Biliary dyskinesia is a common disease. Women get sick 10 times more often than men.
Contraction of the gallbladder occurs under the influence of the hormone cholecystokinin, which is secreted by the cells of the mucous membrane of the duodenum. Cholecystokinin is released under the influence of food. When food enters the duodenum, cholecystokinin is released, the gallbladder contracts, and the sphincter of Oddi relaxes. Bile is secreted into the duodenum. This whole process depends on the condition and tone of the gallbladder muscles, sphincters and the nature of the food.
By origin, primary and secondary dyskinesias of the gallbladder and biliary tract are distinguished
- Primary dyskinesia
occurs due to a violation of the neuromuscular regulation of the motor activity of the gallbladder and biliary sphincters. It is believed that this type of dyskinesia occurs in patients of asthenic physique who have neurotic or psycho-emotional disorders. In addition to the diagnosis of biliary dyskinesia, such patients are often diagnosed with neurocirculatory dystonia or vegetative-vascular dysfunction. The causes of dyskinesia are diseases of the endocrine system, in particular diseases of the thyroid gland, gonads, and menopause. - Secondary dyskinesia
of the gallbladder and biliary tract occurs in patients with diseases of other organs of the gastrointestinal tract (chronic gastritis, duodenitis, enteritis, colitis). Dyskinesias occur especially often in diseases of the duodenum, when, due to damage to the cells of the mucous membrane of the duodenum, their release of cholecystokinin is disrupted. Secondary dyskinesias also occur in patients with cholelithiasis or chronic cholecystitis.
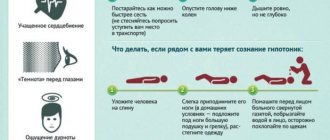
Arterial hypotension
Arterial hypotension is a decrease in blood pressure. The diagnosis is made if blood pressure is reduced from normal by 20% or more. Treatment of arterial hypotension presents the same problem as arterial hypertension - increased blood pressure. Pathology can be primary and secondary. The secondary form often occurs against the background of:
- heart failure;
- arrhythmias;
- fasting;
- lack of vitamins;
- stomach ulcer;
- endocrine shifts.
Main symptoms:
- weakness and lethargy;
- drowsiness;
- often - apathy;
- absent-mindedness;
- headache.
The use of low blood pressure medications is not necessary. It is possible to normalize blood pressure if you adhere to a healthy lifestyle, including exercise, proper nutrition, and stress prevention. If there is no effect, you should look for the cause - the provoking disease - and eliminate it.
Read more about arterial hypotension (for example, about the symptoms of drug-induced hypotension that occurs while taking certain medications) on our website https://www.dobrobut.com/.
Causes of dyskinesia
In case of biliary dyskinesia, the doctor will definitely find out the causes of the disease; this is important for drawing up an effective treatment regimen. There are primary and secondary JVP. Primary ones are less common; they are usually associated with the anatomical and structural features of the ducts or gallbladder. These include the following:
- septa in the cavity of the bladder;
- weakness of the walls of the gallbladder;
- increased number of ducts;
- bending of the gallbladder;
- abnormal location, mobility of the bladder;
- double, intrahepatic bladder, etc.
Secondary dyskinesias appear as a result of other diseases. The latter include viral hepatitis, neurocirculatory dysfunction, diseases of the digestive system (gastritis, cholecystitis, cholelithiasis, etc.). Other causes may include allergic reactions, diseases of the pelvic organs in women, endocrine disorders, chronic inflammatory processes, infections, and parasitosis.
In some cases, secondary dyskinesia develops as a result of improper and/or irregular nutrition. Prolonged fasting, mono-diets, frequent consumption of fatty, spicy, fried foods can lead to disruption of bile movement.
