of atherosclerosis, normalize blood pressure, reduce swelling, shortness of breath, and also reduce the risk of developing such serious complications as myocardial infarction and stroke. The effectiveness of diet therapy has been proven by international and Russian national studies. Some studies have class 1A evidence, that is, highly conclusive. These are studies concerning the effectiveness of consuming fish oil, as well as the effects on the human body of the so-called Mediterranean style of nutrition, which contains large amounts of seafood, fish, vegetables and fruits. These recommendations are approved by the American Heart Association and the European Society of Cardiology, which indicates their high level of evidence.
A balanced diet is a balanced, regular (at least 4 times a day) diet with limited salt intake. Research by scientists has shown that if you limit your salt intake, the risk of myocardial infarction and other heart events can be reduced by 25%. It is very useful to increase the consumption of foods containing potassium and magnesium (seaweed, raisins, beets, apricots, zucchini, pumpkin, buckwheat). All individuals should receive professional advice on food choices and follow a diet that is associated with minimal risk of developing CVD.
General recommendations (determined according to cultural traditions):
- food should be varied, energy consumption should be optimal to maintain ideal weight;
- The consumption of the following foods should be encouraged: fruits and vegetables, whole grains and breads, low-fat dairy products, lean meats, fish;
- consume products containing fish oil and w-omega, which have special protective properties;
- the total fat content should not exceed 30% of the total energy composition, and the saturated fat content should not exceed a third of all fat consumed; the amount of cholesterol consumed should be less than 300 mg/day;
- with an isocaloric diet, saturated fats should be replaced partly with carbohydrates, partly with monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats from vegetables and marine animals.
Basic principles of nutrition for cardiovascular diseases:
Diet No. 10 - do's and don'ts
| Can | It is forbidden |
| Dietary salt-free bread, toast, white bread croutons | Fresh bread, pancakes, pancakes, baked goods |
| Vegetable soups with cereals, milk soups | Broths from meat, poultry, fish, mushrooms. Soups with legumes |
| Lean beef, veal, rabbit, chicken, turkey. Boiled or baked without fat | Fatty meat, geese, ducks, offal, sausages, smoked meats, lard and corned beef, canned meat |
| Lean fish and seafood - boiled or steamed | Fatty fish, salted, smoked fish, caviar, canned fish |
| Milk, low-fat cottage cheese, yogurt, kefir | Salty and fatty cheese, sour cream, cream |
| Soft-boiled eggs, omelettes. No more than 1 egg per day | Fried eggs, hard-boiled eggs |
| Cereal dishes, pasta made from durum flour | Legumes |
| Boiled and baked vegetables. Raw vegetables rarely and carefully | Pickled, salted vegetables. Radishes, onions, garlic, mushrooms, radishes, green peas, cabbage |
| Fresh ripe fruits and berries, honey, jam, dried fruits | Fiber fruits, chocolate, cakes |
| Weak tea, fruit and vegetable juices | Natural coffee, cocoa, strong tea, alcohol |
| Vegetable oils, occasionally unsalted butter | Cooking fats and margarines, lard |
Head 1st therapeutic department Dedovets E.S.
Fully or partially limited products
- Avoid fatty meats, cooking fats, fatty poultry meat (duck, goose), meat and fish broths, sausages, canned food and all kinds of smoked meats.
- Kidneys, brains, fish roe, liver due to high cholesterol content.
- Puff pastry and pastry, pastries with cream.
- Fatty fish, canned fish, smoked fish.
- Fatty dairy products (cheese, curd mass, cream, cottage cheese, sour cream).
- Radishes, all types of radishes, sorrel, spinach, legumes and mushrooms in any form are excluded.
- The consumption of chocolate, ice cream, strong tea and coffee, grape juice, and cocoa is prohibited.
- Limit egg yolks, rice, semolina and pasta. For obesity - grapes, sugar, jam, raisins. Honey can be used in minimal quantities. If you are prone to flatulence, you should limit the consumption of milk, white cabbage and all legumes.
