Blood transfusion is widely used in modern medicine. As you know, when the bloodstream becomes empty, death occurs. Donor blood is necessary not only for large blood losses, but also for certain diseases. Thanks to blood transfusion, thousands of people can save lives and improve their health. The theory of blood compatibility appeared relatively recently - in the middle of the last century. Thus, it became possible to avoid the severe consequences of transfusion caused by incompatibility.
Blood transfusion is a serious procedure that requires strict adherence to certain rules. Incompatibility between the recipient and the donor can lead to serious consequences, that is, to the death of the patient. When inappropriate blood is transfused, red blood cells stick together (agglutination reaction) and are destroyed. Blood group compatibility is carefully checked before the procedure is performed.
Rh factor
During scientific research in 1940, an antigen was found in the blood of macaques, which later received the name Rh factor. It is hereditary and depends on race. Those people who have this antigen in their blood are Rh positive, and if it is absent, they are Rh negative.
Transfusion compatibility:
- Rh negative is suitable for transfusion to people with Rh negative;
- Rh positive is compatible with any Rh blood.
If you use Rh-positive blood for a patient with a Rh-negative category, then special anti-Rhesus agglutinins will be produced in his blood, and with another manipulation, red blood cells will stick together. Accordingly, such a transfusion cannot be carried out.
Any transfusion is stressful for the human body. Whole blood is transfused only if the loss of this biological fluid reaches 25% or higher. If less volume is lost, blood substitutes are used. In other cases, transfusion of certain components, for example, only red blood cells, is indicated, depending on the type of lesion.
Problems during pregnancy
Pregnancy for a woman with no Rh factor in her blood has the same consequences, regardless of her blood type. Gynecologists send both spouses to the laboratory to determine Rh.
The expected course of pregnancy may be complicated by an Rh conflict with the fetus if the child receives Rh-positive genes from the father. The first pregnancy is considered more favorable because the mother's immune system begins to reject the fetus only at the end of the term. The child is born with jaundice, liver dysfunction, and anemia. Such a baby is taken under control and receives timely treatment. With age he becomes completely healthy.
During a repeat pregnancy (even taking into account previous abortions), ready-made antibodies are present in the woman’s blood, and they begin to act on the fetus from the first weeks. This threatens miscarriage and disruption of the formation of internal organs.
Modern medicine has learned to combat this pathology by introducing anti-Rhesus globulin, which has the ability to bind and neutralize the effect of maternal antibodies. Rhesus negative women should take care of the future of their children.
How to determine blood type
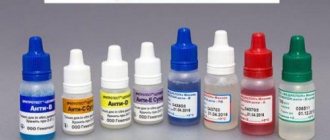
To determine the blood group during transfusion, standard serum is taken and the blood being tested is dripped into it. This serum contains certain antibodies. The blood reaction occurs with antigens in the red blood cells. They are either similar to antibodies in serum or they are not. Red blood cells in different blood groups agglutinate with a certain serum, that is, they accumulate into a small mass.
- Example: to detect the third (B) and fourth blood group (AB), serum containing anti-B antibodies is used.
- For the second (A) and fourth (AB), serum containing anti-A antibodies is prepared.
- Blood group 1 (0) does not cause any reactions with any serum.
Blood group test
Story
The fourth blood group is the youngest and rarest. There are less than 10% of people with such indicators on Earth. People with AB indicators appeared on our planet about 1000 years ago. Today, there are several versions of why the blood suddenly changed its usual indicators.
Theory one. According to some scientists, the mixed group appeared as a result of interethnic marriages. It is believed that the first children with such indicators were born in marriages of Europeans and Mongols. Such unions were not possible before, and therefore the mixing of blood that gave such a group was not observed.
Theory two. Blood group AB is a protective reaction of the body. According to this theory, during times of widespread incidence of various viral infections, nature launched a protective mechanism by combining antigens A and B on the red blood cells of one person. Thus, the immune system was significantly strengthened, which made it possible to resist diseases such as measles, rubella, influenza, rabies and pneumonia.
However, this theory does not explain why there are so few people with these indicators.