Today, the theory of neurogenic and psychogenic origin of JVP is being considered. It is believed that neuroses, stress and some psycho-emotional reactions stimulate dysfunction of the biliary tract. This is because the movement of bile is partly regulated by the autonomic nervous system. It, in turn, functions on the basis of hormones and neurotransmitters produced by the central nervous system. Therefore, psychological discomfort is reflected in muscle tone and motility of the gallbladder.
Physical inactivity, excess weight, and bad habits can be fertile ground for the development of disorders.
Causes of muscle hypotension in children and adults
Muscle hypotonia means a persistent decrease in muscle tone.
The main causes of the pathology:
- congenital disorders of neuromuscular complexes;
- muscle dystrophy;
- lack of protein in the diet (this is one of the most common causes of muscle hypotension in children);
- decreased physical activity;
- action of toxins (poisons);
- traumatic brain injuries;
- lack of thyroid hormones.
The main symptoms of muscle hypotension:
- deterioration in motor activity;
- drooling and problems pronouncing words and sounds;
- rapid onset of fatigue during active movements.
The diagnosis is made based on symptoms and additional methods (CT, MRI, electromyography), which are used to analyze the severity of the pathology.
The basis of treatment is eliminating the cause. An important role is played by therapeutic exercises, physiotherapy, and massage for muscle hypotension.
Types of dyskinesia of the gallbladder
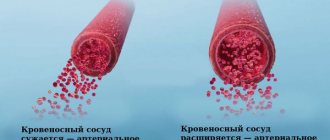
When bile moves quickly, we talk about hyperkinetic biliary dyskinesia; when bile moves slowly, we talk about hypokinetic dyskinesia. These types differ in symptoms, causes, and approaches to therapy. The hyperkinetic form is more typical for young patients, the hypokinetic form is more typical for people over 40 years of age.
There is another classification based on the characteristics of the tone of the duct sphincters. Hypermotor dyskinesia is observed in cases where the tone is increased, hypermotor - when there is a decrease in the contractile function of the circular muscles. Most often, the hypertensive type of disease corresponds to hyperkinetic, and the hypotonic type corresponds to hypokinetic.
It is important to understand that dyskinesia of the gallbladder is often not accompanied by organic changes in the ducts or gallbladder; only a disturbance in the movement of bile is observed. However, with this disease, the likelihood of developing secondary diseases, for example, inflammatory ones, increases.
Hypotension of the renal pelvis
Hypotension of the renal pelvis is a decrease in its tone. Main reasons:
- congenital malformations;
- prolonged forced lying position (for example, after heavy operations);
- hormonal changes in the body (puberty, menopausal wilting);
- disruptions in nervous support;
- damage to the wall of the pelvis (for example, a stone).
The nosology is manifested by stagnation of urine and worsening of its discharge.
How to treat hypotension of the renal pelvis? In mild cases, it is enough to eliminate its cause; in severe cases, it will be necessary to involve surgical intervention to narrow the “loose” pelvis.
Hypotension of the gallbladder
Hypotension of the gallbladder is a deterioration in its ability to contract. It is fraught with deterioration in bladder emptying, leading to digestive disorders in the duodenum. Its main reasons:
- violation of a healthy diet, abuse of “bad” foods - fatty, fried, spicy;
- malnutrition of the tissues of the bladder wall;
- failure of the nervous system;
- parasitic infection.
Main symptoms:
- periodic attacks of pain in the right hypochondrium;
- bloating;
- alternating constipation and diarrhea;
- nausea and vomiting.
To confirm the diagnosis, duodenal intubation is performed.
In most cases, help with gallbladder hypotension consists of dietary nutrition. In some cases, the prescription of choleretic drugs will be required. In case of severe hypotension, the gallbladder is removed.
