Detailed description of the study
Insulin is a hormone produced by B cells of the pancreas, which reduces the concentration of glucose in the cell and stimulates the synthesis of proteins and fats. Determination of insulin concentration is used to determine the type of diabetes mellitus, select a therapeutic drug, and determine the degree of pancreatic B-cell insufficiency.
An increase in insulin levels is observed in the following diseases: obesity, type 2 diabetes mellitus, normal pregnancy, acromegaly, Itsenko-Cushing syndrome, insulinoma. With a decrease in insulin concentration, type 1 diabetes mellitus develops, as well as type 2 diabetes mellitus with insulin requirement.
Insulin regulates carbohydrate metabolism, maintaining blood glucose at the required level, and also participates in fat (lipid) metabolism.
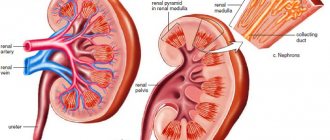
The concentration of insulin in the blood directly depends on the concentration of glucose: after eating, a large amount of glucose enters the blood, in response to this the pancreas secretes insulin, which triggers mechanisms for moving glucose from the blood into the cells of tissues and organs. Insulin also regulates biochemical processes in the liver: if there is a lot of glucose, the liver stores it in the form of glycogen (a glucose polymer) or uses it for the synthesis of fatty acids. When insulin synthesis is impaired and its concentration is reduced, glucose cannot enter the body's cells and hypoglycemia develops. Cells lack glucose, the main substrate for energy production. If this condition is chronic, then metabolism is disrupted and pathologies of the kidneys, cardiovascular, and nervous systems begin to develop, and vision suffers.
Diabetes mellitus is a disease in which there is a lack of insulin production. Diabetes is of types 1 and 2. The first type develops when the pancreas produces insufficient insulin, the second type (the most common) - when cells lose sensitivity to the effects of insulin on them.
In the initial stages, diabetes mellitus is treated with a special diet and medications that enhance the production of insulin by the pancreas or stimulate the body's cells to consume glucose by increasing their sensitivity to this hormone. When the pancreas stops producing insulin, it requires injection.
An increased concentration of insulin in the blood is called hyperinsulinemia. At the same time, the glucose content in the blood decreases sharply, which can lead to hypoglycemic coma and even death, since the functioning of the brain depends on the concentration of glucose. Elevated levels of insulin in the blood can also be caused by the presence of a tumor that secretes it in large quantities - insulinoma. In this case, the concentration of insulin in the blood can increase tens of times within a short time. Diseases associated with the development of diabetes mellitus: metabolic syndrome, pathology of the adrenal glands and pituitary gland, polycystic ovary syndrome.
How to prepare for the test
You need to take a test to determine your insulin level by following a number of rules. Otherwise, the results obtained will be unreliable. What you need to know about the analysis:
- Venous blood is used as a biomaterial;
- blood is taken on an empty stomach, provided that the last meal was no later than 10 hours before the start of the study;
- 5 days before the delivery of the biomaterial, it is necessary to exclude exhausting physical activity;
- at least 3 days before the test must be spent without drinking alcohol;
- if the patient is undergoing a course of drug treatment, the doctor must be warned about this, who, if necessary, will stop the therapy at the time of the study or postpone the tests until the course of treatment is completed;
- any stressful situations can affect the natural level of the hormone in the blood, so it is important to try to avoid conflicts and not worry a few hours before donating blood.
The result is usually ready the next day.
Differential diagnosis
Symptoms of hypoglycemia are polymorphic and nonspecific. The presence of neuropsychiatric disorders and the low prevalence of the disease often lead to diagnostic errors. As a rule, differential diagnosis is required with conditions such as epilepsy, catatonia, hebephrenia, neurasthenia, hysteria, migraine, psychosis, alcoholism, brain tumors, neurovegetative dystonia with hypoglycemic conditions. However, Whipple's triad is pathognomonic for Harris syndrome:
- the occurrence of attacks of hypoglycemia after prolonged fasting or physical exercise
- a decrease in blood glucose during an attack below 1.7 mmol/l in children under two years of age and below 2.2 mmol/l in children over two years of age
- relief of a hypoglycemic attack by intravenous administration of glucose or oral administration of glucose solutions [4].
Insulin index of certain foods
The insulin index is an innovation in the science of proper nutrition and a detailed table with its exact value for various foods is still in an “open” state, is incomplete and is constantly being updated with new data.
But for the most popular food products, all the necessary calculations have already been carried out and we have quite accurate information that can be used by diabetics and ordinary citizens who want to lose excess weight.
Insulin index of greens and vegetables
Potato insulin index
Insulin index of berries, fruits and fruits
Insulin index of dairy products
Insulin index of sweets and treats
Insulin index of cereals and grains
Insulin index of bread, pastries and confectionery products
Insulin index of other common foods
Knowing the insulin index of foods is not enough. For the best result, it is important to take into account the compatibility of products. A great option is to combine vegetables with proteins and fats (vegetable salad with olive oil and a piece of poultry). Starchy foods (porridge, beans, potatoes, white rice, beets) are good to eat with leafy vegetables and oils.
Avoid combining fast carbohydrates with starchy, protein foods (a sandwich or burger is one of the typical combinations). It is not the best option to mix protein foods (fish, meat, poultry) with starchy foods (that is, with traditional side dishes - white rice or mashed potatoes).
