Read in this article:
- Normal or pathological?
- What to do if the pressure on the right and left hands is different?
- Increase and decrease in pressure
- Reasons for the differences
- How to recognize blockage of blood vessels?
- How can the doctor help?
- How to avoid serious pathologies?
Everyone knows that blood pressure is measured on the arm. But if you put the blood pressure cuff on your left arm first and then on your right, the results may well be different.
Normal or pathological?
The difference in pressure levels on the right and left hands is a fairly common occurrence, but it is accompanied by many myths and misconceptions. Some of them may be dangerous. For example, in the literature there is information that approximately 20% of people whose tonometers show different numbers on different hands die within 10 years. It also notes that we are talking about a difference of 20 mm Hg. and more.
After such a “discovery,” most people check their own pressure on both hands. And if differences are discovered, the person panics and tries to take action. Most often they involve self-medication, which is not always safe for the body.
Meanwhile, the difference in pressure is a variant of the norm, and only 15-20% of such people need treatment, and only after a serious examination. With such a question, you need to go to a therapist, who will prescribe all the necessary tests, compare them with your medical history and identify the cause of the differences.
If necessary, the doctor issues a referral to a specialist: a cardiologist, a vascular surgeon, a neurologist. Accurate diagnosis and treatment prescribed based on it will help prevent complications and restore normal blood pressure.
Characteristics of blood pressure
Blood pressure level is directly related to the pumping function of the heart muscle and vascular elasticity.
Enter your pressure
Move the sliders
120
on
80
Pressure is present in the arteries to ensure that the body's organs receive the oxygen and nutrients they need. Upper pressure (systolic) is determined at the moment when muscle contraction occurs. After contraction, the heart relaxes until the next pumping of blood. This provokes a decrease in blood pressure. During the period when blood pressure reaches a minimum value, the lower pressure (diastolic) is determined. Blood pressure is measured in special units - millimeters of mercury. When measuring blood pressure, the highest value is noted first.
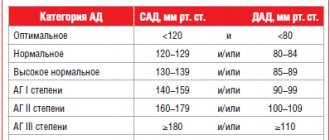
Normal pressure for the upper limbs
The limits of blood pressure changes can change throughout a person’s life and depending on past or congenital diseases. The average value for a healthy adult is 120/80 mmHg. Art. The table shows the limits of normal values for different age categories and representatives of both sexes. It is noteworthy that blood pressure increases with age in both men and women.
| Age, years | Boundary values of blood pressure, mm Hg. Art. | |
| Women | Men | |
| 20 | 116/72 | 123/76 |
| from 20 to 30 | 120/75 | 126/79 |
| from 30 to 40 | 127/80 | 129/81 |
| from 40 to 50 | 137/84 | 135/83 |
| from 60 to 70 | 144/85 | 142/85 |
| more than 70 | 159/85 | 145/82 |
Normal pressure for lower extremities
In a healthy person, blood pressure in the leg is higher than in the arm. This is a normal state of affairs. But it is important to remember that the pressure reading on the leg should not be more than 20 mmHg higher than the reading from the forearm. Art. If the patient has a narrowing of the main arteries of the legs, the pressure in the legs will be lower. The indicator may differ by 30-50% from that obtained when measured on the hand.
What to do if the pressure on the right and left hands is different?
If you get different data when measuring pressure on two arms, you need to analyze several factors:
- The magnitude of the differences is within 10 mmHg. is not a cause for concern. But the larger the gap, the higher the risk of pathology;
- Compliance with the norm - when the indicator on one hand corresponds to the norm or indicates increased blood pressure, and on the second it is higher - this is a less dangerous situation. The likelihood of a pathological process is greater when the pressure on one hand is normal and the pressure on the other is low;
- Right-handed-left-handed - increased pressure on the main working hand is considered normal;
- Age – the difference in pressure on the two arms is more often recorded in adolescence and old age;
- Physical activity level – differences may occur due to vigorous exercise or heavy work;
- Unusual symptoms and health complaints – their presence indicates the need for examination.