Diagnosis of dyskinesias of the gallbladder and biliary tract
It is carried out using duodenal intubation. In the hypertensive form of dyskinesia, the administration of a bile secretion stimulator (magnesium sulfate) often causes a painful attack and the gallbladder bile fraction is released quickly or intermittently, the contraction phase of the gallbladder can be shortened. With hypokinetic dyskinesia, bile flows out of the gallbladder after a long period of time after stimulation, and the release of bile occurs slowly. Cholecystography and intravenous cholegraphy, radiocholecystography are also performed. These tests detect changes in the filling and emptying of the gallbladder and help rule out other diseases of the biliary tract and gallbladder.
Gastric hypotension
Stomach hypotension syndrome is not a very common pathology. Its reasons may be:
- poor nutrition;
- the effect of various toxins on the stomach wall;
- lack of potassium in the body;
- protracted stomach diseases.
With pathology, stagnation of contents in the stomach develops, which manifests itself:
- painful sensations;
- feeling of fullness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- weight loss of the patient.
The main method of treatment is to provide a balanced diet. Its principles:
- mechanical, chemical and thermal sparing;
- eating small meals frequently;
- Chewing food thoroughly.
Physical therapy also plays a role, which is aimed at strengthening the abdominal press.
Treatment of dyskinesias of the gallbladder and biliary tract
First of all, it is necessary to normalize the diet, work and rest, and the state of the nervous system. For the hypertensive type of dyskinesia, a diet is prescribed excluding fried, spicy foods, seasonings, smoked foods, and alcoholic beverages. It is recommended to eat small portions, often. For pain, antispasmodics and sedative herbal mixtures are prescribed.
Physiotherapeutic and sanatorium-resort treatment and physical therapy are prescribed. With the hypokinetic variant of dyskinesia, the diet is somewhat expanded. Drugs that stimulate the motor activity of the biliary tract (xylitol, sorbitol, magnesium sulfate) are used. It is recommended to carry out duodenal intubation with the release of the gallbladder from bile or “closed tubes”, when the patient is recommended a special technique by which he can independently stimulate the contraction of the gallbladder. Physical therapy and sanatorium-resort treatment are mandatory.
Signs of intestinal hypotension
The basis of intestinal hypotension is:
- disruption of the innervation and blood supply to the intestines (as consequences of injuries and operations);
- congenital pathologies of the neuromuscular apparatus of the intestinal wall;
- gross violation of dietary principles;
- regular stress.
Signs of intestinal hypotension manifest themselves in the form of symptoms of partial dynamic (motor) intestinal obstruction:
- prolonged constipation;
- accumulation of gases in the intestines and bloating;
- pain along the intestines;
- reflex nausea, sometimes vomiting.
A colonoscopy is mandatory to distinguish intestinal hypotension from its organic damage.
The appointments are:
- correction of diet;
- mandatory consumption of plant fiber - it stimulates peristalsis;
- complex of therapeutic exercises;
- physiotherapy – paraffin on the abdominal wall, electrophoresis;
- drinking mineral water.
Dyskinesia (dysfunction) of the biliary tract
Treatment for gallbladder dysfunction includes:
- mode,
- diet therapy;
- drug therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- hydrotherapy;
- Spa treatment.
Treatment of patients with dysfunction of the gallbladder and sphincter of Oddi is often carried out on an outpatient basis.
Treatment of hypertensive type of gastric dyskinesia:
- With the hypertensive type of dyskinesia, a state of psycho-emotional comfort and peace is very important for patients. After the elimination of the pain syndrome and signs of exacerbation, the patient’s regimen expands.
- Diet therapy is essential. The general principles of the diet are a diet with frequent meals of small amounts of food (56 meals a day) with the last meal immediately before bed, which promotes regular emptying of the bile ducts and eliminates bile stagnation.
For the hypertensive type, it is recommended to limit foods that stimulate bladder contractions - animal fats, meat, fish, mushroom broths, eggs.
A good effect in this form of functional disorders is provided by drugs belonging to the group of cholespasmolytics.
The group of cholespasmolytics and anticholinergics includes the following drugs:
- Atropine sulfate, 0.1% solution is prescribed orally, 5-10 drops. appointment.
