Shortness of breath (dyspnea) is a painful feeling of lack of air, in extreme terms taking the form of suffocation.
If shortness of breath occurs in a healthy person against the background of physical activity or severe psycho-emotional stress, it is considered physiological. Its cause is the body's increased need for oxygen. In other cases, shortness of breath is caused by some disease and is called pathological.
According to the difficulty of the inhalation or exhalation phase, shortness of breath is distinguished as inspiratory and expiratory, respectively. A variant of mixed shortness of breath with limitation of both phases is also possible.
There are several types of shortness of breath. Dyspnea is considered subjective if the patient feels difficulty breathing, dissatisfaction with inhalation, but this cannot be measured and there are no factors for its occurrence. Most often it is a symptom of hysteria, neurosis, and thoracic radiculitis. Objective shortness of breath is characterized by a violation of the frequency, depth of breathing, duration of inhalation or exhalation, as well as increased work of the respiratory muscles.
general characteristics
Dyspnea is perceived by patients as a subjective feeling of lack of air, ineffectiveness of breathing movements, and tightness in the chest.
The symptom is accompanied by characteristic objective signs: increased or slower inhalations and exhalations, pallor or cyanosis of the nasolabial triangle, convulsive loud inhalation, suffocation. Often, to alleviate the condition, a person with dyspnea stops moving, takes a forced position - sits on a chair or bed, leans forward a little, leaning on straight arms. Most often, the appearance of shortness of breath is associated with physical exertion, and at the beginning of the disease the disorder is provoked only by significant activity, and as it progresses, patients feel a lack of air after normal activities. In addition to respiratory disorders, pathological symptoms are possible: pain and discomfort in the chest, headache, dizziness, decreased performance. If shortness of breath is observed when performing usual work or at rest, you should consult a specialist.
How to understand that you need a doctor's help
It is not always possible to independently determine the causes of shortness of breath during exercise or at rest. A pulmonologist will help with this; you should make an appointment with him if you experience shortness of breath and have trouble breathing . In case of an acute sudden attack with a significant deterioration in well-being, the patient needs emergency help. If you are concerned about shortness of breath and lack of air without exercise , then you need to visit a doctor as planned.
At your appointment, the pulmonologist will ask a number of questions, the answers to which will allow you to determine the exact cause of shortness of breath when walking , exercising, or at rest. List of main questions:
- how long has the symptom bothered you?
- severe shortness of breath occurs when walking and running or bothers you even when resting;
- which is more difficult - inhalation or exhalation;
- will the condition stabilize if you lie down;
- Are there any accompanying symptoms?
Development mechanism
Shortness of breath is caused by a variety of complex reflex mechanisms involving higher nervous structures, so there are several theories of its development. Many doctors cite changes in oxygen and carbon dioxide levels in the blood as the immediate cause of impaired breathing frequency and quality. An increase in the concentration of carbon dioxide, leading to a decrease in pH, has a significant stimulating effect on the bulbar centers, peripheral chemoreceptor zones of the arteries and central receptors located in the medulla oblongata.
At the same time, protective mechanisms are activated, the respiratory center of the brain stem sends activating impulses to the bronchopulmonary system, causing a pathological increase in breathing. The appearance of shortness of breath is associated with impulses from the fusiform nerve endings of the respiratory tract, which are activated as a result of various pathological processes. Sometimes increased work of the respiratory center is observed during descending cortical influences caused by hysterical or neurotic conditions.
The connection of the symptom with the temperature of the internal environment of the body has been proven. With hyperthermia, the sensitive areas of the respiratory center are washed with warmer blood, which causes their activation - so-called thermal shortness of breath occurs. A decrease in body temperature, on the contrary, leads to a decrease in respiratory movements. The development of dyspnea is influenced by the amount of muscle load and metabolic level. Most researchers believe that this mechanism is due to two types of reactions - slow humoral and fast neurogenic.
Subjective sensations in the form of lack of air and suffocation are primarily associated with the spread of excessive excitation from the centers of the medulla oblongata to the limbic structures and the cerebral cortex. This causes the appearance of negative emotional reactions of fear and anxiety in patients with shortness of breath. Sometimes unpleasant symptoms develop due to a discrepancy between the body's needs for ventilation and the functionality of the breathing apparatus to provide it.
First aid rules
If a person experiences expiratory shortness of breath that is caused by unknown causes, the first thing to do is call a medical team. Before the ambulance arrives, you can help ease the victim’s breathing. To do this, you need to open all the windows to allow fresh air into the room. If there are any objects on the patient’s body that obstruct breathing, they must be removed. You can additionally turn on the fan and direct it towards the person. It's good if you can use an oxygen mask.
