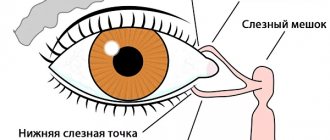
What is dysfunctional uterine bleeding?
- dysfunctional uterine bleeding of the juvenile period - between the ages of 12 and 18 years;
- dysfunctional uterine bleeding of reproductive age - develops in women 18-45 years old;
- dysfunctional uterine bleeding of the premenopausal (menopausal) period - occurs during menopause (45-55 years).
According to the criterion of the presence or absence of ovulation, dysfunctional bleeding is:
- ovulatory;
- anovulatory (80% of cases).
According to statistics, uterine bleeding is the most common pathology of the female reproductive system.
Causes of dysfunctional uterine bleeding
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding is a consequence of a violation of the hormonal regulation of ovarian function by the hypothalamic-pituitary system. Due to impaired secretion of luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones of the pituitary gland, which are responsible for follicle maturation and ovulation, disruptions in folliculogenesis and menstrual function are observed. In this case, the ovary can either ripen, but without ovulation, or not ripen, that is, the corpus luteum does not form in any case.
As a result of these pathological processes, the female body is in a state of hyperestrogenism - progesterone is not synthesized in the absence of the corpus luteum, and the uterus is exposed to estrogen. A disruption of the uterine cycle occurs when the endometrium grows greatly (hyperplasia), and then is rejected. Because of this, uterine bleeding becomes severe and prolonged. Dysfunctional uterine bleeding may stop on its own, but usually reappears after some time. Therefore, it is very important to exclude recurrence of the disease.
Causes of juvenile dysfunctional uterine bleeding
During puberty, dysfunctional bleeding occurs more often than other gynecological pathologies (in 20% of cases). Their reasons are:
- mental/physical trauma;
- avitaminosis;
- overwork;
- dysfunction of the thyroid gland/adrenal cortex;
- childhood infections (measles, chicken pox, rubella, whooping cough);
- Acute respiratory infections, chronic tonsillitis.
Causes of dysfunctional uterine bleeding during reproductive age
In women of reproductive age, the disease occurs less frequently - in 5% of cases. Its development is led by:
- climate change;
- intoxication poisoning;
- infectious diseases;
- harmful working conditions;
- abortions;
- medications that cause disorders at the level of the hypothalamic-pituitary system.
Causes of dysfunctional uterine bleeding in the premenopausal period
During menopause, dysfunctional uterine bleeding occurs in 15% of cases from other gynecological pathologies. Gynecologists explain their occurrence by the fact that with age, the pituitary gland produces fewer gonadotropins and does so irregularly. This, in turn, causes disturbances in the egg cycle (formation of the corpus luteum, ovulation, folliculogenesis). Due to a lack of progesterone, the endometrium begins to grow. Its rejection leads to severe uterine bleeding.
Popular questions
I am 47 years old, I have multiple uterine fibroids, two fibroids, a large and a medium one (76 mm and 40 mm) had blood flow along the periphery, yesterday I had an ultrasound on the same machine and by the same doctor, it turned out that the large fibroid has not changed in size, but there is no blood flow, can this be the case, until yesterday I had an ultrasound scan there 2 times, once every six months, and the blood flow was IR 0.5 and IR 0.55 in the periphery, what is the risk of this, could there be necrosis due to malnutrition?
and can it shrink in size without blood flow? A decrease in blood circulation in the nodes of uterine fibroids indicates the process of completing the growth of the formation. This requires ultrasound control after 3 months. In the absence of pain, fever, or ultrasound changes in the node described as necrosis, it is not possible to assume this process.
I am 31 years old and have fibroids. Buserelin spray was prescribed for 2 months. If side effects occur, tell me if there are any medications. I’m very afraid because according to reviews it’s a very scary drug. And approximately how long does it take for side effects to appear?
