A microstroke in men is associated with thrombosis or spasm of small vessels in the brain. This pathology differs from other circulatory disorders in that it leads to the death of neurons and the formation of a focus of necrosis.
An attack of a micro-stroke is a loud signal from the body that it is necessary to see a doctor as soon as possible and check your health. The statistics are disappointing: those who do not seek help soon experience new attacks or develop a full-blown stroke.
The insidiousness of a micro-stroke lies in its transience. Symptoms rarely last longer than 24 hours, and men tend not to pay much attention to them. Even if a person subsequently undergoes a routine examination by a doctor, the latter may miss critically important symptoms.
The staff of the Yusupov Hospital includes candidates and doctors of medical sciences, doctors of the highest category. Extensive practical experience in the field of diseases of the central nervous system allows us to work with patients with microstroke at any stage: diagnosis, treatment, rehabilitation or prevention of cerebrovascular accidents in the future.
The difference between a stroke and a microstroke
In some sources, a microstroke is otherwise called a transient cerebrovascular accident. A transient - in other words, a temporary disturbance - passes within a day and is more like overwork and the consequences of a stressful state. During a micro-stroke, a small number of brain structures undergo necrosis, and the consequences of this may not be immediately noticeable. However, with a full-blown stroke, many more brain structures die, which seriously affects the quality of life.
The signs of stroke and micro-stroke in men are similar, the difference is that with a micro-stroke they go away much faster. It is for this reason that men often do not receive the necessary treatment on time and experience relapses.
Expert opinion
Author: Andrey Igorevich Volkov
Neurologist, Candidate of Medical Sciences
A microstroke, in accordance with medical terminology, is usually called a minor stroke. It is characterized by the same clinical picture as a major stroke. Signs include headache, inability to follow simple directions, loss of sensation in extremities, inability to smile, stick out tongue, and slurred speech. The difference between a minor stroke is that the neurological damage is reversible. The volume of the lesion is assessed using the NIHSS scale.
Clinical manifestations disappear within 24 hours, but do not completely affect the blood vessels of the brain. With microstrokes, necrosis of a very small area of the brain is possible, which can only be diagnosed based on the results of MRI and computed angiography. These types of diagnostics are available at the Yusupov Hospital.
At the first symptoms, it is important to get into the “therapeutic window” (4 hours). When starting therapy during this period, according to research, treatment is most effective. In this case, the zone of brain necrosis is limited to a small area.
Among the first measures: intravenous thrombolytic therapy, support of oxygenation of brain tissue, blood pressure monitoring, heart rate correction, prevention of tongue retraction and the formation of bedsores.
Prognosis and possible complications
Stroke in old age often has severe complications and consequences. The most favorable prognosis is partial restoration of functions affected by damage to parts of the brain.
Most often, older people who have suffered from this disease have problems with disorientation, speech and coordination of movements. However, this is only possible if medical care was provided in a timely manner.
If medical assistance is not provided within 2-3 hours after the onset of the first symptoms, then the person is susceptible to complications such as:
- Paralysis, paresis.
- Serious speech defects (up to its complete absence).
- Strabismus and other vision pathologies.
- Urinary and fecal incontinence.
- Dysphagia (impaired swallowing).
- Cardiac ischemia.
- Poor circulation of the inner ear, often hearing loss.
- Parkinson's disease.
In most cases, people who have had a stroke are unable to lead a normal life and require constant care.
Causes of microstroke in men
The cause of microstroke in men is chronic diseases. These include cerebral atherosclerosis, in which cholesterol plaques form in the blood vessels of the brain. They clog arteries, causing some brain tissue to not receive adequate blood supply.
Arterial hypertension is another reason. If it is accompanied by sudden changes in blood pressure, this can negatively affect the condition of the blood vessels and cause their spasm.
Doctors also warn that the following factors can lead to the disease:
- arrhythmia;
- diabetes;
- obesity.
Additional risk factors are bad habits: smoking, alcohol abuse. A sedentary lifestyle and addiction to high-calorie, fatty foods also negatively affect the condition of blood vessels and the body as a whole.
What are the causes, symptoms, consequences of this phenomenon?