It is especially important to measure the pressure on both arms for people who do not monitor the indicator regularly and use a tonometer occasionally. But even with daily measurements, it is worth comparing the indicators from both hands once a month.
So, a simple rule: the difference in pressure on the two arms is within 10 mm Hg. – physiological norm. Approximately 50-60% of people will get exactly this result with the appropriate measurements. If the differences are more significant, you should consult a doctor.
Blood pressure measurement. Memo.
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of blood in the major arteries of a person. There are two complementary indicators of blood pressure:
- upper (systolic) blood pressure is the level of blood pressure that occurs at the moments of maximum contraction of the heart muscle
- lower (diastolic) blood pressure is the level of blood pressure that occurs at moments of maximum relaxation of the heart muscle.
The unit of measurement for blood pressure is the millimeter of mercury (mmHg). Let's say the blood pressure level is 130/90, which means the following: the systolic pressure level is 130 mm Hg. Art., and diastolic – 90 mm Hg. Art.
A tonometer is used to measure blood pressure. Tonometers are mechanical and electronic.
To measure blood pressure using a mechanical tonometer, a phonendoscope is required.
Electronic tonometers are semi-automatic and automatic. In semi-automatic ones, air is pumped into the cuff manually, in automatic ones - with a compressor built into the pressure gauge.
Electronic tonometers determine not only blood pressure, but also heart rate (pulse).
Conditions for measuring blood pressure
- The measurement should be carried out in a comfortable, quiet environment, the room should be at room temperature.
- In this case, approximately 30-60 minutes before determining blood pressure, you should exclude smoking, drinking tonic drinks, alcohol, caffeine, as well as physical activity.
- Blood pressure can only be measured after the patient has rested for at least five minutes. If there was significant emotional or physical stress before the procedure, in order to achieve correct blood pressure readings, you need to increase the rest period to 15-30 minutes.
- Blood pressure should be measured in the morning and evening. When measuring blood pressure regularly, measurements should be taken at the same time 2 times a day, recorded and shown to the doctor at the next appointment. To increase accuracy, make a series of 3 measurements (this is especially important for patients with arrhythmia), the interval between measurements should be at least 2 minutes.
- The measurement should be taken while sitting (leaning on the back of a chair, with relaxed and uncrossed legs, the hand resting on the table, at heart level), in a calm environment, after a 5-minute rest. The legs should be straightened and on the floor, and the arms should be straightened and placed freely at heart level. It should be remembered that the shoulder should not be compressed by clothing, especially since it is incorrect to measure blood pressure through clothing. During the measurement you should not move or talk.
- During the initial measurement, blood pressure should be determined in both arms and subsequently measured blood pressure on the arm where the pressure was higher. (A blood pressure difference in the arms of up to 10-15 mm Hg is normal.)
- The bladder must be emptied before measuring blood pressure.
Measuring blood pressure with a manual tonometer (Korotkoff method)
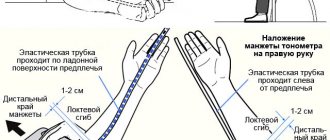
- The tonometer cuff should be at the level of the heart (middle of the chest) 2 cm above the elbow. A finger should fit between the uninflated cuff and the arm. The cuff must cover at least 80% of the shoulder circumference and at least 40% of the length of the shoulder. It is possible (but not recommended) to place a cuff on a sleeve made of thin fabric, if this does not interfere with the measurement.
- Place the phonendoscope membrane on the pulsation point of the brachial artery (approximately in the area of the cubital fossa).
- Quickly inflate the cuff using a bulb (remember to close the bulb valve first to prevent air from escaping) to a pressure level of 20 mmHg. Art. exceeding systolic (determined by the disappearance of the pulse).
- Slowly deflate the cuff (using the valve) at a rate of 2 mmHg. Art. per second The first beat (sound, tone) heard corresponds to the value of systolic (upper) pressure. The level of cessation of sounds corresponds to diastolic (lower) pressure. If the tones are very weak, you should raise your hand, bend and straighten it several times and repeat the measurement.
