- Causes of high blood pressure
- Idiopathic form of the disease
- Symptoms of intracranial pressure
- Manifestations of liquor-hypertensive syndrome in children
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of intracranial pressure
- Drug treatment
Intracranial pressure is otherwise called intracranial pressure.
An increase in intracranial pressure is called intracranial hypertension, which is characterized by a moderate or pronounced clinical picture. This pathology is also known under the names “cerebrospinal fluid hypertension syndrome”, “cerebrospinal fluid hypertension syndrome”. The term “cerebrospinal fluid” refers to cerebrospinal fluid. The disease can occur in an acute form and become chronic. Acute most often occurs against the background of traumatic brain injury (TBI), back injuries and infectious lesions of the brain. Chronically elevated intracranial pressure is observed in patients with brain tumors and cysts, and symptoms increase as the tumor enlarges. The pathology persists after severe surgical interventions, injuries to the spinal cord and brain, inflammatory processes that led to disturbances in liquorodynamics - the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid.
Intracranial pressure is reduced mainly by medicinal methods; surgical intervention is used only in particularly difficult cases.
Causes of high blood pressure
The disease occurs in adults and children. Its causes can be congenital or acquired. They are conventionally divided into four groups:
- Volumetric formations.
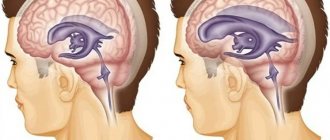
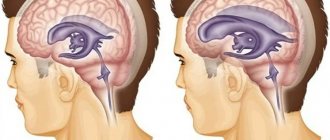
This category includes brain tumors, cysts, abscesses, and vascular aneurysms. The tumor takes up space in the skull, compresses certain areas of the brain, and displaces its structures. This leads to a change in intracranial pressure. In young children, intracranial pressure higher than normal may be due to congenital developmental anomalies. Most often, specialists diagnose microcephaly or hydrocephalus. Trauma during childbirth, asphyxia, and oxygen starvation of the fetus can lead to pathology. At risk are babies born prematurely. - Edema.
Characteristic in the development of a number of diseases: encephalitis, meningitis, arachnoiditis, ischemic stroke, as a result of head injury, intoxication, hypoxia. Edema can be local, that is, affecting individual areas of the brain, or diffuse.
- Increased blood supply inside the skull.
This pathology occurs with dyscirculatory encephalopathy and a number of other diseases. In this case, the blood flow increases or its outflow from the vessels supplying the brain becomes more difficult. Due to increased blood supply, blood pressure rises. - Disorders of cerebrospinal fluid dynamics.
In the human body, the brain is surrounded by cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which moves at a certain speed and affects brain tissue, thereby creating intracranial pressure. Part of the cerebrospinal fluid enters the blood, and the missing amount of fluid is produced to replace this volume. Thanks to this, constant pressure is achieved, which is considered normal. Infectious and inflammatory diseases, back and head injuries lead to various disorders of the secretion and circulation of cerebrospinal fluid. In this case, the absorption of cerebrospinal fluid becomes slow or its production is excessively activated. Liquorodynamic disorders can develop against the background of congenital anomalies in the structure of the spinal cord and brain. Intracranial dystension occurs, in which the pressure on the brain becomes uneven. Excessive accumulation of fluid in the cranium causes compression of individual areas and vessels, which leads to changes in intracranial pressure.
In addition to injuries and inflammation, disruption of the production and circulation of cerebrospinal fluid can cause treatment with potent drugs. At risk are patients who are forced to take hormonal drugs, antibiotics, and corticosteroids for a long time. Excessive amounts of vitamin A due to abuse of retinol preparations can lead to changes in intracranial pressure.
Diet therapy
For intracranial hypertension, a diet is indicated. It is necessary to limit the consumption of foods that can have a stimulating effect on the nervous and cardiovascular systems, cause fluid retention in the body, as well as those that are difficult to digest and cause the development of flatulence.
Rubbing lavender oil into your temples can sometimes help relieve headaches.
You should eat according to a schedule, keeping approximately equal intervals between meals, at least 5 times a day in small portions. You should have dinner at least three hours before going to bed.