The causes of TIA are atherosclerotic damage to the arteries, arterial hypertension, heart disease, diabetes mellitus, etc. The above reasons account for approximately 95% of TIAs and are dominant in elderly and senile people. In approximately 5% of cases, more often in young people.
TIAs are caused by other reasons:
- arterial dissection;
- vasculitis, congenital anomalies of the arteries;
- migraine;
- hematological disorders;
- infections;
- malignant neoplasms;
- oral contraceptives;
- pregnancy and postpartum period;
- pathological tortuosity of blood vessels;
- extravasal compression of the vertebral arteries by pathologically altered cervical vertebrae.
It should be noted that TIA is characterized by a sudden onset and rapid regression of symptoms, most often within 1 hour.
You need to pay attention to the following symptoms:
- Weakness in one upper and/or lower limb. Facial paralysis may occur.
- Numbness of half the face and/or limbs.
- Transient visual impairment in one eye.
- Speech disorders: difficulties in remembering words, pronouncing or perceiving words.
- Coordination problems: Loss of balance when moving your arms, legs, or body. The patient may stagger or fall when walking or standing.
- Diplopia: double or blurred image.
- Dizziness: The patient describes it not as a strange sensation in the head, but as if he himself is dizzy.
- Difficulty swallowing.
- Behavioral disturbances: the patient does not perceive what is said or makes uncoordinated movements. Possibly excessive sleep cravings. Possible agitation or psychosis.
TIA can be a precursor to all types of stroke, but most often precedes the development of atherothrombotic stroke. Against the background of TIA, 25-50% of atherothrombotic strokes, 11-30% of cardioembolic, 11-14% of lacunar and 9-11% of hemorrhagic strokes develop.
First signs
The symptoms of a microstroke in men rarely differ from the symptoms of a regular stroke. The first warning sign is a severe headache. Its distinctive feature is that painkillers do not help.
Pain syndrome periodically leads to distortions of perception and problems with coordination. In case of severe pain, it is important to analyze your overall well-being. It can worsen in different ways, depending on what part of the brain is affected by lack of oxygen or a ruptured artery.
You need to know what symptoms occur during a microstroke in men in order to seek medical help in time. You should be wary of:
- weakness in the limbs;
- spontaneous vision problems;
- difficulties in understanding someone else's speech;
- vomiting and nausea;
- negative reaction to bright lights and loud sounds;
- short-term memory lapses.
Similar symptoms of a microstroke in older men may be more pronounced than in younger men. However, it is not recommended to attribute them to age-related changes, no matter how old the person is. This is fraught with several relapses and damage to a large area of the brain.
Also, in both situations, moments of imaginary well-being periodically arise. It is understood as the improvement that occurs after an attack. Patients mistakenly believe that the disease has passed and there is no danger to health. Still, it is recommended to go to the hospital and make sure that the likelihood of repeated attacks is excluded.
Dangerous age and consequences of stroke
After age 55, the risk of stroke increases significantly. For men, the most dangerous age is considered to be from 45 to 55 years, since during this period they have a stroke 2 times more often than women.
If a person can be saved, the stroke still does not go away without leaving a trace. The person may be left partially paralyzed and lose control of urination and bowel movements. Cognitive functions decrease—problems with memory, speech, and information perception appear.
Recovery after a stroke is possible, but it often requires a lot of time and effort from both the patient and his loved ones. Therefore, it is better to prevent a stroke than to deal with its consequences later.
Symptoms of a male microstroke
Doctors inform how to recognize a mini-stroke in a man with a sharp deterioration in his health. One simple test is to ask the person to smile and then stick out their tongue. If pathological circulatory disorders are present, the smile will be asymmetrical, and the tongue will be turned or curved in one direction.
Symptoms of a cerebral microstroke in men can manifest themselves in difficulties in verbal communication. Often the victim cannot utter a simple phrase. In addition, coordination of movements may suffer: if you ask a person to hold his arms in an extended position, then after 3-4 seconds one of the arms will begin to fall on its own.
In addition, experts warn that during a microstroke, specific symptoms may appear that ordinary people usually do not pay attention to.