Table of prohibited products
| Proteins, g | Fats, g | Carbohydrates, g | Calories, kcal | |
Vegetables and greens | ||||
| radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 19 |
| white radish | 1,4 | 0,0 | 4,1 | 21 |
| red radish | 1,2 | 0,1 | 3,4 | 20 |
| black radish | 1,9 | 0,2 | 6,7 | 35 |
| spinach | 2,9 | 0,3 | 2,0 | 22 |
| sorrel | 1,5 | 0,3 | 2,9 | 19 |
Fruits | ||||
| bananas | 1,5 | 0,2 | 21,8 | 95 |
Berries | ||||
| grape | 0,6 | 0,2 | 16,8 | 65 |
Mushrooms | ||||
| mushrooms | 3,5 | 2,0 | 2,5 | 30 |
Nuts and dried fruits | ||||
| raisin | 2,9 | 0,6 | 66,0 | 264 |
Cereals and porridges | ||||
| semolina | 10,3 | 1,0 | 73,3 | 328 |
| rice | 6,7 | 0,7 | 78,9 | 344 |
Flour and pasta | ||||
| pasta | 10,4 | 1,1 | 69,7 | 337 |
Confectionery | ||||
| jam | 0,3 | 0,2 | 63,0 | 263 |
| jam | 0,3 | 0,1 | 56,0 | 238 |
| candies | 4,3 | 19,8 | 67,5 | 453 |
| pastry cream | 0,2 | 26,0 | 16,5 | 300 |
| cookie | 7,5 | 11,8 | 74,9 | 417 |
Ice cream | ||||
| ice cream | 3,7 | 6,9 | 22,1 | 189 |
Cakes | ||||
| cake | 4,4 | 23,4 | 45,2 | 407 |
Chocolate | ||||
| chocolate | 5,4 | 35,3 | 56,5 | 544 |
Raw materials and seasonings | ||||
| mustard | 5,7 | 6,4 | 22,0 | 162 |
| mayonnaise | 2,4 | 67,0 | 3,9 | 627 |
Dairy | ||||
| milk 3.6% | 2,8 | 3,6 | 4,7 | 62 |
| milk 4.5% | 3,1 | 4,5 | 4,7 | 72 |
| cream | 2,8 | 20,0 | 3,7 | 205 |
| sour cream 25% (classic) | 2,6 | 25,0 | 2,5 | 248 |
Cheeses and cottage cheese | ||||
| cheese | 24,1 | 29,5 | 0,3 | 363 |
| cottage cheese 11% | 16,0 | 11,0 | 1,0 | 170 |
| cottage cheese 18% (fat) | 14,0 | 18,0 | 2,8 | 232 |
Meat products | ||||
| pork | 16,0 | 21,6 | 0,0 | 259 |
| pork liver | 18,8 | 3,6 | 0,0 | 108 |
| pork kidneys | 13,0 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 80 |
| pork fat | 1,4 | 92,8 | 0,0 | 841 |
| salo | 2,4 | 89,0 | 0,0 | 797 |
| beef liver | 17,4 | 3,1 | 0,0 | 98 |
| beef kidneys | 12,5 | 1,8 | 0,0 | 66 |
| beef brains | 9,5 | 9,5 | 0,0 | 124 |
Sausages | ||||
| smoked sausage | 16,2 | 44,6 | 0,0 | 466 |
| smoked sausage | 9,9 | 63,2 | 0,3 | 608 |
| sausages | 10,1 | 31,6 | 1,9 | 332 |
| sausages | 12,3 | 25,3 | 0,0 | 277 |
Bird | ||||
| smoked chicken | 27,5 | 8,2 | 0,0 | 184 |
| duck | 16,5 | 61,2 | 0,0 | 346 |
| smoked duck | 19,0 | 28,4 | 0,0 | 337 |
| goose | 16,1 | 33,3 | 0,0 | 364 |
Fish and seafood | ||||
| smoked fish | 26,8 | 9,9 | 0,0 | 196 |
| salted fish | 19,2 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 190 |
| Red caviar | 32,0 | 15,0 | 0,0 | 263 |
| black caviar | 28,0 | 9,7 | 0,0 | 203 |
| canned fish | 17,5 | 2,0 | 0,0 | 88 |
| cod (liver in oil) | 4,2 | 65,7 | 1,2 | 613 |
Oils and fats | ||||
| animal fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
| cooking fat | 0,0 | 99,7 | 0,0 | 897 |
Non-alcoholic drinks | ||||
| instant coffee dry | 15,0 | 3,5 | 0,0 | 94 |
| black tea | 20,0 | 5,1 | 6,9 | 152 |
| * data is per 100 g of product | ||||
Diet menu for angina pectoris (Diet)
5-6 meals a day are organized. For the whole day, 150 g of gray bread, 100 g of rye bread, 50 g of sugar (including sugar in dishes) and 20 g of butter are allowed. Food should be cooked without salt and then added. In order not to go beyond the permitted amount of salt, you need to exclude prepared meat products and cheeses that contain a large amount of salt.
