What is glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) is the amount of blood filtered every minute through tiny filters in the kidneys called glomeruli. While it may seem complicated, GFR is essentially an estimate of how well your kidneys are working .
[The] main job of our kidneys is to remove waste and excess water from the blood. This excess water and waste material turns into urine. The kidneys process about 180 liters of blood each day to produce about 1.5 liters of urine. When the filtration rate decreases, which means your kidneys are working less well and it may mean you have kidney disease. []
KIDNEY ANATOMY
GFR depends on many factors, such as [R]:
- Time of day
- Diet
- Physical activity
- Age
- Pregnancy
- Obesity
- High blood sugar (hyperglycemia)
- Taking antihypertensive medications (used to reduce high blood pressure)
- Acute and chronic kidney diseases
What is the calculation used for?
Determination of GFR is a diagnostic measure that helps to preliminary assess abnormalities in organ function. A decreased or increased value indicates pathological changes in them. Without an accurate calculation, some diseases cannot be identified. Additional studies will only confirm the diagnosis.
The GFR value is determined by:
- renal circulation rate;
- blood pressure level;
- the number of nephrons involved in filtration;
- the rate of tubular secretion (determined by only one test - the Reberg study).
These indicators help assess the condition of organs and the presence of dangerous pathologies. Some of them, if not identified in time, will require kidney transplantation in the future. To avoid a labor-intensive operation that threatens complications and repeated interventions, a comprehensive diagnosis is carried out, including the calculation of GFR.
Glomerular filtration rate test
It is difficult to directly measure glomerular filtration rate, so scientists have developed a formula to indirectly estimate GFR. Today, the most widely used equation for calculating GFR is one that was developed in 2000 and modified in 2009. It takes into account your age, gender, ethnicity (race), and your creatinine level. [, , ]
Creatinine is the end product of the creatine-phosphate reaction in muscles during energy metabolism, work, and when muscle injuries occur. It is eliminated from the blood by the kidneys, so the amount of creatinine in the blood is an important indicator of the efficiency of the kidneys.
Since muscle mass changes little from day to day, creatinine production and utilization rates are fairly constant. When the glomerular filtration rate of the kidneys decreases, the level of creatinine in the blood increases. High creatinine = impaired kidney function . [,,]
SCHEME OF Glomerular FILTRATION OF THE KIDNEY
Many laboratories automatically report your GFR level when you test your blood creatinine. Monitoring GFR values often helps in early detection of kidney dysfunction, which is important for preventing further kidney damage.
Mechanism of increase in creatinine
Creatinine is formed in human muscles. It is the end product of protein metabolism. Normally functioning kidneys remove it completely from the body in the amount of 1-2 g per day. The content of creatinine in the blood varies among people, and the indicators vary depending on the person’s gender, age, muscle mass, diet, and other factors not related to the state of the urinary system.
But a significant increase in creatinine always indicates renal pathology. The mechanism of the disorder is simple: when nephrons die against the background of one or another kidney disease, the kidneys do not stop coping with urine filtration.
Some features of GFR analysis
Because creatinine is released by muscles, external or internal conditions that affect the muscles will also affect GFR. People with muscle disease, obesity , amputations, or paralysis require alternative ways to determine glomerular filtration rate. Also, more accurate analysis is needed for young people (under 18 years of age) and pregnant women, as they experience changes in muscle mass, which can lead to an underestimation of GFR. []
To solve this problem, new formulas have been developed that link GFR to another marker of kidney function, cystatin C. Unlike creatinine, cystatin C can be found in almost all tissues of our body. Many studies have shown that the level of cystatin C in the blood is a more accurate indicator of kidney function than the level of creatinine. In addition, some formulas include cystatin C and creatinine, and this is the most accurate test of glomerular filtration rate to date. [, , , ]
Finally, there are special equations for calculating GFR in children that take into account the child's height. []
What is creatinine clearance and how to calculate it
digestive, cardiovascular, urinary, respiratory. Muscle contraction requires special substances, an important one of which is creatine phosphate. Chemical reactions in the body break down this substance into components that enter the muscular system. Clearance helps determine the volume of blood that clears creatinine from the kidneys in a minute. This is an important indicator of the speed of glomerular filtration, i.e. tiny bundles of blood vessels located in nephrons. They perform the main function of filtering all harmful components and decay substances in the urine through the kidneys.
Creatinine clearance is an indicator that determines the volume of purified blood in 60 seconds during filtration by the kidneys.
In the presence of a number of pathologies or specific conditions, it is necessary to assess the filtering function of the kidneys.
For this purpose, indirect methods are used, which consist in measuring creatinine clearance. Analysis of the results will help prescribe therapy to maintain the functioning of the excretory organs.
Normal glomerular filtration rate (GFR) values
Many different equations can be used to obtain the estimated glomerular filtration rate (GFR). In addition, normal levels of GFR will vary among different ethnic groups. Some laboratories will report two groups—African-American and Caucasian.
All equations for calculating GFR provide a range of values from 0 to about 140. The lower the value, the less efficiently your kidneys work.