You should follow the recommendations of your doctor. When using this drug, drug-induced menopause occurs. This may be accompanied by vegetative manifestations - fever, hot flashes, mood swings, sleep disturbance and genitourinary syndrome - dryness in the genital tract. The use of Climafemin Ginocomfort will help improve your well-being, and the Ginocomfort gel with mallow extract will cope with dryness.
Good day. We discovered a 45mm fibroid (submucous), and there is bleeding after menstruation. It's been 2 weeks already. The doctor talks about the operation. I'm waiting for the commission. What operation is done in this case? They scared me that it was possible to remove the uterus. I'm 38 and still want to give birth.
Hello! You should tell your doctor about your reproductive plans. This will resolve the issue in favor of organ-sparing surgery - conservative myomectomy. Method - hysteroscopic or strip surgery is decided collectively, taking into account technical capabilities, medical practice, type of submucosal node, its location, etc.
Good afternoon, I am 31 years old, I have fibroids. Buserelin spray was prescribed for 2 months. If side effects occur, tell me if there are any medications. I'm very afraid, because... According to reviews, it is a very terrible drug. And approximately how long does it take for side effects to appear?
Hello!
You should follow the recommendations of your doctor. When using this drug, drug-induced menopause occurs. This may be accompanied by vegetative manifestations - fever, hot flashes, mood swings, sleep disturbance and genitourinary syndrome - dryness in the genital tract. The use of climafemin Ginocomfort will help improve your well-being, and the Ginocomfort gel with mallow extract will cope with dryness. For an accurate diagnosis, contact a specialist
Symptoms of dysfunctional uterine bleeding
In young girls and women of childbearing age, dysfunctional uterine bleeding has the following symptoms:
- Bloody discharge from the genital tract appears outside of menstruation. Their color can range from red to dark burgundy. May be abundant and contain clots.
- Before bleeding, menstruation may be delayed for several weeks (up to one month).
- The duration of menstruation increases by 3-4 days, the discharge during the “extra period” is spotting.
- The menstrual cycle is not regular.
- A woman complains of increased fatigue, dizziness, and pale skin.
During premenopause, dysfunctional uterine bleeding manifests itself:
- irregular, prolonged bleeding that occurs after menstruation (menometrorrhagia);
- regular uterine bleeding with an interval of up to 21 days (polymenorrhea);
- frequent, long and heavy menstruation (hypermenorrhea);
- intermenstrual bleeding (metrorrhagia).
If you notice similar symptoms, consult a doctor immediately. It is easier to prevent a disease than to deal with the consequences.
What can you do at home?
If the problem has not resolved itself within three hours, then the following tips will help you:
- Apply a cold compress to your cheek. You can use a cold product or ice previously wrapped in cloth.
- Roll up sterile gauze, apply to the hole and bite for 10-15 minutes.
- Make strong tea. Soak a piece of bandage in liquid and apply to the damaged mucous membrane for 3-5 minutes.
- If you experience high blood pressure, you need to normalize it with medication. The specific drug and dosage are prescribed by the doctor.
Diagnosis of dysfunctional uterine bleeding
In addition to listening to the patient’s complaints, gynecological examination and ultrasound diagnosis of the pelvic organs, recognizing dysfunctional uterine bleeding involves the use of additional research methods. So, if we are talking about examining girls of juvenile age, the following is carried out:
- taking a blood test for hormones and coagulation;
- hysteroscopy.
Diagnosis of dysfunctional uterine bleeding in reproductive age includes:
- exclusion of organic pathologies of the genitals (spontaneous abortion, endometriosis, tumor neoplasm, ectopic pregnancy, etc.);
- hysteroscopy;
- curettage of the endometrium for histological examination of the material.
When diagnosing dysfunctional bleeding in women of menopausal age, gynecologists determine whether bloody discharge from the genital tract is another menstruation (since menstruation can sometimes begin at this age). Additionally, hysteroscopy and diagnostic curettage are performed. If there is a suspicion of a tumor, the doctor prescribes a computer or nuclear magnetic tomography to the patient.
