The concept of “functional diagnostics” combines various methods of studying and assessing the functions of organs and systems of the body, which can be carried out both at rest (electrocardiography, electroencephalography, echocardiography) and during exercise (bicycle ergometry and treadmill test, transesophageal cardiac pacing, breathing test during electroencephalography and other). Loading implies the artificial creation of conditions under which the organ or system under study functions in “extreme” conditions, allowing for the detection of hidden pathological changes. In some situations, stress tests with various drugs are used, where the provoking factor is chemicals. The most common example is a test with drugs that dilate the bronchi when studying the function of the respiratory system. A separate class should be allocated to long-term studies (24-hour Holter electrocardiogram monitoring, 24-hour blood pressure monitoring, etc.).
The main methods of functional diagnostics in outpatient practice are standard studies of the functions of the cardiovascular system, which are equally necessary both for primary diagnosis and for further monitoring of the condition of the heart and blood vessels. These methods include:
- Electrocardiography (ECG);
- Echocardiography (ECHO-CG);
- 24-hour Holter ECG monitoring (CMECG);
- 24-hour blood pressure monitoring (ABPM).
Heart diagnostic methods
During the initial visit, the doctor will interview the patient and find out whether he has complaints of pain, shortness of breath, increased heart rate, high blood pressure and other symptoms.
In modern medicine, several types of diagnosing heart diseases are used:
- electrocardiogram (ECG);
- bicycle ergometry (ECG with exercise on an exercise bike);
- treadmill (ECG with exercise on a treadmill);
- computed tomography of the heart;
- coronary angiography of the heart;
- EchoCG (ultrasound of the heart);
- myocardial biopsy;
- 24-hour monitoring of heart and blood pressure according to Holter.
Diagnostic capabilities of our center’s cardiologists
As a result of the consultation, based on the patient’s complaints, survey data and objective examination, the cardiologist can make a preliminary diagnosis, confirm or exclude a previously made diagnosis, and make a conclusion about the patient’s current condition. However, additional examinations are necessary to determine the full picture of the disease and clarify the diagnosis. During the initial consultation, the cardiologist can make some treatment prescriptions that the patient can carry out while being examined. The consultation with a cardiologist usually lasts at least an hour.
In order to study coronary circulation, our cardiologists prescribe various functional tests - Holter ECG monitoring, stress and stress tests to identify pathology of blood flow in the coronary arteries.
To determine the function of the heart chambers and ejection fraction, our cardiologists perform echocardiography with and without exercise. An examination by our cardiologists allows us to establish a second expert opinion and prescribe adequate treatment and refer the patient to cardiac surgeons.
Electrocardiogram
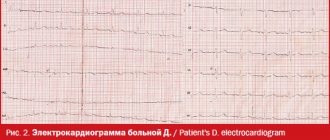
ECG is considered the most important method for diagnosing the heart. Electrodes are placed on the patient's chest to read heart impulses. The cardiogram is recorded on paper tape.
An ECG detects a number of heart diseases, such as ischemia, myocardial infarction, all forms of arrhythmia, and shows the physical condition of the heart.
To detect ischemia, electrocardiography with exercise (bicycle ergometry and treadmill) is also used. The patient sits on a treadmill or exercise bike while wearing electrodes to read heart impulses. The doctor prescribes the amount of load taking into account the age, gender and other individual characteristics of the patient.
A 24-hour ECG is also used, which is continuous monitoring using a portable device, which monitors heart rhythm disturbances under various circumstances. This research method is prescribed to detect silent ischemia, with unclear causes of fainting, as well as to monitor the performance of pacemakers.
Electrocardiography (ECG)
The primary, most common and frequently prescribed method for testing cardiac function is electrocardiography (ECG).
An ECG is a recording of the electrical activity of the heart at rest, at a given point in time, on paper or electronic media.
