The bigger, the better?
However, since it is quite difficult to get the required amount of this mineral from food (to do this you will have to drink a liter of milk or eat a kilogram of cottage cheese daily), people switch to preparations containing calcium. And they often drink it in excessive doses, they say, to make sure it is absorbed.
Questions and Answers How to deal with calcium deficiency in the body? It is very dangerous. And not only because with an excess intake of calcium, its absorption not only does not improve, but, on the contrary, worsens, but also because for the body such an excess is almost more harmful than a deficiency. Studies have shown that daily consumption of high doses of calcium increases the risk of mortality in mature and elderly women by 1.5 times over the next 10 years from myocardial infarction, stroke, and other causes. The danger arises due to the fact that unabsorbed calcium settles in the form of deposits on the coronary vessels, heart valves and brain vessels. And taking more than 1,000 mg of calcium per day (in the form of dietary supplements or multivitamins) increases the risk of heart complications even more - by 20%.
The risk exists not only for the heart and blood vessels. With excessive consumption of synthetic calcium, stones (calcium oxalates) form in the kidneys and bile ducts. Scientists also have an assumption that taking large amounts of calcium supplements leads to prostate cancer and the proliferation of pathogenic microflora in the intestines.
Finally, excess calcium interferes with the absorption of other beneficial substances - vitamins and minerals (especially iron), which also increases the risk of many diseases and deficiency conditions.
Test yourself. Are you getting enough calcium? More details
Scientists link physical activity to calcium deposits in arteries
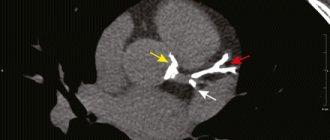
With calcification of the coronary arteries, calcium salts are deposited in the wall of the vessels bringing arterial blood to the myocardium. This is usually asymptomatic, and only a few years after the onset of calcification, heart pain, weakness, and dizziness appear.
Regular physical activity has long been strongly associated with a reduced risk of obesity, diabetes, heart attacks and strokes, and, overall, premature death. However, as new work from cardiologists at the University of Leicester has shown, the most athletic people have calcification of the coronary arteries. Scientists talked about this in more detail in an article in the journal Heart
.
Scientists have previously found signs of coronary artery calcification in physically active people.
Calcification is a serious risk factor for heart attack caused by decreased blood supply to the heart.
Calcinosis is more often observed in older people, mainly men with poor diet. However, it can also occur in people 20-30 years old without any cardiovascular disease.
The researchers collected data from healthy adults who underwent regular comprehensive examinations at two large medical centers in Seoul and Suwon, South Korea, between March 2011 and December 2021. At each health examination, participants completed a questionnaire that included questions about personal and family history, lifestyle, and educational level. Weight (BMI), blood pressure and blood fat levels were also assessed. Physical activity was divided into low, moderate and intense.
Obesity, blood pressure, cholesterol: what spoils the brain from childhood
Obesity, high blood pressure and high cholesterol in children are associated with cognitive decline in adulthood...
11 May 15:06
The scientists then tracked changes in the coronary arteries for an average of three years. The final analysis included data from 25.5 thousand people, mostly men. 47% of them had low physical activity, 38% had moderate physical activity, and 15% had intense physical activity, for example, jogging 6.5 km a day.
Those who were more physically active tended to be older and less likely to smoke. They also had lower levels of total cholesterol, higher blood pressure and more calcium deposits in their coronary arteries.
The relationship between the level of physical activity and the condition of the arteries appeared over time, regardless of their initial condition.
Higher physical activity was associated with faster progression in both those who did not have calcium deposits at the start of the study and those who already had them.
The study does not determine the cause of these changes, the researchers note. They have several guesses.
Physical activity can increase arterial narrowing through mechanical stress and damage to the vessel walls, as well as through physiological reactions such as increased blood pressure and levels of certain hormones. Physical activity also affects the effects of food.
Researchers also do not exclude that, despite calcification, the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases does not increase.
Running from death
The benefits of running have been convincingly proven by scientists. A large study has shown that regular runners...
18 August 18:15
“The benefits of physical activity for the cardiovascular system are undeniable,” they emphasize, recalling national recommendations of 150-300 minutes per week of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity or 75-150 minutes of vigorous activity. “However, patients and physicians need to be aware that physical activity may accelerate the progression of coronary artery calcification.”