The normal filtration rate in young people is considered to be around 90 – 120 ml per minute. [] However, depending on the laboratory, normal results may be reported as a range of more than 90 or more than 60 ml/min/1.73m2. []
OPERATION SCHEME OF THE Glomerulus of the Kidneys by FILTERING BLOOD AND FORMING URINE
GFR decreases with age . In people over 70 years of age, glomerular filtration rates below 60 ml/min/1.73 m2 can be considered normal. []
CHANGES IN GFR (glomerular filtration rate) WITH AGE
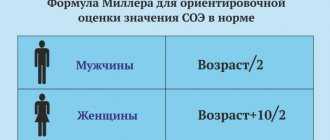
Calculation methods
The filtration rate is determined in various ways. Some of them are completely new, others have been known for a long time. All calculations are based on an assessment of the concentration in the blood of certain breakdown products - inulin, creatinine, urea - which are not normally retained in the body. The best studies are considered to be studies of the clearance of creatinine, which is formed in the muscles, but is easily excreted by the kidneys in urine. These tests do not exclude small errors. Much depends on age, gender, amount of muscle mass.
Standard formula
This technique for calculating the rate of the filtration process is based on an analysis of the volume of daily urine. Dividing its quantity by time, laboratory workers calculate the indicators. The unit of measurement is ml/min.
If the value does not fit within the norm, then further research is carried out to identify the disease. An actively used method, one of the first developed (1973, published in 1976). However, determining speed using the formula has disadvantages. It is inaccurate if GFR values are close to normal or slightly reduced. The reason is the variable value of creatinine, it depends on gender, age, and race. Tubular secretion is also not assessed by this method.
CCr = {((140 - age) x weight) / (72xSCr)} x 0.85 (in women), where CCr is creatinine clearance; SCr is serum creatinine measured in mg/dL.
According to Schwartz
This glomerular filtrate rate formula is designed solely for determining GFR in children. Blood serum is also used here.
CCr = kx height / SCr
Height in the formula is measured in centimeters, k (age coefficient) is equal to 0.0484, for children under 3 years old k = 0.0313, for male adolescents - 0.0616. The unit of measurement for serum creatinine is µmol/L.
CKD-EPI
This is the newest formula for analyzing glomerular filtration rate, determined by the amount of creatinine. It was edited in 2011. Being the most effective, this equation gives an accurate estimate if GFR values exceed 60 ml/min/1.73 m2. If the patient is not an average citizen, the method is not used.
The study is excluded after amputation of limbs, in case of exhaustion or obesity, pregnancy, in early and old age, if kidney problems are not observed.
CCr = 141 x min (SCr / k)α x max (SCr / k) -1.209 x 0.993 Age x 1.018 (for women) x 1.159 (for blacks), where k is 0.9 for men, 0.7 for of the weaker sex, α - -0.411 and -0.329, respectively. Serum creatinine is measured in mg/dL.
This method for determining GFR and kidney pathology is very similar to the previous calculation. The same group of scientists worked on it as on CKD-EPI, but this happened a little earlier. Only some coefficients have been changed, so it is also unacceptable for people with small or large muscle mass.
CCr = 175 x SCr-1.154 x age-0.203 x 1.212 (for the Negroid race) x 0.742 (for women)
In this formula, the unit of measurement for serum is also mg/dL.
The main drawback of the technique is the distortion of GFR downward when its real value is high.
There is another option for determining kidney GFR. This is the clearance of endogenous creatinine, called the Rehberg test. This method uses not only blood serum, but also daily urine, collected according to strict rules:
- Food intake is stopped 12 hours before the procedure, alcohol - one day.
- Diuretics are prohibited; the last time the drug is allowed is 48 hours before urine collection.
- The day before the collection of biomaterial is a period that excludes physical activity and strong emotions.
- Smoking is taboo half an hour before GFR tests.
The formula is relatively simple: CCr = (U x V) / P
CR = (CCr - V / CCr) x 100%
The method has an Achilles heel - if urine is collected incorrectly, the results are greatly distorted, so it is rarely used in practice.
Low glomerular filtration rate
When other factors (age, body weight, race) are excluded, a decreased GFR indicates impaired kidney function. It can be an acute kidney disease or a chronic disease that is often irreversible and continually progresses.
Chronic kidney disease (CKD), as measured by GFR, has the following stages:
- Stage 1: normal GFR: > 90 ml/min
- Stage 2: weak GFR: 60 to 89 ml/min
- Stage 3: moderate CKD, GFR: 30-59 ml/min (30-60% of the kidneys are not affected)
- Stage 4: severe CKD, GFR: 15-29 ml/min (15-30% of kidneys not affected)
- Stage 5: renal failure, GFR < 15 ml/min (less than 15% renal function)
However, for values between 60-89 ml/min/1.73 m2, doctors will only consider kidney disease if there is additional evidence of kidney damage, such as polycystic kidney disease (cysts in the kidneys), proteinuria (protein in the urine). ), or hematuria (blood in the urine). If there are no such pathologies, and the GFR is more than 60 ml/min/1.73 m2, then this is considered a normal condition. []
SCHEME FOR REDUCING THE Glomerular FILTRATION RATE (GFR)
GFR values that remain below 60 ml/min/1.73 m2 for more than 3 months are an indicator of chronic kidney disease . If your glomerular filtration rate is around 60 or below, then talk to your doctor as soon as possible. The doctor may suggest a more in-depth study of the kidneys (blood tests, urine tests, or ultrasound).