It is advisable to prepare dishes using dietary methods - boiling, baking, steaming. Be sure to include fresh vegetables and fruits in the diet, since the diet must meet the body's needs for vitamins and microelements.
The diet should be based on the following products:
- milk (if there is no individual intolerance) and fermented milk products;
- vegetables, raw and cooked, especially cucumbers, tomatoes, pumpkin, potatoes, carrots, beets, zucchini, all types of cabbage, green peas, bell peppers, leafy greens;
- fresh and prepared fruits and berries;
- dried fruits;
- meat – it is recommended to give preference to veal, beef, rabbit, turkey, chicken;
- Fish and seafood;
- eggs;
- cereals;
- pasta;
- bread and non-bread bakery products;
- butter and vegetable oils;
- fruit and vegetable juices, green, black, herbal tea, coffee with milk.
It is recommended to exclude from the diet baked goods, confectionery products, strong meat, fish and mushroom broths, fatty meats, smoked sausages, caviar, fatty and salty cheeses, legumes, radishes, radishes, onions, garlic, mushrooms, horseradish, mustard, mayonnaise , black coffee, cocoa, alcohol, marinades, pickles and other canned goods.
Patients with excess body weight should normalize it, since metabolic disorders affect, among other things, CSF flow.
You should limit your salt intake to 5 g per day.
If the patient is obese, it is necessary to reduce the daily calorie intake by 200-300 kcal while maintaining nutritional value. Patients suffering from intracranial hypertension are prohibited from adhering to strict low-calorie diets.
Symptoms of intracranial pressure
You can suspect a problem based on the following signs:
- headache;
- nausea and vomiting in the absence of gastrointestinal diseases;
- increased fatigue;
- irritability;
- changes in blood pressure, pulse rate;
- decreased libido.
Headache is the main symptom of liquor-hypertensive syndrome. Patients note the dependence of pain on body position and time of day. For many people, headaches begin to hurt more severely in the evening and at night, when a person is in a lying or reclining position. In this case, the production of cerebrospinal fluid increases, and its outflow worsens, which increases compression.
There is a feeling of fullness, pressure from the inside, which is localized in the fronto-parietal areas. The patient complains of a feeling as if something is pressing on the eyes from the inside, and blurred vision occurs. This feeling intensifies when the eyeballs move. When examining the fundus, the doctor will note swelling of the optic nerve - one of the main signs of increased intracranial pressure.
Because of the headache, a person feels bouts of nausea, but after vomiting, the state of health does not improve. In severe cases, the disease is accompanied by fainting and confusion.
In the chronic form of the disease, the quality of life decreases significantly. The patient becomes emotionally labile, stress resistance and performance decrease. Many people feel worse when the weather changes, that is, they develop increased meteosensitivity. It manifests itself as headaches and dizziness, sleep disturbances, fluctuations in blood pressure, muscle and joint pain, and general malaise.
Manifestations of liquor-hypertensive syndrome in children
In some cases, increased intracranial pressure in children does not manifest itself with pronounced symptoms. This is due to the fact that the skull bones of newborns are softer, so hypertension is compensated.
With severe disturbances, it manifests itself as tearfulness and anxiety, sleep disturbance. The newborn refuses to feed and often spits up after feeding. A typical sign of increased intracranial pressure in a child is “protrusion” of the fontanelle. Compression of certain areas of the brain negatively affects the physical and intellectual development of children. In addition to behavioral disorders, disorders of vital functions and delayed psychophysical development are possible. In severe cases, the result of prolonged intracranial hypertension in a child is the formation of mental retardation.
Diagnostics
If there are signs of liquor-hypertensive syndrome, you should make an appointment with a neurologist. To make a diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a set of procedures:
- fundus examination;
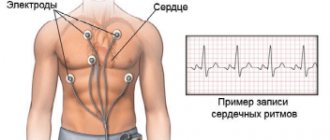
- echoencephalography;
- X-ray of the skull;
- CT or MRI of the head
- Ultrasound of blood vessels supplying the brain;
- angiography.
In severe clinical cases, the doctor may prescribe a lumbar puncture, which helps determine accurate indicators of intracranial pressure.