Cerebral hypertensive crisis
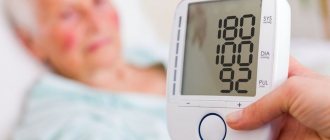
The crisis is characterized by a critical drop in blood pressure. In a very short period of time it can reach values around 180/120 mm Hg, and this is not the maximum value.
Even if the patient initially suffered from arterial hypertension, a characteristic distinguishing feature of the crisis is the time during which the pressure drop occurs. As a rule, indicators increase by several tens of units in a matter of minutes. As a result, the patient experiences deterioration in health. The main risk during a crisis is that the blood vessels of the brain may not withstand such a sharp change.
Transient ischemic attack
It is understood as a sharp change in the functioning of the arteries and veins located in the head.
Most often it manifests itself with a transient drop in the level of vision. It is noted that some people lose certain fragments from their field of vision. Sometimes vision disappears in only one eye, less often - completely.
The attack is also associated with problems in the functioning of the vestibular apparatus, which causes the gait to become shaky and unstable.
Acute hypertensive encephalopathy
Hypertensive encephalopathy is also associated with hypertension and, in fact, is one of its most dangerous manifestations. As a rule, it is accompanied by increased blood pressure and severe headaches. Their localization is first in the occipital part, then spreads to the entire head.
They also note a feeling of nausea, clouded consciousness and difficulty in coordinating movements.
With encephalopathy, intracranial pressure increases, changes occur in the condition of the veins and arteries of the brain. This is one of the most striking manifestations of not only a microstroke, but also a regular stroke.
Risk factors for microstroke:
Oddly enough, factors that are quite ordinary for most of us can provoke a mini-stroke.
- Not following a healthy diet; excess animal fats in the daily diet; overeating leading to obesity.
- Unhealthy lifestyle (drinking alcohol, smoking).
- Insufficient physical activity (exacerbated by sedentary work).
- Low stress resistance and constant experience of stress factors.
- Poor ecology (high percentage of exhaust gases, low oxygen content indoors and outdoors).
- Cold climatic conditions (they contribute to increased blood pressure) or a sharp change in the usual climate to the opposite.
- The age factor, and previously people over 60 years of age were at risk; today, prevention of micro-strokes is necessary even for 35-year-olds.
Diagnostics
Modern diagnosis of a microstroke in a man involves a set of procedures that will reveal whether an attack has occurred, as well as establish the localization of the focus of necrosis.
Prehospital diagnostics
The prehospital stage is based on medical history and neurological examination. It is extremely important for the patient not to waste time and make an appointment, since the most significant manifestations disappear within 24 hours.
Instrumental diagnostics
The most popular and effective device for detecting acute cerebrovascular accident is a tomograph. It can be used to perform magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography.
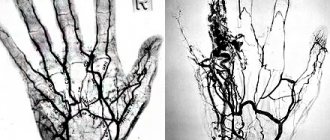
Such studies analyze the current state of the brain and identify dead areas in it. In addition, an angiography procedure is performed using tomography. A special contrast agent is injected into the circulatory system of the subject, thanks to which the entire vascular network will be visible in the image. In this way, you can see the location of all the vessels and find out whether they contain cholesterol plaques that form plugs.
Differential diagnosis of various types of stroke
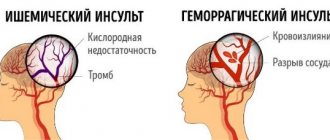
Prehospital and instrumental methods allow for differential diagnosis of different types of stroke. Most often we are talking about ischemic and hemorrhagic types. Each of them requires its own approach.
Specialists at the Yusupov Hospital carry out all the necessary tests and studies to determine what type of disease the patient is facing. When making a diagnosis, it is imperative to pay attention to both visual signs and test results. In particular, retinal hemorrhage may indicate an ischemic stroke. However, specialists do not limit themselves only to external manifestations, but carry out a full examination of the cardiovascular system. The patient is also sent for magnetic resonance and computed tomography procedures, radiography and other studies that allow an accurate diagnosis to be made and the development of a therapeutic plan to begin.
Stroke is an acute circulatory disorder in the brain that causes damage and death of nerve cells.
The danger of a stroke lies in its unexpected and very rapid development, which in many cases ends in death, therefore, at the first signs of a stroke, emergency medical attention is required! Prompt medical attention can minimize brain damage and prevent possible complications.