- Normal blood pressure level: 110-139 / 60-89 mm Hg. Art. for adults
Rules for self-measurement of pressure with an electronic tonometer.
- Make yourself comfortable: free your hand from clothing and place it so that the cuff is level with your heart.
- Make sure that the rolled up sleeve does not squeeze your arm.
- Place the edge of the cuff 2-3 cm above the elbow joint, so that the cuff tube is on the midline of the inside of the arm.
- Apply the cuff snugly, but not tightly.
Rules for measuring blood pressure with a wrist device:
- Take off your watch and bracelet. Pay attention to the correct position of the wrist tonometer body relative to the palm. The correct position of the wrist tonometer body is recommended by photographs or drawings on the tonometer box or in the description of the tonometer.
- Place the cuff on your left wrist, positioning your hand so that your thumb is pointing up.
- Place the cuff directly on the skin, 1 - 1.5 cm above the wrist crease, wrap the cuff around your arm until it fits snugly.
- Bend your arm so that the device is positioned at the same level as your heart.
- During the measurement, relax and refrain from talking.
Errors when measuring pressure:
Mistake No. 1: Using inappropriate pressure measuring instruments.
Many people, for the sake of convenience, buy wrist tonometers - blood pressure monitors that are worn on the patient's wrist. A high-quality, branded wrist tonometer is a very good and convenient thing, but most wrist tonometers are intended exclusively for young patients, for people no older than 45 years. Wrist blood pressure monitors are not suitable for people over 45 years of age! And if a person, say 60 years old, uses a wrist tonometer, he will get completely incorrect results when measuring pressure. Many older people do not know this; they use wrist tonometers and rely on their readings. And blood pressure pills are also taken based on the readings of the wrist tonometer. And then they are surprised that taking the pills makes them feel bad.
Mistake No. 2. The habit of measuring blood pressure 2 or 3 times in a row.
Many people, especially those who use automatic tonometers, like to immediately measure the pressure a second time after the first pressure measurement “to be on the safe side.” It seems that, in their opinion, this will be more accurate. But it turns out the other way around - when measuring again, the pressure numbers may differ from the previous result by 20-30-40 units! This dispersion of numbers has led many people to consider automatic blood pressure monitors to be inaccurate. “What kind of device is this that gives different readings every time!” - dissatisfied buyers of such a device are indignant, having poorly studied the instructions for the electronic tonometer. Meanwhile, the instructions for most of these devices clearly indicate: repeated pressure measurements on the same arm can be carried out no earlier than 7-10 minutes after the previous measurement. Then everything will be fine with the device readings. If you really want to measure your blood pressure, then measure the blood pressure on your other arm a second time. But keep in mind that on the right and left hands the pressure numbers may differ by 10-15 units (10-15 mmHg). This is fine. In general, when used correctly, good electronic blood pressure monitors from trusted companies are very accurate and reliable. And their testimony can be trusted. They give fairly accurate readings. Unless the person taking the blood pressure makes the following mistake:
Mistake No. 3. The habit of measuring pressure in a hurry.
Most people measure their blood pressure almost on the run, casually. But it's not right. To get the correct numbers when measuring blood pressure, before this procedure you need to sit quietly for 5-10 minutes and relax. And further. Do not talk while measuring blood pressure! If, while measuring your blood pressure, you are talking, or worried, or taking your blood pressure right after going outside, the tonometer will show 20-30 extra units of pressure. Or even all 40. By the way, it is for this reason that many people whose blood pressure is basically normal turn out to be hypertensive when visiting doctors.
Imagine the scene: a patient comes to the clinic. Going to the doctor itself is a cause for concern for many people. And then there were a lot of people, a turbulent situation, a queue. For anyone, even a healthy person, the pressure in such a situation will jump by 10-20 units. But here, finally, is the coveted doctor’s office (after 30-40 minutes of waiting in line). The sight of a white coat causes stress in many people - “white coat syndrome”. We get an additional plus of 10-20 units to the pressure.
Measure your blood pressure correctly and be healthy!
