until November 30, 2021 First procedure 1000 rub.
(30 minutes) Medical massage is one of the effective physiotherapeutic methods of treatment and recovery. Massage relaxes muscles and tones tissues, improves joint function, and stimulates blood circulation. The procedure prevents lymph stagnation and swelling, fights pain, and has a calming and relaxing effect.
How did massage appear and why was the attitude towards it controversial?
The word “massage” comes from the French language (masser - to rub). Moreover, the procedure itself was known even to primitive peoples. The first official evidence of massage techniques appeared in Ancient China, in the 3rd millennium BC. Even then, there were medical and physical education educational institutions, where one of the disciplines was massage.
During the Middle Ages, massage therapists were subjected to severe persecution. The Holy Inquisition was convinced that pain relief and healing through the touch of hands was a clear sign of the devil. Witch doctors were declared sorcerers and witches and burned at the stake. Only 300 years ago in Europe the works of scientists about massage and its healing properties began to appear again.
Fortunately, in our country there has never been a bias towards the procedure, and therefore the methodology has developed over many centuries. In Ancient Rus', massage was revered both as a full-fledged healing tool and as a pleasant element when going to the bathhouse (rubbing, patting with a broom). Nowadays, massage is recommended for the prevention and treatment of many diseases, and along with manual methods, modern hardware technologies are appearing.
E. A. Morozova. Medical, therapeutic and cosmetic massage
Massage for diseases of the cardiovascular system
Massage as a part of a complex of therapeutic measures for diseases of the cardiovascular system improves the body's regulatory capabilities, vascular circulation indicators and cardiac activity itself.
Usually a massage of the back, collar area, and sometimes, according to indications, a massage of the upper and lower extremities is prescribed.
The peculiarity of massage for diseases of the cardiovascular system is a slow pace and rhythmic movements with the patient in a semi-sitting position.
For functional neuroses - flat circular stroking, rubbing the left half of the chest, light vibration, kneading from the apex of the heart to the base, very light. The movements are slow and rhythmic, you can use light vibration.
With angina pectoris, the patient's sitting position is light stroking, rubbing, kneading longitudinally and transversely, gentle patting, stroking and light shaking of the chest. You need to start the massage from the back - trapezius muscle, back of the neck, sternocleidomastoid muscle, intercostal muscles and interscapular muscles, moving to the area of the heart, pectoral muscles, left shoulder, joints, inner surface of the forearm from the little finger. Stroking, rubbing, kneading, tapping, light chopping in the area of the VII cervical vertebra and light rhythmic vibration are used. Finish the massage with a wide, slow, rhythmic stroke. With weak heart activity - patting in the area of the heart and shoulder blade, shaking of the chest with breathing movements.
Massage for rheumatic heart defects
Massage is prescribed in the absence of concomitant inflammatory processes. The back, chest, intercostal muscles, heart area, sternum, left costal arch, upper and lower limbs are massaged. Stroking, rubbing, kneading (longitudinal and transverse), patting, shaking the chest with breathing movements are used.
When massaging the area of the heart and sternum - superficial and deep stroking, rubbing, kneading the pectoral muscles, continuous vibration, patting in the heart area, stroking from the sternum to the spine, squeezing and stretching the chest with inhalation and exhalation.
The lower and upper limbs are massaged with broad strokes, using all techniques.
The course of treatment consists of 12 procedures of 20 minutes each.
Massage for chronic coronary heart disease
For chronic coronary heart disease, massage in combination with therapeutic exercises eliminates congestion, improves coronary circulation, accelerates metabolic processes, including redox processes in the muscles, has a beneficial effect on the patient’s psyche, and activates the patient for physical and mental work.
Massage is prescribed in the absence of pain in the heart, shortness of breath, arrhythmia at rest, and normal blood pressure.
We start the massage from the feet. We stroke the feet, lower legs, joints towards the groin area, gently, circular rubbing of the dorsum of the feet alternates with stroking; Shallow kneading of the lower leg, felting, longitudinal kneading alternate with stroking and passive, then active movements, moving (according to indications) to the buttocks and back. On the back we massage the trapezius muscle. We stroke and rub with the latissimus dorsi, interscapular region, intercostal muscles to the back of the head; rake-like rubbing from the sternum to the spine; kneading the pectoralis major muscle and left shoulder, light vibration in the area of the heart, hands - general stroking, rubbing, kneading from the little finger to the shoulder joint. Stroke the chest again.
The course includes 12–15 procedures, 20 minutes each day.
Massage for hypertension stages I–IIA
We massage the head, neck, collar area while sitting, paying attention to the IV cervical and II thoracic vertebrae. Movement from top to bottom, rhythmic, medium strength.
Head - light massage using the usual technique, focusing on the occipital protuberances - rake-like stroking, circular rubbing, moving and stretching the scalp.
Then we move to the neck. Planar forceps-like stroking with the transition to the sternocleidomastoid muscles, forceps-like kneading with the transition to the collar area. If blood pressure is high, massage the abdomen while lying down, as the pressure may drop sharply.
The course of treatment is 12–15 procedures for 15 minutes every day.
Massage for hypotension
Unlike massage for hypertension, for hypotension the basis of the technique is movements from the bottom up: massage of the gluteal muscles and iliac crests, shaking of the pelvis, massage of the lower extremities with emphasis on the calf muscles. Hypotonic illness is often accompanied by intestinal atony - in this case, intestinal massage is also done. The technique ends with a massage of the collar area.
The massage begins from the underlying areas to the overlying ones. Sacrum, buttocks and iliac bones - planar, enveloping stroking. Rubbing the buttock in a circular manner (you can use your fist or elbow). Shading, sawing, crossing, longitudinal kneading of the lumbar region, transverse kneading of the anterior abdominal wall, vibration stroking, patting and shaking the pelvis.
Massage the lower limbs in stages, first the back part, then, turning the patient on his back, and the front part. Plane enveloping stroking of the lower leg and thigh, circular rubbing, planing, sawing, longitudinal and transverse kneading. Vibrating, felting, patting, chopping, shaking limbs - passive and active movements.
We mentally divide the stomach in half from the navel with a horizontal line. During the massage, we pull the upper part of the abdomen towards the armpits, and the lower part - towards the groin. Planar shallow stroking to the armpits, rubbing, shading, kneading the longitudinal and transverse anterior wall of the abdomen, rolling. For intestinal atony, pushing, horizontal and vertical shaking of the abdomen.
The collar area is massaged using the usual method, only movements (in the direction and increase of effort) should be directed from bottom to top.
There are 15 procedures of 20 minutes per course of treatment, it is good to combine with exercise therapy and balneotherapy.