Another unpleasant “surprise” that a stroke brings is the disability of the person who experienced it, because Statistics say that 70-80% of people become disabled after a stroke.
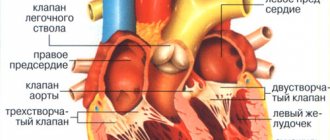
Stroke includes the following pathological conditions, or its types: cerebral hemorrhage, cerebral infarction and subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Causes of stroke
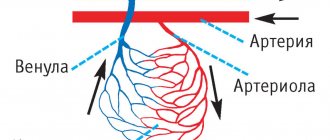
As you and I already know, dear readers, a stroke occurs as a result of a circulatory disorder in a certain area of the brain. This disorder, or pathology, occurs due to blockage and rupture of a brain vessel. Let's look at what actually can provoke this circulatory disorder?
Factors that increase the likelihood of developing a stroke:
- hypertension (hypertension - high blood pressure); - stenosis of the carotid arteries; - thrombosis; - embolism; - blood clotting disorder; - cerebral aneurysms; - heart rhythm disturbances; - atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular diseases; - diabetes; — bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol and drugs); - insomnia; - obesity; - sleep apnea - stopping breathing for more than 10 seconds; - hypothermia of the body; - injuries; - age - with increasing age, the state of health of blood vessels and heart.
Types of stroke
Ischemic stroke (cerebral infarction)
This type of stroke occurs most often - in 90% of all cases. It occurs as a result of narrowing or blocking of the arteries of the brain, due to which the blood flow in it is sharply reduced - ischemia. Due to the lack of blood flow, brain cells are deprived of nutrients and oxygen and can begin to die within just a couple of minutes.
Hemorrhagic stroke (intracerebral hematoma)
Accounts for approximately 10% of cases of the disease. A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel leaks or ruptures.
Transient ischemic attack (TIA) or ministroke
This type is characterized by a short-term (less than 5 minutes) episode of stroke symptoms.
In a mini-stroke, a blood clot disrupts blood flow to part of the brain, but does not cause significant damage because the blockage of the vessel is temporary.
Important! With a mini-stroke, as with a stroke, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance, even if the symptoms have completely disappeared. Symptoms of a mini-stroke indicate that the vessels leading to the brain are partially blocked or narrowed and there is a risk of developing a stroke.
The first signs and symptoms of a stroke
Important! If symptoms of a stroke appear, call an ambulance immediately!!!
Symptoms of a stroke:
- sudden weakness; - paralysis or numbness of the muscles of the face, limbs (often on one side); - speech impairment; - blurred vision; - severe sharp headache; - dizziness; - loss of balance and coordination, gait disturbance.
How to recognize a stroke in a person?
If you notice that a person is not behaving naturally, then do not rush to think that he is drunk; perhaps the person is having a stroke. To recognize this disease, pay attention to the following points:
Stroke recognition technique “UZTs”:
- U - smile. During a stroke, the patient’s smile is usually crooked; the corner of the lips on one side may be directed downward rather than upward.
- S - speak. Say a simple sentence, for example: “The sun is shining outside the window.” With a stroke, pronunciation is often (but not always) impaired.
- P - raise your hands up. If your arms do not rise at the same rate, this may indicate a stroke.
“IMPACT” stroke recognition technique:
- U - smile. After a stroke, the smile becomes crooked and asymmetrical;
- D - movement. Raise both arms and both legs up at the same time - one of the paired limbs will rise slower and lower;
- A - articulation. Say the word “articulation” or several phrases - after a stroke, diction is impaired, speech sounds sluggish or simply strange;
- R - solution. If you find violations in at least one of the points (compared to the normal state), it’s time to make a decision and call an ambulance. Tell the dispatcher what signs of a stroke (STROKE) you have found and a special resuscitation team will arrive quickly.
If you detect signs of a stroke in a person, call an ambulance immediately!!! The faster qualified assistance is provided, the greater the chances of eliminating the consequences of this disease!!!
If you notice signs of a stroke in a person, you must:
- Position the patient so that his head is elevated approximately 30°.
- If the patient loses consciousness and ends up on the floor, move him to a more comfortable position.