Eat up to 500 g of fruits and vegetables daily. A large amount of dietary fiber is also found in bran, prunes, figs, gooseberries, dates, raspberries, cranberries, raisins and dried apricots. Somewhat less - in cereals, sweet peppers, carrots, eggplants, cabbage, oranges, quince, pumpkin.
It is necessary to maintain high-density cholesterol levels with omega-3 PUFAs. Enrich your diet with fenugreek and flax seeds, which help lower cholesterol levels. They can be ground in a coffee grinder and added regularly to food (their daily requirement is 2 g). Large amounts of omega 3 are found in walnuts, tuna, soy, mackerel, and herring.
First day
| Breakfast | oatmeal porridge; · vegetable salad with bran and olive oil; · barley coffee. |
| Lunch | · apple (juice). |
| Dinner | · vegetarian vegetable soup; · steamed meat balls; · vegetable stew; · bread made from whole grain flour; fruit (or compote). |
| Afternoon snack | · rosehip infusion (can be replaced with fruit). |
| Dinner | · baked fish; · vegetable salad with seaweed; · tea with milk. |
| For the night | · apples or kefir. |
Second day
| Breakfast | · protein omelet; · cottage cheese with apple and nuts; · weak green tea. |
| Lunch | · fruits in season. |
| Dinner | · soup with Brussels sprouts; · boiled chicken breast; · vegetables stewed with seaweed; · compote |
| Afternoon snack | · vegetable (fruit) juice. |
| Dinner | · baked hake; · vegetable salad with flaxseed oil; · rosehip juice. |
| For the night | apple or acidophilus. |
Diet modifications
The “10 table” diet has several variations.
Diet "Table 10A"
The “Table 10A” diet is indicated for diseases of the cardiovascular system, accompanied by circulatory failure of stages II-III. The diet is aimed at maximum unloading of the cardiovascular system in case of its diseases in a state of decompensation.
General characteristics of the diet
similar to the “10 table” diet, however, the calorie content of the diet is reduced by reducing the amount of bread (which is given in the form of crackers), eliminating the first course and uniformly reducing proteins, fats and carbohydrates. The consumption of extractives and table salt is limited and the introduction of potassium and calcium into the body is increased. All dishes are prepared without salt, the food is pureed.
Chemical composition and energy value:
- proteins - 70 g,
- fats - 70 g,
- carbohydrates - 300 g,
- table salt is excluded,
- calorie content - 2000 kcal,
- free liquid - 600-800 ml.
Diet:
6 times a day.
Recommended and excluded foods are similar to the “10 table” diet.
Diet "Table 10I"
The indication for the Table 10I diet is acute myocardial infarction. The diet is prescribed to accelerate reparative processes in the myocardium, improve the function of the circulatory system as a whole, and normalize intestinal motor function.
General characteristics of the diet:
reduced calorie content, semi-liquid food, table salt is excluded, restriction of fluids, foods and dishes that cause flatulence.
First 2 days:
The need for food is small, the patient only receives 50 ml of water 7 times a day, and the liquid should not have an irritating effect on the digestive organs. This can be weak, warm, slightly sweetened tea, or a decoction of dried fruits.