How to stop dysfunctional uterine bleeding - treatment of pathology
Treatment of dysfunctional uterine bleeding consists of hemostatic measures. In this case, both conservative and surgical methods can be used. The choice of method to stop uterine bleeding in women of juvenile and reproductive age depends on the amount of blood loss:
1. If the hemoglobin level is above 100 g/l (moderate anemia), symptomatic treatment is used. It includes the use of the following drugs:
- Dicynone;
- Vikasol;
- Ascorutin;
- Aminocaproic acid;
- Oxytocin.
If the tablets are ineffective, hormonal drugs containing progesterone are selected. It can be:
- Non-ovlon;
- Marvelon;
- Mercilon;
- Rigevidon.
As a result of their use, dysfunctional uterine bleeding stops after 5-6 days.
2. If the hemoglobin level is less than 70 g/l (severe anemia), hysteroscopy with separate diagnostic curettage and pathomorphological examination of the scraping are performed. Afterwards hormones are prescribed.
Iron supplements, vitamins B12, B6, C, P, and folic acid also help normalize the condition of a woman suffering from bleeding. In some cases, the question arises about transfusion of fresh frozen plasma and red blood cells.
To exclude the re-development of uterine bleeding, it is recommended to take low doses of Norkolut, Novinet, Silesta, Logest, Duphaston.
Treatment of the disease in menopausal women is aimed at suppressing menstrual and hormonal functions. In this case, a surgical method is used - hysteroscopy and therapeutic and diagnostic curettage. Conservative homeostasis in such a situation is not capable of normalizing a woman’s condition. In especially severe cases, gynecologists perform cryodestruction of the endometrium or supravaginal amputation of the uterus.
Treatment of dysfunctional uterine bleeding with folk remedies
Of the folk recipes to stop dysfunctional uterine bleeding, women can resort to:
- Nettle decoction. 1 tbsp. dry leaves pour a glass of boiling water. Cook for 10 minutes over low heat. Strain. Take 1 tbsp. 5 times a day
- Orange decoction. Pour the peels of 6 oranges into 1.5 liters of water. Cook over low heat until most of the water has evaporated. Take 2 tbsp. 3-4 times a day.
- Infusion of cucumber lashes. Cut off the vines remaining after harvesting, chop them finely, and wash them. Pour 100 grams of greens into 2 glasses of water and boil. Drink 1/2 glass 3 times a day.
Any traditional recipe must be previously agreed with your doctor.
First aid for nosebleeds
According to statistics, every 50th person on the planet faces the problem of nosebleeds. In most cases, this is due to the anatomical structure of the nose. This organ is penetrated by a network of tiny capillaries, which can be damaged even by minor changes in the environment or during physical activity.
We'll talk about the causes and prevention later, but first about how to provide first aid for nosebleeds.
- First of all, it is necessary to eliminate the causes that increase the bleeding; you should not talk, cough, make any movements or be nervous.
- You need to sit down, unfasten your collar, loosen your belt, and tilt your head forward. You should not throw your head back or lie down in bed, otherwise blood will enter the throat, causing coughing and vomiting.
- You should put something cold on the bridge of your nose (a moistened towel or bandage), but an ice pack is better.
- It is advisable to provide a flow of fresh air indoors by opening the windows. On the street - move to the shade. If bleeding occurs in the heat, you can additionally apply cold compresses to the head and chest.
- If the nose continues to bleed, then both wings of the nose should be pressed firmly against the nasal septum. Breathing should be deep, through the mouth. The procedure continues for 5-10 minutes. Don't be afraid of blood getting into your mouth, you just need to spit it out. You can also perform nasal packing. To do this, cotton balls are moistened with a solution of hydrogen peroxide and inserted into the nostrils. In this case, the blood clots quite quickly and the nosebleeds stop. Just do not insert dry cotton swabs into your nose, this can cause the cotton to dry to the walls of the nose and cause bleeding to re-open.