Calcification may also have a beneficial effect, the scientists add. Calcified atherosclerotic plaque is more stable and less prone to tearing off, which can cause blockage of the vessel and, as a result, a heart attack or stroke. A similar result is observed, for example, when taking statins.
“The increased rate of coronary artery calcification is a phenomenon that occurs in response to both effective treatment, such as statin therapy, and exercise,” they note. “Assessing the degree of calcification should not be assumed to assess a patient’s cardiovascular risk.”
To assess risks, experts recommend paying attention to non-calcified plaques.
Physical activity remains the best way to control these risks. Those who are concerned about the condition of their blood vessels should consult a doctor to find out if there are any problems.
The authors of the work add that they did not have objective data on the loads of the subjects - the information was obtained through self-reports. In addition, there were no known cases of heart attacks or strokes, so the actual risks to the cardiovascular system cannot be judged.
Form question
Not only the dose of calcium is important, but also the form in which this mineral is found in a particular drug.
calcium gluconate does not have any advantages. It has a very low percentage of absorption in the intestine, and causes inflammation of the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract and constipation, as well as other complications already mentioned. Calcium chloride is usually used by injection or intravenously, but is difficult to tolerate and is not suitable for everyone (contraindicated in atherosclerosis, a tendency to thrombosis, or hypersensitivity). When taken in tablet form, it causes heartburn, cramps and even ulcerative lesions of the digestive tract.
Calcium lactate (food additive E327, added to juices, canned fruit, bread and pastries) is well absorbed only by the child’s body, and adults, due to the lack of a special enzyme, can absorb it only in small quantities.
Article on the topic
The magic of magnesium. Why is this mineral important for women?
Calcium carbonate (or simply chalk) is suitable only for short-term use. If you use it for more than two weeks, the acid-base balance may be disrupted. Calcium chelate is an easily digestible form. This is physiological, but, alas, the most expensive of all options.
Calcium citrate is a safe, affordable and highly absorbable calcium compound that does not contain natural impurities. Absorbed by 44%, which is 2.5 times higher than that of calcium carbonate. Moreover, its absorption does not depend on the level of acidity. Good absorption of this form of calcium reduces the risk of its deposition in blood vessels, kidneys and other organs.
Calcium (Ca)
In the human body, calcium makes up 1.9% of the total weight, while 99% of all calcium falls on the skeleton and only 1% is found in other tissues and body fluids. Bone ash is 50% calcium salts; Of these, 85% falls on Ca3(PO4)2 and 12% on CaCO3.
Calcium in food, both plant and animal, is in the form of insoluble salts.
Their absorption in the stomach almost does not occur.
Absorption of calcium compounds occurs in the upper part of the small intestines, mainly in the duodenum. Here, absorption
is greatly influenced by bile acids.
The latter form complex, easily dynamic compounds with calcium salts that pass through the wall of the villi. Calcium absorption is a complex process, the intensity of which depends on many factors. Absorption worsens
with excess fat, from the introduction of magnesium, sodium, potassium salts, from the content of large amounts of oxalic and citric acids in food, from an increase in phosphates in food.
Absorbed calcium is excreted by the kidneys, liver and colon epithelium. Unabsorbed calcium is excreted by the intestines. Calcium release
with urine and feces increases with thyrotoxicosis and with the use of thyroxine, as well as with the introduction of excess amounts of acidic substances into the body and with acidosis.
Daily requirement
in calcium for an adult is 0.45 g per day. For pregnant and lactating women, 2 times more is required - up to 1 g per day.
Physiological regulation
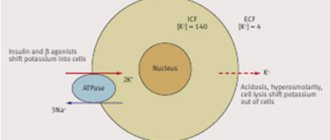
The level of calcium in the blood is controlled by parathyroid hormones and vitamin D through the nervous system.
Parathyroid glands
maintain the level of calcium in the blood by mobilizing it from the bone “depot”.
Vitamin D
promotes the absorption of calcium from the intestines and facilitates the deposition of calcium and phosphorus in the bones.
Normal blood calcium levels
- 9.0-11.5 mg/100 ml. Calcium is found in blood serum in various forms: in the form of non-filterable colloidal compounds and filterable compounds in an amount of 4-5 mg%; the remaining 5-6 mg% of calcium compounds pass through ultrafilters, of which 2 mg% is in ionized form. Colloidal calcium is a calcium reserve.