From the third day to 7-10 days:
The weight of the daily diet is about 1700 g, free liquid - about 600 ml, proteins - 60 g, fats - 30 g, carbohydrates - 180 g, calorie content - about 1200 kcal. Food is given in small portions, pureed. Eating up to 7-8 times a day.
Subsequent days:
The diet is expanded, and by the end of the 2nd week the daily diet contains 70 g of protein, 60 g of fat, 200 g of carbohydrates, and 1600 kcal calories. The food is not pureed, increase the portion of bread and the amount of free liquid to 1000 ml.
Then the patient is transferred to the anti-atherosclerotic diet “Table 10C”.
Reviews and results
This therapeutic nutrition is designed for a long time and should become the rule of life for patients with cardiovascular diseases and high cholesterol levels. The diet takes into account all aspects of nutrition that cause the progression of the disease. Restricting carbohydrates and fats allows you to lose weight, normalize cholesterol and does not negatively affect your health. Patient reviews indicate an improvement in general condition, the appearance of vigor and activity. Many of them changed their lifestyle (excluded smoking and alcohol), included walking and began to actively control their weight.
- “...I liked this healthy diet. First of all, I lost weight, felt better and became healthier overall (for example, I didn’t get sick in winter). At the same time, pills were prescribed, including those to lower cholesterol. Another positive thing is that sugar levels have returned to normal, which in recent years have been at the upper limit of normal. I’m very pleased with the results”;
- “... Recently, pain in the heart area of a compressive nature has appeared, which I associate with weight gain, high blood pressure and psycho-emotional stress at work. This whole bouquet forced me to seriously examine myself and take care of my health. Cholesterol was high, changes on the ECG. First of all, they told me to lose weight, prescribed pills for high cholesterol and blood pressure, nitroglycerin, diet and dosed walking. My result for 5 months minus 6 kg is already good. It has become easier to walk and breathe, and my general condition has improved significantly, but the tests are still not normal. I continue to eat healthy - mostly vegetables and fruits, fish and seafood. Introduced a ban on all sweets and baked goods”;
- “...They diagnosed me with angina, prescribed pills and told me how to eat. It seems to me that this is just proper nutrition, which should have always been followed. It helped me lose weight and improve my condition. Now I’ve decided not to push myself, eat right and walk a lot, if exercise in the gym is prohibited.”
What foods should you avoid if you have angina?
A patient with an established diagnosis will prevent cardiovascular disaster, slow down the progression of atherosclerosis and prevent attacks by limiting the consumption of a number of foods.
Nutrition for angina pectoris focuses on lowering blood cholesterol levels. If you have IHD, it is recommended to limit the following foods:
- fatty types of fish, poultry, meat;
- salo;
- butter;
- yolks;
- sour cream;
- cream;
- fast food;
- tripe;
- caviar;
- rich, strong broths;
- salinity;
- spicy smoked products.
A low-cholesterol diet minimizes lipid imbalance and gets rid of extra pounds.
If a patient with angina is obese, sweet and starchy foods are additionally removed from the diet. Excess weight increases the load on the myocardium and sharply increases the risk of complications of existing cardiovascular diseases (CVD), or provokes their debut. You can calculate your body mass index online here:
| The degree of CVD risk depending on the severity of obesity with t.z. BMI and waist circumference | |||
| BMI, kg/m2 | Characteristics of body weight | Waist circumference | |
| men<102 cm; women<88 cm | men>102 cm; women>88 cm | ||
| Less than 18 | W deficiency | ||
| 18,5-24,9 | Normal W | ||
| 25,0-29,9 | Excess W | Increased | High |
| 30,0-34,9 | Mild obesity | High | Very tall |
| 35,0-39,9 | Moderate obesity | Very tall | Very tall |
| 40 or more | Severe obesity | Extremely high | Extremely high |
Fasting days (after consultation with a cardiologist):
- apple – up to a kilogram of apples per day;
- cottage cheese - half a kilogram in its natural form, cheesecakes, casserole without sauces and gravy;
- dairy – up to a liter of low-fat milk for eight doses per day.