In most cases, bleeding lasts no more than 10 minutes. If the bleeding cannot be stopped even after 20 minutes, or if blood flows very intensely from both nostrils at once, then it is necessary to call an ambulance or take the patient to the nearest medical facility.
After providing first aid, if you managed to stop the bleeding, you can additionally:
- Drink something cool, but you should strictly abstain from coffee and tea, they dilate blood vessels and can cause re-bleeding. You should also not eat food.
- Measure your blood pressure, especially if headaches and tinnitus occur along with bleeding. If the pressure is high, it is necessary to normalize it.
Nothing happens in our life just like that. If nosebleeds are systematic, then the body has a reason for this. It can accompany blood diseases, heart defects, infectious and viral diseases, aneurysms, hypertension, benign (angiomas, polyps, papillomas) and malignant (sarcoma and cancer) neoplasms. Contact your therapist and get tested.
However, nosebleeds do not necessarily signal serious problems. Up to 70% of cases are associated with mechanical damage to the epithelium, due to bruises, strong nose blowing, and too dry indoor air in the winter. In childhood, the cause of bleeding can be the habit of picking the nose with a finger or sticking toys into the nasal passages.
Many people have thin and brittle capillaries and a deviated nasal septum, which can also cause frequent nosebleeds. In these cases, taking additional vitamin C and visiting an otolaryngologist will not hurt.
Danger
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding is not a harmless disease. During the juvenile period it can lead to:
- anemia;
- hormonal disorders;
- infertility;
- endometriosis.
In women of reproductive age, the disease can be caused by:
- infertility;
- anemia;
- endometrial cancer, breast cancer;
- fibrocystic mastopathy;
- uterine fibroids.
In premenopausal and menopausal patients, dysfunctional uterine bleeding can cause anemia, cancer, and also cause the growth of existing tumors into neighboring organs. from a gynecology clinic at the first symptoms of the disease.
.
Recommendations for the prevention and restoration of bleeding from fibroids
We managed to stop bleeding from uterine fibroids, what to do next? It is mandatory to continue clinical observation, especially if surgical treatment was used. Some experts exclude observation of patients who have had their uterus completely removed. However, even after its complete removal, you should be observed by a specialist for a long time to exclude the development of pathologies of the pelvic organs. Removal of appendages during childbearing years even leads to the prescription of constant hormone therapy, which cannot be carried out uncontrolled.
Preventative methods that should help prevent the appearance of fibroids and bleeding include:
- strict adherence to intimate hygiene using special products for gentle care of the intimate area, for example, Ginocomfort intimate hygiene gel;
- prevention of abortions at any stage of pregnancy through the use of modern contraceptives;
- normalization of hormonal levels with the help of medications;
- fast and high-quality treatment of postpartum complications of any etiology;
- Regular visits to a specialist to identify any diseases of the reproductive system.
You should strictly observe the temperature regime (try to avoid long stays in baths and saunas, in the open sun in the heat) and minimize the effect of ultraviolet radiation on the skin.
This is especially true for women over the age of 40, whose risk of developing myomatous nodes doubles.
Prevention
Prevention of dysfunctional uterine bleeding consists of:
- regular visits to a gynecologist;
- submitting a smear once a year for oncocytology;
- competent treatment of gynecological diseases;
- exclusion of abortion;
- reduction of psycho-emotional and physical stress;
- maintaining a menstrual calendar;
- proper nutrition.
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
General recommendations
To avoid such problems, we strongly recommend that you follow the simplest rules of the rehabilitation period:
- Eating can be done no earlier than 3 hours after tooth extraction.
- Don't eat hot or cold foods.
- Give preference to liquid porridges and broths. Supam. Solid foods should be avoided until the hole is completely healed.
- Avoid taking hot baths and saunas.
- Avoid heavy lifting and exercise for a week.
- After tooth extraction, you should not rinse your mouth; this will significantly increase the healing time of damaged tissue.
- Limit brushing your teeth for the first 24 hours.
- You should not drink alcohol for a week after the operation.
- Never apply warm or hot compresses to your cheek.