ECG is the main method for diagnosing heart pathology in outpatient practice and allows you to diagnose:
- disturbances of heart rhythm and intracardiac conduction;
- the presence of hypertrophy of the heart muscle and overload of various parts of the heart, for example, with heart defects, hypertension, heart failure;
- myocardial changes in cardiomyopathies, myocarditis, coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction.
It should be noted that electrocardiography, even normally, is variable, which depends on age, gender, anatomical and constitutional characteristics of a person and other factors. And it is the correct interpretation of the graphic display of heart activity, carried out by a functional diagnostics doctor, analysis of ECG waves and intervals, that allows for correct clinical assessment and differential diagnosis.
ECG is often used in emergency clinical situations requiring emergency treatment:
- complaints of pain in the chest, under the left shoulder blade, pain in the left arm, pain in the epigastric region;
- a feeling of “irregularity” of the heart (interruptions in the work of the heart, palpitations, a feeling of “stopping” of the heart);
- sudden shortness of breath, feeling of lack of air;
- episodes of dizziness, loss of consciousness, “blackout” in the eyes to exclude a cardiac cause of these complaints.
ECG is included in almost all therapeutic programs of dispensary observation, preliminary, periodic and preventive medical examinations.
An ECG begins the examination of all patients who complain of increased blood pressure and who have an indication in their life history (anamnesis) of the presence of chronic or previous acute heart disease.
Myocardial biopsy
Myocardial biopsy is usually performed to detect rejection after heart transplantation. In addition, this type of heart diagnosis helps in identifying myocarditis. Most often, a biopsy of the right ventricle is performed. This study cannot be performed in cases of thrombosis of the atria and ventricles, after a recent myocardial infarction and severe tachycardia.
The Medicenter clinic network has high-precision diagnostic equipment for conducting ECG, ultrasound, echocardiography, daily monitoring, and other types of studies that can identify any diseases of the cardiovascular system.
ECHO-cardiography (ECHO-CG)
If, during an examination, the patient has elevated blood pressure numbers, expansion of the boundaries of the heart, murmurs when listening to the heart, pathological changes are detected on the ECG, and also if changes in the size and shape of the heart are visible on the chest x-ray, its atypical location, or modified aorta and pulmonary artery, the doctor prescribes an ultrasound examination of the heart: transthoracic echocardiography.
ECHO-cardiography (ECHO-CG, cardiac ultrasound) is an ultrasound method for studying the structure and function of the heart. The method is based on capturing ultrasonic signals reflected from the structures of the heart by a sensor and converting them into an image on the monitor screen. When performing ECHO-CG, the doctor evaluates:
- the size of the heart and its chambers, as well as the pressure in them,
- condition of the atria and ventricles (heart chambers) and heart valves,
- the thickness of the walls of the heart, their structure and integrity,
- contractile function of the myocardium (work of the heart muscle),
- features of blood movement inside the heart through the valves
- condition of the outer lining of the heart - the pericardium
- condition of the pulmonary artery and aorta, pressure in them.
ECHO-CG is the main method for diagnosing acute and chronic heart diseases: defects, inflammatory diseases of the heart valve apparatus and its membranes (endocarditis, pericarditis). This study also evaluates and clarifies the degree of myocardial hypertrophy, the presence of dysfunction of the heart muscle when it is damaged (infarction, myocarditis), and the presence of blood clots in the cavities of the heart. A cardiologist or therapist, correlating the data obtained from ECHO-CG with the clinical picture, decides on the tactics for further management of the patient.
Cardiac functional studies
1. Electrocardiography (ECG) is a method of recording the electrical potentials of the heart at rest, during drug tests. ECG registration is carried out using multi-channel electrocardiographs made in Japan (Nihon Kohden, Fukuda), Switzerland (Schiller), Russia (Altonika), which record ECG in both manual and automatic modes with automatic analysis and interpretation of the received data.
Preparation: take previous ECGs and extracts with you.