What diseases can be diagnosed
Analysis of the Reberg-Tareev test is used when various pathologies of the excretory system are suspected. If this figure is less than normal, this means massive death of nephrons. This process may indicate acute and chronic renal failure.
Since GFR can decrease not only due to damage to the structural units of the kidney, but also due to third-party factors, this phenomenon is also observed with hypotension, heart failure, prolonged vomiting and diarrhea, hypothyroidism, diabetes insipidus, as well as difficulty in the outflow of urine due to a tumor or inflammation in the urinary tract.
An increase in GFR is observed in idiopathic acute and chronic glomerulonephritis, diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, and some autoimmune diseases.
Normally, GFR values are constant, in the range of 80-120 ml/min, and only with age this figure can decrease for natural reasons. If these numbers decrease to 60 ml/min, this indicates renal failure.
Factors that reduce glomerular filtration rate
In addition to various kidney diseases (the main cause), there may be other factors that affect the glomerular filtration rate, such as:
- Eating cooked meat before analysis []. This increases the level of creatinine in the blood.
- Short famine or period of long fasting []
- Bodybuilding and Creatine Supplementation []
- Other factors that can increase blood creatinine, such as dehydration or massive blood loss. []
- Taking NSAIDs (anti-inflammatory drugs) and ACE inhibitors (or angiotensin receptor blockers). []
- Including lemongrass tea in your diet. []
Important Notes
Glomerular filtration rate is a very accurate and important test, so there are several other important nuances that must be taken into account when undergoing it.
- It is believed that in an adult after 40 years of age, creatinine clearance drops by 6.5 ml/min every 10 years of life. Therefore, a reduced rate for a young body will be considered normal for an elderly person.
- Drugs such as Cimetidine, Trimethoprim and ketonic acids significantly distort the normal result. This should be taken carefully, especially for those patients who have severe renal failure.
- In order for the analysis to be performed correctly, you must follow all recommendations. Determining the glomerular filtration rate is possible only if a person has collected all the urine that was excreted in one day. Missing even one urination may reduce the accuracy of the result.
Factors that increase the risk of developing chronic kidney disease
- High blood pressure [, ]
- Diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2 [, ]
- Heart diseases []
- Obesity []
- Smoking [, ]
- Family history of kidney disease (genetics) []
- Age (60 years and above) []
- Previous kidney damage []
- Low birth weight [, ]
- Infections of the genitourinary system
- Increased blood cholesterol HDL below 40 mg/dL increase the risk of kidney disease by 2 times)
- Autoimmune diseases (eg, systemic lupus erythematosus)
- Staphylococcal infections (sore throats, pharyngitis)
- Sickle cell anemia
- Goodpasture's syndrome
- Hepatitis C
- Heart failure
- HIV
- Malignant tumors (development of paraneoplastic nephritis)
- Difficulty in urine flow
- Vesicoureteral (or vesicourethral) reflux is the reflux of urine from the bladder into the ureter.
- Worm infestations
- Gastrointestinal disorders (constipation, dysbacteriosis, malabsorption syndrome).
- Kidney tuberculosis
- Pyelonephritis
- Polycystic kidney disease
How to increase glomerular filtration rate
The main opportunity to increase the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) lies in the treatment of the underlying kidney disease that has led to a decrease in this rate. But there are additional ways you can try to increase your GFR and keep your kidneys healthy.
Ways to improve kidney function (increase GFR):
- Keep your blood pressure in a healthy range (around 120/80) [, ]
- Achieve and maintain a healthy body weight [, ] Increased leptin in obesity are associated with decreased GFR and the development of chronic kidney disease. []
- Practice a diet rich in fruits and vegetables []
- Quit smoking or reduce the number of cigarettes you smoke [, , ]
- Practice at least 30 minutes of physical activity at least 5 times a week [, , , ]
- Control blood glucose levels and keep them within normal range [, ]
- Maintain vitamin D levels in the normal range (get enough sun exposure to the skin) [, ]
- Reduce overall oxidative stress in the body []
- Reduce overall inflammation in the body, especially reduce the values of C-reactive protein , tumor necrosis factor (TNF-alpha), fibrinogen , IL-6 cytokine and IL-1b cytokine. []
- Reduce the risks and rate of development of atherosclerosis , due to the direct mutual relationship between atherosclerosis and deterioration of GFR in chronic kidney disease. []
- Normalize intestinal microflora , which, if disturbed, can increase general inflammation and reduce the GFR of the kidneys. [] The key way to normalize microflora is to follow a Mediterranean diet .
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM DISEASES, INTESTINAL MICROFLORA DISORDERS AND THE DEVELOPMENT OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE. NORMALIZATION OF KIDNEY FUNCTION WITH THE HELP OF DIETS (www.intechopen.com)