Sometimes shortness of breath develops in people due to nervous tension and severe stress. In this case, you need to invite the person to sit down, drink water and calm down. The technique of counting to 10 with your eyes closed helps.
When shortness of breath occurs against the background of an allergic reaction, it is necessary to eliminate the patient’s contact with the allergen and offer him antihistamines.
You should not put the patient to bed; it is better to give his body a semi-sitting position. This way, blood will flow better from the lungs and heart, which will allow you to quickly relieve an attack of shortness of breath and suffocation.
Sometimes steaming your feet in a bowl of hot water can help you cope with shortness of breath. This measure is especially effective for patients with cardiac asthma.
If there is a humidifier in the room, you can turn it on. This will make the viscous mucus thinner and remove it from the lungs faster.
Classification
Dyspnea can manifest itself in many diseases and pathological conditions, so to facilitate the diagnostic search it is necessary to accurately determine its type. The classification of the symptom is based on the mechanism of development, the degree of change in respiratory function, and the ratio of the inhalation-exhalation phases. There are physiological shortness of breath, when the frequency of inhalations and exhalations changes in proportion to physical activity, and pathological. Most often the symptom is classified in relation to the respiratory phases:
- Inspiratory dyspnea
. This type of disorder is manifested primarily by difficulty in the inhalation phase. Dyspnea is detected in diseases of the diaphragm and pleura, heart failure, and pulmonary fibrosis. Dyspnea in combination with noisy breathing is typical for pathologies of the trachea and large bronchi. - Expiratory dyspnea
. The symptom is usually observed when the patency of small bronchi and bronchioles is impaired, typical of bronchial asthma. Shortness of breath on exhalation also occurs with chronic obstructive bronchitis, pneumosclerosis, and decreased elasticity of the lung tissue as a result of emphysema. - Mixed dyspnea
. Respiratory failure in both phases often develops in severe stages of heart failure and progressive diseases of the respiratory system. This type of dyspnea can be associated with feverish conditions, pathologies of the central nervous system with direct irritation of the respiratory center.
Taking into account changes in respiratory function, several types of shortness of breath are distinguished: tachypnea - an increase in the frequency of breaths more than 40 per minute, bradypnea - a decrease in respiratory movements less than 12 per minute, apnea - a sudden stop in breathing. There is a classification of the symptom according to the main mechanism of development: central dyspnea is observed with organic or functional changes in the functioning of the respiratory center in the medulla oblongata, the neurogenic version is associated with a weakening of inhibitory influences in the cerebral cortex, the hemic form develops with anemia.
Symptoms
Symptoms of shortness of breath can be very different, but they are always characterized by changes and disturbances in respiratory activity. A person can breathe very quickly and shallowly, or he can take rare and very deep breaths. In both situations, he experiences an acute lack of air, a feeling of suffocation and chest compression.
With inspiratory dyspnea, it is difficult for the patient to take a breath. At the same time, he hears noise while trying to draw oxygen into his lungs. In the case of expiratory dyspnea, it is difficult to exhale, as the lumens of the bronchioles and bronchi begin to narrow.
In medical practice, there are cases of mixed dyspnea, the condition of which is the most dangerous for the body. It can lead to complete respiratory arrest and death.
Are you experiencing symptoms of shortness of breath?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Causes of shortness of breath
Causes of lack of air
A subjective feeling of difficulty in inhaling can be observed in healthy people after intense physical exertion, and in pregnant women. Pathological causes of the symptom are various disorders in the functioning of the respiratory and other body systems. Lack of air is caused by:
- Lung diseases
: lobar and interstitial pneumonia, tuberculosis, sclerotic processes and primary amyloidosis. - Pleurisy
: dry, exudative, hemorrhagic. - Respiratory tract damage
: foreign bodies of the trachea, bronchi, thoracic injury, pulmonary hemorrhage. - Causes from the larynx
: false croup, laryngomalacia, neuropathic paresis. - Tumors
: pleural cancer, bronchioloalveolar cancer, invasive thyroid cancer. - Acute conditions
: cardiac asthma during heart attacks, heart defects, pulmonary embolism. - Neuroses
: panic attack, vegetative-vascular dystonia, cardioneurosis.
