Cardiac arrhythmia: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Arrhythmia is a deviation of the heart rate from the normal value. In a normal state, the range of the number of contractions of the heart muscle is quite wide. The heart rate depends on the physical load on the human body and on the emotional state. With strong emotions, the number of heart beats per minute increases significantly. An increase in the number of heart beats per minute for no apparent reason is called tachycardia. On the contrary, a decrease in the number of beats is bradycardia. If premature vibrations of the heart occur, these contractions are called extrasystoles. If the heart rhythm is delayed or follows paths other than normal, the process is called arrhythmia. This abnormal heartbeat can be either regular or irregular.
Arrhythmia processes can occur in different areas of the heart: in the atrium and in the ventricles. Arrhythmias that occur in the ventricles are for the most part not life-threatening, but cause the most serious condition of the patient. Most arrhythmias do not affect the function of the heart as a blood pump. Therefore, there is no great risk to human life. But such conditions themselves can cause great anxiety to the patient. Although, as soon as a person understands that his condition is not life-threatening, the anxiety goes away.
Symptoms of arrhythmia
The feelings experienced by a person suffering from arrhythmia can vary significantly. The main sign of arrhythmia is the sensation of a beating heart when lying on the left side. But even absolutely healthy people can feel the rhythm of their hearts. If a person suffers from arrhythmia, then he regularly feels an atypical heart rhythm.
If an arrhythmia occurs, then due to a lack of oxygen delivered to the organs, and in particular to the brain, headache, fainting and dizziness may occur. If the symptoms described above occur frequently, you should consult a doctor for examination.
Causes of arrhythmia
The main and most common causes are alcohol abuse, smoking, physical and emotional stress, stress and depression. The quality of heart contractions can be affected by the pathological condition of the thyroid gland; some medications have the effect of arrhythmia. These are, for example, drugs for normalizing high blood pressure and treating lungs. Arrhythmia is often a consequence of severe heart pathology, so first of all it is necessary to treat the underlying ailment that caused it. These are such severe pathologies as ischemic disease, abnormalities in the condition of the heart valves, and manifestations of heart failure. Sometimes arrhythmias appear out of the blue without a specific reason.
Diagnosis of the disease
In diagnosing any type of arrhythmia, it is important to describe the symptoms and sensations as accurately as possible. The doctor needs to know the heart rate, whether it is low or high, how often this condition occurs, how long the attack lasts, whether it is accompanied by dizziness, headaches, whether there were fainting, chest pain, shortness of breath and other strange sensations.
In addition, the doctor needs to tell in what situations these sensations occur: at rest or during physical activity. As the painful process occurs, it begins with sharp pain or its intensity gradually increases. To more accurately determine the patient's condition, various clinical studies are conducted. The main way to detect abnormalities in heart rhythm is a cardiogram. This study makes it possible to obtain a graphical diagram that displays the frequency and intensity of the heartbeat.
Holter monitoring makes a more thorough study of heart rhythm. which can be done in our clinic. The patient carries the monitor with him throughout the day. The device records heart rate at every moment of time. In addition to this, the subject keeps regular records of his actions and feelings. This method allows you to identify serious abnormalities and their frequency more accurately.
If the arrhythmia can be life-threatening, and the patient’s condition is quite serious, then a heartbeat study is carried out while the person is hospitalized. In these cases, an electrophysiological study is performed. Here a special probe is used, inserted through a vein directly into the heart. To accurately diagnose the patient's standing, various stimulants and special methods of monitoring cardiac activity are used.
Treatment of arrhythmia
Often, when a doctor prescribes a small dose of medication and with lifestyle corrections - quitting smoking, alcohol, intense physical and emotional stress - the arrhythmia gradually goes away.