Massage for obliterating endarteritis
Massage is done in the initial stage of the disease and in the absence of signs of thrombophlebitis and the threat of a blood clot. Using the same technique, massage is performed for varicose veins of the lower extremities with trophic changes in the skin, vasospasms, and atherosclerosis of the vessels of the extremities.
Methodology
. The sequence and techniques used are almost common for limb massage. When massaging the lower extremities, you should start with the lumbosacral region, then the buttocks, iliac tuberosities, then the fingers, sole, joints, lower leg, thigh. The massage is performed with the limb in an elevated position.
When massaging the upper extremities - sternocleidomastoid muscles, back muscles, interscapular area, shoulder joint and hand, fingers, joints, forearm and shoulder. All techniques are used in massage.
Attention!
Bypass venous nodes, do not massage!
For a course of treatment there are 10–12 procedures for 15–20 minutes daily.
History of massage - in both India and China, massage was performed by clergy. In addition, schools were created in these countries that taught massage techniques.
Massage products - for the prevention and treatment of various diseases, special ointments are used that have a positive effect on muscles and tissues due to the components they contain.
Leg massage - massage carried out systematically for 2-3 weeks will help prevent cramps and spasms in the muscles of the lower extremities in the future.
Neck massage - before moving on to massaging movements, you need to prepare the skin: it needs to be cleaned, warmed and lubricated with a nourishing cream. The cream should be applied with soft stroking movements from bottom to top.
Prostate massage - the causes of inflammation of the prostate gland are infectious diseases, sexual abstinence or sexual excess. It is recommended to carry out a massage, which...
Lower back pain - sets of exercises should be performed only during periods of attenuation of pain and interrupted when it appears.
Massage and metabolism - If you massage immediately after physical activity, the release of nitrogenous substances will increase by 15%. In addition, massage performed after muscular work accelerates the release of lactic acid from the body.
Massage and blood circulation - under the influence of massage, the movement of all body fluids, especially blood and lymph, accelerates, and this happens not only in the massaged area of the body, but also in distant veins and arteries. So, foot massage can cause redness of the scalp.
A massage therapist in a clinic, a massage therapist in a beauty salon, a chiropractor: what’s the difference?
The massage therapist works on the patient's body with his hands, kneading, patting, stroking, rubbing, shaking, pressing, rolling and vibrating. Unlike a chiropractor, he does not have the right to prescribe treatment or realign joints and vertebrae.
A “manual specialist” is a doctor who graduated from a medical school, residency or internship in the specialty “neurologist” or “traumatologist-orthopedist”. In addition, such a doctor has additionally completed a specialized retraining program in manual therapy.
A massage therapist in a medical clinic is a specialist with a secondary medical education in the specialties “therapeutic physical education”, “medical massage”, “nursing”, “physical rehabilitation and recreation”, “massage nurse”. An option with retraining is possible, but only if you have a secondary medical education. Such a specialist has the right to conduct medical, sports, myofascial and other types of massage. Without confirmed qualifications, a person will not be able to perform such procedures and get a job in a clinic. If this norm is violated, then according to Article 69, Article 323 of the Federal Law, the person bears criminal liability.
A massage therapist in a beauty salon, as a rule, does not have a medical education and provides non-medical massage (cosmetological, relaxing). The theoretical and practical knowledge base of a specialist is limited to short-term courses (53-72 academic hours). In this case, the quality of services is practically not confirmed by anything other than the reputation of the salon.
Why go for a medical massage?
If you experience a feeling of muscle tension and pain in the back, neck, limbs, if you have severe physical and psychological stress, if you notice poor posture - all this is a reason to think about a massage course. The procedures will also be useful during rehabilitation after injuries, problems with the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory diseases, a general decrease in immunity and increased fatigue.
Before enrolling in a medical massage course, you must consult with your doctor. The specialist will determine the required number of sessions (usually 10-15 procedures) and draw up an optimal schedule of procedures. For some diseases, sessions should be daily, for others - with an interval of 2-3 days. The doctor draws up a plan based on your medical history, age, condition, and you must follow the recommendations, because otherwise you can harm yourself.
Remember that massage is not a magic pill. One session is not enough to get rid of any ailments, even if you go to see a highly qualified specialist. It is not advisable to interrupt the course, because in this case it is almost impossible to achieve the desired effect.
Massage for diseases of the cardiovascular system
Massage in the complex treatment of cardiovascular diseases aims to normalize the functional state of the nervous, vascular and sympathetic-adrenal systems, eliminate congestion and improve blood circulation in the small and large circles, activate metabolism and trophic processes in tissues, increase the tone of the heart muscle and its contractility function, promote the development of the functional capabilities of the cardiovascular system and the development of adaptation mechanisms. Under the influence of massage, in patients with diseases of the circulatory system, the indicators of the oscillographic curve, which characterizes the state of vascular tone and blood pressure, change. Changes in hemodynamics are favorable with adequate influences in accordance with the pathogenetic and clinical characteristics of the disease [Belaya N. A., 1974].
Massage for heart defects
.
Indications
: predominantly mitral defects in the absence of signs of current endocarditis, normal temperature and ESR and the absence of left-shifted neutrophils in the blood.
Massage plan
: impact on the paravertebral zones of the thoracic and cervical segments of the spinal cord L1-D12, D5-D2, C7-C3 and reflexogenic zones of the chest (Fig. 64). Massage of the back, intercostal spaces, heart area, sternum and left costal arch; massage of the lower and upper extremities. The patient's position is sitting, with the head resting on the hands, on a bolster or pillow.
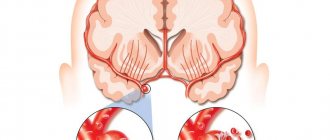
64. Localization of reflex changes in heart diseases (according to O. Glezer and A. V. Dalikho, 1965): a - in front; b - behind; horizontal lines—zones of hyperalgesia; crossed areas - changes in muscles; mesh – changes in connective tissue
Methodology
.
Back massage
: planar stroking in the direction from the underlying segments (L1) to the overlying ones (C3);
stroking the latissimus dorsi and trapezius muscles; rubbing the paravertebral zones and intercostal spaces towards the spine, rubbing the lower edge of the chest on the left and the muscles of the left half of the chest, kneading (longitudinal and transverse) the muscles of the back, the upper edge of the trapezius muscles and the left shoulder, felting the muscles of the left shoulder, patting, shaking the chest cells. Massage of the heart and sternum area
: circular stroking - flat surface and deep, rubbing the sternum and intercostal spaces with the palmar surfaces of the fingers, kneading the pectoral muscles, vibration (continuous, palmar surface of the fingers), patting the heart area, stroking from the sternum to the spine, compression and stretching of the thoracic cells, deep breathing movements.
