When a man and a woman are just starting to build a relationship, they are unlikely to be interested in each other’s blood type, much less its compatibility. And only when a couple thinks about having a child does this question become relevant. Most often, spouses are tested for groups and Rh factor when the woman is already pregnant. Ideally, undergo a comprehensive examination, including a blood compatibility test upon conception, at the stage of pregnancy planning.
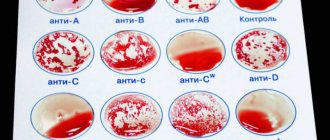
As you know, humans have four types of blood according to their blood group and two according to their Rh factor. The first group is 0 (I), the second is A (II), the third is B (III) and the fourth is AB (IV). In addition, blood can be Rh positive (Rh+) and Rh negative (Rh-).
Blood and Rh compatibility
Doctors say that, as such, blood group incompatibility does not exist. There may be immunological, genetic, HLA incompatibility between spouses, as well as the production of antibodies to the man’s sperm. In this regard, conception may not occur, pregnancies end in miscarriages, the child is born non-viable or dies in the mother’s womb.
As for the blood type of future parents, it has practically no significance when planning pregnancy and does not affect the conception, gestation and birth of offspring.
The situation is different with the Rh factor. In this case, incompatibility of partners with different Rh is possible. As a rule, there are no problems with conception, but there is a possibility of Rh conflict between the woman and the unborn child.
What can incompatible couples do?
The method of treating marital incompatibility depends on the established diagnosis.
- In case of immune infertility, lymphocyte immunotherapy can be performed, which allows changing the state of the mother's immune system in the direction of protecting the embryo. This treatment method can be combined with immune drugs or hormone therapy.
- In case of genetic infertility, it is recommended to use assisted reproduction methods, which make it possible to evaluate its chromosomal and gene set before embryo transfer in order to exclude the transmission of hereditary diseases.
- If there are antisperm antibodies, the couple is recommended to live with a condom for at least 1 month in order to reduce the level of sensitization in the male and female body. At the same time, desensitizing and immunosuppressive therapy is prescribed.
When can Rh conflict occur?
It is possible only in one case - if the mother’s Rh factor is negative, the father’s is positive, and the fetus has inherited the father’s Rh factor.
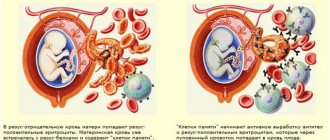
The conflict arises due to the incompatibility of the mother's Rh-negative blood and the red blood cells of the unborn child, on the membranes of which there is a specific protein. When fetal red blood cells enter a woman’s bloodstream, her body perceives them as foreign and begins to produce antibodies against them.
As a rule, during the first pregnancy the amount of antibodies in the blood is small, so they do not affect the developing fetus. In addition, during the first pregnancy, the red blood cells of the unborn baby should not normally enter the mother’s blood, since this is prevented by the blood-placental barrier. Fetal blood enters a woman's bloodstream only during natural childbirth or during a caesarean section.
However, in some cases, it is possible for fetal red blood cells to reach the mother, including:
- Abortion.
- Ectopic pregnancy.
- Miscarriage.
- Taking amniotic fluid for analysis to diagnose fetal pathologies.
- Chorionic villus biopsy is the taking of its villi for analysis to diagnose fetal diseases.
- Bleeding during pregnancy.
- Rh+ blood transfusion.
When a child’s red blood cells come into contact with the mother’s blood, her body begins the process of producing Rh antibodies, which is called sensitization. If none of this has happened to a woman, most likely there will be no conflict during her first pregnancy, and the contact between the blood of mother and child, which occurs during the first birth, does not affect the health of the latter in any way. But if sensitization occurred for the above reasons or during the first birth, then this is irreversible. In subsequent pregnancies, treatment is necessary to prevent Rh conflict.
What tests are taken if partner incompatibility is suspected?
If doctors suspect that a couple has incompatibility based on various parameters, then the following examinations can be carried out for an objective diagnosis:
- determination of antisperm antibodies in male and female bodies (plasma, sperm or cervical discharge is used as biomaterial);
- medical genetic counseling, karyotyping and detection of genetic defects.
A detailed DNA analysis of a woman or man is carried out only if all other diagnostic methods have proven to be uninformative in identifying the causes of infertility. This test is expensive but can identify the exact cause of genetic infertility.
Why is Rh conflict dangerous?
Antibodies that are produced to foreign proteins upon contact between the blood of a woman and the fetus destroy the red blood cells of the unborn child. He develops anemia and also increases bilirubin levels, which usually occurs when red blood cells break down. Bilirubin is toxic and has a negative effect on the brain. The bone marrow of the unborn baby cannot cope with the production of new red blood cells; the spleen and liver are involved in the process. As a result, they increase in size, and this leads to an increase in pressure in the veins, swelling of the subcutaneous fat and other tissues. Such disturbances in fetal development are called hemolytic disease, which can lead to brain pathologies and even intrauterine death. Thus, Rh conflict has the following consequences for the child:
- swelling (dropsy);
- jaundice;
- hypoxia;
- anemia;
- mental retardation;
- intrauterine death.