For the treatment of pronounced arrhythmias, as well as severe conditions, a pacemaker is used. This is a device that replaces the work of the heart. Using electrical impulses, it tells the heart to beat at the correct frequency and intensity. This device is implanted under the patient's skin in the chest area. Special electrodes that are directed to the heart through the vessels and impart an electrical impulse to it. Thanks to modern technological developments in the field of medicine, the batteries that support the operation of the device can last from 8 to 10 years. The device is designed so that neither extraneous microwaves, nor electrical devices, nor radars and other equipment interfere with the operation of the pacemaker. The only exceptions are magnetic resonance imaging devices and other devices intended for physical treatment.
Pacemakers are used mainly in cases where, as a result of arrhythmia, the heart makes a small number of contractions. Then the stimulator normalizes the rhythm and brings the number of contractions to normal. In the opposite case, when the arrhythmia is accompanied by too intense heartbeat, the stimulator is used very rarely.
In some serious cases, arrhythmia requires surgery. If the arrhythmia is caused by coronary heart disease, then in this case an operation called balloon angioplasty or coronary artery bypass grafting is performed. Sometimes arrhythmia is caused by a malfunction of the electrical center in the heart. It is eliminated by catheter ablation, when a catheter is inserted into the heart and a series of radiofrequency current discharges are applied through it.
Arrhythmia that occurs after a heart attack is treated with open-heart surgery, which removes the damaged muscle that is interfering with the normal functioning of the heart.
Heart arythmy
The disease itself, arrhythmia, is a disturbance in the rhythm of heart contractions. The heart rate of a healthy person at rest is normally between 65 and 90 beats per minute. With equal intervals between these contractions, the person himself practically does not feel the work of the heart. Any changes in rhythm, both lengthening and shortening of the intervals between contractions, are considered to be arrhythmia.
Causes of arrhythmia
There are only a few types of cardiac arrhythmia and each of them has its own specific causes, but there are also those that are characteristic of several types at once. Basically, this condition is provoked by smoking, excessive physical activity, endless stress and drinking large amounts of alcohol. Also, pathological processes in the thyroid gland, which are accompanied by a decrease in its function, contribute to an increase or decrease in the heart rate; some medications, in particular antihypertensives and those aimed at treating pulmonary pathologies. The most common cause of arrhythmic conditions is heart disease of organic origin, such as valvular insufficiency or ischemia. Very often the cause of heart rhythm disturbances cannot be diagnosed.
Symptoms of arrhythmia
All symptoms of this pathology are very individual and subjective, since most people who do not have diseases of the cardiovascular system are able to feel the heartbeat. Basically, this is noted in the lying position on the left side and is intermittent. Very often, the feeling of the work of one’s own heart frightens people, but this is not always a consequence of severe cardiac pathology. For patients suffering from heart disease, such conditions arise repeatedly.
Some arrhythmias, in the initial stages, may occur subclinically or with mild symptoms, and some, with a very clear clinical picture, but generally do not have very serious consequences for the body. The most important thing is the pathology of the heart itself, rather than its manifestation as an arrhythmia. Due to rhythm disturbances, a condition such as cardiac failure occurs, which can be accompanied by dizziness and fainting. With such manifestations, emergency diagnosis and timely treatment are necessary.
Treatment of arrhythmia
Some types of arrhythmias do not pose a threat to health and, especially, life. They do not require measures to normalize the rhythm; this happens rarely and mainly occurs against the background of excessive load. If the phenomenon of extrasystole occurs quite often, then this requires special attention and, accordingly, treatment. The process of treating arrhythmia itself, in some cases, is very complex, since the effects of one or another antiarrhythmogenic drug cannot be predicted. In such cases, therapy is selected individually, taking into account all the side effects of the drugs and their dosage. It is also possible to combine several types of medicinal antiarrhythmic substances, which in combination can have the desired effect. It is not uncommon that it is not possible to select a therapy due to the resistance of the arrhythmia, and in some cases these medications can worsen the condition. Or you have to prescribe very high dosages, thanks to which the process can be stopped. Based on the above, the treatment of arrhythmia, both an independent disease and a symptom, should be handled by a very qualified specialist with extensive experience in this topic.