Massage of lower and upper limbs
. It is carried out in a non-physiological position lying on the back. Using broad strokes, the techniques of stroking and intermittent kneading are used. Passive-active movements are produced in the joints of the limbs. The lower extremities are massaged for 3-4 minutes, the upper extremities for 2-3 minutes. The duration of the procedure is 15-20 minutes. Course - 12 procedures, every other day.
Massage for myocardial dystrophy
.
Indications
: chronic failure of the heart muscle due to intoxication and infection, nutritional dystrophies and hypovitaminosis, endocrine diseases and chronic overstrain of the heart muscle.
Massage plan
: impact on the paravertebral zones of the spinal segments L1-D5-D2, C7-C4. Back and neck massage, vibration of the VII cervical vertebra. Compression and stretching of the chest, concussion of the chest. Massage with broad strokes of the lower and upper extremities with the patient lying down.
Methodology
.
Back massage
: planar stroking of the paravertebral zones of the spine from the underlying segments to the overlying ones, circular rubbing of these zones with the ends of the fingers, the ulnar edge of the hand;
continuous vibration and puncturing of the area of the VII cervical vertebra (A.F. Verbov recommends applying an electric vibrator to the area of the spinous process of the VII cervical vertebra), massage of the trapezius and latissimus dorsi muscles - planar and enveloping stroking, rubbing with the ends of the fingers, shading, planing; longitudinal and transverse kneading, rubbing intercostal spaces and costal arches using sawing and crossing techniques. Stroking the entire back with broad strokes. Compression and stretching of the chest, concussion of the chest. Massage of the lower and upper extremities
: use stroking and kneading techniques with broad strokes. The duration of the procedure is 20-25 minutes. The course of treatment is 12-15 procedures, every other day.
Massage for angina pectoris
.
Indications
: atherosclerosis with predominant damage to the coronary vessels, chronic coronary insufficiency with functional spasms of the coronary arteries due to physical overstrain, with excitement and negative emotions (angina pectoris).
A.F. Verbov (1966) recommends, before prescribing a massage, to check pain sensitivity in the Zakharyin-Ged zones, to identify changes in tissues and muscles to clarify the dosage of the massage. N.A. Glagoleva (1971) emphasizes that massage can be used only in the interictal period, and when angina pectoris is combined with hypertension, traumatic cerebropathy, cerebrosclerosis, alternate massage of the collar zone with aminophylline electrophoresis. For concomitant spondylosis without radicular syndrome, N.A. Belaya (1974) recommends “back massage to influence the intervertebral discs and the entire spine.” Krauss (1958) during an attack of angina recommends gentle rhythmic stroking of the left half of the body with simultaneous administration of novocaine.
Massage plan
: impact on the paravertebral zones of the spinal segments C6-C4, D6-D2, D12 -L1 massage of the sternum, heart area, interscapular region and left shoulder, breathing movements, massage of the lower and upper extremities. The patient's position is stable: lying or sitting, with the head resting on the hands, on a bolster or pillow.
Methodology
.
Back massage
: planar stroking of the paravertebral zones from the underlying segments to the overlying ones, the trapezius muscles, the back of the neck and the sternocleidomastoid muscles, rubbing in the area of these zones, kneading (longitudinal and transverse) the latissimus dorsi, trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles muscles, shifting of the back muscles, vibration (intermittent, with the ends of the fingers), gentle patting with the palm, stroking, shaking the chest.
Massage of the area of the upper part of the sternum, the heart area, the interscapular area and the inner surface of the left shoulder
: stroking (circular, flat, superficial and deep, rake-shaped) intercostal spaces from the sternum to the spine;
rubbing the heart area, sternum, interscapular area and intercostal spaces, kneading the pectoral muscles and felting the muscles of the left shoulder, vibration stroking the interscapular area and the heart area, breathing movements. Massage of the lower and upper extremities
is performed with the patient lying on his back. Apply the techniques of stroking and kneading with broad strokes. The duration of the massage procedure is 15-20 minutes. The course of treatment is 12 sessions, every other day.
Massage for chronic coronary heart disease, post-infarction cardiosclerosis
. In the system of medical rehabilitation of patients with chronic coronary heart disease (CHD) and post-infarction cardiosclerosis, therapeutic physical training and massage are widely used. Massage, acting in synergy with dosed physical activity, stimulates the body's biological defenses, promotes faster adaptation and normalization of the functions of the nervous, vascular and sympathetic-adrenal systems. Its neuro-reflex and humoral influence enhances the positive effect of physical exercise, improves coronary circulation, blood circulation in the pulmonary and systemic circles, activates metabolism and trophic processes in tissues, and increases tissue absorption of oxygen. Providing a depletor effect, massage eliminates congestion, facilitates the work of the left atrium and left ventricle, and increases the pumping capacity of the heart. In patients with chronic ischemic heart disease, adequate physical activity (dosed walking, therapeutic exercises) has a more positive effect if they are combined with massage procedures. Massage accelerates the transition of acidic products from muscle tissue into the blood, which increases muscle performance and quickly eliminates fatigue after physical activity. Systematic use of massage during physical training increases the level of redox processes in the muscles. Training the heart helps develop its resistance to various stresses. Massage has a pronounced effect on the psyche, which is also an important factor in the medical rehabilitation of patients with chronic ischemic heart disease and post-infarction cardiosclerosis. The psychotherapeutic effect of massage helps the patient overcome fear and doubts, gives rise to confidence in the possibility of restoring active ability to perform physical and mental work.
Indications
. Massage in combination with therapeutic exercises is indicated for different locations (anterior and posterior wall) and varying severity of both primary and secondary infarctions. The question of when to start massage is decided individually, usually in accordance with the start of therapeutic exercises. Indications are the satisfactory condition of the patient, the disappearance of pain in the heart area, the absence of cardiac arrhythmias and shortness of breath at rest, leukocytosis, increased ESR, normal blood pressure, electrocardiographic data indicating a reverse development of the process or its stabilization due to scarring of the infarction focus. Such clinical data give grounds to start massage in patients with a mild course of a heart attack with small-focal damage to the heart muscle after 5-7 days, with a moderate severity of a large-focal heart attack that proceeds without complications - after 12-15 days of illness, with a severe clinical course of a heart attack with extensive affected area - 20-25 days from the onset of the disease. During the rehabilitation period in post-infarction patients, differentiated massage techniques are used in stages: the hospital period, the early post-hospital period, the period of sanatorium treatment.
Period of hospital treatment
.
Methodology
.