- Bellalgin (analgin 0.25 g; anesthesin 0.25 g; belladonna extract 0.015 g; sodium bicarbonate 0.1 g) take 0.51 tablets 2-3 times a day.
- Besalol (belladonna extract 0.01 g, phenyl salicylate 0.3 g) is prescribed 1 tablet. 2 times a day.
- Metacin is used 1 tablet. 2-3 times a day. For colic, the drug is injected subcutaneously or into the muscle, 1 ml of 0.1% solution.
- Platiphylline is prescribed 1 tablet. (0.005 g) 2-3 times a day before meals for 100 days. For colic, the drug is administered subcutaneously, 1 ml of a 2% solution 1-3 times a day.
- Euphylline (theophylline 80%; ethylenediamine 20%) 1 tablet. (0.15 g) 1 time per day.
- In case of hypertensive dysfunction of the gallbladder, cholespasmolytics of synthetic origin are more often used.
- Noshpa (drotaverine hydrochloride) is prescribed in tablets of 0.04 g 1-3 times a day for 14 days or more or in ampoules of 2 ml of a 2% solution intramuscularly or intravenously 1-2 times a day.
- Papaverine (papaverine hydrochloride) is prescribed orally in tablets of 0.04 or 0.01 g 3 times a day or intramuscularly (intravenously) 2 ml of a 2% solution.
Combined cholespasmolytics include nicoshpan (nicotinic acid 22%; drotaverine hydrochloride 78%) 20 mg 1-2 times a day and papazole (dibazol 0.03 g; papaverine hydrochloride 0.03 g) 1 tablet. 2-3 times a day The disadvantage of drugs in this group is their non-selectivity, i.e. they act on the entire smooth muscle latura, including the urinary tract and blood vessels, and there is also the possibility of developing hypomotor dyskinesia and hypotension of the sphincter apparatus of the gastrointestinal tract.
The modern drug duspatalin (mebeverine), belonging to the group of myotropic antispasmodics, has a direct blocking effect on the fast sodium channels of the myocyte cell membrane, which disrupts the influx of Na+ into the cell, slows down the depolarization processes and blocks the entry of Ca2+ into the cell through slow channels, preventing the development of muscle spasm and pain syndrome. Duspataline has no effect on muscarinic receptors, which means that there are no side effects such as dry mouth, blurred vision, tachycardia, urinary retention, constipation, and weakness. The drug has a prolonged action; it is prescribed no more than 2 times a day in the form of 200 mg capsules for 2-4 weeks. By increasing the flow of bile into the small intestine, myotropic antispasmodics help improve digestion processes and activate intestinal motility, which leads to normalization of stool. Myotropic antispasmodics include selective blockers of calcium channels of smooth muscles: minavirin bromide (dicetel), it is prescribed 50-100 mg 3 times a day; spasmolin (otilonium bromide).
Odeston (7-hydroxy-4-methylcoumarin) is a myotropic antispasmodic with a choleretic effect. The drug enhances the formation and separation of bile, has a selective antispasmodic effect on the sphincter of Oddi and the sphincter of the gallbladder, which promotes good outflow of bile from the liver and biliary tract. Odeston has an indirect choleretic effect by facilitating the passage of bile into the gastrointestinal tract, which enhances the recirculation of bile acids. The advantage of the drug is the absence of adverse effects on the smooth muscles of the vascular walls and intestinal muscles; it does not increase pressure in the bile ducts and also does not impair the secretory function of the digestive glands and the absorption of nutrients. Thus, odeston helps improve digestion and peristalsis, normalize stool, eliminate constipation, and has a positive effect in cases of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction, dyskinesia of the gastrointestinal tract, chronic cholecystitis (including uncomplicated calculous), as well as in cases of disruption of the digestive processes caused by a deficiency of bile in the intestine. The daily dose of odeston is 600 mg (1 tablet 3 times a day). The duration of treatment is individual (from 1 to 3 weeks).