- If the patient has prerequisites for vomiting, turn his head to the side so that the vomit does not enter the respiratory system. If this has already happened, it is necessary to clear the airways by placing the patient on his side and clean the oral cavity.
- Do not let the patient drink or eat food, because if he has spasms in the respiratory tract, he may suffocate.
- Make sure the victim has fresh air available. Open a window or window to allow fresh air into the room. Remove tight clothing, unbutton your shirt collar, or loosen your tight belt or waistband.
- If possible, measure your blood pressure and glucose levels. The recorded indicators must be recorded and reported to the arriving doctors. It should also be noted that if the pressure is high, you should not immediately lower it, because In the first hours of a stroke, increased blood pressure is a necessary norm due to adaptation of the brain. Only over time can the patient be given medication that lowers blood pressure.
- If his pulse cannot be felt, his heart has stopped and his breathing has stopped, immediately begin chest compressions and mouth-to-mouth or mouth-to-nose artificial respiration. Everything else is the task of emergency medical services.
Consequences of a stroke
Each person experiences the effects of a stroke differently. Some people, thank God, have no consequences, others may have temporary or permanent disabilities, for example:
- paralysis or loss of muscle movement; - speech or swallowing problems; - memory loss or difficulty understanding clearly; - pain or numbness in some parts of the body; - loss of ability to take care of oneself.
Remember that a person who has suffered a stroke needs care, love and understanding. Help such a person, be patient
Stroke treatment
Stroke treatment consists of 3 stages:
— provision of emergency medical care; - hospital inpatient facility; — rehabilitation (recovery).
In the first hours of a stroke, doctors provide emergency care.
In the first days in hospital, intensive therapy is provided, which reduces the risk of death, reduces brain damage and prevents the occurrence of a recurrent stroke.
Important! Many different medications can be used to treat any type of stroke, but remember - all medications can only be prescribed by your doctor and should be taken strictly as recommended!
Over the next weeks and months , the patient is prescribed medications, and his health status is constantly monitored (repeated examinations are carried out and tests are taken).
After treatment, the person is rehabilitated in the form of various procedures, physical therapy and massage.
Treatment of ischemic stroke
Treatment for this type of stroke aims to dissolve the clot that is blocking the flow of blood to the brain. Also, during treatment, doctors try to prevent recurrent stroke and other possible complications. For this, medications are used in the form of tablets, injections, droppers and various medical procedures.
Medicines prescribed for the treatment of ischemic stroke:
Tissue plasminogen activator. This is the main medicine that treats ischemic stroke by dissolving blood clots. But it is not suitable for everyone, as it has clear recommendations for use, many contraindications and side effects.
The drug can be used no later than 3 hours after the artery supplying the brain is blocked by a blood clot. It is best when the drug is administered to the patient within an hour of the onset of the stroke. If more than 3 hours have already passed, then the risk of using this drug is higher than the expected benefit. In 6% of people, administration of the drug can cause a hemorrhagic stroke; people over 75 years of age are especially susceptible to this course of events.
Tissue plasminogen activator can be administered if:
- it is precisely confirmed by tests that the stroke is ischemic; — less than 3 hours have passed since the onset of the stroke; — there were no head injuries or heart attacks for the next 3 months; - never had a stroke before; - in the previous 21 days there was no bleeding in the stomach, intestines, kidneys and no blood was noticed in the urine; - there have been no surgical operations in the previous 14 days; - upper blood pressure is below 185 mm Hg, and lower blood pressure is below 110 mm Hg. Art.; — tests showed that the blood clots normally; - blood sugar level is not too high.
Numerous contraindications and dangerous side effects reduce the frequency of use of tissue plasminogen activator.
Antiplatelet agents: Clopidrogel, Dipyridamole, etc.
Antiplatelet drugs do not dissolve a blood clot that has already formed, but they reduce the risk of new blood clots, thereby reducing the risk of another stroke.
Anticoagulants: Warfarin, Dabigatran, Heparin, etc.
Anticoagulants have more serious side effects than antiplatelet drugs, so they are prescribed less frequently.
Also, in the treatment of ischemic stroke, pills for high blood pressure are prescribed, as well as statins, which are taken for elevated levels of “bad” cholesterol.