Patient position: lying on the bed, on the back. Massage of the lower extremities
: superficial stroking of the feet and legs, gentle circular rubbing with the pads of the fingers of the dorsum of the feet, ankle and knee joints, alternating with circular stroking, shallow kneading of the muscles of the legs - felting, longitudinal kneading.
Upper limb massage
: superficial stroking and rubbing of the hands, forearms, elbow joints, gentle longitudinal kneading of the forearm muscles.
Planar stroking of the lateral surfaces of the chest. After 5-7 days from the start of the massage procedures, if the patient is allowed to turn on the right side, massage the back and gluteal areas
: gentle stroking alternates with superficial rubbing of the paravertebral zones of the lumbosacral region and gluteal muscles. Procedure time: 3-7 minutes, daily.
Post-hospital treatment period
.
Methodology
.
Position of the patient: sitting, with the head resting on the hands, on a bolster or pillow, and lying down. Back massage
: stroking and rubbing the paravertebral zones from the underlying to the overlying segments, the latissimus dorsi and neck muscles, rake-like rubbing of the II-VIII intercostal spaces in the direction from the sternum to the spine, rubbing the left scapular and interscapular areas, kneading the back muscles and the upper edges of the trapezius muscles .
Massage of the lower extremities
: stroking with broad strokes and intermittent kneading of the legs and thighs, stroking and rubbing the feet and joints of the lower extremities, shifting the interosseous muscles of the foot, passive movements.
Massage the gluteal muscles, rubbing the iliac crests and sacral area. Stroking the heart area, sternum and costal arches, rubbing the left pectoralis major muscle and sternum, kneading the pectoralis major muscles and muscles of the left shoulder, vibration stroking the heart area. Breathing exercises. Abdominal massage
: flat, superficial circular stroking of the abdominal muscles.
Massage of the upper extremities
- with general strokes. The procedure time is 10-15 minutes, daily or every other day.
In the early post-hospital period, massage in combination with adequate dosed physical activity is intended to promote the restoration of neurohumoral processes, improve the function of the gastrointestinal tract, help coronary circulation and increase its reserves, increase the level of metabolic processes in the myocardium and thus promote the development of endurance and restoration of performance body.
Period of spa treatment
. Patients who have suffered a myocardial infarction are sent for medical rehabilitation to local cardiac sanatoriums after 2-4 months. after hospital treatment. Currently, in connection with the organization of specialized rehabilitation departments in cardiac sanatoriums, patients with chronic ischemic heart disease and post-infarction cardiosclerosis are admitted (but not earlier than 6 months) to resorts of republican and federal significance.
Experience and clinical observations show that rational spa treatment has a positive effect on patients with chronic ischemic heart disease, post-infarction cardiosclerosis, is considered as the third stage of rehabilitation and becomes a factor of secondary prevention, preventing the development of atherosclerosis and its complications. To mobilize adaptive systems and provide a regulatory effect on the function of external respiration, improve coronary circulation, and increase the trophic function of the myocardium, the main thing in medical Rehabilitation at the resort is the use of dosed physical activity for training, adequate to the functional state of the patient’s cardiovascular system. Therapeutic gymnastics, dosed walking, bathing and swimming in warm water in the sea or in a pool, oxygen therapy, and dietary nutrition are used. Balneophysiotherapy and climatotherapy are prescribed strictly differently. Patients undergo a course of segmental reflex massage at the resort.
Massage technique
.
Patient position: lying on a massage table, cushions provide an average physiological position of the body for maximum muscle relaxation. Impact on paravertebral zones D8-C3 from underlying to overlying segments: stroking - planar, with the supporting part of the hand, rubbing - with the ends of the fingers in circular directions, kneading - pressing, shifting, vibration stroking. Stroking and rubbing the intercostal spaces. Massage the latissimus dorsi, trapezius and neck muscles. Chest massage
: gentle, slow stroking and rubbing of the heart, sternum and left costal arch from the xiphoid process to the spine, stroking, rubbing and kneading of the left pectoralis major muscle, left shoulder and scapular area.
Vibrating stroking of the chest. Abdominal massage
: stroking, rubbing, kneading, vibration of the abdominal muscles.
For intestinal atony and constipation - intestinal massage. Massage of the lower and upper extremities
- with general strokes. The duration of the procedure is 15-20 minutes. Course - 12-15 procedures, daily or every other day.
For patients with chronic ischemic heart disease and post-infarction cardiosclerosis, gentle massage is recommended, excluding vigorous influence. Techniques that cause pain are unacceptable, since painful stimuli reflexively cause a number of unfavorable autonomic reactions, which can contribute to increased myocardial ischemia. Underwater shower massage, mechanical massage and hardware vibration massage are contraindicated. In all cases of heart rhythm disturbances and all types of blockades in patients with chronic ischemic heart disease, it is also not recommended to use manual vibration techniques when performing segmental reflex massage.
Massage for hypertension
.
Indications
: stage I-ΙΙ hypertension in the absence of vascular crises and pronounced phenomena of sclerosis of the blood vessels of the brain, heart and kidneys.
Massage plan
: impact on the paravertebral zones of the cervical and upper thoracic spinal segments C7-C2 and D5-D1. Massage of the head, neck, collar area. Patient position: sitting, with the head resting on the hands, on a bolster or pillow.
Methodology
.
Massage of paravertebral zones from the underlying segments to the overlying segments D5-D1 and C7-C2, deep stroking, rubbing, kneading. Massage of the trapezius muscles
: planar and enveloping stroking, semicircular rubbing, gentle shading, longitudinal, transverse kneading, shifting, transverse kneading of the upper clavicular edges of the trapezius muscles.
Massage of the frontal and scalp
: rake-like stroking and rubbing in circular directions, moving and stretching the scalp in the sagittal and frontal directions. Planar and enveloping stroking of the occipital region and the back of the neck. Planar and forceps-like stroking of the sternocleidomastoid muscles, circular rubbing, forceps-like kneading. The procedure is completed with broad stroking strokes of the head, neck and collar area. Procedure time: 10-15 minutes. The course of treatment is 12-20 procedures, every other day or daily.
N.A. Belaya (1974) recommends prescribing massage every other day, alternating it day by day with electrophoresis of medicinal substances, pulsed low-frequency currents using the electrosleep method, inductothermy, aeroionization, and a pulsed UHF electric field. Massage can be combined with various therapeutic baths on the same day, but it is more advisable to prescribe it every other day.
Massage for hypotension
.
Indications
: neurocirculatory dystonia of the hypotonic type (hypotonic disease) and chronic symptomatic hypotension.