For biliary dyskinesia, herbal remedies such as arnica (flowers, tincture), valerian (rhizomes with roots), elecampane (rhizomes with roots), St. John's wort (herb), lemon balm (herb), peppermint (leaves), calendula are used (flowers), marshweed (herb), sage (leaves), convaflavin, olimetin, holagol, calamus, immortelle budra, capitol, snake knotweed, gorse, oregano, St. John's wort, centaury strawberry, calendula, willowherb, horseweed, hoofed grass, nettle , oregano, corn silk, cinquefoil erecta, flax, juniper, mint, dandelion, shepherd's purse, plantain, tansy, wormwood, kidney tea, wheatgrass, strap, rose, chamomile, knotweed, thuja, dill, fennel, hops, chicory, thyme, blueberry, celandine, sage, rosehip
In case of bladder dysfunction caused by increased tone of the sphincters of the biliary system, the intake of medications that have a choleretic and hydrocholeretic effect (bile acids, enzyme preparations, infusions and decoctions of choleretic herbs, synthetic choleretic drugs, gastric juice, etc.) is limited.
In order to stimulate bile secretion, reduce the tone of the common bile duct, which increases the flow of bile into the duodenum, cholekinetics are used - drugs that cause the production of cholecytokinin, which controls the kinetics of the gallbladder and sphincter of Oddi. The effect is due to the irritating effect of drugs of this group on the receptor apparatus of the duodenal mucosa.
In order to stimulate the formation and outflow of bile, as well as an antispasmodic effect, tea is used, which includes the following plants: spinach leaves (Folia Spinaciae), thistle fruits (Fructus Cardui Mariae), cinquefoil herb (Herba Anserinae), celandine herb (Herba Cheh' dorm), yarrow herb (Herba Millefolii), licorice root (Radix Liqumtae), rhubarb rhizome (Rhizoma Rhei), dandelion root and herb (Radix Taraxaci p. Herba), turmeric rhizome, turmeric oil (Rhizoma Curcumae, Oleum Curcumae) , aloe extract (Extractum Aloes).
A number of medicinal plants have a cholekinetic effect: (berberine sulfate), extracts from medicinal plant materials (calamus, rhizomes), barberry (tincture of leaves), sandy immortelle (flowers), lingonberry (leaves, shoots), blue cornflower (flowers), watch trifoliate (leaves), knotweed (herb), oregano (herb), calendula (flowers), coriander (fruit), juniper (fruit), dandelion (roots), shepherd's purse (herb), rhubarb (root), chamomile (flowers ), common thyme (herb), caraway (fruit), yarrow (herb), rose hips (fruit, cholosas), fennel (fruit).
The approximate treatment regimen for hypermotor dyskinesia of the gallbladder is the use of antispasmodics for rapid relief of pain (phosphodiesterase inhibitors - noshpa, papaverine) or anticholinergics (atropine, platyphylline) in combination with hepabene to reduce the tone of the sphincter of Oddi.
Treatment of hypotonic type of gastric dyskinesia. In the treatment of gallbladder dysfunction of the hypotonic type, it is advisable to expand the motor regimen.
These individuals tolerate weak broths, fish soup, cream, and sour cream well. Food with sufficient vegetable fat content (up to 80 g/day) and eggs are used. For 2-3 weeks, vegetable oil is prescribed, 1 tsp. 2-3 times a day 30 minutes before meals. To prevent constipation, raw vegetables are recommended: carrots, pumpkin, zucchini, greens. Bran has a pronounced effect on the motility of the biliary tract (1 tablespoon is brewed with boiling water and added as a gruel to various side dishes).
Prokinetics indicated: cisapride 5-10 mg 3 times a day; domperidone 5-10 mg 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals; metoclopramide 5-10 mg per day.
Drugs from the choleretic group, as well as bile acid drugs, have a good effect.