Theory three. Diet. According to this theory, changes in blood composition are similar to mutations. Some geneticists argue that it was the emergence of new foods that provoked this mutation. In their opinion, chemically processed foods are to blame for the appearance of people with blood group 4. However, the fact of the small number of such people also does not fit into this hypothesis.
Blood compatibility
The most important criterion for choosing a donor for a patient is group compatibility of blood during transfusion. To answer the question why there is no blood compatibility, you need to know that there is no universal group for everyone, but a special table will help you choose the right one, which shows the blood groups that are suitable for everyone:
Blood compatibility chart
- For example, a person of the first group is an ideal blood donor; it is suitable for all other groups; the fourth is a universal recipient.
- The first group (0) can be transferred to all other groups without any problems, but it can only receive its own, the first.
- The second (A) is suitable for the second and fourth, but can accept its own and the first.
- The third (B) is a donor for its own and the fourth group and accepts only the third and first.
- The fourth blood group (AB) is an ideal recipient; it accepts all blood groups, but only the fourth is suitable as a donor.
In addition to human blood groups, there is another important criterion by which the donor and recipient are matched to each other. Great importance is attached to the Rh factor or antigen. It can be positive and negative, they are incompatible.
For example, if blood is transfused from a blood donor with a third blood group and a negative Rh factor to a patient with the same group with a different Rh factor, the patient’s native plasma sticks to the donor’s red blood cells, causing an incompatibility reaction. In medicine, this process is called an agglutination reaction and leads to death. The number of antigens in blood plasma is also determined by different systems.
Features of a man and a woman
Since carriers of blood type 4 are unique, the perception of their sex life is also a little elevated. This concerns the fact that both men and women always like to show attention to themselves and receive it to the fullest. Their chosen ones should always be a little different from everyone else, which can make a wonderful married couple.
With a successful pregnancy, there is no guarantee that such a couple will have a child of the same character. His blood group may be completely different, for example 2nd or 3rd. As a rule, marriages with these blood types are long-lasting and try to show love and care to each other throughout their lives. This strengthens their union for a long time, especially if a healthy baby is born after long-awaited years.
- Author: Boris
How did I become a doctor? Quite a difficult question... If you think about it, there was no choice. I was born into the family of a resuscitation doctor, and every day at dinner I heard my father’s story about how his day went. As a child, this all seemed fantastic, beyond reality. Rate this article:
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- 1
(40 votes, average: 4.3 out of 5)
Share with your friends!
Blood compatibility for conceiving a child
Before pregnancy, planning a child needs to be approached wisely. Reproduction specialists advise parents to determine blood compatibility in advance. The child’s inheritance of a certain set of qualities from each partner will depend on this, and checking Rh compatibility will help protect against hemolysis during pregnancy. If a woman is Rh-, and a man is Rh-positive, a Rh-conflict arises, in which the body perceives the fetus as foreign and begins to fight, actively producing agglutinins (antibodies) against it.
- What disability group is given for grade 3 knee gonarthrosis?
Rhesus conflict poses a danger not only for the expectant mother. Hemolytic disease can occur when positive and negative red blood cells react in the fetal bloodstream. Ottenberg's rule can determine whether conception will be successful based on blood type:
- it will help protect the couple by finding out what diseases can arise during conception and pregnancy;
- establish an approximate scheme of combination of a set of chromosomes during the formation of a heterozygote;
- guess what Rh factor the child may have;
- determine height, eye and hair color.