Massage plan
: impact on the paravertebral zones of the spinal segments S5-S1 L5-L1, D12-D6, massage of the sacrum, gluteal muscles and iliac crests, pelvic concussion, massage of the lower extremities, abdominal massage, intestinal massage. The patient's position is lying down.
Methodology
.
Massage of the paravertebral zones
from the underlying segments (S5) to the overlying ones (D6), the area of the sacrum, gluteal muscles and iliac bones: flat and grasping stroking, rubbing (circular with the ends of the fingers, the ulnar edge of the hand and the supporting surface of the hand), shading, sawing, crossing, rubbing the iliac crests, longitudinal kneading of the lumbar region, transverse lateral areas of the anterior abdominal wall, vibration stroking, gentle patting, pelvic shaking.
Massage of the back surfaces of the lower extremities
.
Plane and enveloping stroking of the legs and thighs. Rubbing the muscles of the legs and thighs with the ends of the fingers, palm, planing, sawing. Kneading is longitudinal and transverse. Vibration (shaking, clapping crosswise with palm and fist), gentle chopping - longitudinally, vibration stroking. Massage of the anterior surfaces of the lower extremities
.
Plane and enveloping stroking of the legs and thighs. Circular rubbing with the palmar surface of the hand and the ends of the fingers. Kneading (longitudinal and transverse), felting. Vibrating stroking, patting, chopping, shaking the limbs. Abdominal massage
: flat circular superficial and deep stroking, enveloping stroking of the upper half of the abdomen - to the axillary, and the lower half - to the inguinal lymph nodes; rubbing - with the ends of the fingers, the ulnar edge of the palm, shading, kneading the front wall of the abdomen (longitudinal and transverse), rolling. Abdominal shaking in horizontal and vertical directions. For intestinal atony - intestinal massage. The duration of the procedures is 15-20 minutes. Course - 15-20 procedures, every other day.
I. N. Asadchikh (1966) recommends that patients with hypotension be prescribed daily massage of the abdomen and legs, after 30 minutes - 1 hour - therapeutic exercises, after 1-1.5 hours a radon bath. O. F. Kuznetsov (1970) used massage of the collar zone in combination with therapeutic exercises and oxygen baths for hypotension and came to the conclusion that some patients with hypotension have a spastic state of blood vessels, while others have an atonic state. Taking into account these conditions, the author recommends a differentiated technique, namely, for a tendency to spastic reactions - sedative therapy (oxygen bath - therapeutic exercises - massage), and for vascular atony - massage - therapeutic exercises - oxygen bath.
Massage for diseases of peripheral vessels of the extremities
. In the treatment of diseases of the peripheral vessels of the extremities, segmental reflex massage is an effective remedy (Fig. 65), especially in obliterating diseases with a paradoxical vascular reaction and a tendency to thrombosis, where direct (direct) massage of the extremities is contraindicated, it is advisable to act on the corresponding segmental zones. Extensive experience in using segmental reflex massage was accumulated during the Great Patriotic War. Its further substantiation in medical practice, the study of its effectiveness and the development of methods were facilitated by the work of V.N. Moshkova (1946), M. R. Mogendovich (1957), O. Glezer and V. A. Dalikho (1965), A. F. Verbova (1966), K. Dineiko (1966), L. A. Kunicheva (1970 ), N.A. Beloy (1974), etc.
65. Localization of reflex changes in diseases of the blood vessels (according to O. Glezer and A. V. Dalikho, 1965): a - in front; b - behind
Indications
segmental reflex massage for diseases of the peripheral vessels of the extremities are:
- atherosclerotic occlusion of the arteries of the upper and lower extremities, vasospasms (Raynaud's disease, etc.);
- varicose veins of the lower extremities, the presence of trophic changes in the skin and minor ulcers, previous phlebitis or thrombophlebitis without a tendency to relapse and erysipelas-inflammatory complications.
Massage technique for diseases of the arteries of the lower extremities
.
The patient's position is lying down. Impact on the paravertebral zones of the spinal segments S5-S1, L1-L5, D12-D10 from the underlying segments to the overlying ones: planar stroking, superficial and deep, rubbing circularly with the ends of the fingers, comb-like rubbing, sawing and crossing, kneading - longitudinal, shifting, vibration - shaking, patting, vibration stroking. Massage of the lumbosacral region and pelvic area
, flat superficial and deep stroking, rubbing the gluteal muscles with the ulnar edge of the palm, the supporting surface of the hand, sawing, rubbing the crests of the iliac bones in the direction from the upper anterior spine to the spine and costal arches from the xiphoid process to the spine, kneading buttock area, pelvic concussion.
Massage of the lower extremities
: stroking the soles, flat and enveloping surface stroking of the front surfaces of the legs and thighs, stroking and rubbing the joints with the palmar surfaces of the fingers, rubbing the soles using a comb-like technique. Passive movements. Breathing exercises. Chest stretch. The duration of the procedure is 12-15 minutes. The course of treatment is 12-15 procedures, every other day.
Massage technique for vascular diseases of the upper extremities
.
Patient position: sitting, with the head resting on the hands, on a bolster or pillow. Impact on the paravertebral zones of the spinal segments D7-D1, C7-C3 from underlying to overlying segments; planar stroking of the back of the neck, sternocleidomastoid muscles and the upper edges of the trapezius muscles, rubbing with the palmar surface of the hand, sawing, shading, kneading the latissimus dorsi muscles, trapezius muscles, sternocleidomastoid muscles, shifting the back muscles. Massage of the scapular and subscapular areas: rubbing with the ends of the fingers, shading, sawing, continuous vibration with the ends of the fingers, patting, chopping. Massage of the upper extremities: grasping stroking of the back and outer surfaces of the forearm and shoulder, stroking the hands, rubbing the palmar surface of the hand with the ends of the fingers and a comb-like technique, rubbing with the ends of the fingers circularly the back and lateral surfaces of the wrist and elbow joints. Massage of deltoid muscles
: stroking, rubbing, kneading. Passive movements. The duration of the procedure is 10-15 minutes. The course of treatment is 12 procedures, every other day.
Massage technique for diseases of the veins of the lower extremities
. Impact on the paravertebral zones of the spinal segments S3-S1, L5-L1, D12-D10. The patient's position is lying on his stomach. Using broad strokes, planar stroking of the lumbar region and the lower third of the chest, stroking the lower edges of the chest with the elbow edges of the hands in the direction from the sternum to the spine, stroking the iliac crests with the supporting part of the hands in the direction from the spine to the inguinal folds. Rubbing the paravertebral zones with the ends of the fingers from the underlying to the overlying segments, rubbing the lower edges of the chest, sacrum and iliac crests, sawing, crossing. Kneading the muscles of the paravertebral and gluteal areas. Vibration (finger tapping, patting, chopping the buttock area). Vibration stroking of the lumbar and buttock areas. Concussion of the pelvis.