Treatment of hemorrhagic stroke
Treatment of hemorrhagic stroke is aimed at quickly stopping the hemorrhage formed in the cerebral artery, as well as removing a blood clot from it that puts pressure on the brain. In such cases, neurosurgical surgery is indicated.
In addition, when treating hemorrhagic stroke, high blood pressure pills are prescribed, which must be taken strictly as prescribed by the doctor.
Recovery after stroke (rehabilitation)
After leaving the hospital, a person who has suffered a stroke needs recovery (rehabilitation). Restorative post-stroke therapy is an extremely important point in the treatment of stroke, because According to statistics, the risk of developing a secondary stroke is 4-14%.
It is very good to immediately send the person to a specialized rehabilitation center.
In such centers, a person will be helped to restore strength, body functions and return to independent life. The effect and duration of recovery depends on the area of the damaged brain and the magnitude of the damage.
Procedures for recovery after a stroke
Therapeutic physical education (kinesitherapy). It is prescribed to restore full range of motion, strength and dexterity, as well as balance and self-care skills. Therapeutic exercises are carried out under the supervision of a doctor, with measurement of pulse and pressure. During physical education, it is necessary to give a person rest.
At first, this is passive gymnastics, the movements are performed for the patient by a rehabilitation therapist or trained relatives, then the exercises become more complicated, the person re-learns to sit, get up, stand and walk, eat, dress independently, and adhere to the rules of personal hygiene.
Massage. The massage consists of slowly and lightly stroking the muscles in which the tone is increased. Rubbing and gentle kneading are also possible.
Anesthesia. To relieve pain, procedures such as electrotherapy, magnetic therapy and laser therapy are recommended. The procedures relieve pain, activate the immune system, improve microcirculation, etc.
Improving tissue trophism. For this purpose they use: ozokerite, paraffin applications, hydro procedures, etc.
Fixing bandage. Prescribed for sore shoulder syndrome.
Speech rehabilitation. To restore your own speech and to understand the speech of others, classes are prescribed with a speech therapist-aphasiologist. They include in-class exercises as well as homework to improve writing, reading and arithmetic.
Psychological and social adaptation. For a person who has suffered a stroke, the support of friends, family and friends who could surround him with care and love is very important. A positive attitude is very important for a complete recovery. A healthy psychological climate in the family, smiles and help are needed. Be patient, communicate, find such a person an activity (hobby) that interests him, and take part in cultural and social events with him. It’s not for nothing that the Holy Scripture says: “A cheerful heart does good as medicine, but a sad spirit dries out the bones.”
Medications for recovery after stroke
After general recommendations for recovery after a stroke, we will consider medications that will help us carry out post-stroke therapy.
Medicines that improve blood supply to the brain: Pentoxifyline, Cavinton, Cerebrolysin, aspirin-based drugs.
Drugs that improve metabolic processes in brain cells: “Ceraxon”, “Actovegin”, “Cinnarizine”, “Ginkgo-fort”, “Cortexin”.
Nootropics (drugs that have a specific effect on higher brain functions). Such drugs can stimulate mental activity, activate cognitive functions, improve memory and increase learning ability: Piracetam.
Stroke Prevention
The main prevention of stroke is identifying and eliminating risk factors. Let's consider the basic rules and recommendations that reduce the risk of developing a stroke or recurrent stroke:
- stay calm and have a positive attitude;
- maintain a normal weight, avoid obesity;
- eat right, focusing your diet on fresh fruits and vegetables so that the body receives all the vitamins and microelements it needs;
- limit your salt intake;
- lead an active lifestyle;
- get enough sleep, the best sleep will be if a person goes to bed at 21:00-22:00;
- give up bad habits (alcohol, smoking, drugs);
- control your blood pressure (if you have hypertension);
- monitor your blood sugar levels, which can be done using a glucometer;
- control the level of “bad” cholesterol in the blood.
Local physician at polyclinic No. 5 A.K. Shevchuk
Treatment of microstroke in men
Treatment of microstroke in men is carried out mainly by neurologists. The basis of therapy consists of several groups of drugs:
- Vasodilators help restore and enhance blood supply, including to the injured area of the brain.