2. Bicycle ergometry (VEM) is an electrocardiographic study with dosed physical activity on a bicycle ergometer. It is used to identify the functional class of angina pectoris, initial and latent forms of coronary heart disease, hypertension, and to determine individual tolerance to physical activity. It is carried out using ECG stress systems “Valenta”, “Schiller” (Switzerland), “Alton-test”, on bicycle ergometers Tunturi (Finland), eBike RS (Germany), Schiller (Switzerland).
Preparation: 2 days before the study, you must stop taking antihypertensive drugs, beta blockers, diuretics; Avoid taking nitrates 1 day before the examination. Stop taking cardiac glycosides 7 days before. The examination is carried out 2 hours after taking a light breakfast. Have an electrocardiogram with you.
3. Holter ECG monitoring is a method of daily recording of an ECG during the patient’s normal life. The device is attached to the patient’s body for a day or for another period of time. In this case, the patient can lead a normal lifestyle, the device takes readings with a given regularity. It is used to diagnose cardiac rhythm and conduction disorders, detect myocardial ischemia, including silent myocardial ischemia. It is carried out using ambulatory ECG monitoring systems Schiller (Switzerland), Machaon (Russia), Holter-Myocard (Russia).
Preparation: Before the examination, remove hair from the front of the chest. Bring with you an electrocardiogram, previous studies, extracts.
4. Echocardiography (ECHO-CG) is a method of ultrasound examination of the heart using Doppler analysis (spectral, color, tissue) for the diagnosis of heart diseases: congenital and acquired defects, coronary heart disease, hypertension, heart tumors, pericarditis. It is carried out using ultrasound machines from the world's leading manufacturers Medison (South Korea), General Electric (USA), Ultrasonix (Canada), Aloka (Japan).
Preparation: Have an electrocardiogram, previous studies, extracts with you.
5. Daily blood pressure monitoring is a method that allows you to assess the daily fluctuations in blood pressure and heart rate of the patient. The device is attached to the patient’s body for a day or for another period of time. In this case, the patient can lead a normal lifestyle, the device takes readings with a given regularity. The method is used to diagnose hypertension, hypotension, “white coat” hypertension, and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment. Outpatient blood pressure monitoring systems are used: Schiller (Switzerland), Altonika (Russia).
Preparation: Have previous studies and extracts with you.
6. Veloergospirometry - cardiopulmonary stress test (KAREN-Test). An electrocardiological study is carried out on a bicycle ergometer (a special type of exercise bike that can accurately dose the load) with measurement of the composition of exhaled air in order to analyze indicators of pulmonary gas exchange. Used to assess the adaptive capabilities of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems. It is used to identify hidden coronary insufficiency and to determine physical performance (diagnosis of the causes of decreased exercise tolerance, planning of physical training and assessment of their effect in cardiopulmonary rehabilitation). Ergospirometry plays a special role in sports medicine. This is the only, unparalleled method for assessing the aerobic capabilities of athletes. It allows you to objectively assess the level of training of an athlete, his prospects in terms of further improving his athletic performance. The test is carried out on bicycle ergometers “Schiller” (Switzerland) and “Cosmed” (Italy) according to standard loading protocols.
Preparation: 2 days before the study, you must stop taking antihypertensive drugs, beta blockers, diuretics; Avoid taking nitrates 1 day before the examination. Stop taking cardiac glycosides 7 days before. The examination is carried out 2 hours after taking a light breakfast. Have an electrocardiogram with you.
The main objectives of cardiological research:
• detection of hidden coronary insufficiency and painless myocardial ischemia (using electrocardiography, bicycle ergometry, Holter ECG monitoring); • diagnosis of heart rhythm and conduction disorders (using ECG, Holter ECG monitoring, echocardiography with color Doppler mapping); • diagnosis of arterial hypertension (using bicycle ergometry, echocardiography with color Doppler mapping, ambulatory blood pressure monitoring); • assessment of the effectiveness of therapy for ischemic heart disease, heart rhythm disorders, arterial hypertension; • determination of individual tolerance to physical activity using bicycle ergometry, treadmill; • neurophysiological.