For the health of the mother, Rh conflict does not pose a danger and manifests itself as an allergic reaction.
What is genetic incompatibility of partners?
Genetic infertility in women and men accounts for about 10% of all types of impaired fertility. The main reason lies in a change in the quality or quantity of genes that are stored on chromosomes. As a result, when the nuclei of eggs and sperm divide, cells with an incorrect chromosome complement can be formed.
The following factors increase the risk of genetic incompatibility:
- excessive doses of radiation;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- marriages between blood relatives;
- hereditary diseases.
Separately, it is worth dwelling on age. The older the partners, the higher the proportion of chromosomal mutations, and this applies to a greater extent to women. On average, after 35 years, the number of eggs that have genetic disorders increases. These changes become especially noticeable in the category of women 40+ (the proportion of mutant oocytes can reach 80%).
In case of severe genetic damage, the mechanism of natural selection is triggered. Embryos with the wrong chromosome set sooner or later stop in their development, which leads to miscarriage or missed abortion. Therefore, if there are repeated pregnancy losses, a genetic consultation is required for the couple.
As part of genetic counseling, a couple may undergo various types of tests:
- karyotyping;
- expert sperm analysis;
- analysis of mutations in specific genes that are most often associated with infertility or recurrent miscarriage;
- FISH study of sperm, eggs, etc.
Treatment
Thanks to medical advances, even Rhesus-incompatible spouses can produce healthy children.
At the first visit to the antenatal clinic, the pregnant woman is immediately sent for a blood test for the Rh factor. If the expectant mother is Rh negative, the future father must also donate blood. If he is Rh negative, then the conflict will not occur, but if he is positive, special monitoring of the woman and the developing fetus is required, since it can inherit the father’s blood. The expectant mother will have to periodically donate blood for Rh antibodies. If their production has begun, special treatment is required. If sensitization is detected in time and timely therapy is started, the child will be born healthy.
First, the doctor constantly checks the condition of the unborn child in order to detect symptoms of Rh conflict. If signs appear, treatment will depend on their severity. The main thing is to support the vital activity of the fetus, which is to combat oxygen starvation and developmental delays. It is important to increase the level of red blood cells in the blood, which may require intrauterine blood transfusion through the umbilical cord vein under ultrasound guidance. But more often a blood transfusion is given to a child after birth. Sometimes this even requires early birth.
If no antibodies are detected in a pregnant woman when donating blood, it means that sensitization has not occurred, but prevention is still required. To prevent the production of antibodies when fetal red blood cells come into contact with maternal blood, anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin is prescribed in a special course, which prevents fetal red blood cells from being recognized as foreign, thus preventing sensitization.
Immunoglobulin is usually prescribed in the following cases:
- if antibodies are not detected at the 28th week of pregnancy;
- such therapy is required after the birth of an Rh-positive child to prevent postpartum sensitization (during the first 72 hours);
- after cases such as abortion, ectopic pregnancy, miscarriage, taking chorionic villi and amniotic fluid for analysis and other risk factors.
The effect of immunoglobulin does not last long - about 12 weeks, so each subsequent pregnancy of an Rh-negative woman requires repeating the course.
Is it possible to do IVF if the spouses are incompatible?
Yes, sure! In vitro fertilization is the method of choice to help couples who are faced with incompatibility. Reproductologists have a unique opportunity to neutralize the negative impact of unfavorable internal environmental factors that disrupt the process of pregnancy.
In reproductive services, couples can receive a full range of services for the diagnosis and treatment of even the rarest forms of infertility. Our center conducts examinations that help identify the exact cause of incompatibility between spouses in order to select the most optimal ways to solve the problem. We accompany the couple at all stages of the journey to long-awaited parenthood. Sign up for a consultation at SM-Clinic at convenient office hours!
Features of pregnancy management for women with negative Rh factor
An obstetrician-gynecologist is obliged first of all to determine the Rh and blood type of a man and a woman. After the tests, the doctor assesses the likelihood of red blood cell breakdown in the unborn child. He clarifies whether there was an ectopic pregnancy before, whether the woman had abortions, or underwent a blood transfusion. A healthcare professional must determine whether sensitization is present. It is necessary to perform desensitization, and, if indicated, take preventive measures to prevent pregnancy complications.
The obstetrician-gynecologist will assign the expectant mother to one of the observation groups. A woman may be classified as a primigravida with no sensitization. The expectant mother can be assigned to the group of sensitized patients without symptoms of hemolytic disease. The third group includes women with hemolytic disease.
The management of pregnancy directly depends on which category the woman belongs to. Medical specialists consider each case individually and select the most appropriate tactics for a particular situation. Timely prevention allows women to give birth to a healthy baby and avoid complications during pregnancy. If you do not see a medical professional, your risk of developing hemolytic disease will increase.
Ways to deal with incompatibility
If immune infertility is diagnosed, lymphocytoimmunotherapy can be performed, which is combined with taking hormones. The main goal of treatment is to change the mother's immune response to the embryo.
When antisperm bodies are detected, therapy involves sexual activity using barrier contraception for the time prescribed by the doctor. In parallel, immunotherapy with allergens is prescribed.
In case of genetic incompatibility, the use of ART is indicated.