Drugs containing bile acids include the following:
- Lyobil (lyophilized bovine bile), tablets 0.2 g, 1-2 tablets. 3 times a day after meals. Course 1-2 months.
- Decholin (sodium salt of dehydrocholic acid), ampoules of 5 ml of 5% and 20% solution, administered intravenously 5-10 ml once a day.
- Cholecin (a compound of a salt of deoxycholic acid and a sodium salt of higher fatty acids) is prescribed in 1-2 tablets. 3 times a day before meals.
- Hologon (dehydrocholic acid), tablets 0.2 g, 0.2-0.25 g once a day. The course of treatment is 2-3 weeks.
Preparations of plant origin and medicinal plants that have a choleretic effect have a good effect on the function of the gallbladder: aqueous extracts from medicinal plant raw materials calamus (rhizome), barberry (leaf, root), birch (buds, leaves), immortelle sandy (flowers), barberry multi-veined (herb), knotweed (herb), goldenweed (herb), coriander (fruit), corn (columns with stigmas), burdock (roots), tansy (flowers), wormwood (herb), rowan (fruit ), hops (cones), chicory (herb), choleretic herbs No. 1 and 2, combined herbal remedies (holagogum, cholagol, holaflux, hepatofalplanta, hepabene, kurepar, flamin, fumetere, etc.).
In the presence of hypomotor dysfunction of the gallbladder against the background of increased tone of the sphincters of the extrahepatic bile ducts, Odeston 200 mg 3-4 times a day is added to drugs that enhance the contractile function of the gallbladder.
Effective in the treatment of hypomotor dyskinesia of the gallbladder with normal motor function of the gastrointestinal tract is the combined use of prokinetic drugs (metoclopromide, or domperidone, or 5-10% solution of magnesium sulfate, 1 tablespoon 2-4 times a day for 10-15 minutes before meals) with choleretic drugs containing bile acids or herbal products (allochol, cholenzyme, hepabene). Long-lasting biliary sludge during or after this therapy is an indication for the use of UDCA drugs for up to 3-6 months.
To correct hypomotor dyskinesia of the gallbladder in case of its combination with gastrointestinal tract and/or duodenostasis, a 2-week (if indicated and longer) treatment regimen is used, including prokinetics; choleretic preparations of plant origin or containing bile acids; antibacterial drugs in the presence of symptoms of bacterial contamination of the small intestine.
In the case of hypomotor dyskinesia of the gallbladder and colon, 24-week therapy is recommended, which includes prokinetics and choleretic drugs containing bile acids.
When hypofunction of the gallbladder is combined with intestinal hypermotility and dysbiosis, treatment with hepabene in combination with hilacomfort is indicated. In addition to these medications, intestinal adsorbents such as smecta, phosphalugel, etc. can be prescribed.
It is very effective to use probeless tubes with a decoction of rosehip, corn silk, warm mineral water, 10-25% solution of magnesium sulfate (1-2 tablespoons 2 times a day) or 10% solution of sorbitol or xylitol (50 ml 2 times in a day).
Method of “blind” probing according to Demyanovich
“Blind” probing is prescribed 23 times a week for 1 month. Probing is carried out as follows:
- In the morning on an empty stomach, the patient is given to drink 15-20 ml of a 33% solution of magnesia sulfate, heated to 40-50 ° C (instead of magnesia sulfate, you can use 1-2 egg yolks, warm olive or corn oil; 10% solutions of sorbitol, xylitol; warm mineral water type Essentuki-17; a glass of beet juice).
- It is necessary to place the patient on the right side on a cushion with a heat pad or paraffin application on the right side.
- During the procedure, take deep breaths (to open the sphinter of Oddi) - 23 breaths every 5 minutes.
Patients with biliary tract dysfunction are advised to use acupuncture and rational psychotherapy, which improves the psycho-emotional state, reduces the intensity of autonomic reactions and pain. It is important for the doctor to contact the patient, explain the causes of the disease and possible ways to eliminate it. Trust in the doctor largely determines the success of treatment.