The purpose of these procedures is primarily to identify the cause of hypertension. Based on the data obtained, the specialist determines a treatment regimen and prescribes additional diagnostics.
Infusion of plantain leaves
In folk medicine, fresh plantain leaves have been used for a long time for the aseptic treatment of boils, wounds and abscesses, but few know about the property of this plant to reduce the level of ICP. The hypotensive properties of plantain are due to the fact that this plant contains a huge amount of phytoncides, tannins, polysaccharides, organic acids, as well as carotenoids, flavonoids, vitamins K, C and many other biochemical active substances. Plantain helps hypertensive patients not only when ICP increases, but also with vascular and heart diseases. It also has diuretic properties and reduces the burden of edema.
Typically, plantain infusion is prepared from the leaves of the plant. In order to obtain a sufficiently effective herbal medicine, use the following recipe:
- crushed plantain leaves (3-4 tablespoons) are mixed with not very hot water (half a liter);
- the resulting mixture is infused for a day;
- To achieve the required clinical effect, you should use the infusion several times a day, one or two spoons.
Treatment of intracranial pressure
Conservative and surgical methods are used to reduce intracranial pressure. The operation is performed if the cause of the disorder is a tumor, cyst, or congenital abnormality of the brain structure. Removing the tumor eliminates compression and normalizes blood pressure. To eliminate hydrocephalus, the cerebral shunt technique is used.
The operation can be performed planned or urgently. Emergency intervention is carried out in severe forms of the disease, when it can lead to dislocation syndrome. This is a dangerous complication in which cerebral structures are displaced due to compression. The cerebellar tonsils are wedged into the foramen magnum, and the brain stem is compressed. It includes important nerve centers responsible for respiratory function and heart function. Damage to these areas poses a threat to life.
Prevention
There are several preventive rules on how to get rid of intracranial pressure:
- exercises (regularity is important);
- mandatory adherence to the daily routine;
- undergoing sanatorium-resort treatment;
- timely treatment of the underlying disease;
- following a specially designed diet;
- getting rid of bad habits;
- avoiding overheating.
Also, to prevent ICP, it is recommended to use a collection of motherwort and lemon balm: 200 mg of the raw material is poured into two liters of boiling water. All this should brew for about a day. Then the mixture is filtered and taken three times a day, one glass.
Drug treatment
In most cases, medications are selected for the patient to normalize intracranial pressure. These include:
- osmodiuretics;
- diuretics;
- potassium preparations;
- detoxifying agents;
- antiviral agents and antibiotics to eliminate the infectious and inflammatory process;
- vascular drugs;
- neurometabolic agents.
Based on the results of a comprehensive diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe magnesium sulfate for injection or piracetam for injection.
Attention! The selection of drug treatment for intracranial pressure is made by the doctor based on the diagnosis and after the diagnosis is made. To normalize the condition, it is important for the patient to reconsider his lifestyle, adjust his daily routine, and avoid psycho-emotional overload. Moderate physical activity is beneficial: walking, swimming.
Prognosis for liquor-hypertensive syndrome directly depends on the cause of its occurrence. With timely treatment of neuroinfections and liquorodynamic disorders, good dynamics and results can be achieved.
Mulberry decoction
The following is the recipe for preparing and using this herbal medicine:
- Mulberry branches must be cut into pieces with pruning shears; you can also use wire cutters. Both fresh and dry branches are suitable. The size of the pieces should reach 2 cm.
- Throw 100 g of raw material into a liter of cold water, bring it to a boil and cook over low heat for 20 minutes.
- The resulting composition is removed from the heat, carefully wrapped and infused for about one hour.
- Drink the drug three times a day, half an hour before meals, one glass.
This decoction is taken until the condition improves. The course of therapy may last a month, two or even three. The drug is considered harmless; it does not cause any damage to the body even with long-term treatment.
There is another recipe for how to lower intracranial pressure at home using mulberry tea. To do this, pour 200 g of fruits with one liter of boiling water, and then add 200 g of honey. Drink one glass of this tea in the morning on an empty stomach. Therapy is carried out until positive changes are noted in the general condition of the body.