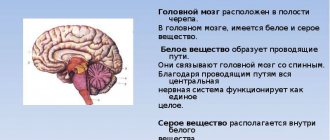
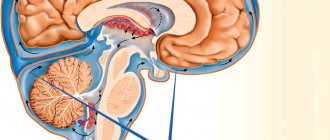
Residual encephalopathy is a brain disease caused by tissue damage and death of nerve cells (neurons). It occurs in people of all ages, including children. The disease can be congenital or acquired. Pathological changes develop if blood supply to the brain is disrupted and cells experience oxygen starvation. This condition can be provoked by traumatic brain injury, vegetative-vascular dystonia, atherosclerosis, hypertension, infections, ischemia, stroke, diabetes mellitus, toxic substances, radiation, uncontrolled medication use, use of drugs and psychotropic drugs, and brain surgery. Congenital encephalopathy can occur as a result of complicated pregnancy, intrauterine development abnormalities, bad habits of the expectant mother, or birth injuries.
Symptoms of residual encephalopathy
In the congenital form of the disease, nervous disorders are observed.
The child becomes irritable or apathetic, his mood often changes, memory deteriorates, and seizures are possible. Acquired residual encephalopathy is a “time bomb” because it can be asymptomatic for several years. At the initial stage, the functions of dead cells are taken over by other neurons. But with age, the brain loses its compensatory properties.
As a result, the following symptoms are found:
- headache and dizziness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- insomnia at night and drowsiness during the day;
- weakening of visual and hearing acuity;
- slurred speech;
- deterioration of mental abilities;
- lack of coordination;
- lethargy;
- lethargy or increased excitability;
- convulsions and fainting;
- paresis (weakening of motor functions) and paralysis.
Without treatment, serious neurological disorders may develop: epilepsy, Parkinson's disease, mental retardation, hydrocephalus, neuropathy, cerebral palsy, autism, myelopathy, dementia. In especially severe cases, the brain loses 95% of its functionality, and the patient is diagnosed with disability.
Grodno Regional Children's Clinical Hospital
Details Published May 10, 2018
Encephalopathy in children
The diagnosis of encephalopathy in children has become increasingly common, which greatly frightens thousands of parents. This disease is indeed very serious and requires urgent initiation of comprehensive treatment to avoid various complications. Timely initiation of adequate therapy can lead to a complete recovery of the child. A doctor's diagnosis of encephalopathy can be perplexing for parents who don't know what it is. This term implies a whole group of diseases of the child’s brain that are not associated with inflammatory processes. This diffuse disorder develops under the influence of various causes and consists of damage to brain cells.
What is it?
Perinatal encephalopathy (PEP) is a brain dysfunction caused by hypoxic, traumatic, infectious, toxic-metabolic effects on the central nervous system of the fetus and newborn. In the structure of the pathology of the nervous system of childhood, perinatal encephalopathy accounts for more than 60%. The consequences of perinatal encephalopathy in children can vary from minimal brain dysfunction and vegetative-vascular dystonia to hydrocephalus, cerebral palsy and epilepsy. What reasons underlie this pathology?
The leading cause of brain damage to the fetus and newborn in the perinatal period is intrauterine hypoxia. Intrauterine hypoxia occurs in diseases of the pregnant woman (heart defects, diabetes mellitus, pyelonephritis, hypertension, etc.), unfavorable pregnancy (threat of miscarriage, intrauterine infections, hemolytic disease of the fetus, gestosis, fetoplacental insufficiency) and childbirth (narrow pelvis, premature birth, protracted or rapid labor, weakness of labor, etc.). A harmful effect on the fetus can be caused by bad habits of the pregnant woman (smoking, drinking alcohol and drugs), taking medications that are potentially dangerous to the fetus, occupational hazards, and environmental problems.
In addition, perinatal hypoxic encephalopathy can develop in the first days after birth, for example, with respiratory distress syndrome, congenital heart defects, neonatal sepsis, etc. Regardless of the immediate cause, in all cases of hypoxic damage to the central nervous system, the trigger is a lack of oxygen. Other dysmetabolic disorders usually occur following hypoxic damage to the central nervous system. Birth trauma also plays a role.
During perinatal encephalopathy, there is an acute period (the first month of life), an early recovery period (up to 4-6 months) and a late recovery period (up to 1-2 years) and a period of residual effects.
Mild perinatal encephalopathy is the most common form. The manifestation of this form is the following symptoms: increased spontaneous motor activity of the newborn, difficulty falling asleep, shallow restless sleep, frequent crying, muscle dystonia, tremor of the chin and limbs. This behavior of the baby can significantly worry the parents, but it is important to know that with proper care, regimen and selected treatment, the listed disorders are usually reversible and regress during the first month of life. Premature infants with a mild form of perinatal encephalopathy constitute a group at increased risk for the development of convulsive syndrome.