Stroking of the legs and thighs is carried out only superficially; grasping stroking, intermittent or rake-like, is performed, bypassing protruding varicose veins. Comb-like stroking of the plantar surface of the feet. Gentle felting and vibration stroking of the muscles of the legs and thighs. Stroking and rubbing the ankle, knee and hip joints. Passive movements. Compression and stretching of the chest. Breathing movements. Procedure time: 12-15 minutes. Course - 12 procedures, every other day. Hydromassage and sinocardial massage are indicated.
Indications for medical massage
The procedures will help in getting rid of many ailments: from obesity to flat feet. Medical massage is recommended for all types of injuries to the musculoskeletal system (fractures, dislocations and sprains of joints, muscle spasms, all kinds of sprains and overloads of muscles and joints, torsion or rupture of ligaments). The course brings relief with:
- degenerative diseases of the spine and other dysfunctional diseases of the skeletal system;
- arthritis and tendonitis;
- diseases associated with respiratory failure;
- rehabilitation after muscle paralysis and peripheral nerve damage;
- neuroses and stress;
- osteochondrosis;
- stomach ulcers and gastritis;
- atherosclerosis;
- neuralgia;
- coronary disease;
- diabetes, etc.
The type of massage is selected depending on the pathology. The impact can be both general and local (aimed at restoring a specific function).
Contraindications for medical massage
Massage cannot be performed in some cases. Namely:
- skin diseases;
- immediately after a bone fracture and tendon rupture;
- increased body temperature;
- tumor diseases;
- phlebeurysm;
- hemorrhage, hemophilia, hemorrhagic diathesis;
- developed atherosclerosis;
- advanced stages of hypertension;
- infectious diseases.
Some patients feel weak after the session, observe redness of the skin and make the erroneous conclusion that massage is contraindicated for them. This reaction is just a side effect, which manifests itself less intensely in some and more intensely in others. But after the procedure there should not be a feeling of total “overwhelm” and complete powerlessness, dizziness, or a sharp rise in temperature. Such a response from the body indicates the incompetence of the massage therapist.
What to look for when choosing a massage therapist
Incompetent massage therapists are a big problem in the medical world. Such specialists have harmed the health of many people. There are several signs that this is not a medical professional who is trying to help, but a person aimed solely at commercial gain.
You should be wary if the massage therapist:
- gives a 100% guarantee of complete recovery;
- says that there are no contraindications to massage;
- promises, using the author’s method, to remove all toxins and waste from the body in 3 sessions, get rid of 10 kg of excess weight with one touch, etc.;
- insists on replacing the treatment prescribed by the doctor with dietary supplements and other magic pills;
- names the exact duration of the course in absentia.
Remember that medical massage is a fairly serious physiotherapeutic procedure in which such negligence is unacceptable. Do not risk your health, contact a medical institution, and not dubious specialists.
Our Clinic has professionals with many years of experience and medical education. They are well versed in anatomy, neurology and other fields, which help them form a correct idea of what processes occur in your body. Your health is in good hands here.
When performing a massage, you must follow a number of rules:
- The room should be warm to avoid excessive heat transfer after the massage, i.e. the temperature in the room should not be lower than 22-24 degrees.
- The massage is performed in a lying position on a table. The table on which the massage is performed should be covered with a blanket and a clean diaper. The room should have good lighting, but direct rays of light should not fall into the child's eyes.
- When performing a massage, hand movements should be soft, gentle, without jolts. Rings and any other jewelry should not be worn on hands.
- After the massage, the child should be dressed in warm, dry underwear to keep warm
- Massage is carried out after feeding, but not earlier than 1-1.5 hours, or before feeding. You should not massage your child before bedtime, as this excites him. After the massage, the child should rest.
- Massage movements are carried out along the course of the vessels - from the periphery to the center.
- When performing an abdominal massage, you should spare the liver area; you should not massage the genitals.
- When performing a back massage, patting and tapping the kidney area are excluded.
- Classes begin from the 10-15th day of life.
- Classes are held 3-4 times a day for 5-7 minutes.
How to prepare for a session
To achieve maximum healing effect and feel comfortable, it is recommended to follow several rules.
Namely:
- take care of hygiene;
- do not wear jewelry that may interfere with the specialist’s manipulations;
- give up perfume;
- eat no later than 1 hour before the procedure;
- Avoid epilation of legs and other areas on the eve of the procedure - massage oil can get into micro-wounds and provoke inflammation;
- if exposure is expected in the abdominal area, you need to eat no later than 3 hours before the procedure.
During the session, you need to relax as much as possible so that the massage therapist can work on the skin and muscles without encountering muscle resistance. After completing the procedure, you should lie quietly for several minutes.
Local contraindications
If there are contraindications from this list, massage can be done, but you need to avoid a certain area:
- — Abrasions, allergic rashes and wounds, fresh tattoos
- - Moles, nevi and warts. Massage is allowed in areas where moles do not protrude above the surface of the skin, that is, without touching them. If moles are large, located throughout the body, and cannot be avoided during massage, then this feature is considered an absolute contraindication.
- - Menstrual cycle. The massage therapist avoids impacting the abdominal area, and in the first few days, impacting the lower back
Local contraindications for acute and chronic diseases:
- - Hernia. Correction of an umbilical hernia using massage is allowed only in infants; in adults it is removed surgically
- — Stones in the gall bladder, liver and kidneys. In this case, massage in the abdominal area is prohibited.
- — Diseases of the mammary glands. Massaging this area of the body is strictly prohibited, including for mastopathy.
- - Psoriasis. It is forbidden to influence psoriatic rashes, as their number may increase
- - Endoarteritis. The feet and the area below the knee are excluded from the impact sites: narrowing of blood vessels can lead to tissue death due to increased blood flow
- - Trophic ulcers. Gentle massage is allowed in the early stages of the disease. When sclerotization of peripheral vessels occurs, feet with ulcers are not treated
- — Pregnancy, recent childbirth (up to 2 months) or recent abortion are contraindications for abdominal massage
- - Benign tumors. For neoplasms of the reproductive sphere (prostate adenoma, uterine fibroids, ovarian cysts), it is necessary to avoid the abdomen and lower back areas. Restrictions remain even after removal of tumors; the specialist will avoid the area where surgery was performed.
If there has been skin irritation or itching on some part of the body for a long time, this should also be avoided during massage.
These symptoms may indicate the onset of a disease that the patient is not yet aware of.