- Nootropics improve cognitive abilities. They are used to stimulate mental activity and improve memory, which may have been damaged due to an attack.
- Antiplatelet agents are prescribed if there is a risk of thrombosis. These drugs prevent platelets from sticking together and attaching to arterial walls.
- Angioprotectors have a positive effect on the entire vascular bed and improve metabolic processes in them. These drugs are prescribed to almost all patients.
The therapy is also complemented by physiotherapeutic procedures. Men are prescribed various types of massage and given recommendations for physical therapy.
Recovery
During rehabilitation, patients are prescribed medications to maintain the level of cognitive activity, as well as to control blood pressure levels. In particular, these are antihypertensive drugs that stop attacks of high blood pressure.
During recovery, it is important to take medications that improve the physical and chemical properties of the blood and prevent blood clots.
Also, during rehabilitation, patients are recommended to engage in physical therapy, but it is important not to overload so that there is no risk of a recurrent attack.
Comprehensive stroke treatment
First of all, doctors need to stop the hemorrhage, relieve swelling, and carry out prophylaxis immediately after the patient’s admission to the hospital, which will prevent a recurrence of the attack. Next, the patient will receive symptomatic treatment based on the individual clinical picture.
Typically, the therapeutic regimen is developed in an interdisciplinary meeting. The commission includes a therapist, cardiologist, pharmacologist and some other specialized specialists. This helps minimize the risk of complications or adverse reactions from the use of certain medications.
The body’s functionality is supported through the following procedures:
- IVL (artificial pulmonary ventilation);
- cleaning the oral cavity from vomit and mucus;
- breathing exercises;
- maintaining blood pressure at the required level;
- droppers that help thin the blood and restore salt balance;
- treatment with anticoagulants;
- if swallowing ability is lost, feeding through a tube.
The success of therapy will depend on the quality of medical care provided and the condition of the patient’s body. Rehabilitation will also play a major role, but it begins only after the 3rd week of continuous treatment of an attack.
Consequences
If you consult a doctor in a timely manner and follow all instructions, the negative consequences are minimized.
At the same time, if you suffer an acute cerebrovascular accident on your legs, you may experience a series of repeated attacks within a short time. In the worst case scenario, ignoring symptoms threatens the further development of a major stroke. With the most unfavorable prognosis, it is fraught with a decrease in the quality of life and pathological changes in the functioning of consciousness.
Recovery of older women after stroke
The most favorable period for starting rehabilitation is the first 3-4 weeks. It is important to remember that due to age, women already have a limited reserve of recovery capabilities. This is due to the presence of other chronic diseases (osteoporosis, chronic joint diseases, pathological fractures, etc.), previously suffered and untreated micro-strokes, and a low ability to form new networks of neurons.
Recovery after a stroke takes from 6 months to 2 years. Further, all changes in the body become irreversible.
Prevention
General prevention tips boil down to maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Men are advised to adjust their diet and give up unhealthy foods in favor of natural ones. So, experts advise minimizing the consumption of fatty foods and adding vegetables and fruits to the menu.
To avoid repeated attacks, you should stop smoking and drinking excessive alcohol.
You can play sports and visit the gym several times a week, but you should not be overzealous in your training. Excessive load can negatively affect the state of the cardiovascular system and is more likely to harm the body than have a positive effect.
Men experiencing cardiac problems should carefully monitor changes in their well-being. Ideally, you can keep a diary and record blood pressure readings in it from morning to evening.
What to do if a person has a stroke?
- First of all, call an ambulance. Sometimes the minutes count.
- Provide fresh air, open windows and doors, and free the person’s neck from constricting clothing.
- Leave the person where the attack occurred. The patient cannot be moved.
- Elevate the person's head and upper body 30 degrees by placing several pillows under the thoracic spine.
- If vomiting occurs, turn the person's head to the side and ensure that the vomit passes away so that the person does not suffocate.
- In the event of an epileptic attack, carefully hold the person, turn his head to the side and insert an object wrapped in cloth into his mouth - a stick, a comb, a spoon.
- In case of cardiac arrest, immediately begin compressions through the chest and perform artificial respiration.
- Wait for the ambulance.