The moderate form of perinatal encephalopathy usually occurs with central nervous system depression syndrome and hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome, weakening of normal reflexes; local neurological lesions (convergent strabismus, drooping of the upper eyelid); widespread muscle weakness; Frequent, causeless screams. The above changes are reversible during the first 3-4 months of life. It is necessary to closely monitor the child and in case of prolonged manifestations of character, consult a doctor for advice on this issue.
The severe form of perinatal encephalopathy is characterized by a precomatose or comatose state immediately after birth. Severe cases of encephalopathy often progress.
In the acute period, treatment of a child with perinatal encephalopathy is carried out in the neonatal pathology department. Drug therapy is prescribed taking into account the prevailing syndromes of perinatal encephalopathy. In order to normalize the metabolism of nervous tissue and increase its resistance to hypoxia, infusion therapy is carried out - the introduction of solutions of glucose, potassium, calcium, magnesium preparations, etc. Drug therapy may consist of taking: neuroprotectors (nootropic drugs, amino acids), which are designed to restore the structure of the brain and prevent negative effects on neurons; drugs to improve blood supply to the brain; B vitamins, which help improve metabolic processes in brain cells; medications that eliminate symptoms (relieving muscle hypertonicity, convulsions, correcting motor dysfunctions).
At home, in parallel with any prescribed treatment, it is important to provide the child with proper and balanced nutrition and regular walks in the fresh air. It is also important to normalize the daily routine with regulation of sleep and wakefulness. For children with encephalopathy, the choice of medications is carried out by a neurologist at the clinic. Physical therapy, swimming, massage, physiotherapy (amplipulse therapy, electrophoresis), homeopathic therapy, herbal medicine can also help in the treatment of this pathology. The effectiveness of treatment of brain damage in a newborn depends on the timely diagnosis, the appointment of full and comprehensive treatment in accordance with existing problems, as well as strict implementation of all specialist recommendations. In this case, most children have a favorable prognosis for recovery without developing consequences in adulthood.
Diagnosing encephalopathy in a newborn can be a real tragedy for parents. But damage to the nervous system with such a disease often does not become a death sentence for the child, since the vast majority of manifestations of the disease can be cured.
Department for newborns and premature babies of the Healthcare Institution "GodKB"
Diagnosis of the disease
To make a correct diagnosis, a neurologist listens to the patient’s complaints and studies the medical history. According to indications, the doctor refers the patient for instrumental and laboratory examinations (diagnostic methods are selected individually):
- X-ray of the cervical spine;
- echoencephalography;
- electroencephalography;
- ultrasound examination of the brain;
- duplex scanning;
- rheovasography;
- computed or magnetic resonance imaging;
- blood and urine tests.
Total information
Schizophrenia is a polymorphic endogenous disease that affects the human mental apparatus. Polymorphism suggests that it occurs in different forms. The reason for its origin is the internal state of the psyche, so we are talking about an endogenous nature. As for the direct impact on a person, schizophrenia affects the brain, or more precisely, thinking and emotional reactions.
This psychopathology is detected in approximately 1% of people. The peak incidence occurs at 20-28 years in men, and at 26-32 years in women. However, schizophrenia is also diagnosed in children, as well as in the elderly. Moreover, it is often combined with anxiety disorders, depression, alcoholism and drug addiction, so it is not always possible to identify the disease at an early stage.
Many people believe that schizophrenia is a split personality. Others believe that it is always accompanied by hallucinations. In fact, “multiple personality disorder” is too simple a word for such a complex disease. In schizophrenic disorders, there is a disintegration of personal qualities and a person’s loss of contact with reality.
If we talk about hallucinations, they do not occur with every type of pathology. Moreover, the presence of this symptom may not indicate a schizophrenia spectrum disorder. Residual schizophrenia refers to those forms in which hallucinations are extremely rare.
Treatment of residual encephalopathy
Neurologists at Elena Malysheva’s clinic select individual treatment for each patient, taking into account the causes of the disease, symptoms and their severity, and the severity of the condition.
Typically, residual encephalopathy is treated with conservative methods, which may include:
- drug therapy – eliminates unpleasant symptoms, restores brain activity, normalizes metabolism and cerebral circulation;
- physiotherapy – activates the body’s defenses, mobilizes them to fight the disease;
- therapeutic massage – stimulates blood flow to the brain, providing it with nutrients and oxygen;
- physical therapy – activates blood circulation, restores motor activity, improves coordination.
If the disease is detected in a timely manner, complete recovery can be achieved. In advanced cases, it is impossible to completely restore the functioning of the brain, but it is possible to slow down the progression of the pathology and significantly improve the general condition of the patient.