Increase and decrease in pressure
The closest thing to pathology is a decrease in pressure on one arm with normal or slightly elevated levels on the other. Much depends on lifestyle and which hand is the working one. For example, in a right-handed person who ignores physical activity, the pressure on the right hand is usually lower than on the left. The same situation is typical for left-handers who engage in physical labor or sports. The difference may gradually increase, approaching 20 mmHg.
Why is this happening? The blood supply to the upper extremities is provided by two arteries. The left one comes from the aorta, the pressure in it is high. The right one comes from the brachiocephalic trunk, where the rate is lower.
Another situation: a right-handed person devotes a lot of time to sports training. At the same time, the muscles on the right strengthen, become denser, and their volume increases. In this case, the arteries are compressed and the pressure increases. But even in this case, the indicators are considered normal if the difference does not exceed 20 mm Hg.
Note! If the pressure readings on the two hands are different, the higher one is considered true.
Reasons for the differences
Only a doctor can determine the exact cause of the difference in pressure in the two arms. But there are some signs that you can analyze yourself:
- On one arm the pressure is normal, on the other it is increased - this may be due to vegetative-vascular dystonia or individual characteristics of the structure of the arteries;
- On one hand the pressure is increased, on the other - even higher - such manifestations are caused by constant stress, lack of sleep, hypertension, vegetative-vascular dystonia;
- On one arm the pressure is low, on the other – within the normal range or high – there is a possibility of obstruction of the arteries and problems with the blood supply to the arm.
Problems with arterial patency are caused by compression of large vessels, which narrows or blocks the lumen.
Arterial obstruction develops against the background of:
- Atherosclerosis - cholesterol deposits inside the vessels create plaques that block the lumen;
- Thrombosis, thromboembolism - blood clots are called blood clots that form inside the vessels and impede blood flow;
- Aneurysms - sac-like expansions appear on the blood vessels, preventing normal blood flow;
- Aorto-arteritis – inflammation of the vascular walls, causing thickening of the membranes;
- Scalenus syndrome – the subclavian artery is surrounded by muscles that can harden and compress the arteries.
The causes of obstruction of large vessels can be injuries, surgical operations, the appearance of malignant or benign neoplasms in the soft and bone tissues of the chest or shoulder.
How to recognize blockage of blood vessels?
Blockage of blood vessels, which does not allow blood to circulate normally, may well manifest itself in a decrease in pressure in one arm. In such situations:
- The brush loses strength;
- The fingers become pale and cold;
- Numbness appears;
- Blueness of the skin appears on the fingers or the entire hand.
When the pressure on the right hand decreases and at the same time dizziness and headaches, vomiting and nausea, difficulty speaking and distortion of the face, weakening of attention and memory, paralysis of the body on one side appear, this indicates problems with blood circulation in the brain. The fact is that nutrients to the brain and right arm come through arteries that start from the aorta in the form of one trunk.
How can the doctor help?
When the difference in pressure in two arms exceeds 15 units, you need to consult a doctor and undergo a diagnostic examination. Regular blood pressure measurements are required; consultation with a specialist may be required.
Treatment in such situations is selected individually and may consist of:
- Taking medications with a blood thinning effect - this helps restore vascular patency and improve blood circulation;
- Exercise therapy to activate blood circulation;
- Physiotherapeutic procedures.
Sometimes conservative methods do not bring results. Then a surgical operation is prescribed to remove atherosclerotic plaques, blood clots, install stents on the vessels, and replace damaged arteries with prostheses.
The main thing to remember is that a timely visit to the doctor is the main condition for identifying the problem and the key to eliminating it.
Why are pressure measurements taken in the leg area?
Blood pressure readings are taken on the legs for diagnostic purposes. If the doctor suspects that the patient has a narrowing of the vessels of the lower extremities, the patient undergoes such a study. Measuring blood pressure in the legs is considered a fairly effective method because it immediately reflects changes in the patient's blood flow. In addition, the ratio of blood pressure readings in the legs and arms is calculated - the ankle-brachial index. The index is used to assess the severity of arterial damage in the legs. In addition, by calculating the index value, the doctor can monitor the development of detected arterial disease.