What methods of influence will the massage therapist use?
Medical massage includes many techniques and methods. The nature of the effect depends on the patient's medical history and condition. For example, procedures after an injury can be combined with cold exposure - this helps relieve swelling and increase joint mobility. However, several types of medical massage can be distinguished:
- Classic . Performed using oil, it is based on the use of basic massage techniques. The nature of the movements is stroking and rubbing.
- Spot . The specialist acts on certain points with his fingers or elbows. By pressing on a bioactive point in the body, certain centers responsible for pain and regeneration processes are activated.
- Periosteal . Necessary for diseases of the musculoskeletal system, which are closely related to pathologies of internal organs. Massage improves lymph flow and blood circulation, helps relieve pain.
- Connective tissue . The massage is aimed at improving the functioning of the ligaments. Due to this, you can get rid of pain, reduce swelling and stiffness, and restore joint mobility.
- Reflex . The technique is based on the idea that the human body is a complex self-healing system in which all elements are closely connected. Exposure to certain areas gives a response, and on the basis of this a conclusion is made about a possible dysfunction of the organ. With the right technique, neurological diseases and various diseases of the internal organs can be cured. The methodology of this type of massage is considered one of the most difficult because it requires specific knowledge from the field of neurology.
- Hardware . Based on the use of special equipment. The impact can be due to ultrasound, infrared radiation, weak electric shocks, etc.
The type of massage is selected individually; other physiotherapeutic procedures can be prescribed in combination.
Techniques and methods of massage for diseases of the cardiovascular system
Hypertonic disease
Before a massage session, it is necessary to measure your blood pressure: you can start procedures only when it is normal. The massage is performed in a sitting position, and begins in the collar area, first with light stroking, then by rubbing the corners of the shoulder blades and shoulder girdles, and ends with a massage of the neck in front.
Hypotonic disease
The main feature of massage procedures for hypotension is that they are performed energetically, using vibration or shock techniques. They are carried out with the patient lying on his stomach, and the main areas of influence are the sacrum and the area of the iliac bones. In addition, in case of hypotension, abdominal massage, carried out by longitudinal and transverse kneading, rolling and sawing, has a very good effect.
Heart disease
For heart defects, the main areas to be massaged are the chest, back, upper and lower extremities. As for the technique, it largely depends on the clinical picture of the disease. For example, in case of circulatory insufficiency of degrees I and II, the main objects of influence of massage therapists are the limbs, and if blood circulation is normal, then the left scapular area is massaged, both from the chest and from the back.
Obliterating endarteritis
For patients suffering from this disease, massage is performed in areas such as the pelvic region, lower back and back. If the disease is diagnosed in the first or second stages, then the procedures are performed with the patient lying on his back or stomach. The session begins with stroking the back or abdomen up to the head, continues with squeezes and double ring kneading. The lower limbs are also massaged, which must be bent at the knees during the procedure. For this, concentric and spiral stroking is used.
Vegetovascular dystonia
For patients suffering from this disease, procedures are best performed in the morning. The best position for this is lying on your stomach. The effects begin by stroking the neck and back of the head from the crown down, and continue with intensive rubbing of the cervical spine in circular and spiral movements.
Recommendations for improving the effect after massage
Ideally, after the session you can come home and rest for 30-40 minutes, relax. You can take a warm bath with sea salt or natural essential oils. It is also recommended to increase the amount of fluid consumed and eat right.
Diagnostics before the first massage session is a mandatory procedure. It is performed with the goal of not harming and helping the patient.
Extracts from the medical record, photographs and doctor’s reports, and a referral for a massage do not replace the examination of the patient by the massage therapist himself.
If there are any doubts on the part of the massage therapist, before the session, the specialist can invite a doctor to the office for consultation, who is always available in our clinic. An additional completely free consultation with a doctor is a concern for your health and an indicator of our responsible attitude.
Remember: a specialist at our clinic has the right to refuse you a massage session if he considers that the procedure may harm you.
Using various techniques, massage therapists help the patient get rid of various health problems. These include: dysfunction of the cardiovascular system, joint diseases, muscle dysfunction, consequences of fractures, obesity and much more.
In some cases, one massage is enough to combat the disease, but often massage is an integral part of general medical therapy.
Massage for chronic heart failure
General recommendations and restrictions when performing massage
Chronic heart failure (CHF) can become a complication of many heart diseases. Most often it occurs as a result of ischemic disease: due to the long-term existence of angina pectoris, after myocardial infarction, etc. CHF is an irreversible disease. It means that the heart muscle has undergone changes, during which the heart has ceased to fully pump blood. Because of this, stagnation occurs, edema forms, fluid accumulates in body cavities, patients begin to notice shortness of breath and reduced tolerance to physical activity. It is impossible to influence all these factors, much less restore the previous state of the myocardium in chronic heart failure. Once such a diagnosis has been made, it can no longer be removed. However, there are many ways that can help influence the pathogenesis of the disease. This includes drug therapy, physical therapy and various physiotherapeutic techniques, including massage. With their correct and combined use, it is possible to achieve a significant regression of symptoms, and in patients with a mild course of the disease, even their complete disappearance.
The possibilities of massage for CHF are limited, but quite significant. Thus, with the help of classical procedures, it is possible to expand the capillary network, stabilize vascular tone, normalize blood pressure and reduce the severity of shortness of breath and edema, “expelling” blood from the venous bed. Chinese acupressure has a slightly different effect. Its use allows you to increase the power of the heart, reduce oxygen starvation of organs and normalize microcirculation. However, the main point of its application is the main disease process underlying ischemic changes in the heart - atherosclerosis. Chinese doctors believed that using this technique would help slow down the rate of development of the disease.
Chronic heart failure has a different course, and depending on this, massage for this disease may be indicated or contraindicated. Its implementation is permitted in patients who suffer from stage I or II of CHF. These include those patients whose symptoms either appear only with increased load, or exist constantly, but in a mild form. Only patients whose disease exists in a compensated form can be admitted to physiotherapy. They should feel fairly well and show no signs of blood congestion. If a person regularly taking medications continues to have shortness of breath and swelling in the legs, he should not undergo such treatment procedures. It is necessary to review the drug treatment plan and achieve improvement in the condition. Massage is allowed only when the patient’s well-being has stabilized. Otherwise, it can lead to overload of the heart muscle and aggravation of pathological changes.
Before prescribing a massage, patients must be fully examined. Sometimes it happens that under the guise of exacerbation (decompensation) of chronic heart failure, an acute process, such as a heart attack, is hidden. It can occur in a painless form, which is often found, for example, in patients with diabetes. If in such a case you send a person to a massage course, this can significantly affect his health.
