Hypotension, or, as this phenomenon is also called, arterial hypotension, is a condition of the human body in which blood pressure is reduced compared to normal levels. The norm is the ratio of systolic (upper) and diastolic (lower) pressure 120/80 mmHg. Art. (small deviations are acceptable). Hypotension is characterized by a decrease in blood pressure below 90/60 mmHg. Art. It is necessary to treat hypotension when it adversely affects the general condition of the human body.
There are several types of physiological lowering of blood pressure:
- hypotension as an individual variant of the norm, not accompanied by any unpleasant symptoms;
- compensatory adaptive hypotension (develops in people living in high mountain areas);
- orthostatic hypotension (due to sudden movement of the body from a horizontal to a vertical position, due to active physical exercise);
- postprandial hypotension (a decrease in blood pressure after eating).
Causes of hypotension
Depending on the causes of this condition, the following forms of hypotension are distinguished.
Primary. This is a special form of neurosis-like disease of the vasomotor centers of the brain. The main causes of primary hypotension: severe stress, prolonged emotional stress.
Secondary. It is often a concomitant pathology with certain diseases of the thyroid gland, hepatitis, anemia, tumor diseases, gastric ulcers, tuberculosis, rheumatism, cirrhosis of the liver, brain injuries, when taking a number of medications, etc.
Often, hypotension is a sign of vegetative-vascular dystonia (VSD), a condition of the body that is characterized by disruption of the autonomic nervous system, which regulates the functioning of organs. This can lead to disruption of the regulation of the cardiovascular system of the nervous and endocrine systems, and, accordingly, to disruption of heart rate, thermoregulation, decreased vascular tone, etc. VSD develops due to hormonal imbalances, neuroses, severe stress and psychological trauma, exposure harmful occupational factors, alcohol abuse.
Hypotension can also develop in healthy people, for example, in athletes with regular physical activity. In this case, low blood pressure acts as a kind of protective reaction of the body. A sharp change in climatic or weather conditions, increased humidity, the action of electromagnetic fields, radiation, etc. can also lead to a decrease in pressure.
Symptoms of low blood pressure
In addition to feeling unwell, hypotension brings with it more significant problems:
- Reduced pressure leads to insufficient blood supply to all organs and oxygen starvation of the brain, which is more sensitive to lack of oxygen.
- The result is weakness, lethargy and fatigue.
- Signs of low blood pressure also include dizziness, often motion sickness in transport, daytime drowsiness and disrupted night sleep, which only intensifies fatigue and weakness.
- One of the most unpleasant symptoms of hypotension is orthostatic hypotension. When standing up suddenly and changing body position, dizziness becomes stronger.
There are primary and secondary hypotension.
| Primary arterial hypotension | This is an independent disease in which hereditary predisposition and constitutional characteristics play an important role (usually young women of asthenic physique - slender, tall, emotional). |
| Secondary hypotension | It develops against the background of other diseases, such as hepatitis, peptic ulcers, anemia, allergic reactions, in case of poisoning, as a result of the side effects of certain drugs. In this case, hypotension is not considered as a disease, but as a symptom that goes away after the cause is eliminated. |
Symptoms of hypotension
The main symptom of hypotension is a decrease in blood pressure to 90/60 mm Hg. Art. or lower. Each person can measure their blood pressure independently at home using a tonometer. In addition, signs indicating arterial hypotension include the following:
- feeling of general weakness, lethargy, drowsiness;
- increased sweating;
- disturbances in heat exchange processes (cold extremities);
- increased heart rate;
- sleep disorders;
- emotional instability (periods of irritability, apathy);
- dizziness and headache (mostly dull in the frontal and temporal regions);
- aching pain in the heart;
- dyspnea.
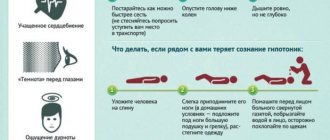
Sometimes hypotension can manifest itself as fainting, especially in rooms where there is little fresh air. In general, people with low blood pressure react negatively to changes in air temperature, changes in air humidity, as well as to various emotional stimuli. Isolated cases of these symptoms may not indicate the presence of hypotension, but if there are several symptoms and they are constant, then you should consult a doctor.
conclusions
Arterial hypotension is a rather dangerous condition that causes hypoxia of brain and heart tissue. It develops both as a result of individual congenital characteristics or lifestyle, and due to specific pathologies. Despite the fact that the condition is mostly reversible, the situation requires close attention due to possible complications.
Timely assistance with low blood pressure has a huge impact on the patient’s future prognosis. Therefore, if you have hypotension in your family, it is extremely important to know the rules of action in such cases.
Consequences and complications of hypotension
Often, rare cases of hypotension, manifested by weakness, lethargy, nausea and other nothing more than unpleasant symptoms, are not accompanied by fatal consequences for the body. They only cause discomfort and reduce performance. However, a constant or systematic decrease in pressure can negatively affect the functioning of the heart, so treatment of hypotension is required.
Cardiac manifestations . People with hypotension have an increased risk of serious cardiovascular problems. A fast pulse means the heart is working hard. This is a kind of compensatory mechanism in order to provide tissues with oxygen, which is lacking due to the slow movement of blood through vessels with low tone. However, a rapid pulse is a serious burden on the heart.
Hypotension and pregnancy . Hypotension during pregnancy is a reason to go to an emergency appointment with a doctor. If the expectant mother systematically experiences low blood pressure, this can lead to oxygen starvation of the fetus due to poor oxygen supply to the placenta. This, in turn, threatens disruptions in the development of the unborn baby. It has been established that pregnant women with low blood pressure experience toxicosis and gestosis more often and more severely. Changes in blood pressure during pregnancy are often difficult to detect: fatigue, weakness, nausea and other signs of hypotension are often confused with characteristic symptoms of pregnancy caused by hormonal imbalance.