Causes of difficulty exhaling
Expiratory shortness of breath with convulsive short inhalation and prolonged exhalation is often a sign of various diseases of the bronchopulmonary system. The symptom is often accompanied by a feeling of tightness in the chest. Difficulty in exhalation manifests itself in the following pathological conditions:
- Bronchial asthma
: allergic, mixed, occupational. - Obstructive damage to the respiratory tract
: bronchitis and COPD, bronchiectasis, tracheal and bronchial stenosis. - Pulmonary pathology
: pneumosclerosis, emphysema, deficiency of the enzyme alpha1-antitrypsin. - Occupational diseases
: byssinosis, gasoline pneumonia. - Complications of pharmacotherapy
: taking NSAIDs (especially aspirin), infusions of blood or plasma with a high content of citrates. - Rare causes
: Williams-Campbell syndrome, Mendelssohn syndrome, tumors in the tracheal bifurcation area.
Treatment and diagnosis of dyspnea in Kaliningrad
If you are concerned about shortness of breath and are looking for a qualified pulmonologist in Kaliningrad, make an appointment at our pulmonology center. For you:
- only competent, caring specialists;
- a full range of procedures for diagnosing lung diseases;
- comprehensive care for pathologies of the respiratory system: treatment of COPD, treatment of asthma;
- rehabilitation after coronavirus infection;
- comfortable living conditions.
You can make an appointment at our pulmonology center by calling 8 (4012) 971-961.
Diagnostics
Patients with complaints of shortness of breath or difficulty in exhaling seek help from a pulmonologist or local physician. The diagnostic search involves conducting laboratory and instrumental studies of the respiratory system and functional tests. The most informative ways to clarify the cause of shortness of breath are:
- Assessment of external respiration
. Spirometry is a non-invasive and accessible method of research, during which the main parameters of the respiratory system are recorded - vital capacity of the lungs, forced expiratory volume in the first second. A bronchodilation test is indicated to differentiate between COPD and asthma. - X-ray examination
. Performing an X-ray of the chest organs in 2 projections allows us to detect typical pathological changes (diffuse sclerosis, emphysema, space-occupying formations), which usually cause shortness of breath. Further examination involves the use of computed tomography and MRI. - Laryngoscopy
. To identify narrowing of the lumen of the larynx and visualize foreign bodies, the mucous membranes are examined using a special laryngoscope. In the absence of signs of damage, laryngoscopy is complemented by tracheobronchoscopy for a detailed study of the structure of the bronchial tree with the collection of material for cytomorphological examination. - Electrocardiography.
An ECG is performed to exclude cardiac causes of shortness of breath. If the results are questionable, the cardiovascular system is examined in an expanded format: phonocardiography and cardiac ultrasound with Doppler ultrasound are prescribed. In case of possible periodic disturbances, Holter monitoring is used. - Lab tests
. Assessing blood oxygen saturation and carbon dioxide levels is necessary to determine the degree of respiratory distress. A general blood test may show signs of inflammatory processes (increased ESR, leukocytosis). A biochemical blood test is also recommended.
To identify the etiological factor of shortness of breath, allergy tests are performed; the results of an extended immunogram are informative. If suspicious formations are detected on radiographs, a transbronchial lung biopsy is performed. To diagnose rare congenital defects as a possible cause of dyspnea, specialized specialists are involved.
Inhaled bronchodilators are used to quickly relieve shortness of breath
Types of shortness of breath in a child
There are different types of shortness of breath, which are classified depending on the cause of its occurrence.
In general, doctors distinguish the following types of shortness of breath according to severity:
- light;
- average;
- heavy.
According to the mechanism of development, the following types of shortness of breath can be distinguished:
- inspiratory. In this case, it is very difficult for children to take breaths. As a rule, this type of shortness of breath occurs in various pathologies and inflammatory processes;
- expiratory. In this case, it is quite difficult for children to exhale. As a rule, this pathology occurs due to changes in the bronchi, some heart diseases that cause clinical shortness of breath;
- mixed. This type combines the previous two. It is very difficult for children to both inhale and exhale. Very often, this type of shortness of breath occurs in children who have suffered from infectious diseases.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
If an attack of shortness of breath suddenly begins, the patient must be calmed down, seated on a chair or bed so that the torso is in an elevated position. To make breathing easier, it is advisable to remove tight clothes, a belt, and unbutton your shirt collar. It is necessary to ensure the flow of fresh air into the room - open a window or door. The use of herbal sedatives is allowed. Frequent occurrence of breathing difficulties indicates the development of a disease or the progression of existing diseases. In such a situation, it is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Conservative therapy
The treatment regimen is selected individually, taking into account the cause of dyspnea. An important place in the treatment of chronic conditions accompanied by shortness of breath is occupied by lifestyle correction: quitting smoking, regularly performing a special set of physical exercises. In case of hypoxemia, oxygen therapy sessions are performed. Etiotropic, pathogenetic and symptomatic drug therapy with drugs from the following groups is indicated:
- Bronchodilators
. Short-acting beta-agonists in the form of inhalers are used to quickly relieve attacks of shortness of breath. Long-term β2-agonists, methylxanthines, are used as basic therapy. - Expectorants
. Medicines are effective for chronic bronchitis and COPD. They stimulate the discharge of sputum and improve the permeability of the bronchial tree. In some cases, expectorant drugs are combined with mucolytics. - Antibiotics.