Compatibility table of blood groups and Rh factor
The ratio of the blood type of the father and mother determines the possible inheritance of qualities and genes by the child. Incompatibility does not mean the inability to get pregnant, but only indicates that problems may arise. Knowing in advance is better than finding out when it's too late. It is better to check with your doctor which blood groups are incompatible for conceiving a child. Compatibility table of blood groups and Rh factor:
| Blood type | 0(I)Rh+ | 0(I)Rh- | A(II)Rh+ | A(II)Rh- | B(III)Rh+ | B(III)Rh- | AB(IV)Rh+ | AB(IV)Rh- |
| 0(I)Rh+ | + | — | + | — | + | — | + | — |
| 0(I)Rh- | — | + | — | + | — | + | — | + |
| A(II)Rh+ | + | — | + | — | + | — | + | — |
| A(II)Rh- | — | + | — | + | — | + | — | + |
| B(III)Rh+ | + | — | + | — | + | — | + | — |
| B(III)Rh- | — | + | — | + | — | + | — | + |
| AB(IV)Rh+ | + | — | + | — | + | — | + | — |
| AB(IV)Rh- | — | + | — | + | — | + | — | + |
The probability of a child inheriting the Rh factor:
| Dad | Mother | Baby |
| Positive | Positive | 75% positive 25% negative |
| Positive | Negative | 50/50 |
| Negative | Positive | 50/50 |
| Negative | Negative | Completely negative |
Advantages and disadvantages of AB (IV) Rh (-)
The main disadvantage of the 4th backing track is the high likelihood of a difficult pregnancy if the partner is Rh positive. But they learned to treat it. The main thing for a woman with a fourth negative who is carrying a child is to closely monitor her health. In addition to this aspect, there are also disadvantages:
- susceptibility to diseases of the respiratory system and digestive tract;
- manic disorders in men due to prolonged depression.
The blood type is given at conception and does not change throughout life. Therefore, you should not be upset because of its presence. It is better to pay attention to the advantages that it gives to its carriers:
- Any Rh (-) blood is suitable for 4 negative.
- A donor with IV Rh (-) can help many people.
- Increased cortisol levels provide good endurance.
Blood type is not good or bad. It is enough to monitor your health to minimize the likelihood of developing deficiencies associated with the group or Rh factor. People with “new” blood are able to prolong the lives of many people and give humanity many discoveries thanks to their intellectual abilities.
Blood group compatibility
In the 20th century, the idea of transfusion arose. Blood transfusion is a useful procedure that restores the total volume of blood cells; plasma proteins and red blood cells are replaced. The compatibility of the blood groups of the donor and recipient during transfusion is important, affecting the success of the blood transfusion. Otherwise, agglutination will occur - a fatal gluing of red blood cells, resulting in the formation of a blood clot, which leads to death. Blood compatibility for transfusion:
| Blood type | Recipients | Which ones can you transfuse from? |
| 0(I) | I, II, III, IV | I |
| A (II) | II, IV | I, II |
| B(III) | III, IV | I, III |
| AB(IV) | IV | I, II, III, IV |
First
The first blood group is considered to be the foundation of human civilization. Our ancestors developed the habits of excellent hunters, brave and persistent. They are ready to spend all their strength to achieve their intended goal. Modern first-bloods need to be able to plan their actions in order to avoid rash actions.
Main character traits:
- natural leadership;
- extroversion;
- better organizational skills.
Strengths:
- strong digestive system;
- physical endurance;
- increased ability to survive.
Weaknesses are considered:
- Types of arthrosis and their degrees for which a disability group is given
- increased acidity (risk of peptic ulcer);
- predisposition to allergies, arthritis;
- poor clotting;
Second
City dwellers. Evolution moved forward and people began to engage in agriculture. When plant protein became the source of human energy, the vegetarian second blood group arose. Fruits and vegetables began to be used as food - the human digestive system began to adapt to changing environmental conditions. People began to understand that following the rules increases their chances of survival.
Main character traits:
- communication skills;
- constancy;
- composure.
Strengths:
- good metabolism;
- excellent adaptation to change.
Weak sides:
- sensitive digestive system;
- weak immune system.
Third
People with the third blood group are called nomads. It is difficult for them to experience an imbalance within themselves, in the team. It is better to live in mountainous areas or near water bodies. They suffer from a lack of motivation because their bodies produce large amounts of cortisol when they are stressed.
Main character traits:
- flexibility in decisions;
- openness to people;
- versatility.
Strengths:
- strong immunity;
- tolerate changes in diet well;
- creative.
Weak sides:
- Is disability allowed for arthrosis of the knee and other joints?
- susceptible to autoimmune diseases;
- lack of motivation and self-confidence.
Fourth
Holders of the rarest, fourth blood group occurred as a result of the symbiosis of the second and third. A bohemian, easy life is what characterizes its representatives. They were tired of everyday decisions and devoted themselves to creativity. The total number of people with such a group is only 6% on the planet.