Pharmacological correction of psychoneurological disorders is carried out with antidepressants. For this purpose, tricyclic antidepressants are used: amitriptyline, drugs with a serotonin reuptake mechanism (fevarin, Framex, etc.).
For vegetative-vascular dystonia and neurotic-neurosis-like syndrome, “minor” tranquilizers (Elenium, Tazepam, etc.) and sedatives are recommended: tincture of valerian, motherwort, 40 drops. 3-4 times a day or an infusion of these plants (10 g per 200 ml) 1 tbsp. l. 4 times a day.
Physiotherapeutic procedures are used in the treatment of gallbladder dysfunction:
- To improve microcirculation and trophic processes in patients with hypertensive dyskinesia, inductothermy is indicated.
- For hypotension, diadynamic currents and faradization of the gallbladder are prescribed.
- UHF has anti-inflammatory and bactericidal effects.
- Microwave therapy improves blood flow, tissue trophism, enhances redox processes, has anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects, and relieves spasms of the biliary tract.
- Applications of paraffin and ozokerite improve blood flow and tissue trophism, have a resolving effect and the ability to cause an antispasmodic effect in hypertensive biliary dyskinesia.
- For hypertensive dyskinesias, electrophoresis of a 5% novocaine solution and a 10% magnesium sulfate solution is indicated.
- Baths (pine, pearl) are prescribed every other day, for a course of 10-12 baths.
- Showers (rain, fan, circular) are recommended for 35 minutes, 10-15 procedures per course.
- Massage of the cervical collar area No. 10. Galvanic collar on the collar area.
- Electrophoresis of calcium chloride, bromine solution on the collar area, for a course of 7-10 procedures. Electrophoresis of 5% novocaine solution, 0.1% papaverine solution, 5% magnesium sulfate on the area of the right hypochondrium, for a course of 7-10 procedures.
Forecast:
The prognosis for dyskinesia is favorable. Working capacity has been preserved.
Hypotony of the uterus
With this pathology, the contractility of the uterus is impaired. Hypotony of the uterus in women during pregnancy is not as fraught as during childbirth. Factors contributing to the development of uterine hypotension:
- malformations of its development;
- neoplasia;
- scars (for example, after surgery);
- multiple births or polyhydramnios;
- numerous births.
Hypotony of the uterus is manifested by weakened labor.
Treatment is carried out with drugs that increase uterine tone - these are Oxytocin, Methylergometrine, Dinoprostone.
Treatment methods
Therapy is expected to be comprehensive - diet and medication, and in difficult cases surgery is indicated.
Conservative therapy
Patients are prescribed table No. 5 according to Pevzner. Fried, fatty, alcohol, carbonated drinks and foods that cause gas formation are excluded from the diet. The main goal of this diet is to reduce the load on the biliary system and prevent a sharp outflow of bile. If there is no severe pain, you can eat as usual, but without harmful foods. Food should be varied and nutritious. You need to eat 4-6 times a day in small portions. The diet should be combined with taking B vitamins, as well as E, K, A, C.
- Choleretic drugs.
- Broad spectrum antibiotics.
- Antispasmodics.
- Quitting smoking and active lifestyle.
Surgery
The operation is carried out when there is some kind of obstruction that needs to be removed. It could be a cyst, tumor, scar. Different methods are used for different diseases:
- Praderi drainage - is carried out when forming an artificial connection between the small intestine and the bile duct so that there is no narrowing of the operated area. Also performed after removal of the gallbladder to maintain normal pressure in the common bile duct.
- Stenting - when the duct narrows, an expanding stent is installed into it - a thin tube made of metal or plastic. The stent restores patency.
- Endoscopic papillosphincterotomy is a gentle operation to remove stones from the ducts using a special probe.