We recommend
“Buckwheat tea: beneficial properties, contraindications and reviews” Read more
Here are some more simple tips to consider when planning a diet for diabetics:
and people suffering from prediabetic conditions.
- For a very long time, the thesis has flourished in dietetics that such “healthy” foods with a low glycemic index, such as cottage cheese, are best consumed at night; this, in theory, should promote weight loss and active “nighttime” fat burning. But with the advent of new research on the insulin index, the outdated postulates of nutrition science must be adjusted.
It has now become clear that cottage cheese has a very high AI and is not suitable for consumption in the afternoon by people with diabetes and those with insulin resistance.
- Products with an insulin index above average go very poorly with fatty foods.
- When drinking alcohol with a “bad” AI, it is better to avoid high-fat snacks.
- The first half of the day is a great time to refuel with something tasty with a high insulin index. It is best to have dinner with fish, vegetables, seafood and other “goodies” with a low insulin and glycemic index, in order to eliminate the possibility of sharp evening insulin surges and protect the body from gaining excess weight.
Symptoms of unstable indicators
Diagnosis of diabetes
Signs of persistently high or low insulin include:
- polydipsia (permanent feeling of thirst);
- pollacuria (frequent urge to empty the bladder);
- dryness and tightness of the skin, rashes on the epidermis;
- polyphagia (increased appetite);
- vegetative-vascular disorders.
Symptoms characteristic of women are:
- inability to conceive a child (infertility);
- increased sweating (hyperhidrosis);
- the appearance of age spots on the face.
Symptoms are most pronounced during menopause. You should not ignore uncomfortable sensations, associating them only with the characteristics of menopause. Insulin instability may indicate serious illness.
Treatment and prognosis
Treatment of insulinoma in most cases is surgical: enucleation of the tumor, distal resection of the pancreas in appropriate localization. Conservative therapy is carried out in the case of an unresectable tumor and its metastases, as well as if the patient refuses surgical treatment. The five-year survival rate among radically operated patients is 90%, and if metastases are detected, it is 20% [8].
Sources
- Clinical endocrinology: manual (3rd ed.)/Ed. N. T. Starkova. - St. Petersburg: Peter, 2002. - 576 p.
- MedUniver
- MedUniver
- Endocrinology. Volume 2. Diseases of the pancreas, parathyroid and gonads. Ed. S. B. Shustova. - St. Petersburg: SpetsLit, 2011. - 432 p.
- Balabolkin M.I., Klebanova E.M., Kreminskaya V.M. Differential diagnosis and treatment of endocrine diseases (guidelines). M.: “Medicine”, 2002. - 751c.
- Dizon AM et al. Neuroglycopenic and other symptoms in patients with insulinoma // Am. J. Med. 1999, p. 307.
- Okorokov A. N. Diagnosis of diseases of internal organs. Volume 2. - M. Med. lit., 2008–576 p.
- Kalinin A.P. et al. Insulinoma. Medical newspaper, 2007, No. 45, p. 8–9
Why do you need to know your insulin level?
When the body cannot independently control metabolic processes, a serious failure occurs in the functioning of the entire organ system. For example, if insulin is produced in excess of normal, this may cause persistently low blood sugar. The human brain takes only glucose as food. Whatever gets into the stomach, enzymes and hormones, through complex chemical reactions, convert it into glucose, thanks to which the brain receives nutrition.
High levels of insulin can lead to a sharp decrease in blood sugar levels, which inevitably leads to coma.
Other reasons that increase insulin levels may include:
- acromegaly;
- type 2 diabetes;
- long-term use of hormonal contraceptives;
- Cushing's disease.
Excess insulin is also often observed in obese people and in those whose bodies cannot tolerate galactose. The consequences of excessive hormone production can also be:
- dizziness;
- convulsions;
- sweating;
- manifestation of seizures;
- increased heart rate;
- impaired quality of vision.
And low insulin levels are characteristic of type 1 diabetes, inflammation of the pancreas and pituitary insufficiency.
Information about the insulin used
Listed below are the types of insulin used at Memorial Sloan Kettering (MSK).
| Type | Name | Start of action | Maximum action | Duration of action |
| Fast acting | Aspart (NovoLog®) | 5–15 minutes | 30–60 minutes | 3–4 hours |
| Lispro (Humalog®) | 5–15 minutes | 60–90 minutes | 3–4 hours | |
| Fast acting | Novolin® R Regular | 30–60 minutes | 2–5 hours | 6–8 hours |
| Humulin® R Regular | 30–60 minutes | 2–4 hours | 6–8 hours | |
| Medium action | Novolin® N (NPH) | 1–2 hours | 6–12 hours | 12–14 hours |
| Humulin® N (NPH) | 1–2 hours | 6–12 hours | 12–16 hours | |
| Long-lasting | Glargine (Lantus®) | 1–2 hours | No maximum action time | Up to 24 hours |
| 1–2 injections of Detemir (Levemir®) daily | 1–2 hours | No maximum action time | Up to 24 hours | |
| Combined fast and medium action | NovoLog® Mix 70/30 (N/Aspart) | 30 minutes | 1–12 hours | 5–18 hours |
| Novolin® 70/30 (N+R) | 30–60 minutes | 4–12 hours | 14–16 hours | |
| Humalog® Mix 75/25™ (N/Lispro) | 5–15 minutes | 1–12 hours | 14–18 hours |
to come back to the beginning