Along with the treatment of the arrhythmia itself, it is necessary to pay attention to the underlying disease as a result of which it developed. If there is heart failure, then, accordingly, it is necessary to treat it first, but if the cause is hyperthermia, then, accordingly, it is necessary to take measures to reduce body temperature. In most cases, the patient himself is able to stop an attack of arrhythmia, since the patient knows his body better than the doctor, but this is not always justified.
There are situations when the patient does not have the opportunity to see a specialist. Especially for this case, I will try to explain how the doctors themselves act in this situation. Of course, it is not possible to give recommendations for the treatment of all types of arrhythmias, since this process is very individual and each patient needs his own approach. Currently, many drugs have appeared on the Russian market that can correct heart rhythm, but none of them is a panacea. I repeat once again that the most important thing in correct diagnosis and prescription of therapy should be an individual approach, taking into account all concomitant pathologies, and knowledge of the mechanisms of the process itself, medical experience and diseases of the circulatory system is also necessary.
Examinations for arrhythmias
The human heart works throughout life. It contracts and relaxes approximately 60 to 100 times per minute at rest. During the systole phase, the heart contracts, ensuring blood flow and delivery of oxygen and nutrients throughout the body. In the diastole phase it rests. It is very important that the heart contracts at regular intervals. Any violation of the frequency, rhythm and sequence of contractions of the heart muscle leads to problems.
Contractions of the heart muscle are provided by electrical impulses that originate in the sinus node and then spread along the conduction pathways, reaching the muscle fibers. Therefore, in order for the cardiac “motor” to work properly, rhythmic regulation of electrical impulses and their clear, coordinated conduction throughout the heart is necessary.
The rhythm of heart contractions is regulated by the endocrine system (through hormones contained in the blood) and the autonomic nervous system. Therefore, the main causes of rhythm disturbances are changes in nervous and endocrine regulation. Your doctor, Lyubov Andreevna, is absolutely right in directing you to do a hormone test.
Tachycardia and bradycardia
An increase in heart rate (more than 100 per minute) is called sinus tachycardia. In this case, the contractions of the heart muscle are full and the picture of the heart on the electrocardiogram (ECG) does not change, an increased rhythm is simply recorded. Tachycardia can be a healthy person’s reaction to stress, an unusual situation or physical activity.
A decrease in heart rate (less than 60 per minute) is called sinus bradycardia. This condition often occurs in physically trained people. However, bradycardia is also accompanied by diseases of the endocrine organs, poisoning, hypothermia, etc.
In addition, among the heart rhythm disturbances there are extrasystole (extraordinary contractions), atrial fibrillation (erratic, completely disturbed rhythm), paroxysmal tachycardia (sudden increase in heart rate to 150-200 beats per minute), etc.
With tachycardia, extrasystole or atrial fibrillation, a person describes his sensations as “strong heartbeat” or “interruptions in the heart”, he feels fading, cardiac arrest. In this case, dizziness occurs, and in rare cases, loss of consciousness.
The traditional way to deal with interruptions in heart function is to take Corvalol, Valocordin, etc. However, self-medication is unacceptable, because along with relatively harmless arrhythmia, which responds well to treatment, there are life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias. Only a cardiologist or arrhythmologist can determine the degree of danger of arrhythmia and its origin. After a full examination, he prescribes treatment. If arrhythmia is not an independent disease, but a symptom of another disease, then the primary disease must be treated.
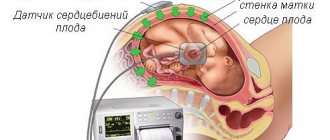
The main method for diagnosing heart rhythm disorders is an electrocardiogram. But if arrhythmia develops episodically and is difficult to “catch”, daily Holter ECG monitoring is used - recording an electrocardiogram over several hours or days. In this case, the patient leads a normal lifestyle (the sensors installed on the chest do not interfere), but notes the actions he performs by the hour (sleep, rest, physical activity). When deciphering, the doctor compares the ECG data with the patient’s records: finds out the frequency, duration, time and causes of the arrhythmia.