Main character traits:
- mysterious;
- individual.
Strengths:
- resistant to autoimmune diseases;
- resist allergic manifestations.
Weak sides:
- fanatics, capable of going to extremes;
- Drugs and alcohol should be avoided.
Diet tips
In the last century, the theory of the dependence of nutrition on blood type was very popular. The Rh factor was not taken into account at all. It was believed that there were certain foods that were most important for a person with each blood type. They also pointed out unhealthy foods that pollute the body and contribute to the occurrence of diseases.
Here's someone who only ate meat
The origin of all people with the first group is genetically related to the first anthropoid individuals that did not have antigens in the blood. They hunted and ate only meat. Due to drastic environmental changes, it is impossible for today’s “hunters” to consume meat alone; they will also need other healthy products.
The diet was proposed to be followed throughout life. Although the theory has long been refuted by long-term research, it still has followers. Therefore, we present everything that concerns the first blood group.
What is possible
People with this trait are considered obese. A balanced diet requires limiting sweets and flour products.
- Dishes made from lean beef or lamb, fish, and seafood are shown.
- Porridge should be prepared only from whole grains (buckwheat is the most useful).
- You should give preference to dishes made from pumpkin, broccoli, spinach, seaweed with onions, and parsley.
- You can drink green tea, herbal teas, rosehip decoction.
Conventional recommendations will have to be taken critically
What not to do
It is not recommended to combine milk and meat dishes, especially pork, in a daily diet.
- Sausage, smoked meats, and fatty meats are prohibited.
- Dairy products and eggs.
- It is proposed to give up sour fruits and berries, olives, citrus fruits, oranges, tangerines, and strawberries.
- Oatmeal and semolina are limited.
- Butter, hard cheeses, ice cream, ketchup, and mayonnaise are considered contraindicated.
- Potatoes, legumes, cabbage.
- Black tea, coffee, orange juice, kefir and milk.
The theoretical foundations of nutrition based on blood type provide for a gradual transition to a strict diet and allow temporary relaxations. Some consider this approach the only rational way to lose weight or maintain weight and health.
Modern medicine does not approve of excesses in nutrition, but is also against strict vegetarianism. Food must contain all the necessary components, otherwise it will take a long time to restore the imbalance with medications.
What to do if there is a Rh conflict?
If the expectant mother and fetus are threatened by the consequences of Rh conflict, she should be under constant medical supervision.
In addition to regular blood tests to assess antibody levels (the more, the worse for the baby), a pregnant woman with a serological conflict should constantly undergo ultrasound examination for any signs of hemolytic disease of the fetus. Ultrasound examination allows you to measure blood flow in the artery of the child’s brain and assess the condition of the amniotic fluid and placenta. If anemia is suspected, the doctor prescribes additional diagnostic measures, most often cordocentesis. This is an accurate and commonly used test to obtain cord blood. Under ultrasound control, the umbilical vessels are dissected using a thin needle, after which about 0.5-1 ml of blood is taken. Such a blood test answers the question of what degree of anemia we are dealing with and what kind of blood the fetus has. This study allows you to plan further procedures.
Can incompatibility be cured?
Unfortunately, treatment of incompatibility is impossible, but, nevertheless, even with such a diagnosis there is a chance to carry and give birth to a healthy child.
The most important thing is the prevention of serological conflict and its early diagnosis. The expectant mother should be closely monitored by a doctor to undergo blood tests every few weeks, check antibody levels and check the intrauterine development of the fetus using ultrasound.
Most gynecologists, when identifying this phenomenon, prescribe the use of anti-D-immunoglobulin, which is administered by injection between 28 and 32 weeks of pregnancy, which increases the likelihood of avoiding the consequences of the conflict. A repeat dose is given 72 hours before the baby is born. After this time, the anti-D immunoglobulin vaccine will no longer serve its purpose. Administration of immunoglobulin during the first pregnancy often saves the life of the second child. The vaccine is also given after a miscarriage, abortion, amniocentesis, cesarean section, or bleeding during labor.