CHF is a complication of heart disease. The term “complication” means that a patient with such a diagnosis necessarily has an underlying pathology - stable or unstable angina, previous heart attack, arterial hypertension. Therefore, if any of the underlying diseases is included in the list of contraindications for massage, it should be abandoned. Such contraindications are acute heart attack and post-infarction period, unstable angina, acute coronary syndrome, angina pectoris of III-IV functional class (when chest pain occurs with minimal exertion and at rest), severe arterial hypertension, hypertensive crises and post-crisis state.
Methods of classical massage
For chronic heart failure, massage the back, arms and legs.
First, a series of techniques are performed on the back. The first thing to do is stroking in the direction from bottom to top. The movements are made with the base of the palms, the arms are moved in a straight line. Along the spine, the stroking is plane, on the sides - grasping. Then the massage therapist performs rubbing. This technique involves the pads of the index, middle, ring and little fingers. Repeat stroking over the entire area of the back.
After this, individual sections are worked on. On the area located along the spinal column, first deep stroking is carried out with the backs of bent fingers, then one of the types of rubbing. In this area, the most convenient type is sawing. It is replaced by kneading and vibration. Vibration should not be carried out too intensely in the area between the shoulder blades. Of its varieties, chopping with the edges of the palms and patting are the most preferable. Finally, stroking is carried out.
In a similar way, techniques are performed in the projection of the trapezius muscles and in the posterolateral part of the chest, where the latissimus dorsi muscles are located.
If the patient has a mild form of the disease (stage I), tonic techniques can be administered in doses over the heart area. This may be gentle chopping and patting over the anterior surface of the chest or in the interscapular space. In addition, such patients are allowed to perform squeezing movements on the chest, squeezing it from the sides between the palms.
If chronic heart failure has existed for a long time and is accompanied by dilatation of the heart cavities, it is recommended to perform stimulation at a point located in the lower part of the neck. An index finger or thumb is placed over the central process of the lower cervical vertebra (it is noticeable as a small protrusion) and small-amplitude vibration is applied.
After exposure on the back, they move on to the upper and then lower limbs. All the techniques that are performed there are aimed at draining blood from the peripheral veins. Stroking, rubbing, squeezing, kneading can be used. Movements should not be intermittent, but extended, and carried out in certain directions. First, massage the hand (foot), then the forearm (shin) and lastly the shoulder (thigh). The massage therapist's hands move from bottom to top, from fingers to body.
In patients with chronic heart failure, after starting a course of massage, protein may be detected in urine tests. In this case, you should reduce the intensity of the massage and avoid performing deep techniques in the lumbar region.
The total duration of the massage procedure is about 20 minutes. If well tolerated, taking into account the large massage area, the duration of the session can be increased to 30 minutes. Treatment is carried out in a course of 20-30 procedures. They are performed every day without breaks. If the slightest signs of deterioration in the patient’s condition appear, massage is refused.
Acupressure technique
Stimulation of all points is carried out using low-intensity, calming techniques. Typically, pressing is done with elements of rotation. At each point the effect is performed for about 3 minutes. All active areas, with the exception of the last one, are paired and are located on both sides of the body.
The first two are on the upper limb. Point 1 lies in the area of the ulnar fossa, in its outer part, on the side of the hand where the first finger of the hand is located. The impact must be carried out first on the right hand, and then on the opposite. The patient should sit with his hands resting freely on his knees. The back of the hand “looks” upward while massaging this point.
Point 2 is located below. It can be found on the back of the hand between the first two metacarpal bones (in the space separating the thumb and index finger), approximately in the middle of this area. During its stimulation, the massage therapist’s finger should rest against the second metacarpal bone. The massage is performed first on the right side.
Point 3 is localized on the lower leg. It is determined 3 cun down from the middle of the lower edge of the kneecap and 1 cun outward, to the side where the little finger is located. Unlike the already mentioned areas, here the massage is performed on both sides at once. The sitting patient's legs should be straight.
Point 4, also located on the leg, is located on the inner surface of the lower leg. Its location is 3 cun from the inner ankle towards the knee joint. The exposure is carried out for 3 minutes, simultaneously on both legs.
The 5th point can be found on the back, at the level of the gap separating the IV and V vertebrae of the thoracic region. From this zone you should measure 3 cun to the right and left. Here is the desired point, which must be stimulated on both sides at once with the pads of the thumbs. In this case, the person must lie down.
Point 6 lies above the middle of the spines of the shoulder blades on the right and left. The spines of the scapulae, which have an almost horizontal direction, are easily palpable through the skin. Massage of symmetrical areas is carried out at the same time.
To move on to the next longing massage, you need to return to the lower leg again, stepping back 3 cun towards the knee from the level of the outer ankle. To perform techniques at this point, the patient should sit down again.
Points 8 and 9 are located on the stomach; in order to massage them, the patient must be placed on his back. The 8th lies on both sides of the navel, on each side of it at a distance equal to 4 tsuns. During exposure to it, tension of the abdominal muscles is unacceptable. Point 9 is located along the same vertical line, but much lower. This area is located just above the pubis, and to find it you need to measure 4 cun from the top of the pubic bones.
Point 10 is located in the center of the bend of the wrist, on the palm side. Techniques are performed first on the right. 11th is very close. It is easy to determine by stepping back from the previous one by 1 cun towards the ulnar fossa. The impact is carried out according to the same rules.
Point 12 lies even higher, on the shoulder. If a person bends his arm slightly at the elbow, the biceps muscle (biceps) becomes easily visible through the skin. The active area is located at its inner edge (with the arm lowered, in the part closer to the body). Location level: 3 cun above the cubital fossa. The massage is carried out in the same way as for the previous two points.
Next, the impact is applied to point 13. It is also symmetrical, both areas are massaged at the same time. The patient should lie on his stomach. This acupuncture zone lies not far from the 5th point, only the 5th is located between the IV and V thoracic vertebrae, and this one is one vertebra below. In addition, it is located closer to the spine, 1.5 cun from the midline.
Points 14 and 15 are determined at the lowest level. The 14th is located on the inner surface of the foot, in the highest part of its arch, in front of and below the level of the inner ankle. The next one lies behind her, just under her inner ankle.
Finally, the last active point is single and is stimulated not in the same way as the others, but by a tonic method. It can be rubbed and deeply pressed for 30 s - 1 min. This point is located between the central processes of the II and III lumbar vertebrae.
The course of treatment for chronic heart failure should be long, up to a month, and massage sessions should be performed daily. The courses are repeated 3-4 times a year, two of them must be completed in the off-season.
- Rate the material