Types and severity of cerebral encephalopathy
This psychoorganic syndrome, as already mentioned, can be congenital, and we will talk about it below in more detail. Acquired is divided into types depending on what caused the damage and death of brain cells, and, as a consequence, the development of symptoms:
- Angioencephalopathy (dyscirculatory or vascular) is a consequence of hypertension, atherosclerosis, and venous diseases that impair the blood supply to the brain. It mainly affects older people.
- Post-traumatic encephalopathy (missed punch or boxer encephalopathy, Martland syndrome) - occurs as a result of head injury immediately or after some time. Athletes are at risk.
- Toxic encephalopathy is the result of poisoning with alcohol, a number of drugs, drugs, toxic substances, such as lead, carbon monoxide, chloroform.
- Hypoxic encephalopathy of the brain develops when there is oxygen deficiency or starvation of nerve cells in the brain and their death. In turn, it is divided into perinatal, that is, birth, residual, asphyxia (suffocation), postanoxic or resuscitation-related,
- Radiation encephalopathy is a lesion that affects all brain cells under the influence of ionizing radiation.
- Toxic-metabolic encephalopathy is provoked by a long-term presence and gradual increase in the amount of metabolic products in the body, disruption of the process of their breakdown and elimination. There are such types of encephalopathy as hepatic, bilirubin, diabetic, hypoglycemic or hyperglycemic, uremic, Reye's syndrome, etc.
Also known:
- Wernicke encephalopathy, developing against the background of vitamin deficiency, frequent vomiting, lack of nutrition, AIDS, alcoholism;
- Hashimoto encephalopathy – accompanies inflammation of the thyroid gland.
The course of encephalopathy occurs in several ways. Apathetic is characterized by severe fatigue, general weakness, asthenia, and increased irritability. This later develops into a disorder of mental activity, emotional and mental instability, and a decrease in self-criticism.
The euphoric scenario implies swagger, increased mood, and narcissism. And another option is an explosive course, with a decrease in criticality, excessive irritability, rudeness, antisocial behavior, affective lability, and loss of interests.
There are 3 degrees of severity of encephalopathy:
I degree - there are almost no symptoms, there are no external manifestations of the syndrome, but instrumental studies show diffuse changes in brain tissue.
II degree – mild disturbances of brain activity.
III degree – pronounced neurological disorders requiring assignment of a disability group to the patient.
Advantages of treatment at Elena Malysheva’s clinic
Correct diagnosis is important for the successful treatment of residual encephalopathy, which can be very difficult.
Highly qualified neurologists with many years of experience practice at Elena Malysheva’s clinic. In their work, they use modern equipment of the latest generation, which ensures correct diagnosis and contributes to successful treatment. If you notice the slightest deviation in your health, do not ignore the problem. Contact a specialist, which will allow you to identify and cure the disease as soon as possible, preventing dangerous consequences that lead to personality degradation.
You can make an appointment with a neurologist by calling (3412) 52-50-50, or by ordering a call back.
How does congenital encephalopathy manifest?
- Baby's anxiety
- Constant crying
- Increased response to bright lights or loud noises
- Abnormal head position during sleep (tilting back)
- Bulging eyes
- Frequent and profuse regurgitation after eating
Doctors usually make the diagnosis of congenital encephalopathy immediately after the baby is born. During examination, doctors observe heart rhythm disturbances, too weak a cry, and the absence of innate reflexes, including sucking.
If the symptoms of the pathology appear a little later, then doctors make a diagnosis of residual encephalopathy. This type of disease can recur even after a long period of time. Provoking factors include acute respiratory viral infections, bacterial infections, blood pressure surges, and a strong blow to the head.
Consult your pediatrician
Don't delay treatment
Prevention
Prevention of the development of residual encephalopathy in children consists of:
- regular visits to specialists during pregnancy to identify early signs of pathology, as well as indications for emergency or planned delivery;
- immediate treatment and prevention of various injuries and infections (bacterial, viral, fungal) in a child;
- maintaining a daily routine and physical activity appropriate to the baby’s age;
- proper balanced nutrition;
- the mother’s refusal of bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol) during pregnancy and feeding.
Symptoms
Manifestations of the disease are usually pronounced, regardless of age. Symptoms can vary in various combinations. As a rule, patients experience increased fatigue with attacks of weakness, nausea with the urge to vomit, worsening sleep with insomnia or, conversely, drowsiness. Patients often complain of aching headaches (migraines), which cannot be relieved by taking a painkiller pill. Memory and the ability to perform mental work become worse; vision and hearing may also deteriorate. With such a quality of life, a person’s mood drops – until the onset of depression. Due to constant inconvenience, he becomes indifferent to what is happening nearby. The ability and the very desire to act disappears, even if he was previously active, now he is more characterized by apathy. In addition to this picture, numbness of the limbs, convulsions, speech disturbances, and loss of consciousness may appear. At a more advanced stage, problems begin with performing movements, speech becomes incomprehensible to others. Memory is impaired, leading to dementia.