It is important to say that a sharp and sudden decrease in pressure with a deterioration in health may indicate intense internal bleeding, a heart attack and other internal problems that pose a threat to human life. In such cases, you should immediately consult a doctor (call an ambulance).
Content:
- What is hypotension?
- Low blood pressure - causes
- Low blood pressure - symptoms?
Arterial pressure
– the main indicator of hemodynamics, which determines the speed and volume of blood flow in all tissues. The condition refers to polyetiological pathological processes. This means that it develops due to the influence of several causes. Clinical symptoms include manifestations of hemodynamic disturbances with oxygen starvation of tissues.
Diagnosis of hypotension
To diagnose hypotension, the therapist performs a number of actions:
- carefully collects complaints, analyzes the description of each of the symptoms of hypotension;
- finds out whether there is a hereditary predisposition, negative factors, etc.
- examines the patient and listens to the heart and lungs;
- performs thorough three-time pressure measurements, and, if necessary, establishes pressure monitoring for a week or more, daily pressure monitoring;
- gives a referral to a cardiologist, neurologist or endocrinologist;
- analyzes the conclusion on the composition of blood and urine, which includes a general and biochemical analysis, a blood test for glucose levels, protein spectrum, ion composition;
- determines the level of catecholamines and endocrine profile in urine and blood;
- refers for ultrasound of the heart, Doppler, electrocardiography;
- performs load tests.
In some cases, additional studies are performed before treatment: CT or MRI of the head, ultrasound of the kidneys, adrenal glands, and thyroid gland.
Treatment of hypotension
If hypotension is a sign of another disease, treat it. In case of primary hypotension not associated with other diseases, comprehensive non-drug and medicinal measures are carried out to prevent secondary changes in organs and systems associated with chronic lack of oxygen.
General recommendations. Patients are advised to follow a strict daily regimen, including adequate sleep, a reasonable ratio of work and rest, good nutrition, dosed physical activity, walking for at least 2 hours a day, regular airing of rooms, humidification of the air, giving up bad habits, sudden changes in body position, hardening and etc.
Medication correction. To normalize vascular tone, heart rate, and neutralize the effects of negative environmental factors, the following groups of drugs are prescribed: adaptogens, psychomotor stimulants, analeptic drugs, adrenomimetics (for emergency care in case of a sharp drop in pressure), anticholinergics (for vagotonia), nootropics, complexes of vitamins and minerals and etc.
Phytotherapy. Drug treatment of hypotension can be accompanied by taking general tonic adaptogen drugs, stimulants (in particular, coffee and tea), baths with plant decoctions, consumption of herbal infusions, etc.
Physiotherapy. Hypotension therapy is often supplemented with physiotherapeutic methods such as electrophoresis with novocaine, potassium iodide endonasally or orbital-occipital technique, electric sleep and ultraviolet irradiation of the skin, microwave therapy on the adrenal gland area, hot chest wraps, massage, oxygen baths, douches and rubdowns, etc.
Diet for arterial hypotension
During the treatment of arterial hypotension, it is important to follow simple nutritional rules:
- The patient's daily diet should contain sufficient amounts of B vitamins, vitamin C and proteins. Vitamin B3 is especially important (egg yolk, carrots, yeast, liver, milk, green parts of plants, etc.).
- Eat 5-6 times a day in small portions.
- The amount of salt is not limited. If there are no diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, you can eat spicy foods.
- There are beans, nuts, meat, cereal grains, vegetables (especially potatoes).
- Drink coffee, tea, clean water without gas.
If you have hypotension, you should not go hungry or lack sleep. If you feel worse, you can eat candy and drink a glass of sweet tea.
Prevention of hypotension
In order to prevent the development of hypotension, it is recommended to follow the following rules of prevention and a healthy lifestyle:
- eat well;
- strictly adhere to the daily routine, sleep at least 8 hours a day;
- be physically active in order to constantly keep blood vessels in good shape (running, swimming, walking in the fresh air);
- give up bad habits, control body weight;
- Monitor your blood pressure and visit your doctor regularly.
If you require diagnosis or treatment of hypotension, contact the ABC-Medicine clinic. If you have any questions or make an appointment, you can call +7 (495) 223?38?83.
Diastolic pressure - what is it?
When measuring pressure, the tonometer shows 2 values, their correct interpretation is not familiar to every person:
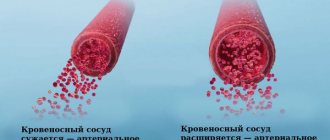
- The upper numbers, cardiac pressure, mean the force with which the left ventricle of the heart pumps blood into the arterial bed. Blood passes through all vessels, the walls expand, resisting the incoming fluid.
- The lower number characterizes the intensity of blood movement at the moment of relaxation of the heart muscle - the stronger the walls of blood vessels contract, the higher these data are. This is diastolic pressure.
The kidneys, which produce a special hormone - renin, are responsible for the resistance of blood vessels in the body. Therefore, diastolic indicators are also called renal pressure.
If vascular permeability is normal, then the tonometer will show optimal values. As the resistance increases, the lower values also increase, and as the resistance decreases, the diastolic numbers drop below acceptable values.
To determine the state of health, pulse pressure is also important, which is the difference between cardiac and renal parameters. Normally it should be within 40 units.
If diastolic readings deviate from the norm, the first thing you should do is check your kidney function.