More modern electrophysiological research methods are also used to diagnose rhythm disturbances: intracardiac (from the internal cavity of the heart) and transesophageal.
It is in your power to make the diagnosis easier for the doctor. To do this, when preparing for the reception, think through the answers to such questions.
• How long have you been suffering from arrhythmia? Do seizures occur frequently?
• What exactly do you feel during an attack: strong heartbeat, rapid heartbeat, irregular heartbeat, heart palpitations, interruptions, “failures”?
• What triggers your attack (physical activity, certain body position, food intake)? Or does arrhythmia occur in different situations? Do you experience irregular heart rhythms while at rest, for example, while lying in bed?
• How does an arrhythmia attack begin - gradually or suddenly, how does it end? How long does it last?
• What helps relieve an attack of arrhythmia? Changes in body position, medications?
Also bring records of previous ECGs and examination results to your appointment.
When prescribing drug therapy, the doctor tries to select the minimum effective dose. If there is no effect, it is better not to increase the dose, but to choose another drug or their combination. In addition, treatment is constantly adjusted according to the ECG results.
There are several other causes of rhythm disturbances. It also goes astray in the event of the development of heart anomalies, violations of its anatomical structure (congenital and acquired defects). Sometimes arrhythmia is a reaction of the heart to the pathology of other organs and systems, to drinking alcohol, smoking, and also to medications.
Share your experience /
Ask a Question
Five main reasons for nighttime palpitations
The doctor explained that the symptom of nighttime palpitations or tachycardia, as doctors call it, is, in fact, an arrhythmia, a heartbeat disorder. Moreover, it can manifest itself in different ways. This is either a rapid heartbeat (more than 100 beats per minute), or an irregular contraction of the heart, when it does not go smoothly, but intermittently, which can also cause such unpleasant sensations.
The heart rate may, on the contrary, be too low. This is already bradycardia. But in this case, as a rule, people do not wake up. The normal heart rate is from 60 to 100 beats per minute when awake. Moreover, it must be rhythmic.
Palpitations at night can be caused by a variety of reasons. Therefore, if you notice this symptom in yourself, then first of all you should go to a cardiologist and undergo an examination to rule out diseases that are not related to the heart.
And now, in order, about all the causes of nocturnal tachycardia. This:
1. Stress and neuroses. The human body is designed in such a way that the nervous system completely controls all its systems and organs, including the functioning of the cardiovascular system. Sometimes the nervous system operates outside of a person's consciousness. And when a person has neurosis, anxiety, or severe stress, this can lead to arrhythmia, an increase or, conversely, a decrease in blood pressure.
2. Disorders of the endocrine system. For example, thyroid diseases.
3. Night apnea. This is when a person cannot breathe for some time for various reasons. For example, due to diabetes, obesity, problems in the pharynx and larynx. This breath holding can last up to 20 seconds. In this case, a person must first of all find the cause of such a dangerous condition. First you need to see a therapist, and then he will refer you to either an endocrinologist, an ENT doctor, or even a neurologist.
4. Increased pressure. The situation here is twofold. Tachycardia itself can cause increased blood pressure. Conversely, high blood pressure can cause tachycardia. Normal blood pressure is considered 120/80. But at the same time, pressure up to 140/90 is also acceptable. To determine if you have hypertension, you need to measure your blood pressure regularly. A single measurement is not representative. For example, if a person once discovered that he has high blood pressure, this does not mean that he has hypertension, the doctor emphasized.
5. Heart diseases. If nocturnal arrhythmia is associated with heart disease, it may indicate hypertension, coronary heart disease, which includes angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, inflammatory myocardial diseases, which is very rare, but also happens. There are different types of arrhythmia. This is not only tachycardia, but also extrasystole - premature contraction of the atrium or ventricle. The danger of arrhythmia is that with it there is a high probability of blood clots forming in the heart. When the heart beats rhythmically, our blood flows normally. And if the contraction of the heart is uneven, then blood clots can form inside it. They, in turn, can clog a large vessel, which can lead to very sad consequences.