Antimicrobial agents are prescribed for acute and chronic inflammatory damage to the respiratory tract caused by bacterial microflora. When choosing an antibacterial drug, the results of sputum culture are taken into account. - Cardiotonics
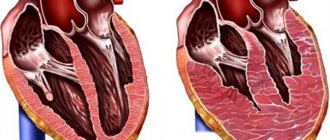
. To reduce shortness of breath in patients suffering from heart disease, cardiac glycosides are used. Pre- and afterload on the myocardium is reduced with the help of peripheral vasodilators and diuretics. - Corticosteroids
. In case of severe respiratory disorders, taking hormonal medications on an ongoing basis is indicated. In patients with bronchial asthma, inhaled forms of glucocorticoid hormones are effective. - Cytostatics
. Courses of chemotherapy with antitumor drugs are recommended for patients with malignant neoplasms of the lungs and bronchi. To enhance the effect, drug treatment is supplemented with radiation therapy.
Shortness of breath and lack of air in an adult: emergency assistance
Choking, sudden deterioration in health, dizziness combined with lack of air is a reason for an emergency visit to a doctor, but assistance must be provided before doctors arrive. If the suspected cause of shortness of breath during or without physical activity is oxygen deficiency, you need to ensure rest - find support or put the patient to bed. You will also need:
- remove tight clothes, free your neck and chest;
- ventilate the room;
- reassure the patient.
Why does shortness of breath occur when walking?
Severe shortness of breath and palpitations when walking in older people occurs with excessive physical exertion while walking up the stairs or long walks after a sedentary lifestyle. Rehabilitation specialists recommend that older people gradually increase physical activity and rest more often.
Severe shortness of breath when walking in older people occurs with increased emotional stress and excess weight. The cause of shortness of breath may be the following diseases:
- Anemia;
- Heart failure;
- Bronchial asthma;
- Cardiac ischemia;
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
With anemia, patients complain of dizziness, weakness, increased fatigue, shortness of breath, which increases when walking. Their nails and hair become brittle, cracks appear in the corners of their lips.
In patients suffering from chronic heart failure, the heart cannot fully perform its functions, and the blood does not deliver enough oxygen to the internal organs. A large amount of carbon dioxide accumulates in the body, which stimulates the respiratory center. For this reason, the frequency of respiratory movements and heart contractions increases, shortness of breath appears, which in older people increases when walking.
Bronchial asthma is a disease that rarely begins in old age. Patients experience expiratory shortness of breath, which makes it difficult to exhale. Attacks of suffocation lead to panic, which intensifies suffocation.
The cause of coronary heart disease is insufficient blood supply to the myocardium due to pathology of the coronary arteries. The disease is initially asymptomatic. Over time, angina attacks occur and shortness of breath appears. Older people may develop myocardial infarction.
A common cause of shortness of breath in older people is chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. It develops as a result of frequent respiratory diseases in smokers. Patients are first bothered by a constant cough, then shortness of breath develops, worsening when walking.
Shortness of breath can develop in older people suffering from thyrotoxicosis, diabetes, and obesity. In the first case, the patient's metabolism accelerates, the need for oxygen increases, the frequency of contractions of the heart muscle increases, and hypoxia (lack of oxygen) appears. In patients with diabetes, as the disease progresses, the blood vessels are affected, and oxygen starvation occurs in the body, which causes shortness of breath. Obesity makes it difficult for internal organs to function and leads to shortness of breath in older people. It gets worse when walking.
In patients with pulmonary vasculitis, the vessels suffer, the vessels that supply blood to the lungs suffer. Shortness of breath is one of the first symptoms of the disease, as inflammation interferes with the normal patency of the arteries, which causes oxygen starvation.