Ratio
The above forms of calcium depend on the pH concentration of CO2, on the ratio of albumins and globulins and the amount of inorganic phosphorus.
What functions does calcium perform in the body?
Scientists have calculated that normally there are about 20 g of calcium per kg of human weight, and 98% of this amount is contained in bone and joint tissues. Everyone knows about this, but what does the remaining 2% of calcium, found in soft tissues, blood, and intercellular fluid, do?
The functions of this microelement are as follows:
- Provides strength to bones, including teeth, and cartilage tissue.
- Regulates the strength of heart contractions and their rhythm.
- Normalizes blood pressure.
- Provides strength to the walls of blood vessels.
- Participates in cholesterol metabolism, promotes the removal of “bad” cholesterol from the body.
- Supports normal functioning of the nervous system.
- Participates in the formation of hormones of the thyroid gland and other endocrine organs.
- Participates in the process of hematopoiesis and blood clotting.
- Helps strengthen cell membranes.
- Reduces the activity of allergens entering the body.
- Provides good condition of skin, nails, hair.
- Takes part in the formation of cellular immunity and the formation of antibodies.
These are just the basic functions of calcium. It is also part of many enzymes involved in metabolism.
What foods are rich in calcium
To prevent the body from experiencing calcium deficiency, the following foods should be included in the diet every day:
- milk and all products made from it - various cheeses, cottage cheese, kefir and yoghurts, cream and sour cream;
- seafood - mussels, oysters, sardines, salmon, kelp (sea kale);
- raw eggs;
- fresh vegetables - onions, cabbage - preferably cauliflower and broccoli;
- fresh and dried herbs - parsley, watercress, celery, cilantro, spinach;
- fruits - oranges, pineapple, apricots, grapes, currants;
- legumes – beans, peas, soybeans;
- nuts, seeds, sesame, poppy seeds.
Important: it is better to focus on plant sources of calcium, because they contain vitamin D and other biologically active substances that promote the absorption of calcium.
Diagnostics
Calcium metabolism disorders are determined by laboratory tests. To determine the cause of the pathology, more extensive research is required, so specialists prescribe hardware studies. Additionally, differential diagnosis can be carried out.
Examination methods:
- urine test (general) - with elevated Ca levels, a mineral will be present in the biomaterial and the alkaline reaction will be pronounced;
- blood test (biochemical) - a significant increase/decrease in ionized and total calcium is detected in the plasma;
- ultrasound examination - the entire endocrine system is examined for the presence of tumors, tissue enlargement and other abnormalities;
- radiography - used to examine bones to determine the possible development of osteoporosis, fractures, cystic formations and other pathological processes;
- densitometry - used to accurately determine the density of bone tissue;
- radiography (with contrast agent) - helps to identify ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract and parathyroid adenoma in the retrosternal space;
- computed tomography - examines the urinary system and kidneys for the presence of stones;
- magnetic resonance imaging - allows you to obtain the most accurate data about tumor formations of the thyroid glands;
- spintigraphy is a study using radioactive isotopes, with the help of which it is possible to visualize the area under study.
Diagnostics allows you to obtain the maximum amount of information to identify provoking factors, characteristics of the disease and possible complications. Treatment can begin only after receiving the examination results.
Causes of hypocalcemia
Endocrine organs are sensitive to effects on them, so calcium metabolism can be disrupted for various reasons.
A decrease in plasma Ca may occur for the following reasons:
- neck trauma with bleeding;
- complication after surgery on the thyroid gland;
- inflammatory processes;
- ionizing radiation;
- metastasis in endocrine organs;
- adrenal insufficiency;
- autoimmune diseases;
- systemic diseases.
Identifying the causes is considered the basis of treatment, since if the influence of negative factors continues, therapy will not be effective.
How much calcium do we need?
The following calcium intake levels are recommended:
| Age | Calcium intake, mg |
| 7 - 9 years | 700 |
| 10-12 years old (boys) 10-12 years old (girls)1 13-16 years old | 900 1200-1400 1200-1400 |
| 17-18 years old | 1200 |
| 19-49 years old | 1000 |
| 50+ | 1000-15002 |
1 On average, girls mature 2 years earlier than boys. 2 The recommended minimum is 1000 mg, but if the risk of osteoporosis is high, increased calcium intake is necessary.